POLIR-Society-Organization-Psychology-Emotions情绪-Emotion Wheel情绪轮: What It Is and How to Use One
Example of Application:
- https://www.interaction-design.org
- Course: “Emotional Design — How to Make Products People Will Love”
- Putting Some Emotion into Your Design – Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions
- 提高 “认识情绪”的能力 | 初探“普拉奇克情绪轮”
POLIR-Society-Organization-Psychology-Emotions情绪
Emotion Wheel情绪轮: What It Is and How to Use One
Affect: Emotions+Moods

EMOTIONS > Emotion Wheel: What It Is and How to Use One
Emotion Wheel: What It Is and How to Use One
By Katharine Chan, MSc, BSc, PMP Updated on September 12, 2022
Reviewed by Sabrina Romanoff, PsyD
Table of Contents
Have you ever had trouble pinpointing the exact feeling you were feeling? It may be easy to say when you feel happy, sad, or angry. However, humans are complicated beings who experience a wide range of emotions. It can be difficult to have complete clarity of all your emotions.
One of the signs of emotional intelligence is the ability to recognize and identify your own emotions and what others are feeling. A greater understanding of emotions can lead to better communication skills, improved relationships, and healthier coping abilities.
An emotion wheel is a tool that can be used to identify and understand feelings.2 Find out more about the history of the emotion wheel, different versions of it and how to use it in your life.
Related : Which Human Emotion Are You? Take the Quiz
PWE(Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions)
Robert Plutchik was an American psychologist who created one of the most popular emotion wheels in 1980 called Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions.
The wheel was developed to help illustrate different emotions as part of his psychoevolutionary theory of basic emotions.
He theorized that core emotions serve to trigger us due to our survival instincts and have an evolutionary purpose. In addition, he believed that the concept of emotions applies to all animals and humans due to similar limbic system functions.
Upgraded PWE:Centered at "Neutral" and Inverted.
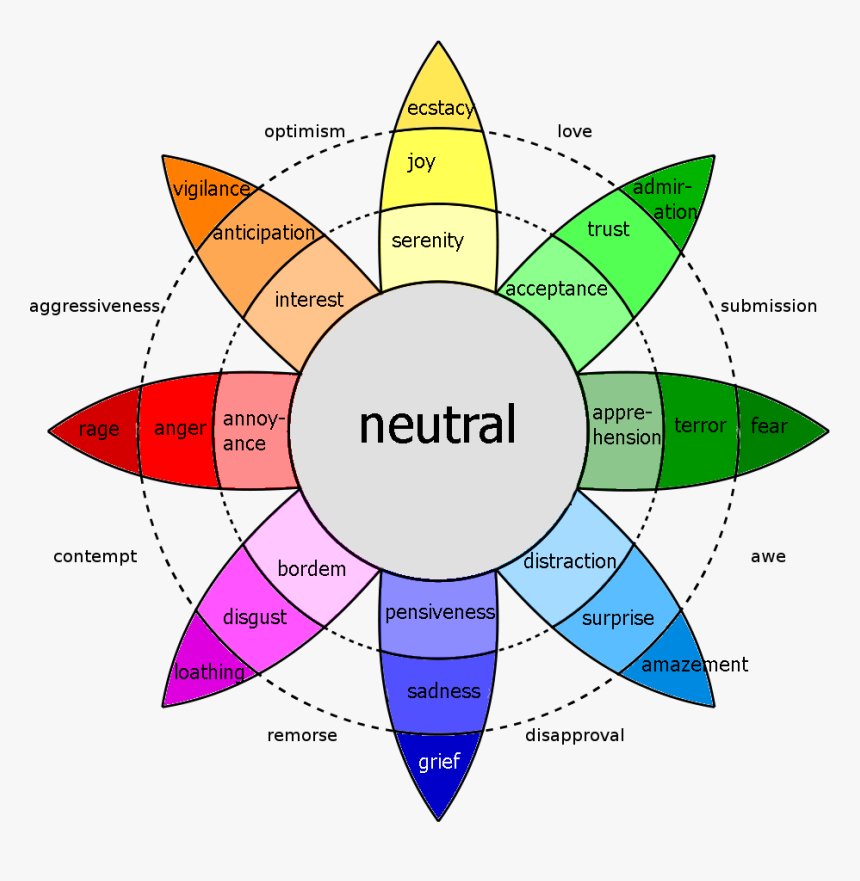
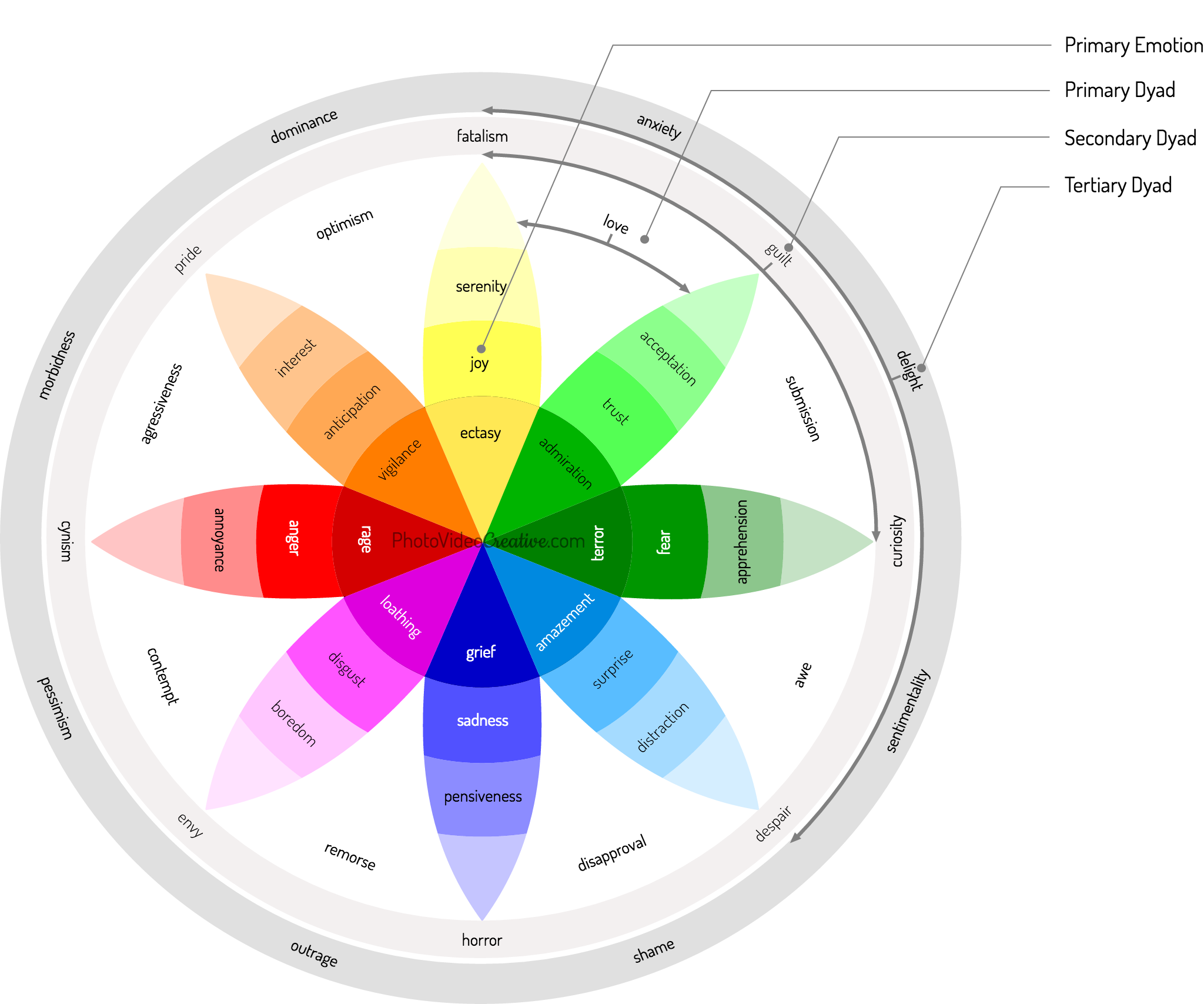
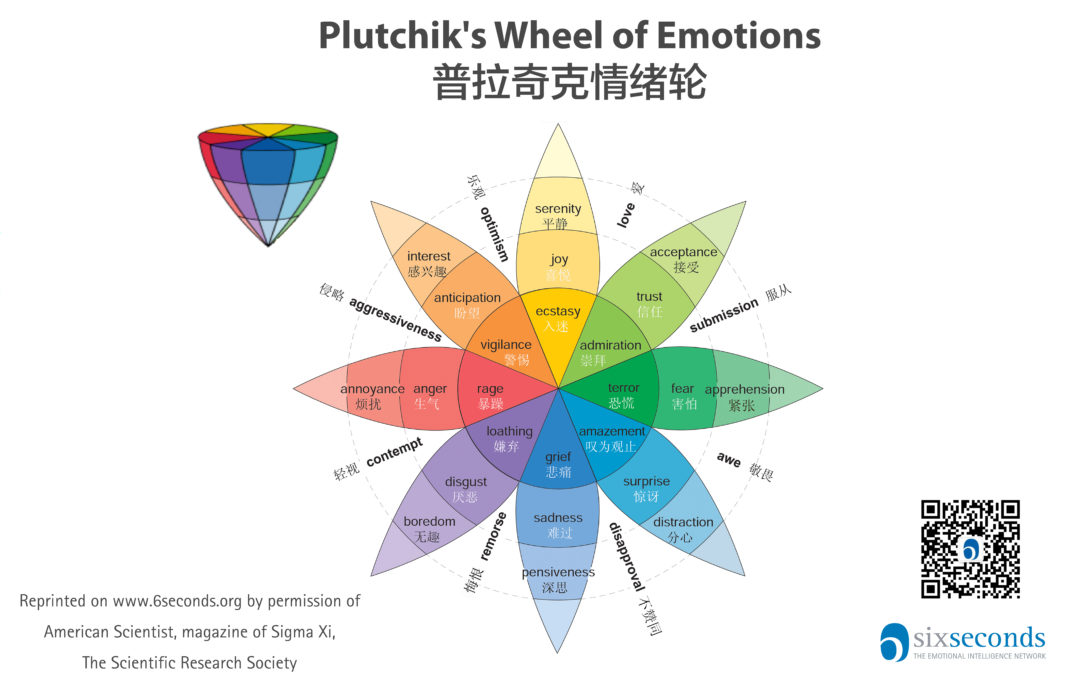
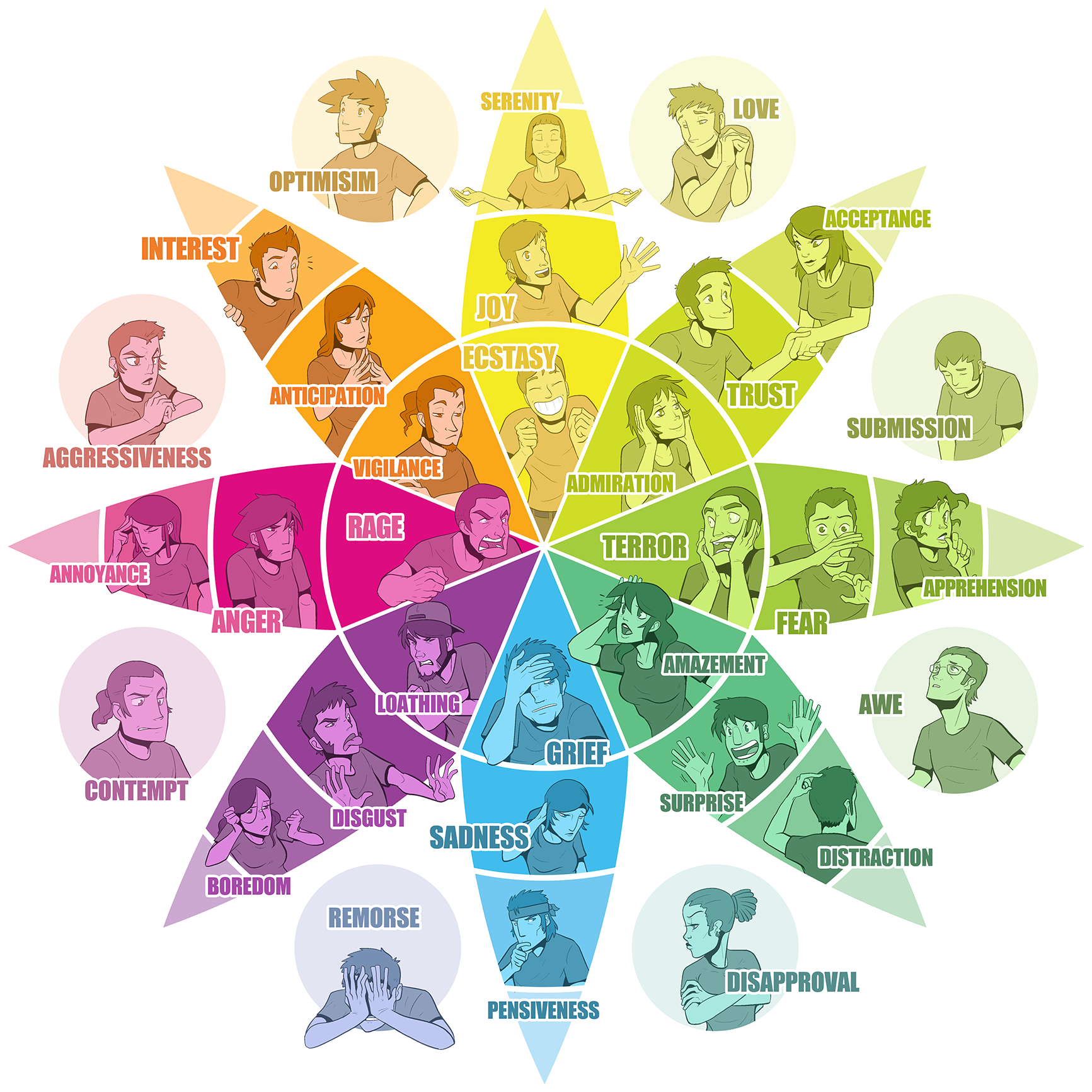
8 Core Emotions
The design of Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions is a flower with 8 petals located inside an octagon. It consists of 8 core emotions which are grouped into polar opposites and located across each other:
\(\large \begin{array}{lll} \\
&\bm{ Sadness } & versus &\bm{ joy } \\
&\bm{ Anger } & versus &\bm{ fear } \\
&\bm{ Expectation } & versus &\bm{ surprise } \\
&\bm{ Acceptance } & versus &\bm{ disgust } \\
\end{array}\)
10 points of PWE
Plutchik posited 10 points with regard to emotion:
- Emotions are found at all evolutionary levels of species. They are equally applicable to all animals as they are to human beings.
- Emotions evolved differently in different species and may be expressed differently between those species.
- The purpose of emotions is an evolutionary survival response enabling the organism to survive when confronted by environmental challenges.
- While emotions can be displayed and evoked through different mechanisms in different organisms there are common elements to emotions that can be identified across all emotional animals.
- There are 8 basic, primary emotions.
- Other emotions are simply a combination of these 8 basic emotions or are derived from one (or more) of these basic emotions.
- Primary emotions are "idealized" and their properties must be inferred from evidence but cannot be accurately stated in full.
- Each primary emotion is paired with another and is a polar opposite of that pair.
- Emotions can and do vary in degrees of similarity to each other.
- Emotions exist in varying degrees of intensity.
Range of Intensity of emotion from PWE
The core emotions appear in the second circle and the intensity of the color of each layer represents the intensity of the emotion. The emotions in the outer layer are soft-colored and milder whereas the ones in the center of the wheel are darker and more intense.
Each core emotion can be expressed at different intensities:
\(\large \begin{array}{lll} \\
&\bm{ Joy } & ranges\ from &\bm{ serenity } & to &\bm{ ecstasy } \\
&\bm{ Trust } & ranges\ from &\bm{ acceptance } & to &\bm{ admiration } \\
&\bm{ Fear } & ranges\ from &\bm{ timidity } & to &\bm{ terror } \\
&\bm{ Surprise } & ranges\ from &\bm{ uncertainty } & to &\bm{ amazement } \\
&\bm{ Sadness } & ranges\ from &\bm{ gloominess } & to &\bm{ grief } \\
&\bm{ Disgust } & ranges\ from &\bm{ dislike } & to &\bm{ loathing } \\
&\bm{ Anger } & ranges\ from &\bm{ annoyance } & to &\bm{ fury } \\
&\bm{ Anticipation } & ranges\ from &\bm{ interest } & to &\bm{ vigilance } \\
\end{array}\)
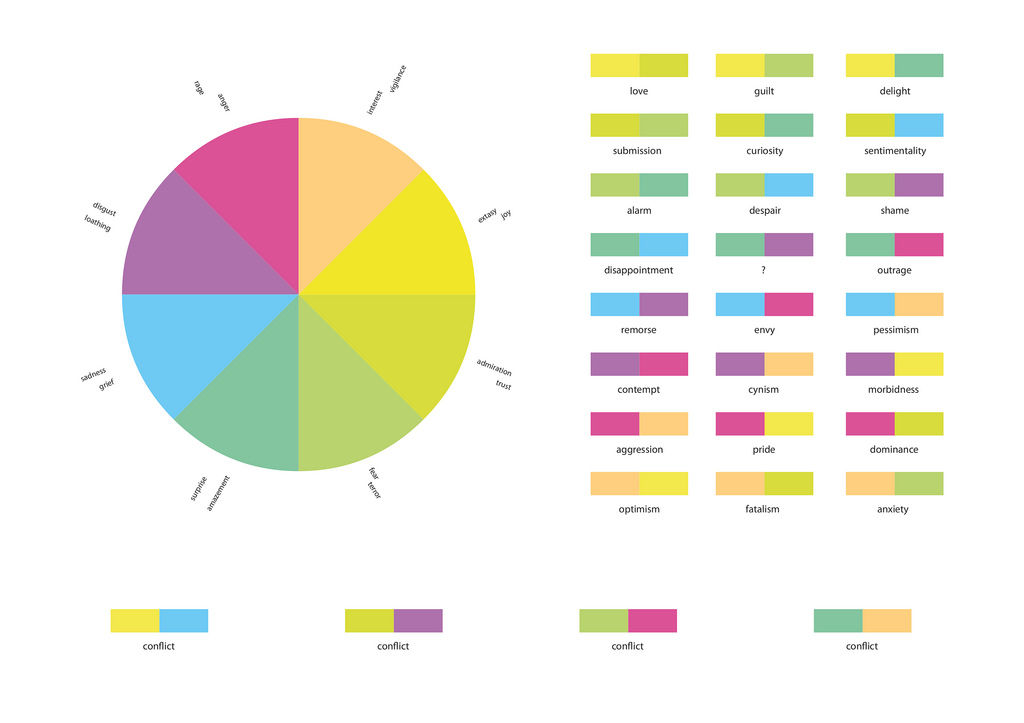
Combining Emotions
Combining different core emotions will create new emotions. Some examples include:
\(\large \begin{array}{lll} \\
\bm{ Joy } & +& \bm{ Trust } & = \bm{ Love } & \leftrightarrow \bm{ Remorse } \\
\bm{ Trust } & +& \bm{ Fear } & = \bm{ Submission } & \leftrightarrow \bm{ Contempt } \\
\bm{ Fear } & +& \bm{ Surprise } & = \bm{ Awe } & \leftrightarrow \bm{ Aggressiveness } \\
\bm{ Surprise } & +& \bm{ Sadness } & = \bm{ Disapproval } & \leftrightarrow \bm{ Optimism } \\
\bm{ Sadness } & +& \bm{ Disgust } & = \bm{ Remorse } & \leftrightarrow \bm{ Love } \\
\bm{ Disgust } & +& \bm{ Anger } & = \bm{ Contempt } & \leftrightarrow \bm{ Submission } \\
\bm{ Anticipation } & +& \bm{ Anger } & = \bm{ Aggressiveness } & \leftrightarrow \bm{ Awe } \\
\bm{ Serenity } & +& \bm{ Interest } & =\bm{ Optimism } & \leftrightarrow \bm{ Disapproval } \\
\end{array}\)
Do You Know What Love Really Is?
The Wheel of Emotion
From this initial emotional theory Plutchik then developed a Wheel of Emotion.
It was designed to help the user understand** the nuances of emotion** and how emotions contrast with each other.
He developed both 2 and 3 dimensional models for this.
The 3D model is the "cone-shaped model of emotion".
They were first described back in 1980.
The wheel can be used by designers to examine the complexities of emotion and to act as a "colour palette" for emotional design – with the idea being that blending different emotions will create different levels of emotional response and intensities of that response.
The wheel is a simple model and there are almost certainly additional emotional inferences that could be drawn from a more complex model – however, it focuses on the basic emotions that most designers are likely to want to elicit in their users and as such provides a useful starting point.
## Criticisms of Plutchik's Model
The biggest criticism of this model is its failure to take into account the pairing of Pride and Shame.
These are emotions which designers often play to.
For example, [gamification](https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/gamification) efforts may attempt to tap into a user's pride through [leaderboards](https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/leaderboards) or badges. Conversely charitable and campaigning organizations may try to tap into shame to encourage action.
It is also often felt that the model is too simplistic and that there are greater emotional nuances not captured within it.
However, it is generally agreed that the Wheel of Emotion is a good starting point when considering what emotions a design may elicit. It does not prevent the UX designer from looking for additional tools to aid in emotional design.
Other Emotion Wheels
Although Plutchik’s Wheel of Emotions is one of the more popular ones, you may not resonate with how it’s used or find it helpful. Therefore, there are a couple of other emotion wheels that have been developed since.
The GEW(Geneva Emotion Wheel)
Geneva's Wheel isn't in the shape of a wheel but is instead designed as a square with four main quadrants.
The GEW(Geneva Emotion Wheel)
SWISS CENTER FOR AFFECTIVE SCIENCES, University of Geneva, Swiss
Geneva Emotion Research Group
The development of this instrument has been supported by funds from the Gottlieb-Daimler- and Karl Benz-Foundation, Germany, the Swiss National Fund for Research, and the Swiss National Centre for Affective Sciences to Klaus Scherer.
The GEW(Geneva Emotion Wheel) is a theoretically derived and empirically tested instrument to measure emotional reactions to objects, events, and situations.
It divides emotions into four categories:
\(\large \begin{array}{lll} \\
&\bm{ Unpleasant } & , &\bm{ High\ Control } \\
&\bm{ Unpleasant } & , &\bm{ Low\ Control } \\
&\bm{ Pleasant } & , &\bm{ High\ Control } \\
&\bm{ Pleasant } & , &\bm{ Low\ Control } \\
\end{array}\)
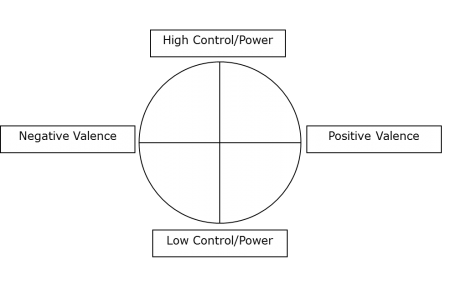
It's based on whether the emotion is pleasant or unpleasant and the level of control or power you feel you have over it or the circumstances that caused it.
For instance, the feeling of surprise is located on the border of pleasant and unpleasant and is categorized as low control. Surprises aren't always pleasant and it can be challenging to control that feeling.
Anger is a high control, unpleasant emotion,
Sadness is a low control, unpleasant emotion.
What If I Can't Identify My Emotion?
One of the features that the Geneva Wheel has that Plutchik's doesn't is an area for “no emotions” or “other emotions."
This is useful for those who experience emotional numbness and removes the pressure of finding a word to match the feeling you're feeling.
Sometimes, the stress of labeling an emotion can outweigh the benefits of identifying it.
Downloads
References
The development of the GEW is described in the following documents, which you can download for private use:
- Scherer, K. R. (2005). What are emotions? And how can they be measured? Social Science Information, 44(4), 693-727.
- Scherer, K.R., Shuman, V., Fontaine, J.R.J, & Soriano, C. (2013). The GRID meets the Wheel: Assessing emotional feeling via self-report. In Johnny R.J. Fontaine, Klaus R. Scherer & C. Soriano (Eds.), Components of Emotional Meaning: A sourcebook (pp. 281-298). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Sacharin, V., Schlegel K., & Scherer K. R. (2012). Geneva Emotion Wheel Rating Study. Unpublished report.
Junto's Wheel
Junto's Wheel was created as a for-profit tool by the Junto Institute to help businesses improve the emotional intelligence of their employees.
It consists of three inner circles and has a simple layout that is easy to use and understand.
Basic emotions are located in the center:
\(\large \begin{array}{lll} \\
&\bm{ Love } \\
&\bm{ Fear } \\
&\bm{ Anger } \\
&\bm{ Sadness } \\
&\bm{ Surprise } \\
&\bm{ Joy } \\
\end{array}\)
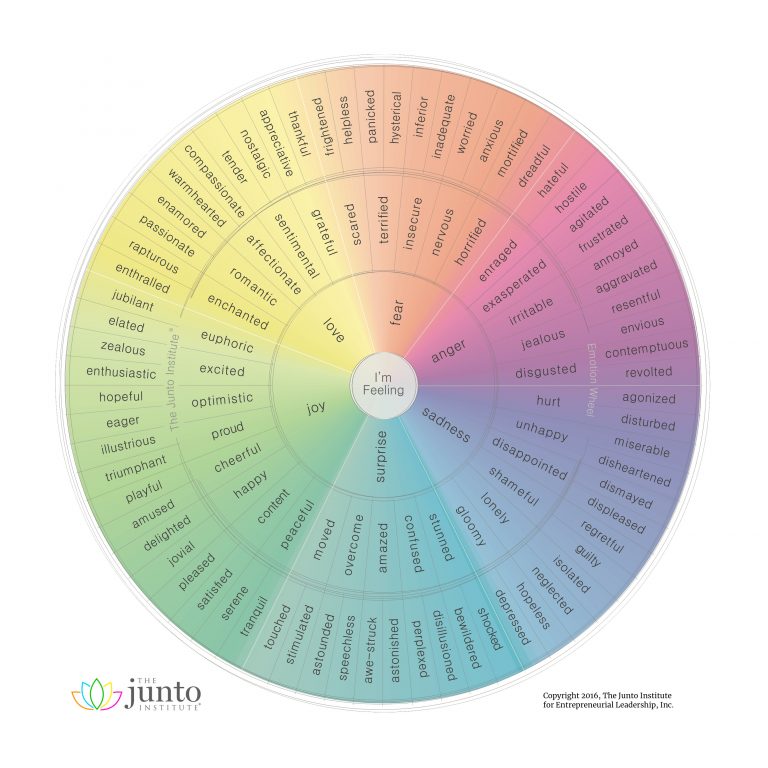
As you move to the outer edge of the wheel, the emotions become more complex and specific.
This can be helpful when **trying to understand the deeper layers** of **your initial feelings**.
For instance, you're feeling angry. However, after some self-reflection,
you realize you're also feeling jealous, resentful, and frustrated.
This Wheel Separates Love and Happiness
It is a comprehensive wheel with over 100 different emotions.
Unlike the other wheels, it separates love from happiness and categorizes it as a different emotion.
Tips For How to Use An Emotion Wheel
Putting words to our negative feelings is effective in reducing their intensity and effect.
How to Use and Emotion Wheel
Using an emotion wheel can be helpful for you to learn how to understand your emotions.
Here are some tips to get you started:
- Name your emotion:
Maybe you had a bad day at work. You feel uneasy and not like yourself.
Look at the wheel and** go through the list of emotions to find one or more** that describes that feeling.
Giving words to those feelings can help you feel more in control of them.- Reflect on why you're feeling this way:
The next step is to dig a little deeper to discover potential causes for these feelings.
When people are emotionally heightened, it's often not due to a single event but a series of experiences.
Spend some time reflecting on your day, past week, month, or even year.
For instance, maybe you're feeling sad but nothing sad happened that day.
However, it's been months since you've seen your friends.
You may be feeling lonely and isolated and craving some social interaction.- Take action:
Once you've identified the reasons for how you're feeling,
you can take action to manage your reaction to them and deal with the triggers.
This can mean changing your routine, doing activities that boost your mood, talking to a friend about what's been going on, or writing in your journal about it.
Sometimes having clarity about your emotions allows you to accept them for what they are and is sufficient enough for you to move forward.
Also Yourself to Feel What You Feel
There isn't a right or wrong way to identify your emotions. Using an emotion wheel is one of the many ways you can do this. The most important thing to remember is to not try to push emotions down, ignore them or bottle them up as that can harm our physical health, mental health, and general well-being.
A Word From Verywell
Confronting your emotions and dealing with them is incredibly beneficial in the long run.7If you find it difficult to manage your emotions, it can be helpful to talk to a therapist or healthcare professional. They can help you understand yourself better, develop mechanisms to improve your mental well-being, and provide a safe space for you to explore your thoughts and emotions.
| Created By | Reviewed By | Date |
|---|---|---|
 Katharine Chan, MSc, BSc, PMP Katharine is the author of three books (How To Deal With Asian Parents, A Honest Dating Guide and A Straight Up Guide to a Happy and Healthy Marriage) and the creator of 60 Feelings To Feel: A Journal To Identify Your Emotions. She has over 15 years of experience working in British Columbia's healthcare system. |
 Sabrina Romanoff, PsyD is a licensed clinical psychologist and a professor at Yeshiva University’s clinical psychology doctoral program. |
Updated on September 12, 2022 |
Verywell Mind
- articles are reviewed by mental health professionals.
- Reviewers confirm the content is thorough and accurate, reflecting the latest evidence-based research.
- Content is reviewed before publication and upon substantial updates. Learn more.
POLIR-Society-Organization-Psychology-Emotions情绪-Emotion Wheel情绪轮: What It Is and How to Use One的更多相关文章
- 利用Unity3D与Oculus实现机器情绪安抚师的一种方案
(一张最原始的Unity3D中音乐可视化粒子海的图,想象一下,如果这幅场景出现在虚拟设备中,辅以根据音乐频谱变化的色彩与悦动频率,会是怎样的效果呢?) Unity3D有着非常完备的虚拟三维场景交互开发 ...
- SpringBoot定时任务 - 经典定时任务设计:时间轮(Timing Wheel)案例和原理
Timer和ScheduledExecutorService是JDK内置的定时任务方案,而业内还有一个经典的定时任务的设计叫时间轮(Timing Wheel), Netty内部基于时间轮实现了一个Ha ...
- CET4词汇
abandon vt.丢弃:放弃,抛弃 ability n.能力:能耐,本领 abnormal a.不正常的:变态的 aboard ad.在船(车)上:上船 abroad ad.(在)国外:到处 ab ...
- PHP OO 编程笔记
1. 类中的方法不是全局方法,可以和外部的普通方法重名,例如: <?php function time(); 则会报错:不能重新声明方法 Fatal error: Cannot redeclar ...
- isEqual
"; NSString *str2 = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@", str1]; 大家明白, str1和str2在内存中的地址是不 ...
- 如今领占主导地位的19种AI技术!
如今领占主导地位的19种AI技术! http://blog.itpub.net/31542119/viewspace-2212797/ 深度学习的突破将人工智能带进全新阶段. 2006 年-2015 ...
- ios开发之--仿(微信)自定义表情键盘
先附上demo:https://github.com/hgl753951/CusEmoji.git 效果图如下:
- [译]处理文本数据(scikit-learn 教程3)
原文网址:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/tutorial/text_analytics/working_with_text_data.html 翻译:Tacey Won ...
- 英特尔实感SDK 代码示例
原文地址 摘要 本套代码示例针对巴西英特尔实感动手实验室创建,旨在帮助参与人员了解如何使用英特尔® 实感™ 软件开发套件. 12 个示例使用 C# SDK 包装程序,提供了简单的基于控制台的应用,支持 ...
- 《Power》读书笔记
原创作品 版权所有 转载请注明出处! 序言 权力是“争”来的,不是“等”来的. 会计.工商管理.营销和销售部门.财务人员(背景).企业咨询小组 在位晋升而竞争的时候,对于公平竞争原则,有些人会采取变通 ...
随机推荐
- <HarmonyOS第一课03>ArkTS语法介绍
视频链接: https://developer.huawei.com/consumer/cn/training/course/slightMooc/C101717496870909384?ha_sou ...
- Manus邀请码,Manus:科技圈新“炸点”,还是又一场狂欢?
嗨,大家好,我是小华同学,关注我们获得"最新.最全.最优质"开源项目和高效工作学习方法 想要邀请码获取方式往下看哟,同学~~~ 2025年3月6日,AI圈被一款名为Manus的产品 ...
- 3.4K star!全能PDF处理神器开源!文档转换/OCR识别一键搞定
嗨,大家好,我是小华同学,关注我们获得"最新.最全.最优质"开源项目和高效工作学习方法 PDF-Guru 是一款开箱即用的全能型PDF处理工具,支持跨平台文档转换.智能OCR识别. ...
- JavaScript中通过闭包来实现私有变量的一种方法
'use strict'; const SecretHolder = (function () { const secrets = new WeakMap(); return class { cons ...
- iOS快捷指令——记录今天、今年已过进度的工具
起因是看到了 大佬博客 里面一个计时的小工具,于是也想搞一个来提醒自己珍惜时间. 经过一段时间对快捷指令的摸索,最终选择了如下的方式完成: 快捷指令的链接在这里给出: https://www.iclo ...
- odoo14里面附件传输接口
@http.route('/fmcg/download/pdf', type='http', auth="public", csrf=False, cors='*') def up ...
- IDEA jrebel热部署插件破解-最新版
前言 JRebel插件2022.4.2及之后版本在线地址激活方式已不可用,所以采用本地地址 + 生成的GUID方式 激活 (本文章写的时候,用的JRebel最新版本2023.2.1) 如果需要在线激活 ...
- 「Note」您想来点数据结构吗?
大分块系列 最初分块 \(\color{black}{P4119}\) 考虑数列分块+值域分块 数列分块需要维护: \(nid_{i,j}\) \(fid_i\) \(f_i\) 块 \(i\) 中数 ...
- 「Log」2023.8.16 小记
序幕 早上昏迷,九点才到校,少听了四道题,问题不大. 点咖啡喝. SAM 题也抽象.线段树合并,不会. 写个 AC 自动机板子. \(\color{royalblue}{P3808\ [模板]AC\ ...
- 【中文】【吴恩达课后编程作业】Course 1 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第四周作业(1&2)
[吴恩达课后编程作业]01 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第四周 - PA1&2 - 一步步搭建多层神经网络以及应用 上一篇:[课程1 - 第四周测验]※※※※※ [回到目录]※※※※※下一篇: ...
