一种新型聚类算法(Clustering by fast search and find of density peaksd)
最近在学习论文的时候发现了在science上发表的关于新型的基于密度的聚类算法
Kmean算法有很多不足的地方,比如k值的确定,初始结点选择,而且还不能检测费球面类别的数据分布,对于第二个问题,提出了Kmean++,而其他不足还没有解决,dbscan虽然可以对任意形状分布的进行聚类,但是必须指定一个密度阈值,从而去除低于此密度阈值的噪音点,这篇文章解决了这些不足。
本文提出的聚类算法的核心思想在于,对聚类中心的刻画上,而且认为聚类中心同时具有以下两种特点:
- 本身的密度大,即它被密度均不超过它的邻居包围
- 与其他密度更大的数据点之间的“距离”相对更大

通俗的理解为:给一个节点求与其距离小于一个值的节点的个数,用这个个数表示节点的密度,此时求出来的就是节点的局部密度,

经过上边的过程,每个点都可以找到两个距离与之对应,然后建立一个二维坐标轴,在坐标轴上把图形画出来,如下图

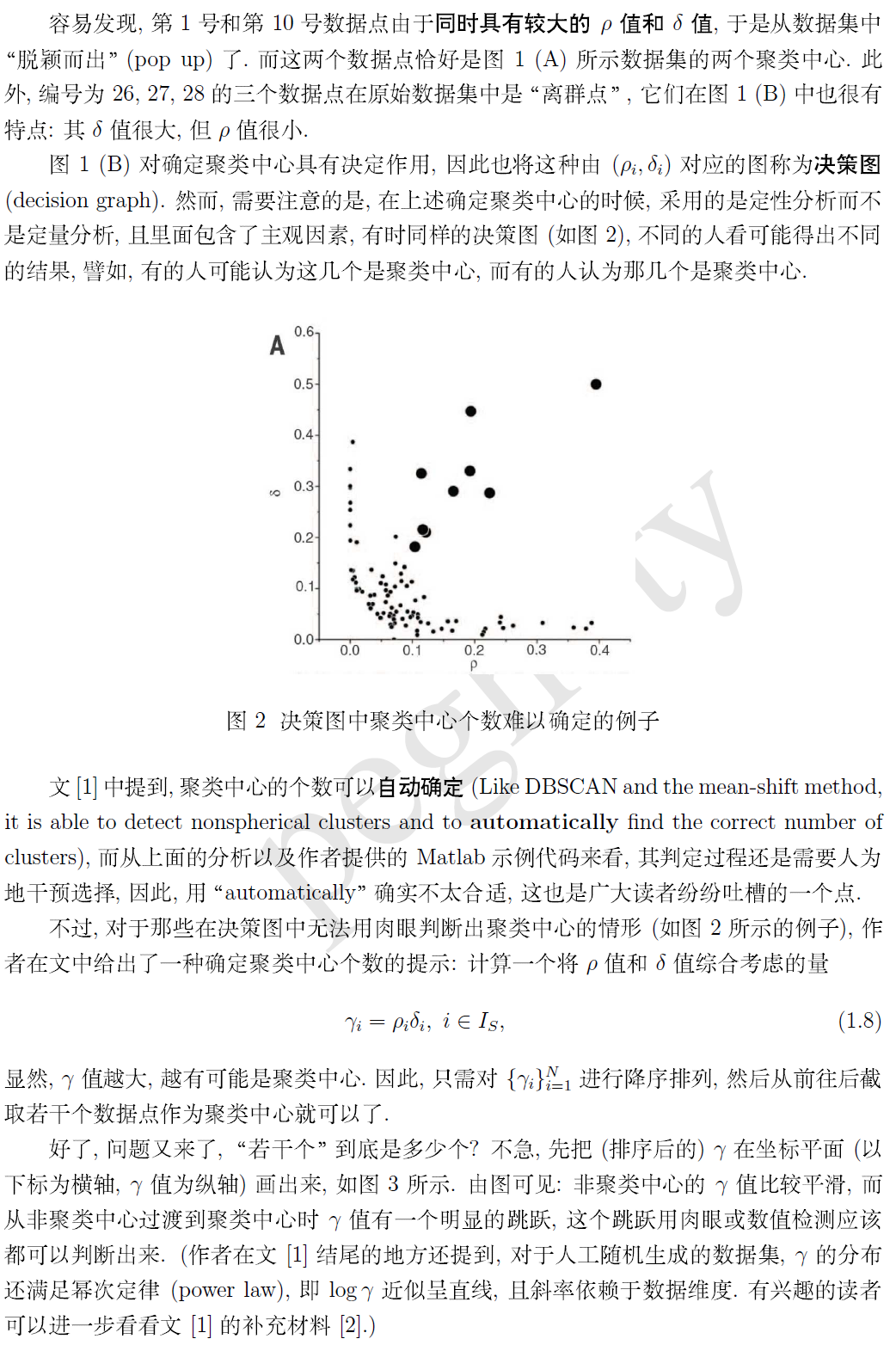
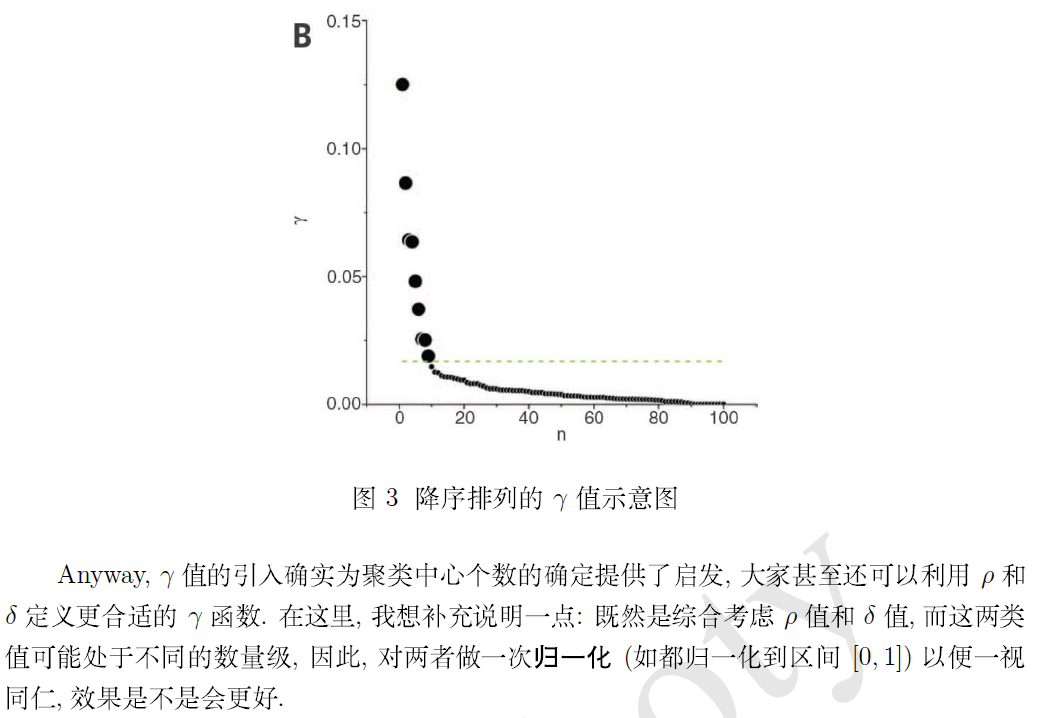




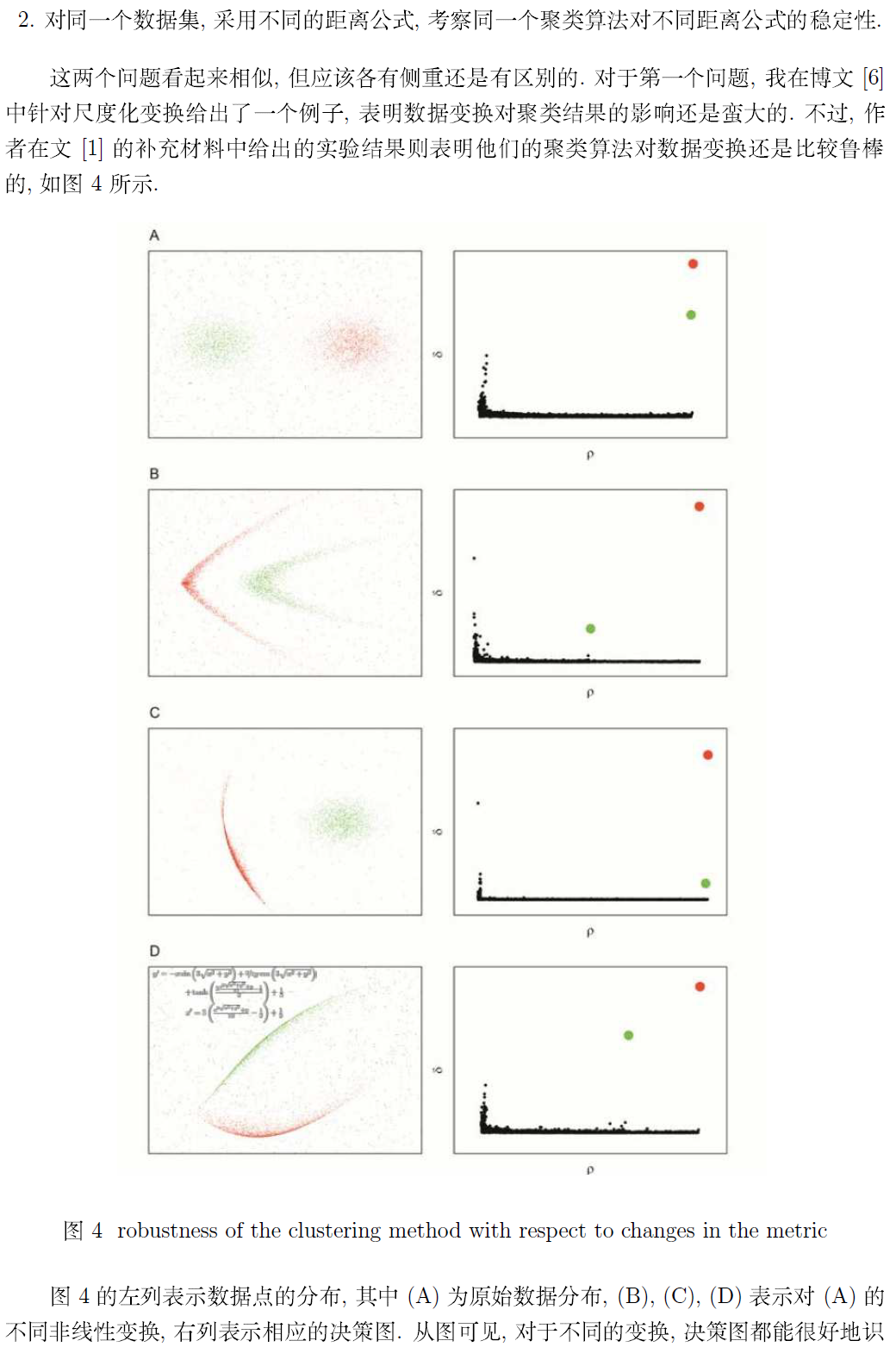


最后,附上作者在补充材料里提供的 Matlab 示例程序 (加了适当的代码注释)
clear all
close all
disp('The only input needed is a distance matrix file')
disp('The format of this file should be: ')
disp('Column 1: id of element i')
disp('Column 2: id of element j')
disp('Column 3: dist(i,j)') %% 从文件中读取数据
mdist=input('name of the distance matrix file (with single quotes)?\n');
disp('Reading input distance matrix')
xx=load(mdist);
ND=max(xx(:,));
NL=max(xx(:,));
if (NL>ND)
ND=NL; %% 确保 DN 取为第一二列最大值中的较大者,并将其作为数据点总数
end N=size(xx,); %% xx 第一个维度的长度,相当于文件的行数(即距离的总个数) %% 初始化为零
for i=:ND
for j=:ND
dist(i,j)=;
end
end %% 利用 xx 为 dist 数组赋值,注意输入只存了 0.5*DN(DN-) 个值,这里将其补成了满矩阵
%% 这里不考虑对角线元素
for i=:N
ii=xx(i,);
jj=xx(i,);
dist(ii,jj)=xx(i,);
dist(jj,ii)=xx(i,);
end %% 确定 dc percent=2.0;
fprintf('average percentage of neighbours (hard coded): %5.6f\n', percent); position=round(N*percent/); %% round 是一个四舍五入函数
sda=sort(xx(:,)); %% 对所有距离值作升序排列
dc=sda(position); %% 计算局部密度 rho (利用 Gaussian 核) fprintf('Computing Rho with gaussian kernel of radius: %12.6f\n', dc); %% 将每个数据点的 rho 值初始化为零
for i=:ND
rho(i)=.;
end % Gaussian kernel
for i=:ND-
for j=i+:ND
rho(i)=rho(i)+exp(-(dist(i,j)/dc)*(dist(i,j)/dc));
rho(j)=rho(j)+exp(-(dist(i,j)/dc)*(dist(i,j)/dc));
end
end % "Cut off" kernel
%for i=:ND-
% for j=i+:ND
% if (dist(i,j)<dc)
% rho(i)=rho(i)+.;
% rho(j)=rho(j)+.;
% end
% end
%end %% 先求矩阵列最大值,再求最大值,最后得到所有距离值中的最大值
maxd=max(max(dist)); %% 将 rho 按降序排列,ordrho 保持序
[rho_sorted,ordrho]=sort(rho,'descend'); %% 处理 rho 值最大的数据点
delta(ordrho())=-.;
nneigh(ordrho())=; %% 生成 delta 和 nneigh 数组
for ii=:ND
delta(ordrho(ii))=maxd;
for jj=:ii-
if(dist(ordrho(ii),ordrho(jj))<delta(ordrho(ii)))
delta(ordrho(ii))=dist(ordrho(ii),ordrho(jj));
nneigh(ordrho(ii))=ordrho(jj);
%% 记录 rho 值更大的数据点中与 ordrho(ii) 距离最近的点的编号 ordrho(jj)
end
end
end %% 生成 rho 值最大数据点的 delta 值
delta(ordrho())=max(delta(:)); %% 决策图 disp('Generated file:DECISION GRAPH')
disp('column 1:Density')
disp('column 2:Delta') fid = fopen('DECISION_GRAPH', 'w');
for i=:ND
fprintf(fid, '%6.2f %6.2f\n', rho(i),delta(i));
end %% 选择一个围住类中心的矩形
disp('Select a rectangle enclosing cluster centers') %% 每台计算机,句柄的根对象只有一个,就是屏幕,它的句柄总是
%% >> scrsz = get(,'ScreenSize')
%% scrsz =
%%
%% 和 就是你设置的计算机的分辨率,scrsz() 就是 ,scrsz() 就是
scrsz = get(,'ScreenSize'); %% 人为指定一个位置,感觉就没有那么 auto 了 :-)
figure('Position',[ scrsz()/. scrsz()/1.3]); %% ind 和 gamma 在后面并没有用到
for i=:ND
ind(i)=i;
gamma(i)=rho(i)*delta(i);
end %% 利用 rho 和 delta 画出一个所谓的“决策图” subplot(,,)
tt=plot(rho(:),delta(:),'o','MarkerSize',,'MarkerFaceColor','k','MarkerEdgeColor','k');
title ('Decision Graph','FontSize',15.0)
xlabel ('\rho')
ylabel ('\delta') subplot(,,)
rect = getrect();
%% getrect 从图中用鼠标截取一个矩形区域, rect 中存放的是
%% 矩形左下角的坐标 (x,y) 以及所截矩形的宽度和高度
rhomin=rect();
deltamin=rect(); %% 作者承认这是个 error,已由 改为 了! %% 初始化 cluster 个数
NCLUST=; %% cl 为归属标志数组,cl(i)=j 表示第 i 号数据点归属于第 j 个 cluster
%% 先统一将 cl 初始化为 -
for i=:ND
cl(i)=-;
end %% 在矩形区域内统计数据点(即聚类中心)的个数
for i=:ND
if ( (rho(i)>rhomin) && (delta(i)>deltamin))
NCLUST=NCLUST+;
cl(i)=NCLUST; %% 第 i 号数据点属于第 NCLUST 个 cluster
icl(NCLUST)=i;%% 逆映射,第 NCLUST 个 cluster 的中心为第 i 号数据点
end
end fprintf('NUMBER OF CLUSTERS: %i \n', NCLUST); disp('Performing assignation') %% 将其他数据点归类 (assignation)
for i=:ND
if (cl(ordrho(i))==-)
cl(ordrho(i))=cl(nneigh(ordrho(i)));
end
end
%% 由于是按照 rho 值从大到小的顺序遍历,循环结束后, cl 应该都变成正的值了. %% 处理光晕点,halo这段代码应该移到 if (NCLUST>) 内去比较好吧
for i=:ND
halo(i)=cl(i);
end if (NCLUST>) % 初始化数组 bord_rho 为 ,每个 cluster 定义一个 bord_rho 值
for i=:NCLUST
bord_rho(i)=.;
end % 获取每一个 cluster 中平均密度的一个界 bord_rho
for i=:ND-
for j=i+:ND
%% 距离足够小但不属于同一个 cluster 的 i 和 j
if ((cl(i)~=cl(j))&& (dist(i,j)<=dc))
rho_aver=(rho(i)+rho(j))/.; %% 取 i,j 两点的平均局部密度
if (rho_aver>bord_rho(cl(i)))
bord_rho(cl(i))=rho_aver;
end
if (rho_aver>bord_rho(cl(j)))
bord_rho(cl(j))=rho_aver;
end
end
end
end %% halo 值为 表示为 outlier
for i=:ND
if (rho(i)<bord_rho(cl(i)))
halo(i)=;
end
end end %% 逐一处理每个 cluster
for i=:NCLUST
nc=; %% 用于累计当前 cluster 中数据点的个数
nh=; %% 用于累计当前 cluster 中核心数据点的个数
for j=:ND
if (cl(j)==i)
nc=nc+;
end
if (halo(j)==i)
nh=nh+;
end
end fprintf('CLUSTER: %i CENTER: %i ELEMENTS: %i CORE: %i HALO: %i \n', i,icl(i),nc,nh,nc-nh); end cmap=colormap;
for i=:NCLUST
ic=int8((i*.)/(NCLUST*.));
subplot(,,)
hold on
plot(rho(icl(i)),delta(icl(i)),'o','MarkerSize',,'MarkerFaceColor',cmap(ic,:),'MarkerEdgeColor',cmap(ic,:));
end
subplot(,,)
disp('Performing 2D nonclassical multidimensional scaling')
Y1 = mdscale(dist, , 'criterion','metricstress');
plot(Y1(:,),Y1(:,),'o','MarkerSize',,'MarkerFaceColor','k','MarkerEdgeColor','k');
title ('2D Nonclassical multidimensional scaling','FontSize',15.0)
xlabel ('X')
ylabel ('Y')
for i=:ND
A(i,)=.;
A(i,)=.;
end
for i=:NCLUST
nn=;
ic=int8((i*.)/(NCLUST*.));
for j=:ND
if (halo(j)==i)
nn=nn+;
A(nn,)=Y1(j,);
A(nn,)=Y1(j,);
end
end
hold on
plot(A(:nn,),A(:nn,),'o','MarkerSize',,'MarkerFaceColor',cmap(ic,:),'MarkerEdgeColor',cmap(ic,:));
end %for i=:ND
% if (halo(i)>)
% ic=int8((halo(i)*.)/(NCLUST*.));
% hold on
% plot(Y1(i,),Y1(i,),'o','MarkerSize',,'MarkerFaceColor',cmap(ic,:),'MarkerEdgeColor',cmap(ic,:));
% end
%end
faa = fopen('CLUSTER_ASSIGNATION', 'w');
disp('Generated file:CLUSTER_ASSIGNATION')
disp('column 1:element id')
disp('column 2:cluster assignation without halo control')
disp('column 3:cluster assignation with halo control')
for i=:ND
fprintf(faa, '%i %i %i\n',i,cl(i),halo(i));
end
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/aimatfuture/article/details/39405261
http://blog.csdn.net/zxdxyz/article/details/40655231
一种新型聚类算法(Clustering by fast search and find of density peaksd)的更多相关文章
- Science14年的聚类论文——Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks
欢迎转载,转载请注明:本文出自Bin的专栏blog.csdn.net/xbinworld. 这是一个比较新的聚类方法(文章中没看见作者对其取名,在这里我姑且称该方法为local density clu ...
- Science论文"Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks"学习笔记
"Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks"是今年6月份在<Science>期刊上发表的的一篇论文,论文中 ...
- 处理输入为非对角阵的Clustering by fast search and find of density peak代码
Clustering by fast search and find of density peak. Alex Rodriguez, Alessandro Laio 是发表在Science上的一篇很 ...
- Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks
参考:http://www.52ml.net/16296.html 这个算法的优点就在于,它首先一步就能找到聚类中心,然后划分类别.而其他算法需要反复迭代才能找到中心聚类. 就是不知道代码该怎么写.. ...
- 发表在 Science 上的一种新聚类算法
今年 6 月份,Alex Rodriguez 和 Alessandro Laio 在 Science 上发表了一篇名为<Clustering by fast search and find of ...
- 密度峰值聚类算法(DPC)
密度峰值聚类算法(DPC) 凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/ 1. 简介 基于密度峰值的聚类算法全称为基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值的聚类算法(cl ...
- 各类聚类(clustering)算法初探
1. 聚类简介 0x1:聚类是什么? 聚类是一种运用广泛的探索性数据分析技术,人们对数据产生的第一直觉往往是通过对数据进行有意义的分组.很自然,首先要弄清楚聚类是什么? 直观上讲,聚类是将对象进行分组 ...
- Science上发表的超赞聚类算法
本博客已经迁往http://www.kemaswill.com/, 博客园这边也会继续更新, 欢迎关注~ 作者(Alex Rodriguez, Alessandro Laio)提出了一种很简洁优美的聚 ...
- Science上发表的超赞聚类算法(转)
作者(Alex Rodriguez, Alessandro Laio)提出了一种很简洁优美的聚类算法, 可以识别各种形状的类簇, 并且其超参数很容易确定. 算法思想 该算法的假设是类簇的中心由一些局部 ...
随机推荐
- 解密QQ——队列
一.问题引入 小明和小丽同在一个自习室上自习,小明感觉小丽是一个很不错的女孩,于是他鼓足勇气向小丽要QQ号,然而小丽也是个矜持的女孩,当然不会直接告诉他,所以小丽给了小明一串加密过的数字,同时她也告诉 ...
- 嵌入式开发之zynq---Zynq PS侧I2C驱动架构
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-24148050-id-120532.html http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/390538368?page=1 ht ...
- 使用OpenSSL创建自己的CA root certificate
在密码学中,CA(Certificate Authority,认证机构)是指一个被多个用户信任的机构,该机构能够创建和指派公钥证书. 为规范起见,我们先介绍本文可能涉及的术语, asymmetric ...
- 指定webapi 返回 json 格式 ; GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.Formatters.Clear()
因为 Internet Explorer 和 Firefox 发送了不同的 Accept 头,所以 web API 在响应里就发送了不同的内容类型. 解决方法,在 Global.asax的 App ...
- WAS7.0安装补丁升级程序无法替换文件 java/docs/autorun.inf解决办法
OS:Win7 64bit WAS版本:WASND_7.0_Windows_x64_C1G2JML.zip WAS补丁升级程序版本:7.0.0.13-WS-UPDI-WinAMD64 异常信息: Ca ...
- crontab(定时任务操作)
定时任务顾名思义就是在某一时间点自动进行任务操作.在做Pgsql的备份利用crontab进行定时操作, 使用起来比较方便.故分享具体的定时编辑命令:crontab -e 首先从crontab的文件分析 ...
- spark LinearRegression 预测缺失字段的值
最近在做金融科技建模的时候,字段里面很多缺少值得时候,模型对于新用户的预测会出现很大的不稳定,即PSI较大的情况. 虽然我们依据字段IV值得大小不断的在调整字段且开发新变量,但是很多IV值很大的字段直 ...
- (Dos)/BAT命令入门与高级技巧详解(转)
目录 第一章 批处理基础 第一节 常用批处理内部命令简介 1.REM 和 :: 2.ECHO 和 @ 3.PAUSE 4.ERRORLEVEL 5.TITLE 6.COLOR 7.mode 配置系统设 ...
- 怎么用ABBYY在线浏览PDF文件
ABBYY FineReader 让您可以从在线存储服务中打开图像或 PDF 文件,并将已识别文本保存至在线存储服务中,如 Dropbox.SkyDrive 或 Google Drive 等.通过在 ...
- 织梦漏洞可疑PHP文件/article文件夹
常见可疑文件夹: 1:article文件夹:最近很多织梦系统网站根目录被上传article文件件,里面有很多赌博静态违法html页面,可疑直接删除,此类违法信息大部分是由于您的网站存在dedecms安 ...
