【Spring源码深度解析学习系列】容器的基础XmlBeanFactory(二)
一、配置文件封装
Spring的配置文件读取是通过ClassPathResource进行封装的,如new ClassPathResource("test.xml"),那么ClassPathResource完成的功能是什么呢?
在java中,将不同来源的资源抽象成URL,通过注册不同的handler(URLStreamHandler)来处理不同来源的资源的读取逻辑,一般handler的类型使用不同前缀(协议,Protocol)来识别,如:file: http: jar: 等,然而URL没有默认定义相对Classpath或ServletContext等资源的handler,虽然可以注册自己的URLStreamHandler来解析特定的URL前缀(协议),比如“classpath:”,这个需要了解URL的实现机制,而且url也没有提供一些基本的方法,如检查当前资源是否存在、检查当前资源是否可读等方法。因而Spring对其内部使用到的资源实现了自己的抽象结构:Resource接口来封装底层资源:
public interface InputStreamSource {
/**
* Return an {@link InputStream} for the content of an underlying resource.
* <p>It is expected that each call creates a <i>fresh</i> stream.
* <p>This requirement is particularly important when you consider an API such
* as JavaMail, which needs to be able to read the stream multiple times when
* creating mail attachments. For such a use case, it is <i>required</i>
* that each {@code getInputStream()} call returns a fresh stream.
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* Determine whether this resource actually exists in physical form.
* <p>This method performs a definitive existence check, whereas the
* existence of a {@code Resource} handle only guarantees a valid
* descriptor handle.
*/
boolean exists();
/**
* Indicate whether the contents of this resource can be read via
* {@link #getInputStream()}.
* <p>Will be {@code true} for typical resource descriptors;
* note that actual content reading may still fail when attempted.
* However, a value of {@code false} is a definitive indication
* that the resource content cannot be read.
* @see #getInputStream()
*/
boolean isReadable();
/**
* Indicate whether this resource represents a handle with an open stream.
* If {@code true}, the InputStream cannot be read multiple times,
* and must be read and closed to avoid resource leaks.
* <p>Will be {@code false} for typical resource descriptors.
*/
boolean isOpen();
/**
* Return a URL handle for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as URL,
* i.e. if the resource is not available as descriptor
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* Return a URI handle for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved as URI,
* i.e. if the resource is not available as descriptor
* @since 2.5
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* Return a File handle for this resource.
* @throws java.io.FileNotFoundException if the resource cannot be resolved as
* absolute file path, i.e. if the resource is not available in a file system
* @throws IOException in case of general resolution/reading failures
* @see #getInputStream()
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* Determine the content length for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved
* (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type)
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* Determine the last-modified timestamp for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved
* (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type)
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* Create a resource relative to this resource.
* @param relativePath the relative path (relative to this resource)
* @return the resource handle for the relative resource
* @throws IOException if the relative resource cannot be determined
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* Determine a filename for this resource, i.e. typically the last
* part of the path: for example, "myfile.txt".
* <p>Returns {@code null} if this type of resource does not
* have a filename.
*/
String getFilename();
/**
* Return a description for this resource,
* to be used for error output when working with the resource.
* <p>Implementations are also encouraged to return this value
* from their {@code toString} method.
* @see Object#toString()
*/
String getDescription();
}
InputStreamSource封装任何能返回InputStream的类,比如File、Classpath下的资源和 Byte Array对象。它只有一个方法定义:getInputStream(),该方法返回一个新的InputStream对象。
Resource接口抽象了所有Spring内部使用到的底层资源:File、URL、Classpath等,首先、它定义了3个判断当前资源状态的方法:存在性(exists)、可读性(isReaddable)、是否处于打开状态(isOpen)另外Resource接口还提供了不同资源到URL、URI、File类型的转换,以及获取lastModified属性、文件名(不带路径信息的文件名,getFilename())的方法。为了便于操作,Resource还提供了基于当前资源创建一个相对资源的犯法:createRelative()。在错误处理中需要详细打印出错的资源文件,因而Resource还提供了getDescription()方法用于在错误处理中的打印信息。
对不同来源的资源文件都有相应的Resource实现:文件(FileSystemResource)、Classpath资源(ClassPathResource)、URL资源(UrlResource)、InputStream资源(InputStreamResource)、Byte数组(ByteArrayResource)等。
加载资源文件的代码:
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("beanFactoryTest.xml");
InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
ClassPathResource的实现:
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is;
if (this.clazz != null) {
is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
else if (this.classLoader != null) {
is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
else {
is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
}
return is;
}
FileInputStream的实现:
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return new FileInputStream(this.file);
}
当通过Resource相关类完成了对配置文件进行封装后配置文件的读取工作就全权交给XmlBeanDefinitonReader来处理了。
XmlBeanFactory的初始化有若干方法,Spring中提供了很多的构造函数,以下为使用Resource实例作为构造函数参数的办法。
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
//调用XmlBeanFactory(Resource,BeanFactory)构造方法
this(resource, null);
}
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}

public void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc) {
this.ignoredDependencyInterfaces.add(ifc);
}
ignoreDependencyInterface的主要功能是忽略给定接口的自动装配功能。这样做的目的是什么呢?举例来说,当A中有属性B,那么当Spring在获取A的Bean的时候如果其属性B还没有初始化,那么Spring会自动初始化B,这也是Spring中提供的一个重要特性。但是某些情况下,B不会被初始化,其中的一种情况就是B实现了BeanNameAware接口,Spring中是这样介绍的:自动装配时忽略给定的依赖接口,典型应用是通过其他方式解析Application上下文注册依赖,类似于BeanFactory通过BeanFactoryAware进行注册或者ApplicationContext通过ApplicationContextAware进行注入。
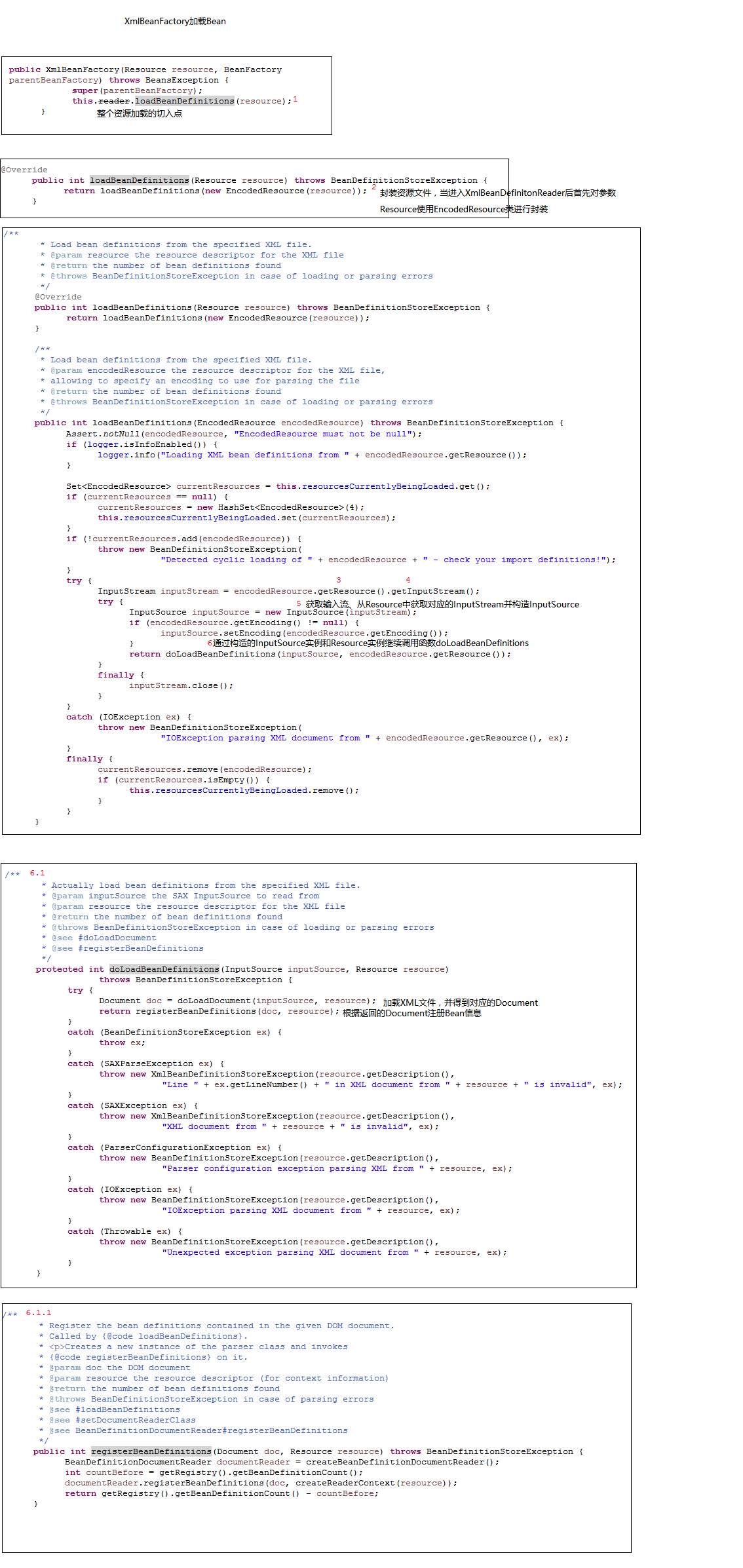
二、加载Bean
【Spring源码深度解析学习系列】容器的基础XmlBeanFactory(二)的更多相关文章
- 【Spring源码深度解析学习系列】Bean的加载(六)
Bean的加载所涉及到的大致步骤: 1)转换对应beanName 为什么需要转换beanName呢?因为传入的参数可能是别名,也可能是FactoryBean,所以需要一系列的解析,这些解析内容包括如下 ...
- 【Spring源码深度解析学习系列】复杂标签属性解析(四)
一.创建用于属性承载的BeanDefinition BeanDefiniton是一个接口,在Spring中存在三种实现:RootBeanDefinition.ChildBeanDefinition.G ...
- 【Spring源码深度解析学习系列】默认标签解析(三)
Spring的标签包括默认标签和自定义标签两种 默认标签的解析方法: ###DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java### private void parse ...
- 【Spring源码深度解析学习系列】核心类介绍(一)
一.DefaultListableBeanFactory 首先看一下结构 由图可知XmlBeanFactory继承自DefaultListableBeanFactory,而DefaultListabl ...
- 【Spring源码深度解析学习系列】注册解析的BeanDefinition(五)
对于配置文件,解析和装饰完成之后,对于得到的beanDefinition已经可以满足后续的使用要求了,还剩下注册,也就是processBeanDefinition函数中的BeanDefinitionR ...
- spring源码深度解析— IOC 之 容器的基本实现
概述 上一篇我们搭建完Spring源码阅读环境,spring源码深度解析—Spring的整体架构和环境搭建 这篇我们开始真正的阅读Spring的源码,分析spring的源码之前我们先来简单回顾下spr ...
- Spring源码分析(四)容器的基础XmlBeanFactory
摘要:本文结合<Spring源码深度解析>来分析Spring 5.0.6版本的源代码.若有描述错误之处,欢迎指正. 经过Spring源码分析(二)容器基本用法和Spring源码分析(三)容 ...
- spring源码深度解析— IOC 之 开启 bean 的加载
概述 前面我们已经分析了spring对于xml配置文件的解析,将分析的信息组装成 BeanDefinition,并将其保存注册到相应的 BeanDefinitionRegistry 中.至此,Spri ...
- spring源码深度解析— IOC 之 默认标签解析(上)
概述 接前两篇文章 spring源码深度解析—Spring的整体架构和环境搭建 和 spring源码深度解析— IOC 之 容器的基本实现 本文主要研究Spring标签的解析,Spring的标签 ...
随机推荐
- Mac 常用快捷键
可以按下组合键来实现通常需要鼠标.触控板或其他输入设备才能完成的操作. 要使用键盘快捷键,需按住一个或多个修饰键,同时按快捷键的最后一个键.例如,要使用快捷键 Command-C(拷贝),请按住 Co ...
- Aspose实现Office转PDF (ASP.NET)
0.添加Aspose的DLL 1.可以直接去官网下载,不过默认是带水印的,如需去除水印可以购买 2.当然也可以在国内的一些下载站下载 3.将Aspose.Cells.dll.Aspose.Words. ...
- 【BZOJ1717】产奶的模式(后缀数组)
[BZOJ1717]产奶的模式(后缀数组) 题面 权限题 hihocoder 洛谷 题解 \(hihocoder\)里面讲的非常好了 这题要求的就是最长可重叠重复K次子串 所谓相同的子串 我们可以理解 ...
- Python Django的生产部署方式
本地化部署的Django有很大的局限性,无法用于生产环境,比如无法抗住多并发,无法长时间的运行,容易造成网页无响应的问题.所以如何将Django部署到真正的生产环境中,让其能够真正的像正常的网页一样工 ...
- 完全卸载hadoop安装的组件(hdp版本)
yum remove -y hadoop_* zookeeper* ranger* hbase_* ranger* hbase_* ambari-* hadoop_* zookeeper_* hbas ...
- SpringMVC【开发Controller】详解
前言 本文主要是讲解在Controller中的开发,主要的知识点有如下: 编码过滤器 使用注解开发 注解@RequestMapping详解 业务方法接收参数 字符串转日期 重定向和转发 返回JSON ...
- Xamarin改变移动开发的五个理由
企业开发者不能简单的抛弃现有的桌面和Web应用,然而又不得不忙着创建各种各样的应用,没有太多的预算来开发移动版本,尤其是原生版本. 采用Xamarin,C#开发人员可以使用一份基础代码创建桌面版和移动 ...
- Linux系统默认权限之umask
默认情况下,目录权限值为755, 普通文件权限值为644, 那么这个值是由谁规定的,追究其原因是 umask [root@adminx]# vim /etc/profile 1.假设umask值为:0 ...
- JavaScript中的execCommand
execCommand方法是执行一个对当前文档,当前选择或者给出范围的命令.处理Html数据时常用 如下格式:document.execCommand(sCommand[,交互方式, 动态参数]) , ...
- Angular4---起步----环境配置安装@angular/cli
学习angular,首先要搭建起angular的手脚架@angular/cli.首先需要NodeJS环境. 1.安装NodeJS 首先检查电脑是否安装了NodeJS环境,打开cmd命令行,运行node ...
