faster-rcnn代码阅读-rpn-data层
这一节讲述rpn-data层,和这一层有关的结构图如下:
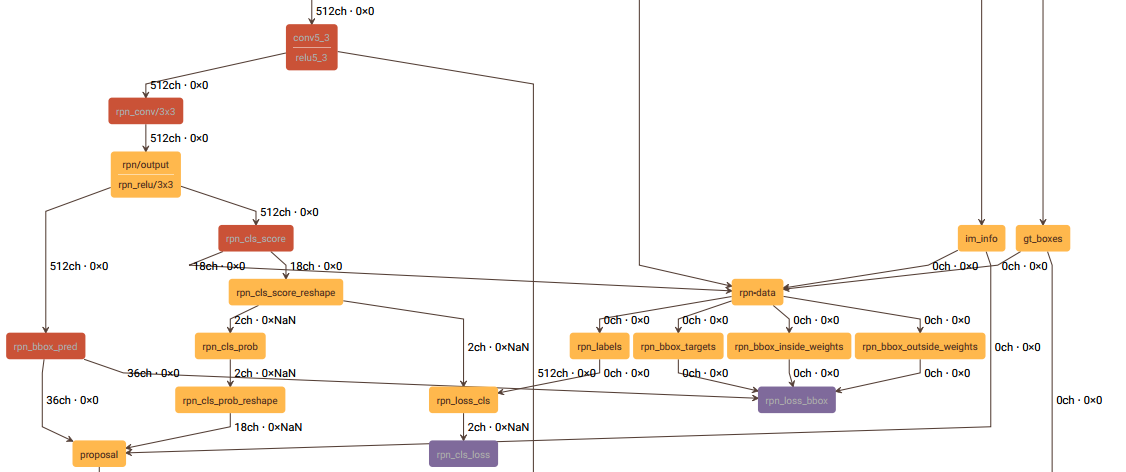
rpn-data层的prototxt定义如下:
layer {
name: 'rpn-data'
type: 'Python'
bottom: 'rpn_cls_score'
bottom: 'gt_boxes'
bottom: 'im_info'
bottom: 'data'
top: 'rpn_labels'
top: 'rpn_bbox_targets'
top: 'rpn_bbox_inside_weights'
top: 'rpn_bbox_outside_weights'
python_param {
module: 'rpn.anchor_target_layer'
layer: 'AnchorTargetLayer'
param_str: "'feat_stride': 16"
}
}
这一层的主要工作如下:
一、生成anchor,并将超出图像区域的anchor去除,得到有效的anchor;
二、给每一个anchor分配label,-1表示忽略该anchor,0表示背景,1表示前景(物体),得到labels;
三、计算RPN阶段的回归目标bbox_targets;
四、计算bbox_inside_weights、bbox_outside_weights,在计算SmoothL1Loss时用于加权;
五、上述过程得到的labels, bbox_targets, bbox_inside_weights, bbox_outside_weights,它们第一个维度的长度和有效anchor的个数是相同的,最后对它们进行扩充,将无效的anchor所对应的labels, bbox_targets, bbox_inside_weights, bbox_outside_weights分别加入其中,使这四个输出第一个维度的长度等于生成anchor的个数。
下面分别介绍这5个部分。
一、生成anchor
1、先生成一个base_anchor,长宽都为16,得出base_anchor的宽高和中心点:w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr;
2、由基准尺度(base_size=16)和3种长宽比0.5, 1, 2计算出3种宽高,再由步骤1得到的中心点计算出3个anchor的坐标;
3、再将3种尺度8, 16, 32和步骤2所得anchor的尺度相乘,得出9种宽高,结合步骤1所得中心点坐标,最终得到9个anchor的坐标。
4、使backbone输出的feature map的每一个位置的坐标间隔为feature map的降采样率(VGG为16),这样,feature map像素坐标的尺度就和输入网络的图像像素的坐标尺度一样了。将步骤3所得到的9个anchor的中心点分别移动到feature map每个像素的坐标位置上,便得到了最终的anchor。
二、分配label
1、构建一个label数组,长度有效anchor的数量,每个元素都初始化为-1;
2、计算每个anchor和所有gt的交并比;
3、将和所有gt的交并比都小于0.3的anchor,label分配为0,即为背景;
4、将和每一个gt交并比最大的anchor,label分配为1,即为前景;
5、将和任意一个gt交并比能大于0.7的anchor,label分配为1,即为前景;
6、RPN阶段的batchsize为256,前景anchor占比为0.5,因此有128个。如果前面得到的前景anchor的数量超过了128,则随机剔除多余的anchor,剔除的部分label置为-1;
7、batchsize为256,除去前景anchor的数量,剩余的即为背景anchor的数量。若背景anchor数量过多,则随机剔除多余的背景,剔除的部分label仍置为-1。
三、计算RPN阶段的回归目标
回归目标其实就是anchor的中心点坐标、宽、高和与之交并比最大的gt的偏差dx, dy, dw, dh,这些偏差不是二者直接作差得到的,而是经过一些转换才得到的,具体见下面的代码:
def bbox_transform(ex_rois, gt_rois):
ex_widths = ex_rois[:, 2] - ex_rois[:, 0] + 1.0
ex_heights = ex_rois[:, 3] - ex_rois[:, 1] + 1.0
ex_ctr_x = ex_rois[:, 0] + 0.5 * ex_widths
ex_ctr_y = ex_rois[:, 1] + 0.5 * ex_heights gt_widths = gt_rois[:, 2] - gt_rois[:, 0] + 1.0
gt_heights = gt_rois[:, 3] - gt_rois[:, 1] + 1.0
gt_ctr_x = gt_rois[:, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths
gt_ctr_y = gt_rois[:, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights targets_dx = (gt_ctr_x - ex_ctr_x) / ex_widths
targets_dy = (gt_ctr_y - ex_ctr_y) / ex_heights
targets_dw = np.log(gt_widths / ex_widths)
targets_dh = np.log(gt_heights / ex_heights) targets = np.vstack(
(targets_dx, targets_dy, targets_dw, targets_dh)).transpose()
return targets
四、计算一些权重,用于SmoothL1Loss的计算
1、bbox_inside_weights:将label为1的anchor权重赋为1,其他的都赋为0;
2、bbox_outside_weights:将前景和背景anchor的总数记为n,则前景和背景anchor权重都赋为1/n,其它的anchor权重都赋为0。
五、结果扩充
这一步的目的是为了使这一层的输出结果的维度和其它层的结果相匹配,直接能和其它层的输出结合起来,一起参与网络的前向和反向计算。
最后给出SmoothL1Loss的主要代码:
template <typename Dtype>
void SmoothL1LossLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
SmoothL1LossParameter loss_param = this->layer_param_.smooth_l1_loss_param();
sigma2_ = loss_param.sigma() * loss_param.sigma();
has_weights_ = (bottom.size() >= );
if (has_weights_) {
CHECK_EQ(bottom.size(), ) << "If weights are used, must specify both "
"inside and outside weights";
}
} template <typename Dtype>
void SmoothL1LossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
LossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(bottom, top);
CHECK_EQ(bottom[]->channels(), bottom[]->channels());
CHECK_EQ(bottom[]->height(), bottom[]->height());
CHECK_EQ(bottom[]->width(), bottom[]->width());
if (has_weights_) {
CHECK_EQ(bottom[]->channels(), bottom[]->channels());
CHECK_EQ(bottom[]->height(), bottom[]->height());
CHECK_EQ(bottom[]->width(), bottom[]->width());
CHECK_EQ(bottom[]->channels(), bottom[]->channels());
CHECK_EQ(bottom[]->height(), bottom[]->height());
CHECK_EQ(bottom[]->width(), bottom[]->width());
}
diff_.Reshape(bottom[]->num(), bottom[]->channels(),
bottom[]->height(), bottom[]->width());
errors_.Reshape(bottom[]->num(), bottom[]->channels(),
bottom[]->height(), bottom[]->width());
// vector of ones used to sum
ones_.Reshape(bottom[]->num(), bottom[]->channels(),
bottom[]->height(), bottom[]->width());
for (int i = ; i < bottom[]->count(); ++i) {
ones_.mutable_cpu_data()[i] = Dtype();
}
} template <typename Dtype>
__global__ void SmoothL1Forward(const int n, const Dtype* in, Dtype* out,
Dtype sigma2) {
// f(x) = 0.5 * (sigma * x)^2 if |x| < 1 / sigma / sigma
// |x| - 0.5 / sigma / sigma otherwise
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, n) {
Dtype val = in[index];
Dtype abs_val = abs(val);
if (abs_val < 1.0 / sigma2) {
out[index] = 0.5 * val * val * sigma2;
} else {
out[index] = abs_val - 0.5 / sigma2;
}
}
} template <typename Dtype>
void SmoothL1LossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
int count = bottom[]->count();
caffe_gpu_sub(
count,
bottom[]->gpu_data(),
bottom[]->gpu_data(),
diff_.mutable_gpu_data()); // d := b0 - b1
if (has_weights_) {
// apply "inside" weights
caffe_gpu_mul(
count,
bottom[]->gpu_data(),
diff_.gpu_data(),
diff_.mutable_gpu_data()); // d := w_in * (b0 - b1)
}
SmoothL1Forward<Dtype><<<CAFFE_GET_BLOCKS(count), CAFFE_CUDA_NUM_THREADS>>>(
count, diff_.gpu_data(), errors_.mutable_gpu_data(), sigma2_);
CUDA_POST_KERNEL_CHECK; if (has_weights_) {
// apply "outside" weights
caffe_gpu_mul(
count,
bottom[]->gpu_data(),
errors_.gpu_data(),
errors_.mutable_gpu_data()); // d := w_out * SmoothL1(w_in * (b0 - b1))
} Dtype loss;
caffe_gpu_dot(count, ones_.gpu_data(), errors_.gpu_data(), &loss);
top[]->mutable_cpu_data()[] = loss / bottom[]->num();
}
其中:
1、bottom[0]为rpn_bbox_pred,即网络预测出的anchor与gt的偏差;
2、bottom[1]为rpn_bbox_targets,即为第三步计算出的anchor与gt的实际偏差;
3、bottom[2]为bbox_inside_weights;
4、bottom[3]为bbox_outside_weights。
这一层的代码链接见这里,此外涉及到的其它函数有generate_anchors,bbox_overlaps。
faster-rcnn代码阅读-rpn-data层的更多相关文章
- Faster RCNN代码理解(Python)
转自http://www.infocool.net/kb/Python/201611/209696.html#原文地址 第一步,准备 从train_faster_rcnn_alt_opt.py入: 初 ...
- Faster rcnn代码理解(4)
上一篇我们说完了AnchorTargetLayer层,然后我将Faster rcnn中的其他层看了,这里把ROIPoolingLayer层说一下: 我先说一下它的实现原理:RPN生成的roi区域大小是 ...
- Faster rcnn代码理解(2)
接着上篇的博客,咱们继续看一下Faster RCNN的代码- 上次大致讲完了Faster rcnn在训练时是如何获取imdb和roidb文件的,主要都在train_rpn()的get_roidb()函 ...
- Faster RCNN代码解析
1.faster_rcnn_end2end训练 1.1训练入口及配置 def train(): cfg.GPU_ID = 0 cfg_file = "../experiments/cfgs/ ...
- Faster R-CNN论文阅读摘要
论文链接: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.01497.pdf 代码下载: https://github.com/ShaoqingRen/faster_rcnn (MATLAB) ...
- Faster R-CNN代码例子
主要参考文章:1,从编程实现角度学习Faster R-CNN(附极简实现) 经常是做到一半发现收敛情况不理想,然后又回去看看这篇文章的细节. 另外两篇: 2,Faster R-CNN学习总结 ...
- Faster rcnn代码理解(3)
紧接着之前的博客,我们继续来看faster rcnn中的AnchorTargetLayer层: 该层定义在lib>rpn>中,见该层定义: 首先说一下这一层的目的是输出在特征图上所有点的a ...
- Faster rcnn代码理解(1)
这段时间看了不少论文,回头看看,感觉还是有必要将Faster rcnn的源码理解一下,毕竟后来很多方法都和它有相近之处,同时理解该框架也有助于以后自己修改和编写自己的框架.好的开始吧- 这里我们跟着F ...
- tensorflow faster rcnn 代码分析一 demo.py
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"]=2 # 设置使用的GPU tfconfig=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placeme ...
- 对faster rcnn代码讲解的很好的一个
http://www.cnblogs.com/houkai/p/6824455.html http://blog.csdn.net/u014696921/article/details/6032142 ...
随机推荐
- PHP ftp_get() 函数
定义和用法 ftp_get() 函数从 FTP 服务器上下载一个文件并保存到本地一个文件中. 如果成功,该函数返回 TRUE.如果失败,则返回 FALSE. 语法 ftp_get(ftp_connec ...
- jmeter之-用Firefox录制https协议证书问题
录制脚本的时候,比如录制https协议的百度网站 https://www.baidu.com ,所有录制设置均正常,但是在jmeter录制控制器里面就是没有任何录制的请求. 这个时候提示说证书不对 1 ...
- java_monitor
转载自http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_9385f6d90101dbqy.html java会为每个object对象分配一个monitor,当某个对象的同步方法(synch ...
- Machine Learning 之一,什么是机器学习。
Machine Learning 机器学习,什么是机器学习.我觉得尚学堂的培训老师讲的很不错,就是两个字来介绍.------拟人. 就是模拟人类的思维方式. 老师举的例子: 和女朋友约会,第一次约会, ...
- 关于Python中函数的使用
函数的概念 # 概念 # 写了一段代码实现了某个小功能; 然后把这些代码集中到一块, 起一个名字; 下一次就可以根据这个名字再次使用这个代码块, 这就是函数 # 作用 # 方便代码的重用 # 分解任务 ...
- 3.4 redux 异步
在大多数的前端业务场景中,需要和后端产生异步交互,在本节中,将详细讲解 redux 中的异步方案以及一些异步第三方组件,内容有: redux 异步流 redux-thunk redux-promise ...
- 7、Appium常用API
嗯,官网已经介绍的很全了.会选几个常用API后期整理. Appium常用API地址:http://appium.io/docs/cn/writing-running-appium/appium-bin ...
- Java多态的本质
今天复习了java多态,感觉收获颇多.多态的实现方式有两种,继承父类和实现接口.本质体现在重写上,不同的类重写时体现出不同的特征.编译时和运行时的不同上.编译时只能调用父类的方法,如果调用了子类独有的 ...
- C# WinfForm 控件之dev报表 XtraReport (一) 初了解
这个控件其实用法和fast也差不了太多但如果没接触过 真有种老虎吃天的感觉 1.这里先不说那些高深的先说最基本的 在窗体中显示一个设计好的 模版 1.1一般设计和这个程序是分着的为了方便我就先把他们合 ...
- uoj#244. 【UER #7】短路
题目 orz myy 这个矩形对称的性质非常优美,所以我们只需要考虑一个\(\frac{1}{4}\)的矩阵,即一个倒三角形 现在我们要求的是从\((1,1)\)到三角形对边上每个点的最短路,不难发现 ...
