Fibre Channel address weaknesses
http://searchitchannel.techtarget.com/feature/Fibre-Channel-address-weaknesses

Figure 2.1 Five layers of a Fibre Channel frame.
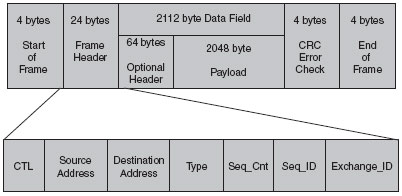
Figure 2.2 shows an example of the header information in Fibre Channel layer 2.



Now that we have established that attacks don't change, but they do get modified, let's discuss another attack that stems network and application history. Manipulation of the 24-bit fabric address can cause significant damage and denial of service in a SAN.
Each node in a SAN has a 24-bit fabric address that is used for routing, among other things. Along with routing frames correctly to/from their source and destinations, the 24-bit address is also used for name server information. The name server is a logical database in each Fibre Channel switch that correlates a node's 24-bit fabric address to their 64-bit WWN. Additionally, the name server is also responsible for other items, such as mapping the 24-bit fabric address and 64-bit WWN to the authorized LUNs in the SAN. Furthermore, address information is also used for soft and hard zoning procedures (discussed in the Chapter 4, "SANs: Zone and Switch Security"). The 24-bit fabric address of a node determines route functions with soft and hard zoning procedures, specifically if a frame is allowed to pass from one zone to the other. While there are several other uses of the 24-bit address, the use of the address in name servers and zoning procedures are by far the most important in terms of security.
The major issues with the 24-bit address is that it is used for identification purposes for both name server information and soft/hard zone routing, almost like an authorization process, but it is an entity that can be easily spoofed. Using any traffic analyzer, the 24-bit source address of a Fibre Channel frame could be spoofed as it performs both PLOGI (Port Login) and FLOGI (Fabric Login) procedures.
In Fibre Channel, there are three different types of login—Port Login, Fabric Login, and Node Login. Two can be corrupted with a spoofed 24-bit fabric address. Before we discuss how spoofing disrupts these processes, let's discuss the login types first.
FABRIC LOGIN (FLOGI), PORT LOGIN (PLOGI), AND NODE LOGIN (NLOGI)
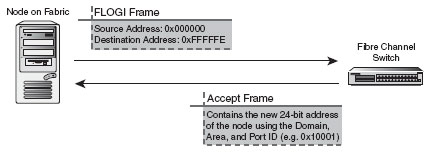
The Fabric Login (FLOGI) process allows a node to log in to the fabric and receive an assigned address from a switch. The FLOGI occurs with any node (N_Port or NL_Port) that is attached to the fabric. The N_Port or NL_Port will carry out the FLOGI with a nearby switch. The node (N_Port or NL_Port) will send a FLOGI frame that contains its node name, its N_Port name, and any service parameters. When the node sends its information to the address of 0xFFFFFE, it uses the 24-bit source address of 0x000000 because it hasn't received a legitimate 24-bit address from the fabric yet. The FLOGI will be sent to the well-known fabric address of 0xFFFFFE, which is similar to the broadcast address in an IP network (though not the same). The FC switches and fabric will receive the FLOGI at the address of 0xFFFFFE. After a switch receives the FLOGI, it will give the N_Port or NL_Port a 24-bit address that pertains to the fabric itself. This 24-bit address with be in the form of Domain-Area-Port address from, where the Domain is the unique domain name (ID) of the fabric, Area is the unique area name (ID) of the switch within the domain, and Port is the unique name (ID) of each port within the switch in the fabric. Table 2.3 shows how the 24-bit address is made.
Table 2.3 24-Bit addresses
24-Bit Address Type
Description
8-bit domain name
Unique domain ID in a fabric. Valid domain IDs are between 1 and 239.
8-bit area name
Unique area ID on a switch within a fabric. Valid area IDs are between 0 and 255.
8-bit port name
Unique area ID on a switch within a fabric. Valid area IDs are between 0 and 255.
A 24-bit address (port ID) uses the following formula to determine a node's address:
An example address for and node on the first domain (domain ID of 1), on the first switch (area ID of 0), and the first port (port ID of 1), would be the following:
After the node has completed the FLOGI and has a valid 24-bit fabric address, it will perform a Port Login (PLOGI) to the well-known address of 0xFFFFFC to register its new 24-bit address with the switch's name server, as well as submit information on its 64-bit port WWN, 64-bit node WWN, port type, and class of service. The switch then registers that 24-bit fabric address, along with all the other information submitted, to the name server and replicates that information to other name servers on the switch fabric. Figures 2.14 and 2.15 show the FLOGI and PLOGI processes.
Figure 2.14 FLOGI process.
Figure 2.15 PLOGI process.
A Node Login is somewhat similar to a Fabric Login, but instead of logging in to the fabric, the node would log in to another node directly (node to node communication). The node will not receive any information from the fabric, but will receive information from the other node as it relates to Exchange IDs (OX_ID and RX_ID) and session information (Seq_ID and Seq_CNT). After this information has been exchanged, the two nodes will begin to communicate with each other directly. Domain_ID x 65536 + Area_ID x 256 + Port_ID = 24 bit Address
1 x 65536 + 0 x 256 + 1 = 65537 (Hex: 0x10001)

Fibre Channel address weaknesses的更多相关文章
- Fibre Channel和Fiber Channel
Fibre Channel也就是"网状通道"的意思,简称FC. 由于Fiber和Fibre只有一字之差,所以产生了很多流传的误解. FC只代表Fibre Channel,而不是 ...
- Fiber Channel SAN Storage
http://www.infotechguyz.com/VMware/FiberChannelSANStorage.html Using Fibre Channel with ESX/ESXi Fib ...
- Firbe Channel光纤信道
简介 中文名:网状信道 外文名:Fibre Channel 简 称:FC 光纤信道是一种高速网络技术标准(T11),主要应用于SAN(存储局域网).其拓扑结构分为三种,点到点.仲裁循环.交换结构 ...
- EtherType
EtherType is a two-octet field in an Ethernet frame. It is used to indicate which protocol is encaps ...
- ibm v3700
raid5总容量计算(n-1)*最小盘容量RAID0:N块盘组成,逻辑容量为N块盘容量之和:RAID1:两块盘组成,逻辑容量为一块盘容量:RAID3:N+1块盘组成,逻辑容量为N块盘容量之和:RAID ...
- openstack Icehouse发布
OpenStack 2014.1 (Icehouse) Release Notes General Upgrade Notes Windows packagers should use pbr 0.8 ...
- Linux就这个范儿 第16章 谁都可以从头再来--从头开始编译一套Linux系统 nsswitch.conf配置文件
Linux就这个范儿 第16章 谁都可以从头再来--从头开始编译一套Linux系统 nsswitch.conf配置文件 朋友们,今天我对你们说,在此时此刻,我们虽然遭受种种困难和挫折,我仍然有一个梦 ...
- WebLogic集群案例分析
WebLogic集群案例分析 2012年8月,某证券交易系统(采用Weblogic中间件),由于基金业务火爆,使系统压力太大,后台服务器频繁死机时,这时工程师们紧急调试系统及恢复操作,等完成这些操作花 ...
- Linux下编译内核配置选项简介
Code maturity level options代码成熟度选项 Prompt for development and/or incomplete code/drivers 显示尚在开发中或尚未完 ...
随机推荐
- fastjson的日期格式化
//SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat 使用日期字段格式序列化(2017-01-01),而不是用时间戳表示日期 JSON.toJSONString(dat ...
- Mysql select语句设置默认值
1.在没有设置默认值的情况下: SELECT userinfo.id, user_name, role, adm_regionid, region_name , create_time FROM us ...
- 一个exception
今天调错,发生了一个错误:java.lang.IllegalStateException: ApplicationEventMulticaster not initialized [closed] 后 ...
- 推荐一款移动端的web UI控件 -- mobiscroll
用mobiscroll 可实现ios系统自带的选择器控件效果,支持几乎所有的移动平台(iOS, Android, BlackBerry, Windows Phone 8, Amazon Kindle) ...
- docker 查看容器的网络连接
#! /bin/bash echo $1 PID=$(docker inspect -f '{{.State.Pid}}' $1) nsenter -t $PID -n netstat |grep E ...
- JS读取json 文件
json文件是一种轻量级的数据交互格式.一般在jquery中使用getJSON()方法读取. $.getJSON(url,[data],[callback]) url:加载的页面地址 data: 可选 ...
- [转]Linux系统下如何查看及修改文件读写权限
转自 :http://www.cnblogs.com/CgenJ/archive/2011/07/28/2119454.html 查看文件权限的语句: 在终端输入:ls -l xxx.xxx (xxx ...
- Guava之ImmutableMap使用示例
ImmutableMap 的作用就是:可以让java代码也能够创建一个对象常量映射,来保存一些常量映射的键值对. 分析以下情景,来具体讨论这个的好处. 假设现在有需求如下:根据数据库存的某个key字段 ...
- 奇怪吸引子---DequanLi
奇怪吸引子是混沌学的重要组成理论,用于演化过程的终极状态,具有如下特征:终极性.稳定性.吸引性.吸引子是一个数学概念,描写运动的收敛类型.它是指这样的一个集合,当时间趋于无穷大时,在任何一个有界集上出 ...
- 用 Vue 改造 Bootstrap,渐进提升项目框架[转]
GitChat 作者:Meathill 原文:用 Vue 改造 Bootstrap,渐进提升项目框架 关注微信公众号:「GitChat 技术杂谈」 一本正经的讲技术 [不要错过文末彩蛋] 前言 Vue ...
