Java第一次blog
7-1 答题判题程序-1
前言
这些题目主要用到对象与类的处理:
对象是现实世界或抽象概念中的实体在计算机程序中的表示。
类则是具有相同属性和方法的对象的集合,是创建对象的模板。通过类,我们可以定义一类对象的共同特征和行为。
1.字符串处理:需要对输入的题目信息和答题信息进行字符串分割、提取和处理,以获取题目编号、题目内容、标准答案和答题结果等信息。
2.对象和类:需要设计题目类、试卷类和答卷类,使用面向对象的思想来封装题目信息、试卷信息和答卷信息,以便于管理和操作。
3.集合类:需要使用集合类来保存题目列表、答案列表和判题结果列表,以便于对题目和答案进行管理和操作。
4.输入输出:可以考虑从文件中读取题目信息和答题信息,并将判题结果输出到数组中,以实现数据的持久化和方便查看。
5.算法设计:需要设计判题的算法,即根据标准答案和用户答案来判断答题结果是否正确,可以使用字符串比较或其他方法来实现。
题量大难度高
题目1

分数 50
作者 蔡轲
单位 南昌航空大学
设计实现答题程序,模拟一个小型的测试,要求输入题目信息和答题信息,根据输入题目信息中的标准答案判断答题的结果。
输入格式:
程序输入信息分三部分:
1、题目数量
格式:整数数值,若超过1位最高位不能为0,
样例:34
2、题目内容
一行为一道题,可以输入多行数据。
格式:"#N:"+题号+" "+"#Q:"+题目内容+" "#A:"+标准答案
格式约束:题目的输入顺序与题号不相关,不一定按题号顺序从小到大输入。
样例:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
3、答题信息
答题信息按行输入,每一行为一组答案,每组答案包含第2部分所有题目的解题答案,答案的顺序号与题目题号相对应。
格式
" #A:"+答案内容
格式约束:答案数量与第2部分题目的数量相同,答案之间以英文空格分隔。
样例:
#A:2 #A:78
2是题号为1的题目的答案
78是题号为2的题目的答案
答题信息以一行"end"标记结束,"end"之后的信息忽略。
输出格式:
1、题目数量
格式:整数数值,若超过1位最高位不能为0,
样例:34
2、答题信息
一行为一道题的答题信息,根据题目的数量输出多行数据。
格式:题目内容+" ~"+答案
样例:
1+1=~2
2+2= ~4
3、判题信息
判题信息为一行数据,一条答题记录每个答案的判断结果,答案的先后顺序与题目题号相对应。
格式:判题结果+" "+判题结果
格式约束:
1、判题结果输出只能是true或者false,
2、判题信息的顺序与输入答题信息中的顺序相同
样例: true false true
输入样例1:
单个题目。例如:
1#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2 #A:2
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1+1=~2
true
输入样例2:
单个题目。例如:
1#N:1#Q:1+1= #A:2
#A:4
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1+1=~4
false
输入样例3:
多个题目。例如:
2
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#A:2 #A:4
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1+1=~2
2+2=~4
true true
输入样例4:
多个题目。例如:
2
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#A:2 #A:2
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1+1=~2
2+2=~2
true false
输入样例5:
多个题目,题号顺序与输入顺序不同。例如
2
#N:2 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:1 #Q:5+5= #A:10
#A:10 #A:2
end
输出样例5:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
5+5=~10
1+1=~2
true true
输入样例6:
含多余的空格符。例如:
1
#N:1 #Q: The starting point of the Long March is #A:ruijin
#A:ruijin
end
输出样例6:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The starting point of the Long March is~ruijin
true
输入样例7:
含多余的空格符。例如:
1
#N: 1 #Q: 5 +5= #A:10
#A:10
end
输出样例7:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
5 +5=~10
true
设计建议:
以下是针对以上题目要求的设计建议,其中的属性、方法为最小集,实现代码中可根据情况添加所需的内容:
题目类(用于封装单个题目的信息):
属性:题目编号、题目内容、标准答案-standardAnswer
方法:数据读写set\get方法、判题方法(答案-answer):判断答案-answer是否符合标准答案-standardAnswer
试卷类(用于封装整套题目的信息)
属性:题目列表(题目类的对象集合)、题目数量
方法:判题方法(题号-num、答案-answer):判断答案-answer是否符合对应题号的题目标准答案-standardAnswer
保存题目(题号-num、题目-question):将题目保存到题目列表中,保存位置与num要能对应
答卷类(用于封装答题信息)
属性:试卷(试卷类的对象)、答案列表(保存每一题的答案)、判题列表(保存每一题的判题结果true/false)
方法:判题方法(题号-num):判断答案列表中第num题的结果是否符合试卷中对应题号的题目标准答案
输出方法(题号-num):按照题目的格式要求,输出题号为num的题目的内容和答题结果。
保存一个答案(题号-num,答案-answer):保存题号为num的题目的答题结果answer。
代码长度限制
16 KB 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 64 MB 栈限制 8192 KB C (gcc) 1
分析题目1可知:
一共要设计出三个类:
题目类,试卷类,答卷类;
如以下代码://有些部分和题目要求不同可自行更改
//问题类
public static class Question {
private int questionNumber;
private String questionContent;
private String standardAnswer;
public void setQuestionNumber(int questionNumber) {
this.questionNumber = questionNumber;
}
public int getQuestionNumber() {
return this.questionNumber;
}
public void setQuestionContent(String questionContent) {
this.questionContent = questionContent.trim();
}
public String getQuestionContent() {
return this.questionContent;
}
public void setStandardAnswer(String standardAnswer) {
this.standardAnswer = standardAnswer;
}
public String getStandardAnswer() {
return this.standardAnswer;
}
}
// 试卷类
public static class ExamPaper {
private int numQuestions;
private Question e[];//用于存储题目
public void saveQuestion(int numQuestions, Question e[]) {
this.numQuestions=numQuestions;
this.e=new Question[e.length];
for(int i=0;i<e.length;i++)
{
this.e[i]=e[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<e.length-1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<e.length-i-1;j++)
{
if(this.e[j].questionNumber>this.e[j+1].questionNumber)
{
Question a=this.e[j];
this.e[j]=this.e[j+1];
this.e[j+1]=a;
}
}
}
}
public int getnum(){
return numQuestions;
}
}
// 答卷类
public static class AnswerSheet {
private ExamPaper examPaper;
private String questionAnther[];//用于存储学生答案
private int i=0;//记录回答的答案个数
public AnswerSheet(ExamPaper examPaper) {
this.examPaper = examPaper;
}
public void saveAnswer(String answer1, String answer2) {
questionAnther=new String[this.examPaper.getnum()];
questionAnther[i]=answer1;
i++;
questionAnther[i]=answer2;
i++;
}
public void saveAnswer(String answer1) {
if(questionAnther==null)
{
questionAnther=new String[this.examPaper.getnum()];
questionAnther[i]=answer1;
}
else
{
questionAnther[i]=answer1;
}
i++;
}
public void output() {//输出结果
for(int j=0;j<this.examPaper.getnum();j++)
{
System.out.println(examPaper.e[j].questionContent+"~"+questionAnther[j]);
}
for(int k=0;k<questionAnther.length;k++)
{
if(k!=questionAnther.length-1)
System.out.printf("%s ",examPaper.e[k].getStandardAnswer().equalsIgnoreCase(questionAnther[k]));
else
System.out.printf("%s",examPaper.e[k].getStandardAnswer().equalsIgnoreCase(questionAnther[k]));
}
}
}
改进1:
private Question e[];可以用hashmap("key:<Integer> questNumber","value:<Question> q");改省很多代码;
private String questionAnther[];//可以用hashmap("key:<Integer> questNumber","value:<String> questionAnther"),省去AnswerSheet中的i;
读取输入代码1
用正则表达式代码实现:
for (int i=0;i<numQuestions;i++)//已知题目个数及输入格式
{
String line=p.nextLine();直接读取输入代码;
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#N:\\ *(\\d+)\\ *#Q:(.+)\\ *#A:(.+)\\ *").matcher(line);//匹配器及捕获器
if (matcher.find())
{
int questionNumber=Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));//捕获组
String questionContent=matcher.group(2);
String questionAnther=matcher.group(3);
Question a1=new Question();
a1.setQuestionNumber(questionNumber);
a1.setQuestionContent(questionContent);
a1.setStandardAnswer(questionAnther);
a[i]=a1;
}
}
q.saveQuestion(numQuestions,a);
AnswerSheet o=new AnswerSheet(q);
String questionAnther1;
String questionAnther2;
if(numQuestions==1)
{
String line=p.nextLine();
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#A:(.+)").matcher(line);
if (matcher.find())
{
questionAnther1=matcher.group(1).trim();
o.saveAnswer(questionAnther1);
}
}
else
{
String line=p.nextLine();
String Line[]=line.split(" ");//分割出想要的答案等(//s)
for(int j=0;j<Line.length;j++)
{
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#A:(.+)").matcher(Line[j]);
if (matcher.find())
{
questionAnther1=matcher.group(1).trim();
o.saveAnswer(questionAnther1);
}
}
}
完整代码1
有问题可自行更改仅供参考。
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner p=new Scanner(System.in);
int numQuestions=p.nextInt();
p.nextLine();
Question a[]=new Question[numQuestions];
ExamPaper q=new ExamPaper();
for (int i=0;i<numQuestions;i++)
{
String line=p.nextLine();
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#N:\\ *(\\d+)\\ *#Q:(.+)\\ *#A:(.+)\\ *").matcher(line);
if (matcher.find())
{
int questionNumber=Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
String questionContent=matcher.group(2);
String questionAnther=matcher.group(3);
Question a1=new Question();
a1.setQuestionNumber(questionNumber);
a1.setQuestionContent(questionContent);
a1.setStandardAnswer(questionAnther);
a[i]=a1;
}
}
q.saveQuestion(numQuestions,a);
AnswerSheet o=new AnswerSheet(q);
String questionAnther1;
String questionAnther2;
if(numQuestions==1)
{
String line=p.nextLine();
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#A:(.+)").matcher(line);
if (matcher.find())
{
questionAnther1=matcher.group(1).trim();
o.saveAnswer(questionAnther1);
}
}
else
{
String line=p.nextLine();
String Line[]=line.split(" ");
for(int j=0;j<Line.length;j++)
{
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#A:(.+)").matcher(Line[j]);
if (matcher.find())
{
questionAnther1=matcher.group(1).trim();
o.saveAnswer(questionAnther1);
}
}
}
o.output();
}
//问题类
public static class Question {
private int questionNumber;
private String questionContent;
private String standardAnswer;
public void setQuestionNumber(int questionNumber) {
this.questionNumber = questionNumber;
}
public int getQuestionNumber() {
return this.questionNumber;
}
public void setQuestionContent(String questionContent) {
this.questionContent = questionContent.trim();
}
public String getQuestionContent() {
return this.questionContent;
}
public void setStandardAnswer(String standardAnswer) {
this.standardAnswer = standardAnswer;
}
public String getStandardAnswer() {
return this.standardAnswer;
}
}
// 试卷类
public static class ExamPaper {
private int numQuestions;
private Question e[];
public void saveQuestion(int numQuestions, Question e[]) {
this.numQuestions=numQuestions;
this.e=new Question[e.length];
for(int i=0;i<e.length;i++)
{
this.e[i]=e[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<e.length-1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<e.length-i-1;j++)
{
if(this.e[j].questionNumber>this.e[j+1].questionNumber)
{
Question a=this.e[j];
this.e[j]=this.e[j+1];
this.e[j+1]=a;
}
}
}
}
public int getnum(){
return numQuestions;
}
}
// 答卷类
public static class AnswerSheet {
private ExamPaper examPaper;
private String questionAnther[];
private int i=0;
public AnswerSheet(ExamPaper examPaper) {
this.examPaper = examPaper;
}
public void saveAnswer(String answer1, String answer2) {
questionAnther=new String[this.examPaper.getnum()];
questionAnther[i]=answer1;
i++;
questionAnther[i]=answer2;
i++;
}
public void saveAnswer(String answer1) {
if(questionAnther==null)
{
questionAnther=new String[this.examPaper.getnum()];
questionAnther[i]=answer1;
}
else
{
questionAnther[i]=answer1;
}
i++;
}
public void output() {
for(int j=0;j<this.examPaper.getnum();j++)
{
System.out.println(examPaper.e[j].questionContent+"~"+questionAnther[j]);
}
for(int k=0;k<questionAnther.length;k++)
{
if(k!=questionAnther.length-1)
System.out.printf("%s ",examPaper.e[k].getStandardAnswer().equalsIgnoreCase(questionAnther[k]));
else
System.out.printf("%s",examPaper.e[k].getStandardAnswer().equalsIgnoreCase(questionAnther[k]));
}
}
}
}
题目2
7-4 答题判题程序-2
分数 73
困难
作者 蔡轲
单位 南昌航空大学
设计实现答题程序,模拟一个小型的测试,以下粗体字显示的是在答题判题程序-1基础上增补或者修改的内容。
要求输入题目信息、试卷信息和答题信息,根据输入题目信息中的标准答案判断答题的结果。
输入格式:
程序输入信息分三种,三种信息可能会打乱顺序混合输入:
1、题目信息
一行为一道题,可输入多行数据(多道题)。
格式:"#N:"+题目编号+" "+"#Q:"+题目内容+" "#A:"+标准答案
格式约束:
1、题目的输入顺序与题号不相关,不一定按题号顺序从小到大输入。
2、允许题目编号有缺失,例如:所有输入的题号为1、2、5,缺少其中的3号题。此种情况视为正常。
样例:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
2、试卷信息
一行为一张试卷,可输入多行数据(多张卷)。
格式:"#T:"+试卷号+" "+题目编号+"-"+题目分值
题目编号应与题目信息中的编号对应。
一行信息中可有多项题目编号与分值。
样例:#T:1 3-5 4-8 5-2
3、答卷信息
答卷信息按行输入,每一行为一张答卷的答案,每组答案包含某个试卷信息中的题目的解题答案,答案的顺序与试卷信息中的题目顺序相对应。
格式:"#S:"+试卷号+" "+"#A:"+答案内容
格式约束:答案数量可以不等于试卷信息中题目的数量,没有答案的题目计0分,多余的答案直接忽略,答案之间以英文空格分隔。
样例:#S:1 #A:5 #A:22
1是试卷号
5是1号试卷的顺序第1题的题目答案
22是1号试卷的顺序第2题的题目答案
答题信息以一行"end"标记结束,"end"之后的信息忽略。
输出格式:
1、试卷总分警示
该部分仅当一张试卷的总分分值不等于100分时作提示之用,试卷依然属于正常试卷,可用于后面的答题。如果总分等于100分,该部分忽略,不输出。
格式:"alert: full score of test paper"+试卷号+" is not 100 points"
样例:alert: full score of test paper2 is not 100 points
2、答卷信息
一行为一道题的答题信息,根据试卷的题目的数量输出多行数据。
格式:题目内容+""+答案++""+判题结果(true/false)
约束:如果输入的答案信息少于试卷的题目数量,答案的题目要输"answer is null"
样例:3+2=5true
4+6=~22~false.
answer is null
3、判分信息
判分信息为一行数据,是一条答题记录所对应试卷的每道小题的计分以及总分,计分输出的先后顺序与题目题号相对应。
格式:题目得分+" "+....+题目得分+"~"+总分
格式约束:
1、没有输入答案的题目计0分
2、判题信息的顺序与输入答题信息中的顺序相同
样例:5 8 0~13
根据输入的答卷的数量以上2、3项答卷信息与判分信息将重复输出。
4、提示错误的试卷号
如果答案信息中试卷的编号找不到,则输出”the test paper number does not exist”,参见样例9。
设计建议:
参考答题判题程序-1,建议增加答题类,类的内容以及类之间的关联自行设计。
输入样例1:
一张试卷一张答卷。试卷满分不等于100。例如:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 1-5 2-8
#S:1 #A:5 #A:22
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
2+2=~22~false
0 0~0
输入样例2:
一张试卷一张答卷。试卷满分不等于100。例如:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 1-70 2-30
#S:1 #A:5 #A:22
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1+1=~5~false
2+2=~22~false
0 0~0
输入样例3:
一张试卷、一张答卷。各类信息混合输入。例如:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 1-70 2-30
#N:3 #Q:3+2= #A:5
#S:1 #A:5 #A:4
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1+1=~5~false
2+2=~4~true
0 30~30
输入样例4:
试卷题目的顺序与题号不一致。例如:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 2-70 1-30
#N:3 #Q:3+2= #A:5
#S:1 #A:5 #A:22
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2+2=~5~false
1+1=~22~false
0 0~0
输入样例5:
乱序输入。例如:
#N:3 #Q:3+2= #A:5
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 3-70 2-30
#S:1 #A:5 #A:22
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
3+2=~5~true
2+2=~22~false
70 0~70
输入样例6:
乱序输入+两份答卷。例如:
#N:3 #Q:3+2= #A:5
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 3-70 2-30
#S:1 #A:5 #A:22
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#S:1 #A:5 #A:4
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
3+2=~5~true
2+2=~22~false
70 0~70
3+2=~5~true
2+2=~4~true
70 30~100
输入样例7:
乱序输入+分值不足100+两份答卷。例如:
#N:3 #Q:3+2= #A:5
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 3-7 2-6
#S:1 #A:5 #A:22
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#S:1 #A:5 #A:4
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
3+2=~5~true
2+2=~22~false
7 0~7
3+2=~5~true
2+2=~4~true
7 6~13
输入样例8:
乱序输入+分值不足100+两份答卷+答卷缺失部分答案。例如:
#N:3 #Q:3+2= #A:5
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 3-7 2-6
#S:1 #A:5 #A:22
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#T:2 2-5 1-3 3-2
#S:2 #A:5 #A:4
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
alert: full score of test paper2 is not 100 points
3+2=~5~true
2+2=~22~false
7 0~7
2+2=~5~false
1+1=~4~false
answer is null
0 0 0~0
输入样例9:
乱序输入+分值不足100+两份答卷+无效的试卷号。例如:
#N:3 #Q:3+2= #A:5
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 3-7 2-6
#S:3 #A:5 #A:4
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
The test paper number does not exist
分析题2目可知:
题目增加了:
1.三种信息可能会打乱顺序混合输入(将读取的数据存入String数组中)。
2.试卷号可输入多行数据(多张卷)题目分值不满100分要输出内容。
3.判分信息(输出分数);
三个类如下代码:有错误在内
//问题类
public static class Question {
private int questionNumber;
private String questionContent;
private String standardAnswer;
private int Score;
public void setQuestionNumber(int questionNumber) {
this.questionNumber = questionNumber;
}
public void setQuestionScore(int Score) {
this.Score=Score;
}
public int getQuestionScore() {
return Score;
}
public int getQuestionNumber() {
return this.questionNumber;
}
public void setQuestionContent(String questionContent) {
this.questionContent = questionContent.trim();
}
public String getQuestionContent() {
return this.questionContent;
}
public void setStandardAnswer(String standardAnswer) {
this.standardAnswer = standardAnswer;
}
public String getStandardAnswer() {
return this.standardAnswer;
}
}
// 试卷类
public static class ExamPaper {
private int Scoresum=0;//记录一张试卷的总分
private int numQuestions=0;
private int examnumber;
private Question e[];//按题目1改
public void saveQuestion(int numQuestions, Question e[]) {
this.numQuestions=numQuestions;
this.e=new Question[numQuestions];
for(int i=0;i<numQuestions;i++)
{
this.e[i]=e[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<numQuestions-1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<numQuestions-i-1;j++)
{
if(this.e[j].questionNumber>this.e[j+1].questionNumber)
{
Question a=this.e[j];
this.e[j]=this.e[j+1];
this.e[j+1]=a;
}
}
}
}
public int getnum(){
return numQuestions;
}
public void setExamnumber(int examnumber) {
this.examnumber=examnumber;
}
public void setExamsum() {
for(int i=0;i<e.length;i++)
Scoresum=Scoresum+e[i].getQuestionScore();
}
public int GetExamsum() {
return Scoresum;
}
}
// 答卷类
public static class AnswerSheet {
private ExamPaper examPaper;//写一个hashmap(<Integer> exmNumber,<ExamPaper> examPaper);
private int ScoreA=0;//回答者的得分
private String questionAnther[];//按题目1改
private int i=0;//去掉
public AnswerSheet(ExamPaper examPaper) {
this.examPaper = examPaper;
}
public void saveAnswer(String answer1,int sort[]) {
if(questionAnther==null)
{
questionAnther=new String[20];
questionAnther[sort[i]-1]=answer1;
}
else
{
questionAnther[sort[i]-1]=answer1;
}
i++;
}
public int Geti(){
return i;
}
public void output(int sort[]) {
int a[]=new int [this.examPaper.getnum()];//记录得分情况也可以加到Question类中
for(int g=0;g<i;g++)
{
for(int k=0;k<i;k++)
{//改为一个循环mapQuestion.get(k).equal(mapAnther.get(k));
if(k+1==sort[g])
System.out.println(examPaper.e[k].questionContent+"~"+questionAnther[k]+"~"+examPaper.e[k].getStandardAnswer().equalsIgnoreCase(questionAnther[k]));
}
}
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
{//mapQuestion.get(k).GetScore();
if(examPaper.e[j].getStandardAnswer().equalsIgnoreCase(questionAnther[j]))
{
ScoreA+=examPaper.e[j].getQuestionScore();
a[j]=examPaper.e[j].getQuestionScore();
}
}
if(this.examPaper.getnum()>i)
{
for(int k=0;k<this.examPaper.getnum()-i;k++)
{
System.out.println("answer is null");
}
}
for(int l=0;l<i;l++)
{
if(l!=i-1)
System.out.printf("%d ",a[l]);
else
System.out.printf("%d%c%d",a[l],'~',ScoreA);
}
}
}
改进2:
部分改进在代码中,hashmap中的key可以写成ArrayList类的集合减少循环次数;
List <Integer> keys = new ArrayList <Integer>(map. keySet());//改正
List<String> returnResult2 = new LinkedList<String>();
Collection<String> values = map.values();
Iterator<String> it2 = values.iterator();
while(it2.hasNext()) {
returnResult2.add(it2.next());
}
完整代码2
有问题可自行更改仅供参考。
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner p=new Scanner(System.in);
String e1=p.nextLine();
int sort[]=new int[10];
String []esum=new String [50];
Question a[]=new Question[20];
int i=0,k=0,j;
while(!e1.equals("end"))
{
esum[i]=e1;
e1=p.nextLine();
i++;
}
ExamPaper q=new ExamPaper();
for(j=0;j<i;j++)
{
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#N:\\s*(\\d+)\\s*#Q:(.+)#A:(.+)").matcher(esum[j]);
if(matcher.find())
{
int questionNumber=Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
String questionContent=matcher.group(2);
String questionAnther=matcher.group(3);
Question a1=new Question();
a1.setQuestionNumber(questionNumber);
a1.setQuestionContent(questionContent);
a1.setStandardAnswer(questionAnther);
a[k]=a1;
k++;
}
else
{
matcher=Pattern.compile("#T:(\\d+)\\s*(.+)").matcher(esum[j]);
if (matcher.find()){
q.setExamnumber(Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1)));
String sum5[]=matcher.group(2).split("\\s");
for (int y=0;y<sum5.length;y++)
{
String []sum4=sum5[y].split("-");
int questionNumber=Integer.parseInt(sum4[0]);
sort[y]=questionNumber;
int Score=Integer.parseInt(sum4[1]);
for(int l=0;l<k;l++)
{
if(a[l].getQuestionNumber()==questionNumber)
{
a[l].setQuestionScore(Score);
}
}
}
j++;
break;
}
}
}
q.saveQuestion(k,a);
q.setExamsum();
if(q.GetExamsum()!=100)
{
System.out.println("alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points");
}
AnswerSheet o=new AnswerSheet(q);
AnswerSheet o1=new AnswerSheet(q);
int numg=0;
String questionAnther1;
for (int x=j;x<i;x++)
{
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#S:\\s*(\\d+)\\s*(.+)").matcher(esum[x]);
if(matcher.find())
{
int examnumber=Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
String ranges=matcher.group(2);
String[] Line=ranges.split("\\s+");
if(numg==0)
{
for(int c=0;c<Line.length;c++)
{
matcher=Pattern.compile("#A:(.+)").matcher(Line[c]);
if (matcher.find())
{
questionAnther1=matcher.group(1).trim();
o.saveAnswer(questionAnther1,sort);
}
}
}
else
{
for(int c=0;c<Line.length;c++)
{
matcher=Pattern.compile("#A:(.+)").matcher(Line[c]);
if (matcher.find())
{
questionAnther1=matcher.group(1).trim();
o1.saveAnswer(questionAnther1,sort);
}
}
}
}
}
o.output(sort);
if(o1.Geti()!=0)
o1.output(sort);
}
//问题类
public static class Question {
private int questionNumber;
private String questionContent;
private String standardAnswer;
private int Score;
public void setQuestionNumber(int questionNumber) {
this.questionNumber = questionNumber;
}
public void setQuestionScore(int Score) {
this.Score=Score;
}
public int getQuestionScore() {
return Score;
}
public int getQuestionNumber() {
return this.questionNumber;
}
public void setQuestionContent(String questionContent) {
this.questionContent = questionContent.trim();
}
public String getQuestionContent() {
return this.questionContent;
}
public void setStandardAnswer(String standardAnswer) {
this.standardAnswer = standardAnswer;
}
public String getStandardAnswer() {
return this.standardAnswer;
}
}
// 试卷类
public static class ExamPaper {
private int Scoresum=0;
private int numQuestions=0;
private int examnumber;
private Question e[];
public void saveQuestion(int numQuestions, Question e[]) {
this.numQuestions=numQuestions;
this.e=new Question[numQuestions];
for(int i=0;i<numQuestions;i++)
{
this.e[i]=e[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<numQuestions-1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<numQuestions-i-1;j++)
{
if(this.e[j].questionNumber>this.e[j+1].questionNumber)
{
Question a=this.e[j];
this.e[j]=this.e[j+1];
this.e[j+1]=a;
}
}
}
}
public int getnum(){
return numQuestions;
}
public void setExamnumber(int examnumber) {
this.examnumber=examnumber;
}
public void setExamsum() {
for(int i=0;i<e.length;i++)
Scoresum=Scoresum+e[i].getQuestionScore();
}
public int GetExamsum() {
return Scoresum;
}
}
// 答卷类
public static class AnswerSheet {
private ExamPaper examPaper;
private int ScoreA=0;
private String questionAnther[];
private int i=0;
public AnswerSheet(ExamPaper examPaper) {
this.examPaper = examPaper;
}
public void saveAnswer(String answer1,int sort[]) {
if(questionAnther==null)
{
questionAnther=new String[20];
questionAnther[sort[i]-1]=answer1;
}
else
{
questionAnther[sort[i]-1]=answer1;
}
i++;
}
public int Geti(){
return i;
}
public void output(int sort[]) {
int a[]=new int [this.examPaper.getnum()];
for(int g=0;g<i;g++)
{
for(int k=0;k<i;k++)
{
if(k+1==sort[g])
System.out.println(examPaper.e[k].questionContent+"~"+questionAnther[k]+"~"+examPaper.e[k].getStandardAnswer().equalsIgnoreCase(questionAnther[k]));
}
}
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
{
if(examPaper.e[j].getStandardAnswer().equalsIgnoreCase(questionAnther[j]))
{
ScoreA+=examPaper.e[j].getQuestionScore();
a[j]=examPaper.e[j].getQuestionScore();
}
}
if(this.examPaper.getnum()>i)
{
for(int k=0;k<this.examPaper.getnum()-i;k++)
{
System.out.println("answer is null");
}
}
for(int l=0;l<i;l++)
{
if(l!=i-1)
System.out.printf("%d ",a[l]);
else
System.out.printf("%d%c%d",a[l],'~',ScoreA);
}
}
}
}
题目3
在答题判题程序-2基础上增补或者修改的内容,要求输入题目信息、试卷信息、答题信息、学生信息、删除题目信息,根据输入题目信息中的标准答案判断答题的结果。
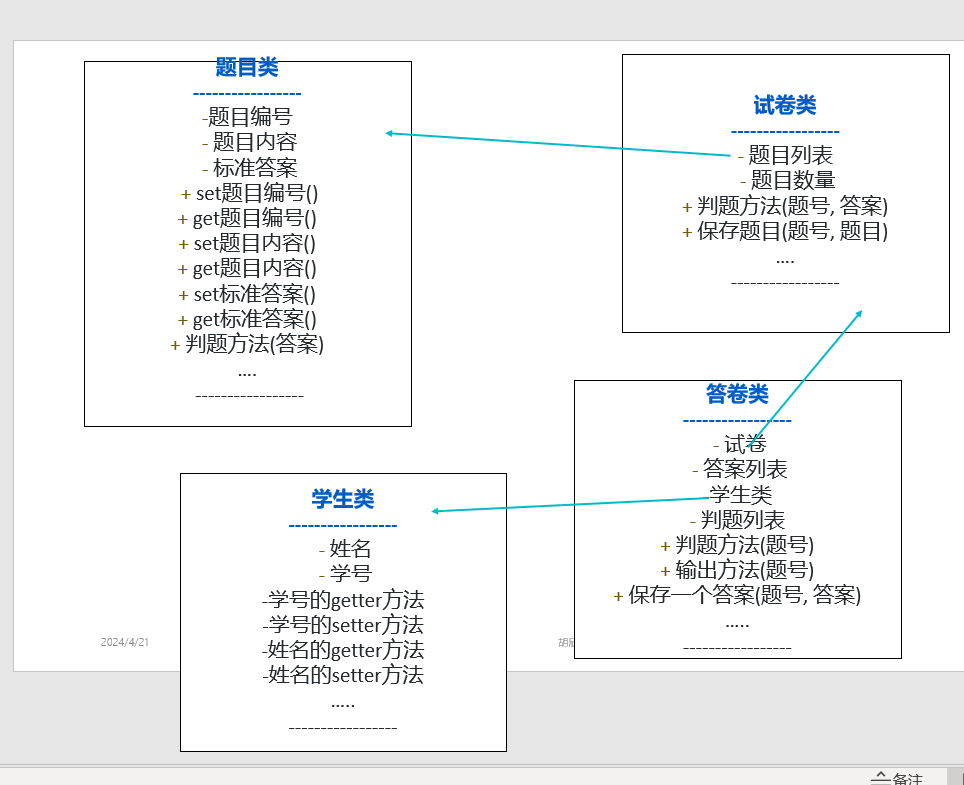
分析题3目可知:
1.需要添加学生类。
2.删除题目信息要对应输出无该题。
3.输出形式的改变。
4.题目信息有错要判断并输出。
新类代码:
//学生类
public static class Student {
private String studentId;
private String name;
public Student(String studentId, String name) {
this.studentId = studentId;
this.name = name;
}
// 学号的getter方法
public String getStudentId() {
return studentId;
}
// 学号的setter方法
public void setStudentId(String studentId) {
this.studentId = studentId;
}
// 姓名的getter方法
public String getName() {
return name;
}
// 姓名的setter方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
改进3:
可在原代码中用hashmap(key<String> StuId,value<Student> Stu);
来对应输入的学号对象;
对matcher读取的错误输入内容添加处理代码:
for(j=0;j<i;j++)
{
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#N:\\s*(\\d+)\\s*#Q:(.+)#A:(.+)").matcher(esum[j]);
if(matcher.find())
{
int questionNumber=Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
String questionContent=matcher.group(2);
String questionAnther=matcher.group(3);
Question a1=new Question();
a1.setQuestionNumber(questionNumber);
a1.setQuestionContent(questionContent);
a1.setStandardAnswer(questionAnther);
a[questionNumber]=a1;
k++;
}
else
{
matcher=Pattern.compile("#T:(\\d+)\\s*(.+)").matcher(esum[j]);
if (matcher.find()){
q.setExamnumber(Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1)));
String sum5[]=matcher.group(2).split("\\s");
for (int y=0;y<sum5.length;y++)
{
String []sum4=sum5[y].split("-");
int questionNumber=Integer.parseInt(sum4[0]);
int Score=Integer.parseInt(sum4[1]);
if(a[questionNumber]!=null)
{
a[questionNumber].setQuestionScore(Score);
a[questionNumber].setState(true);
}
if(a[questionNumber]==null)
{
Question a1=new Question();
a[questionNumber]=a1;
a[questionNumber].setQuestionScore(Score);
a[questionNumber].setState(true);
}
}
j++;
break;
}
}
}
q.saveQuestion(k,a);
q.setExamsum();
AnswerSheet o=new AnswerSheet(q);
AnswerSheet o1=new AnswerSheet(q);
int numg=0;
String questionAnther1;
for (int x=j;x<i;x++)
{
Matcher matcher=Pattern.compile("#S:\\s*(\\d+)\\s*(.+)").matcher(esum[x]);
if(matcher.find())
{
int examnumber=Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
String ranges=matcher.group(2);
String[] Line=ranges.split("\\s+");
if(numg==0)
{
for(int c=0;c<Line.length;c++)
{
matcher=Pattern.compile("#A:(.+)").matcher(Line[c]);
if (matcher.find())
{
String consist[]=matcher.group(1).split("-");
int antherNumber=Integer.parseInt(consist[0]);
questionAnther1=consist[1];
o.saveAnswer(questionAnther1,antherNumber);
}
}
}
else
{
for(int c=0;c<Line.length;c++)
{
matcher=Pattern.compile("#A:(.+)").matcher(Line[c]);
if (matcher.find())
{
String consist[]=matcher.group(1).split("-");
int antherNumber=Integer.parseInt(consist[0]);
questionAnther1=consist[1];
o1.saveAnswer(questionAnther1,antherNumber);
}
}
}
}
else
{
matcher=Pattern.compile("#X:\\s*(.+)\\s*").matcher(esum[x]);\\加的内容
if (matcher.find()){
String []osum=matcher.group(1).split("-");
for(int m=0;m<osum.length;m++)
{
String osum1[]=osum[m].split("\\s");
Student s1=new Student(osum1[0],osum1[1]);
Stu[Stunum]=s1;
Stunum++;
}
}
}
matcher=Pattern.compile("#D:N-(\\d+)\\s*").matcher(esum[x]);\\加的内容
if (matcher.find()){
int delenumber=Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
o.examPaper.setErronum(delenumber);
}
}
总结
对于List类集合和hashmap和正则表达式和代码的可重用性可修改性都需要进一步学习与研究
学到了正则表达式的使用,大量处理数据的能力。
理解了Java类、对象、封装,以及如何使用这些概念来构建程序。
集合框架:学习Java的集合框架,如List、Map等接口及其实现类(如ArrayList、HashMap等),它们用于存储和管理多个对象。
学到了编写函数(方法)来封装复杂的逻辑,并学习常见的设计模式,以优化代码结构和提高可维护性。
掌握Java在eclipse中程序的测试与调试技巧,使用调试器逐步执行代码,检查变量的值,并定位和解决程序中的错误。
学习到Java编程语言的基本语法,包括变量声明、数据类型、运算符、条件语句(if-else)、循环语句(for, while)、数组等。
Java第一次blog的更多相关文章
- JAVA第一次blog总结
JAVA第一次blog总结 0.前言 大一下学期我们开展了OPP这门课程,这也是我们第一次接触到JAVA.与上学期我们在学校里学C语言不同的是,这学期由于疫情原因我们是以网课的方式在学习.在学习中我发 ...
- 南昌航空大学-软件学院-22206104-段清如-JAVA第一次Blog作业
南昌航空大学-软件学院-22206104-段清如-JAVA第一次Blog作业 前言: 这个学期才开始接触java,到现在一个多月的时间,已经差不多可以写出一些基本的简单的程序了.对比上个学期学习的C语 ...
- java第一次作业0
lsl321 java第一次作业 #1. 本章学习总结 你对于本章知识的学习总结 本章我们学习了各种java相关文件的使用,以及码云,博客,pat等程序辅助软件,这些对于我们专业的学习有非常大的帮助, ...
- Java第一次实验 20145104张家明
Java第一次实验 实验报告 实验要求: 1.使用JDK编译.运行简单的Java程序 2.使用IDEA 编辑.编译.运行.调试Java程序 实验内容: 1.使用JDK编译.运行简单的Java程序: 2 ...
- 20155210 潘滢昊 Java第一次实验---凯撒密码
Java第一次实验---凯撒密码 实验内容 实现凯撒密码,并进行测试. 实验代码 import java.io.*; import java.util.Scanner; public class ks ...
- 20145312《Java第一次实验报告》
20145312<Java第一次实验报告> Java开发环境的熟悉(Windows+Idea) 一.实验内容 使用Idea编辑.编译.运行.调试Java程序. 使用JDK编译.运行简单的J ...
- java第一次实验总结&第三周总结
Java第一次实验报告,java开发环境与简单的Java程序 一.实验目的 1.熟悉JDK开发环境 2.熟练掌握结构化程序设计方法 二.实验内容 打印输出所有的"水仙花数",所谓& ...
- Java 第一次课堂测验
周一下午进行了开学来java第一次课堂测验,在课堂上我只完成了其中一部分,现代码修改如下: 先定义 ScoreInformation 类记录学生信息: /** * 信1805-1 * 胡一鸣 * 20 ...
- Java 第一次课堂测试总结。
Java 第一次课堂测试总结. 昨天参加了JAVA的开学测试,课上没有完成计算基点的功能,以下是修改完成后的代码. 首先是ScoreInformation类来存储学生信息. //信1805-1 王正 ...
- Java第一次实验
北京电子科技学院(BESTI) 实验报告 课程: java实验 班级:1352 姓名:吕松鸿 学号:20135229 成绩: 指导教师: 娄嘉鹏 实验日期及时间:20 ...
随机推荐
- HarmonyOS NEXT应用开发案例——二级联动
介绍 本示例主要介绍了List组件实现二级联动(Cascading List)的场景. 该场景多用于短视频中拍摄风格的选择.照片编辑时的场景的选择. 效果图预览 使用说明: 滑动二级列表侧控件,一级列 ...
- 400倍加速, PolarDB HTAP实时数据分析技术解密
简介: PolarDB MySQL是因云而生的一个数据库系统, 除了云上OLTP场景,大量客户也对PolarDB提出了实时数据分析的性能需求.对此PolarDB技术团队提出了In-Memory Col ...
- [GPT] Linux 如何查看 crontab 的运行记录
要查看crontab的运行记录,可以使用以下命令: $ grep CRON /var/log/syslog 或者 $ tail /var/log/syslog 这将在 /var/log/syslo ...
- [Go] freecache 设置 SetGCPercent 的作用
你需要对 freecache 有一个大致了解,freecache 的内存空间是预分配的. 假设你的程序占用了 50M 内存,那么开启 freecache 预分配 200M 空间,总共下来就是 250M ...
- 浅析mvvm模式和mvc模式的区别和联系
三层架构与MVC模式 三层架构 三层架构是一种以实现"高内聚,底耦合"为目标,的代码架构方法,它将整个业务分为,表示层,业务层,数据访问层(Dao层). MVC模式 MVC模式是一 ...
- C语言结构体的内存分配
一.结构体内存分配原则 原则一:结构体中元素按照定义顺序存放到内存中,但并不是紧密排列.从结构体存储的首地址开始 ,每一个元素存入内存中时,它都会认为内存是以自己的宽度来划分空间的,因此元素存放的位置 ...
- [Java]线程生命周期与线程通信
[版权声明]未经博主同意,谢绝转载!(请尊重原创,博主保留追究权) https://www.cnblogs.com/cnb-yuchen/p/18162522 出自[进步*于辰的博客] 线程生命周期与 ...
- pikachu靶机练习平台-xss
第一题:反射性xss(get) 输出的字符出现在url中 第二题:反射性xss(post) 登录后输入<script>alert(1)</script> 第三题:存储型xss ...
- Linux备忘手册
资料来源:技术胖 jspang.com 下载linux学习路径:https://newimg.jspang.com/linux-image01.png Linux备忘手册: 百度网盘 链接:https ...
- C语言:将txt文件的单词导入链表&&删除链表重复单词
文章目录 前言 主要分为两个实现部分,按个人需求浏览 首先明确几个任务 先过一遍如何操作的流程. ①全局变量和结构体代码部分 ②实现:将文件单词导入链表 a: 寻找txt文件中最长单词的函数 b: 导 ...
