edgeR
1)简介
edgeR作用对象是count文件,rows 代表基因,行代表文库,count代表的是比对到每个基因的reads数目。它主要关注的是差异表达分析,而不是定量基因表达水平。
edgeR works on a table of integer read counts, with rows corresponding to genes and columns to independent libraries. The counts represent the total number of reads aligning to each gene (or other genomic locus).edgeR is concerned with differential expression analysis rather than with the quantification of expression levels. It is concerned with relative changes in expression levels between conditions,but not directly with estimating absolute expression levels.
edgeR作用的是真实的比对统计,因此不建议用预测的转录本
Note that edgeR is designed to work with actual read counts. We not recommend that predicted transcript abundances are input the edgeR in place of actual counts.
归一化原因:
技术原因影响差异表达分析:
1)Sequencing depth:统计测序深度(即代表的是library size);
2)RNA composition:个别异常高表达基因导致其它基因采样不足
3)GC content: sample-specific effects for GC-content can be detected
4)sample-specific effects for gene length have been detected
注意:edgeR必须是原始表达量,而不能是rpkm等矫正过的。
Note that normalization in edgeR is model-based, and the original read counts are not themselves transformed. This means that users should not transform the read counts in any way before inputing them to edgeR. For example, users should not enter RPKM or FPKM values to edgeR in place of read counts. Such quantities will prevent edgeR from correctly estimating the mean-variance relationship in the data, which is a crucial to the statistical strategies underlying edgeR.Similarly, users should not add artificial values to the counts before inputing them to edgeR.
2)安装
if("edgeR" %in% rownames(installed.packages()) == FALSE) {source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R");biocLite("edgeR")}
suppressMessages(library(edgeR))
ls('package:edgeR')
3)矩阵构建及差异分析
需要构建2个矩阵:1、表达矩阵;2、分组矩阵( 实验设计);
-------------------------------------------------------表达矩阵-----------------------------------------
3.1、读取表达矩阵文件(Reading in the data)
#读取文件
rawdata <- read.delim("E:/software/R/R-3.5.0/library/edgeR/Meta/TableS1.txt", check.names=FALSE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE)
head(rawdata)
3.2 、构建DGEList对象
这里因为已经有rawdata的count文件,因此直接用DGEList()函数就行了,否则要用readDGE()函数
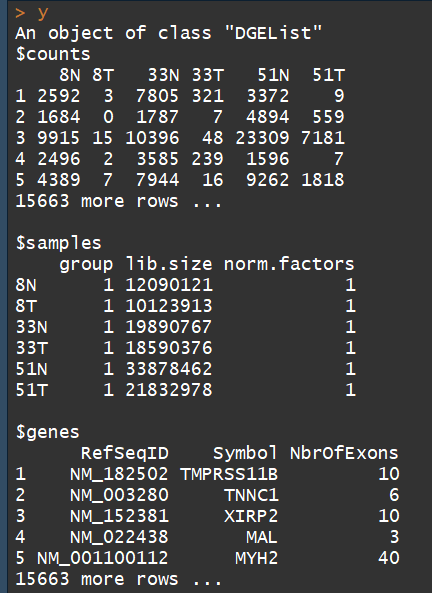
y <- DGEList(counts=rawdata[,4:9], genes=rawdata[,1:3])##构建DGEList对象
DGEList对象主要有三部分:
1、counts矩阵:包含的是整数counts;
2、samples数据框:包含的是文库(sample)信息。包含 lib.size列 :for the library size (sequencing depth) for each sample,如果不自定义, the library sizes will be computed from the column sums of the counts。其中还有一个group列,用于指定每个sample组信息
3、一个可选的数据框genes:gene的注释信息
3.3)数据注释( Annotation)
这里主要是因为该文章数据是前好多年的,因此需要过滤,symbol更新等。
1)The study was undertaken a few years ago, so not all of the RefSeq IDs provided by match RefSeq IDs currently in use. We retain only those transcripts with IDs in the current NCBI annotation, which is provided by the org.HS.eg.db package
2)因为edgeR默认使用NCBI中refSeq的ID,所以通过refseq Id 找到entrezID,然后通过entrezID对symbol更新
#######retain only those transcripts with IDs in the current NCBI annotation provided by the org.HS.eg.db######
library(org.Hs.eg.db)
idfound <- y$genes$RefSeqID %in% mappedRkeys(org.Hs.egREFSEQ)
y <- y[idfound,]
dim(y) ##15550 6
###################### 在注释中加入 Entrez Gene IDs #########################
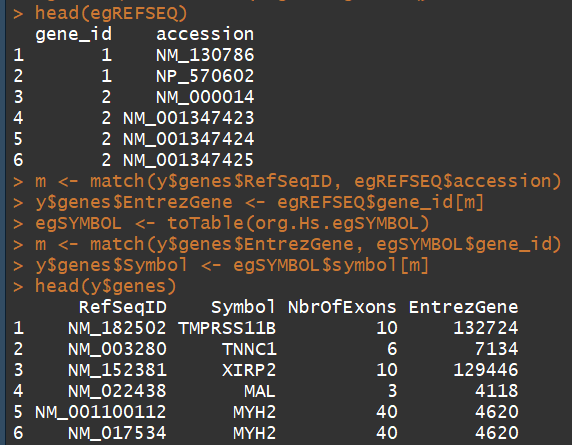
egREFSEQ <- toTable(org.Hs.egREFSEQ)
m <- match(y$genes$RefSeqID, egREFSEQ$accession)
y$genes$EntrezGene <- egREFSEQ$gene_id[m]
#####################用Entrez Gene IDs更新gene symbols##########################
egSYMBOL <- toTable(org.Hs.egSYMBOL)
m <- match(y$genes$EntrezGene, egSYMBOL$gene_id)
y$genes$Symbol <- egSYMBOL$symbol[m]
head(y$genes)
3.4) 过滤和归一化(Filtering and normalization)
过滤一:Different RefSeq transcripts for the same gene symbol count predominantly the same reads. So we keep one transcript for each gene symbol. We choose the transcript with highest overall count:
o <- order(rowSums(y$counts), decreasing=TRUE)
y <- y[o,]
d <- duplicated(y$genes$Symbol)
y <- y[!d,]
nrow(y)
过滤二:Normally we would also filter lowly expressed genes.For this data, all transcripts already have at least 50 reads for all samples of at least one of the tissues types.
y$samples$lib.size <- colSums(y$counts) #Recompute the library sizes
###############################Use Entrez Gene IDs as row names:#####################
rownames(y$counts) <- rownames(y$genes) <- y$genes$EntrezGene
y$genes$EntrezGene <- NULL
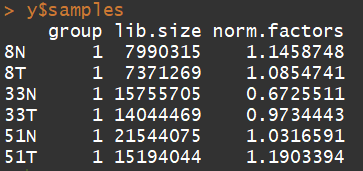
归一化:TMM normalization is applied to this dataset to account for compositional difference between the libraries.
y <- calcNormFactors(y)
y$samples
3.5) 数据的探索(Data exploration)
样本间关系(samples for outliers and for other relationships)
plotMDS(y)
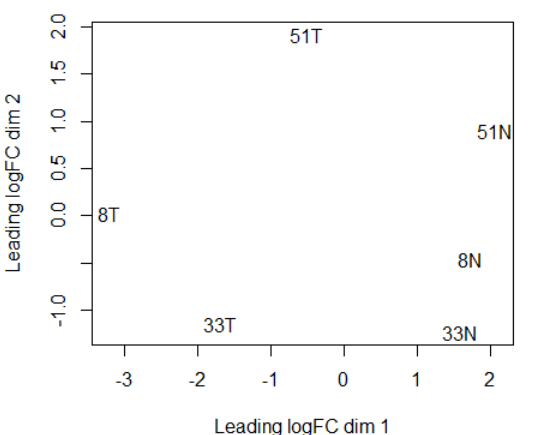
PC1将tumor和nomal组分开,PC2 大略和病号对应。也侧面体现了肿瘤组的异质性
--------------------------分组矩阵(根据实验设计、目的)--------------------------------
Here we want to test for differential expression between tumour and normal tissues within patients, i.e. adjusting for differences between patients.
Patient <- factor(c(8,8,33,33,51,51))
Tissue <- factor(c("N","T","N","T","N","T"))
data.frame(Sample=colnames(y),Patient,Tissue)
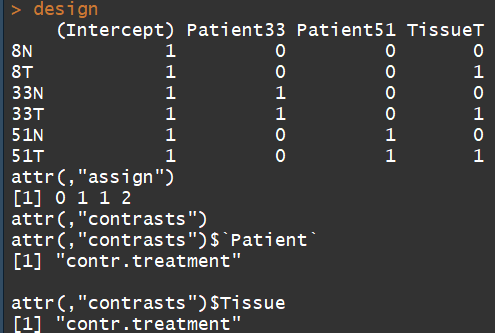
design <- model.matrix(~Patient+Tissue)
rownames(design) <- colnames(y)
design
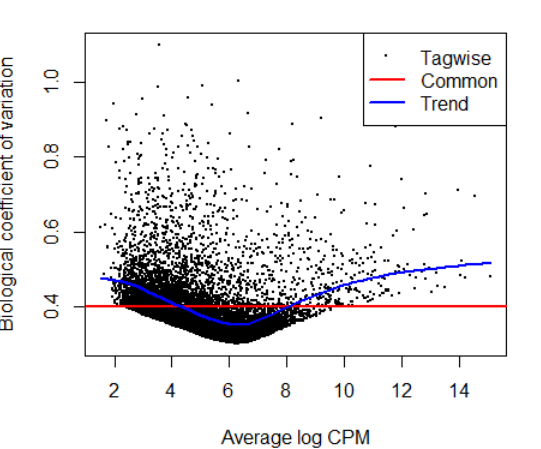
3.4)Estimating the dispersion(estimate the NB dispersion for the dataset.)
y <- estimateDisp(y, design, robust=TRUE)
y$common.dispersion #0.1594505
plotBCV(y)
-----------------------------------差异分析-----------------------------------------
3.5) 差异分析(Differential expression)
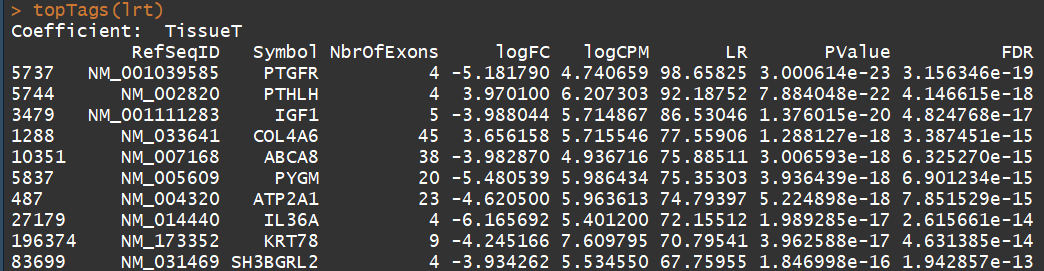
fit <- glmFit(y, design)
lrt <- glmLRT(fit)
topTags(lrt)
summary(decideTests(lrt))
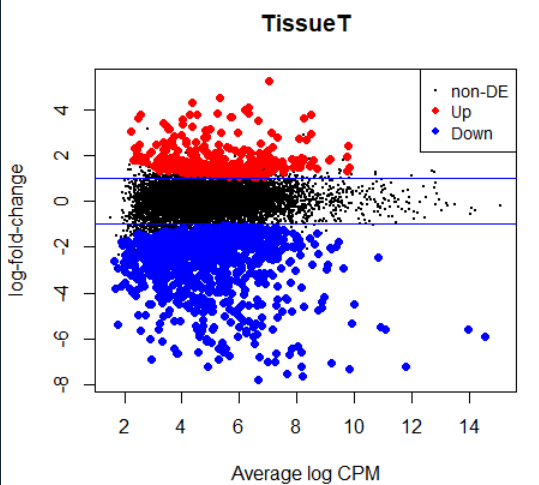
plotMD(lrt)
abline(h=c(-1, 1), col="blue")

------------------------------- Gene ontology analysis----------------------------------------
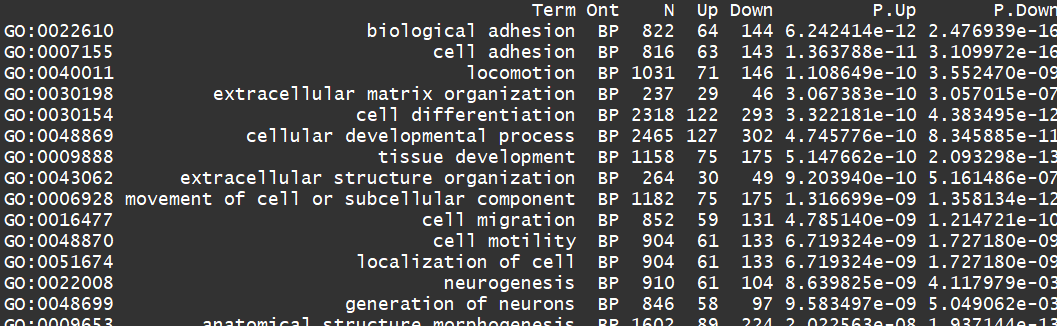
对上调的基因进行BP分析
go <- goana(lrt)
topGO(go, ont="BP", sort="Up", n=30)
edgeR的更多相关文章
- cuffdiff 和 edgeR 对差异表达基因的描述
ASE又走到了关键的一步 要生成能决定是否有差异表达的table. 准备借鉴一下cuffdiff和edgeR 的结果 cuffdiff对差异表达基因的描述: 一共十四列: 第一列, test_id ...
- 简单使用DESeq2/EdgeR做差异分析
简单使用DESeq2/EdgeR做差异分析 Posted: 五月 07, 2017 Under: Transcriptomics By Kai no Comments DESeq2和EdgeR都 ...
- 使用limma、Glimma和edgeR,RNA-seq数据分析易如反掌
使用limma.Glimma和edgeR,RNA-seq数据分析易如反掌 Charity Law1, Monther Alhamdoosh2, Shian Su3, Xueyi Dong3, Luyi ...
- edgeR使用学习【转载】
转自:http://yangl.net/2016/09/27/edger_usage/ 1.Quick start 2. 利用edgeR分析RNA-seq鉴别差异表达基因: #加载软件包 librar ...
- 用TCGA收集的mRNA表达数据作差异表达
做差异表达的软件DEseq和edgeR所需要的数据格式必须是原始counts,经过normalization和log2后的数据都不适合,所以对于做差异表达计算的童鞋可以使用ExperimentHub下 ...
- sql是最成功的第四代语言
SQL发展的前世今生 很多年前,两名年轻的IBM研究员将一门关系型语言带到了数据库领域,旨在使用声明性的方式来操作数据.从Don Chamberlin和Ramond Boyce发表"SEQU ...
- RNA-seq标准化
你的 heatmap 可能用错数据了 (组间表达量标准化) http://www.genek.tv/article/24 RNA-seq的标准化方法罗列 https://www.jianshu.com ...
- 史上最全 | 39个RNAseq分析工具与对比
文献:Sahraeian S M E, Mohiyuddin M, Sebra R, et al. Gaining comprehensive biological insight into the ...
- RNA-seq中的基因表达量计算和表达差异分析
RNA-seq中的基因表达量计算和表达差异分析 差异分析的步骤:1)比对:2) read count计算:3) read count的归一化:4)差异表达分析: 背景知识:1)比对:普通比对: BWA ...
随机推荐
- 把存储过程SELECT INTO到临时表
在开发过程中,很多时候要把结果集存放到临时表中,常用的方法有两种. 一. SELECT INTO1. 使用select into会自动生成临时表,不需要事先创建12 select * into #te ...
- Mycat 数据库分库分表中间件
http://www.mycat.io/ Mycat 国内最活跃的.性能最好的开源数据库中间件! 我们致力于开发高性能的开源中间件而努力! 实体书Mycat权威指南 »开源投票支持Mycat下载 »s ...
- wxWidgets:动态EVENT绑定
我们已经看到如何使用静态EVENT TABLE来处理EVENT:但这种方式不够灵活.下面我们来看看如何在Event和处理函数间实现动态Bind. 仍然以那个简陋的Frame作为例子. 首先删除所有的静 ...
- WifiMonitor的事件发放
Wifi框架中WifiMonitor负责上报wpa_supplicant的消息给WifiStateMachine,WifiNative负责将WifiStateMachine的消息下发给wpa_supp ...
- Qt Creator 预览QtCreator中的界面
当在QtCreator界面编辑器中放置好布局和控件之后,组合键 Alt + Shift + R 可以实现预览功能. 也可以通过以下方式更改快捷键: 具体路径 ...
- bzoj4161: Shlw loves matrixI
Description 给定数列 {hn}前k项,其后每一项满足 hn = a1*h(n-1) + a2*h(n-2) + ... + ak*h(n-k) 其中 a1,a2...ak 为给定数列.请计 ...
- PAT 乙级 1038 统计同成绩的学生C++版
1038. 统计同成绩学生(20) 时间限制 250 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue 本题要求读入N名学生的成绩,将 ...
- Spring IOC - 控制反转(依赖注入) - 配置初始化和销毁的方法
在Spring中如果某个bean在初始化之后,或销毁之前要做一些额外操作可以为该bean配置初始化和销毁的我方法,在这些方法中完成需要的功能. 实验: 通过断点调试模式,测试初始化方法和销毁方法的执行 ...
- 联想Z510升级BCM94352HMB刷网卡白名单曲折经历
联想Z510笔记本:CPU I7 4702MQ没毛病 :内存4G DDR3不上虚拟机办公足够用: 硬盘升级为SSD240G足够用:有线网卡100M,真是垃圾,不过有线网卡是主板上的芯片,这个我可动不了 ...
- php multicast多播实现详解
什么是多播? 网络中存在3中传播形式,单播,广播,多播. 1. 单播 : 就是1->1 2. 广播 : 1->多(广播域内) 3. 多播 : 1->组(一组ip) 1 2 3 4 5 ...
