kaggle 实战 (1): PCA + KNN 手写数字识别
本文采用PCA+KNN的方法进行kaggle手写数字识别,训练数据共有42000行,每行代表一幅数字图片,共有784列(一副数字图像是28*28像素,将一副图像展开为一行即784),更多关于Digit Recognizer项目的介绍https://www.kaggle.com/c/digit-recognizer
由于训练数据量太大,直接采用KNN非常耗时,采用PCA降维的方法,选取25个维度,跑完全部数据只需200秒左右。
加载package
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed
# It is defined by the kaggle/python docker image: https://github.com/kaggle/docker-python
# For example, here's several helpful packages to load in
import numpy as np # linear algebra
import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # import de Matplotlib
from IPython.display import display
from PIL import Image
# Input data files are available in the "../input/" directory.
# For example, running this (by clicking run or pressing Shift+Enter) will list the files in the input directory
import os
print(os.listdir("../input"))
# Any results you write to the current directory are saved as output.
read data
train=pd.read_csv('../input/train.csv')
train.shape
submission = pd.read_csv('../input/test.csv')
test=pd.read_csv('../input/test.csv')
test.shape
y_train = train['label']
y_train.head()
x_train=train.drop(['label'], axis=1)
x_train.head() # affiche le tableau ci-dessous
X_submission =test
PCA 降维探索
pca = PCA(200)
pca_full = pca.fit(x_train)
plt.plot(np.cumsum(pca_full.explained_variance_ratio_))
plt.xlabel('# of components')
plt.ylabel('Cumulative explained variance')

选择50维度, 拆分数据为训练集,测试机
pca = PCA(n_components=50)
X_train_transformed = pca.fit_transform(x_train)
X_submission_transformed = pca.transform(x_test)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train_pca, X_test_pca, y_train_pca, y_test_pca = train_test_split(X_train_transformed, y_train, test_size=0.2, random_state=13)
KNN PCA降维和K值筛选
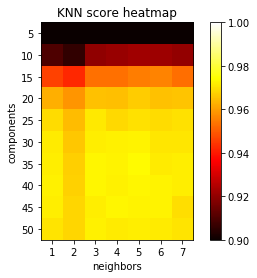
components = [5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50]
neighbors = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
scores = np.zeros( (components[len(components)-1]+1, neighbors[len(neighbors)-1]+1 ) )
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
for component in components:
for n in neighbors:
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=n)
knn.fit(X_train_pca[:,:component], y_train_pca)
score = knn.score(X_test_pca[:,:component], y_test_pca)
#predict = knn.predict(X_test_pca[:,:component])
scores[component][n] = score
print('Components = ', component, ', neighbors = ', n,', Score = ', score)

k 值的意义:

分析k & 维度 vs 精度
scores = np.reshape(scores[scores != 0], (len(components), len(neighbors)))
x = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
y = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
plt.rcParams["axes.grid"] = False
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.imshow(scores, cmap='hot', interpolation='none', vmin=.90, vmax=1)
plt.xlabel('neighbors')
plt.ylabel('components')
plt.xticks(x, neighbors)
plt.yticks(y, components)
plt.title('KNN score heatmap')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
预测
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn.fit(X_train_pca[:, :35], y_train_pca)
predict_labels = knn.predict(X_submission_transformed[:, :35])
对于PCA维度的选取:在多次尝试后,采用35个维度,效果较好。需要注意的是,PCA处理后的训练数据和原始数据是不同的,所以采用PCA处理数据后,并不是选取的维度越多精确度就越好。k 选5 可以达到很好效果
生成提交文件
Submission = pd.DataFrame({
"ImageId": range(1, predict_labels.shape[0]+1),
"Label": predict_labels
})
Submission.to_csv("KnnMnistSubmission.csv", index=False)
Submission.head(5)
kaggle 实战 (1): PCA + KNN 手写数字识别的更多相关文章
- 机器学习(二)-kNN手写数字识别
一.kNN算法是机器学习的入门算法,其中不涉及训练,主要思想是计算待测点和参照点的距离,选取距离较近的参照点的类别作为待测点的的类别. 1,距离可以是欧式距离,夹角余弦距离等等. 2,k值不能选择太大 ...
- 10,knn手写数字识别
# 导包 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClas ...
- KNN手写数字识别
import numpy as np import matplotlib .pyplot as plt from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifi ...
- 一看就懂的K近邻算法(KNN),K-D树,并实现手写数字识别!
1. 什么是KNN 1.1 KNN的通俗解释 何谓K近邻算法,即K-Nearest Neighbor algorithm,简称KNN算法,单从名字来猜想,可以简单粗暴的认为是:K个最近的邻居,当K=1 ...
- Kaggle竞赛丨入门手写数字识别之KNN、CNN、降维
引言 这段时间来,看了西瓜书.蓝皮书,各种机器学习算法都有所了解,但在实践方面却缺乏相应的锻炼.于是我决定通过Kaggle这个平台来提升一下自己的应用能力,培养自己的数据分析能力. 我个人的计划是先从 ...
- K近邻实战手写数字识别
1.导包 import numpy as np import operator from os import listdir from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighb ...
- 深度学习之PyTorch实战(3)——实战手写数字识别
上一节,我们已经学会了基于PyTorch深度学习框架高效,快捷的搭建一个神经网络,并对模型进行训练和对参数进行优化的方法,接下来让我们牛刀小试,基于PyTorch框架使用神经网络来解决一个关于手写数字 ...
- KNN实现手写数字识别
KNN实现手写数字识别 博客上显示这个没有Jupyter的好看,想看Jupyter Notebook的请戳KNN实现手写数字识别.ipynb 1 - 导入模块 import numpy as np i ...
- 用MXnet实战深度学习之一:安装GPU版mxnet并跑一个MNIST手写数字识别
用MXnet实战深度学习之一:安装GPU版mxnet并跑一个MNIST手写数字识别 http://phunter.farbox.com/post/mxnet-tutorial1 用MXnet实战深度学 ...
随机推荐
- mysql数据库中某字段一部分乱码
笔者问题:mysql表(表中数据就是乱码,可能是插入时编码问题,这个问题以后解决)导出excel时数据中有乱码(但是在页面上查看是正常的),我们希望能导出一份没有中文乱码的excel 根据热力站中一次 ...
- SetupFactory 许可协议设置
我用的SetupFactory版本是9.1.0 没有汉化 一开始自己也不知道 百度发现有人在问同样的问题但是没解决 自己找了一会偶然发现 界面左侧 Screens->Before Install ...
- 安装apache的注意事项
在安装apache的时候我们一般都会用yum一键安装,但是很少去考虑相关的依赖包有什么,所以今天特意做一个记录,方便以后编译安装的时候,进展顺利. yum install httpd Installi ...
- python png与jpg的相互转换
python将PNG格式的图片转化成为jpg """ 先来说一下jpg图片和png图片的区别 jpg格式:是有损图片压缩类型,可用最少的磁盘空间得到较好的图像质量 png ...
- 自行制作yum源仓库
背景 客户服务器为内网机器,centos7系统,且无法与外网连接.需要部署对应的LANMP环境及其它软件 解决思路 1.在阿里云服务器,利用阿里云的yum源仓库,下载对应软件及关联软件. 2.在客户机 ...
- Java ----单个list 删除元素
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/lostyears/p/8809336.html 方式一:使用Iterator的remove()方法 public class Test { pu ...
- Dubbo的初步理解和使用
Dubbo(读音[ˈdʌbəʊ])是阿里巴巴公司开源的一个高性能优秀的服务框架,使得应用可通过高性能的 RPC 实现服务的输出和输入功能,可以和 [1] Spring框架无缝集成. Dubbo是一款 ...
- 如何打造7*24h持续交付通道?阿里高级技术专家的5点思考
我们对于研发效能的讨论,本质上是提高整个技术生态中的协同效率.如果仅从研发角度出发,技术团队要实现的终极目标是7*24小时的灵活发布窗口,以及更快的业务迭代能力. 7*24小时发布窗口的实现其实并不简 ...
- 几道51nod上据说是提高组难度的dp题
1409 加强版贪吃蛇 听着懵逼做着傻逼. 每个格子只能经过一次,穿过上下界答案清0,不考虑穿的话就随便dp.如果要穿就是从尽可能上面的位置穿过上界,尽可能下面的位置穿过下界. 那么转移这一列之前找一 ...
- NX二次开发-UFUN删除工程图UF_DRAW_delete_drawing
NX9+VS2012 #include <uf.h> #include <uf_draw.h> #include <uf_part.h> UF_initialize ...
