『科学计算』通过代码理解线性回归&Logistic回归模型
sklearn线性回归模型
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model def get_data():
#506行,14列,最后一列为label,前面13列为参数
data_original = np.loadtxt('housing.data') scale_data = scale_n(data_original)
np.random.shuffle(scale_data)
#在位置0,插入一列1,axis=1代表列,代表b
data = np.insert(scale_data, 0, 1, axis=1) train_X = data[:400, :-1] #前400行为训练数据
train_y = data[:400, -1]
train_y.shape = (train_y.shape[0],1) test_X = data[400:, :-1]
test_y = data[400:, -1]
test_y.shape = (test_y.shape[0],1) # test测试数据没有返回
return train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y def scale_n(x):
return (x-x.mean(axis=0))/x.std(axis=0) if __name__=="__main__":
train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y = get_data() l_model = linear_model.Ridge(alpha = 1000) # 参数是正则化系数 l_model.fit(train_X,train_y) predict_train_y = l_model.predict(train_X) predict_train_y.shape = (predict_train_y.shape[0],1)
error = (predict_train_y-train_y)
rms_train = np.sqrt(np.mean(error**2, axis=0)) predict_test_y = l_model.predict(test_X)
predict_test_y.shape = (predict_test_y.shape[0],1)
error = (predict_test_y-test_y)
rms_test = np.sqrt(np.mean(error**2, axis=0)) print (rms_train, rms_test) plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.scatter(np.arange(test_y.size), sorted(test_y), c='b', edgecolor='None', alpha=0.5, label='actual')
plt.scatter(np.arange(test_y.size), sorted(predict_test_y), c='g', edgecolor='None', alpha=0.5, label='predicted')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.ylabel('House price ($1000s)')
plt.xlabel('House #')
plt.show()
sklearn模型调用民工三连:
l_model = linear_model.Ridge(alpha = 1000) # 模型装载 l_model.fit(train_X,train_y) # 模型训练 predict_train_y = l_model.predict(train_X) # 模型预测
手动线性回归模型
数据获取
房价数据,506行,14列,最后一列为label,前面13列为参数
假如我们需要平方特征,只要修改get_data()中的data_original即可,在13列后添加平方项或者立方项等,由于我们不知道具体添加多少特征的组合更好,神经网络自动提取组合特征的功能就被很好的凸显出来了
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def get_data():
#506行,14列,最后一列为label,前面13列为参数
data_original = np.loadtxt('housing.data') # 读取数据 scale_data = scale_n(data_original) # 归一化处理
np.random.shuffle(scale_data) # 打乱顺序
#在位置0,插入一列1,axis=1代表列,代表b
data = np.insert(scale_data, 0, 1, axis=1) # 数组插入函数 train_X = data[:400, :-1] #前400行为训练数据
train_y = data[:400, -1]
train_y.shape = (train_y.shape[0],1) test_X = data[400:, :-1]
test_y = data[400:, -1]
test_y.shape = (test_y.shape[0],1) # test测试数据没有返回
return train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y
其中:
np.loadtxt('housing.data') # 读取数据
# 本函数读取数据后自动转化为ndarray数组,可以自行设定分隔符delimiter=","
np.insert(scale_data, 0, 1, axis=1) # 数组插入函数
# 在数组中插入指定的行列,numpy.insert(arr, obj, values, axis=None)
# 和其他数组一样,axis不设定的话会把数组定为一维后插入,axis=0的话行扩展,axis=1的话列扩展
预处理
中心归零,标准差归一
def scale_n(x):
"""
减去平均值,除以标准差
"""
x = (x - np.mean(x,axis=0))/np.std(x,axis=0)
return x
线性回归类
class LinearModel():
def __init__(self,learn_rate=0.06,lamda=0.01,threhold=0.0000005):
"""
初始化一些参数
"""
self.learn_rate = learn_rate # 学习率
self.lamda = lamda # 正则化系数
self.threhold = threhold # 迭代阈值 def get_cost_grad(self,theta,X,y):
"""
计算代价cost和梯度grad
"""
y_pre = X.dot(theta)
cost = (y_pre-y).T.dot(y_pre-y) + self.lamda*theta.T.dot(theta)
grad = (2.0*X.T.dot(y_pre-y) + 2.0*self.lamda*theta)/X.shape[0] # 实际上是1个batch的梯度的累加值
return cost, grad def grad_check(self,X,y):
"""
梯度检查: 函数计算梯度 == L(theta+delta)-L(theta-delta) / 2delta
"""
m,n = X.shape
delta = 10**(-4)
sum_error = 0 for i in range(100):
theta = np.random.random((n,1))
j = np.random.randint(1,n) theta1,theta2 = theta.copy(),theta.copy()
theta1[j] += delta
theta2[j] -= delta cost1, grad1 = self.get_cost_grad(theta1, X, y)
cost2, grad2 = self.get_cost_grad(theta2, X, y)
cost, grad = self.get_cost_grad(theta , X, y) sum_error += np.abs(grad[j] - (cost1-cost2)/(delta*2))
print(sum_error/300.0) def train(self,X,y):
"""
初始化theta
训练后,将theta保存到实例变量里
"""
m,n = X.shape
theta = np.random.random((n,1)) prev_cost = None
for loop in range(1000):
cost,grad = self.get_cost_grad(theta,X,y)
theta -= self.learn_rate*grad
if prev_cost:
if prev_cost - cost < self.threhold:
break
prev_cost = cost
self.theta = theta
# print(theta,loop,cost) def predict(self,X):
"""
预测程序
"""
return X.dot(self.theta)
主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y = get_data() linear_model = LinearModel() linear_model.grad_check(train_X,train_y) linear_model.train(train_X,train_y) predict_train_y = linear_model.predict(train_X)
error = (predict_train_y - train_y)
rms_train = np.sqrt(np.mean(error ** 2,axis=0)) predict_test_y = linear_model.predict(test_X)
error = (predict_test_y - test_y)
rms_test = np.sqrt(np.mean(error ** 2,axis=0))
#
print(rms_train,rms_test)
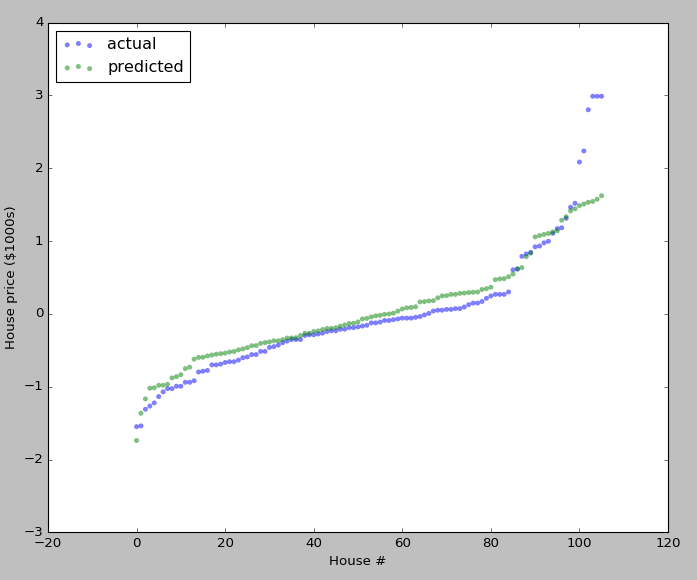
# [ 0.54031084] [ 0.60065021] plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
plt.scatter(np.arange(test_y.size),sorted(test_y),c='b',edgecolor='None',alpha=0.5,label='actual')
plt.scatter(np.arange(test_y.size),sorted(predict_test_y),c='g',edgecolor='None',alpha=0.5,label='predicted')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.ylabel('House price ($1000s)')
plt.xlabel('House #')
plt.show()
Logistic回归
数据获取&预处理
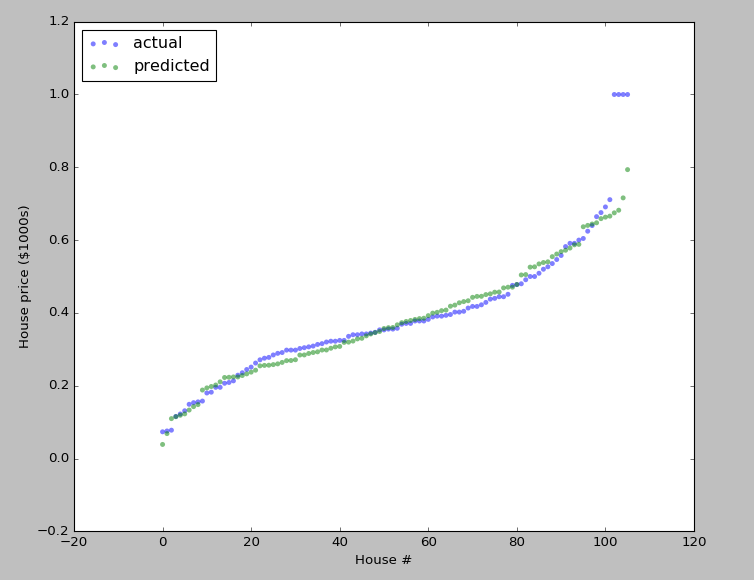
logistic回归输出值在0~1之间,所以数据预处理分两部分,前13列仍然是均值归零标准差归一,label列采取(x-x.min(axis=0))/(x.max(axis=0)-x.min(axis=0))的方式
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math def get_data(N=400):
#506行,14列,最后一列为label,前面13列为参数
data_original = np.loadtxt('housing.data') scale_data = np.zeros(data_original.shape) scale_data[:,:13] = scale_n(data_original[:,:13])
scale_data[:,-1] = scale_max(data_original[:,-1]) np.random.shuffle(scale_data)
#在位置0,插入一列1,axis=1代表列,代表b
data = np.insert(scale_data, 0, 1, axis=1) train_X = data[:N, :-1] #前400行为训练数据
train_y = data[:N, -1]
train_y.shape = (train_y.shape[0],1) test_X = data[N:, :-1]
test_y = data[N:, -1]
test_y.shape = (test_y.shape[0],1) # test测试数据没有返回
return train_X,train_y,test_X,test_y def scale_n(x):
return (x-x.mean(axis=0))/x.std(axis=0)
def scale_max(x):
print (x.min(axis=0))
print (x.max(axis=0))
print (x.mean(axis=0))
print (x.std(axis=0)) return (x-x.min(axis=0))/(x.max(axis=0)-x.min(axis=0))
Logistic回归类
公式参考,
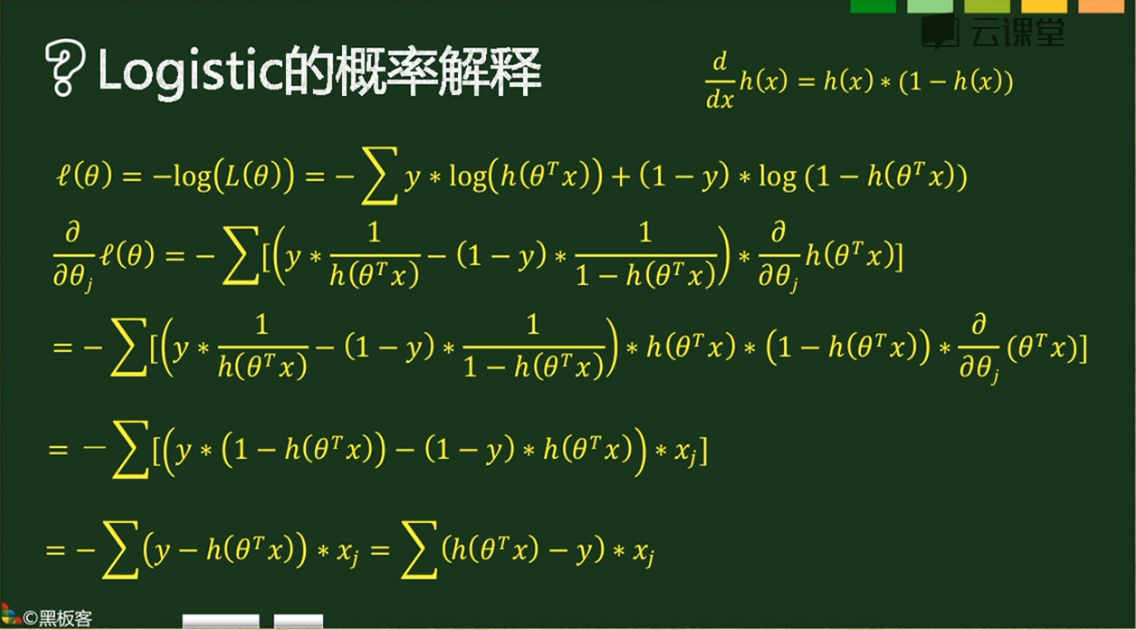
实际代码,
class LogisticModel(object):
def __init__(self,lamda=0.01, alpha=0.6,threhold=0.0000005):
self.alpha = alpha
self.threhold = threhold
self.lamda = lamda def sigmoid(self,x):
return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x)) def get_cost_grad(self,theta,X,y):
m, n = X.shape
y_dash = self.sigmoid(X.dot(theta))
error = np.sum((y * np.log(y_dash) + (1-y) * np.log(1-y_dash)),axis=1)
cost = -np.sum(error, axis=0)+self.lamda*theta.T.dot(theta)
grad = X.T.dot(y_dash-y)+2.0*self.lamda*theta return cost,grad/m def grad_check(self,X,y):
epsilon = 10**-4
m, n = X.shape sum_error=0 for i in range(300):
theta = np.random.random((n, 1))
j = np.random.randint(1,n)
theta1=theta.copy()
theta2=theta.copy()
theta1[j]+=epsilon
theta2[j]-=epsilon cost1,grad1 = self.get_cost_grad(theta1,X,y)
cost2,grad2 = self.get_cost_grad(theta2,X,y)
cost3,grad3 = self.get_cost_grad(theta,X,y) sum_error += np.abs(grad3[j]-(cost1-cost2)/float(2*epsilon)) def train(self,X,y):
m, n = X.shape # 400,15
theta = np.random.random((n, 1)) #[15,1]
#our intial prediction
prev_cost = None
loop_num = 0
while(True): #intial cost
cost,grad = self.get_cost_grad(theta,X,y) theta = theta- self.alpha * grad loop_num+=1
if loop_num%100==0:
print (cost,loop_num)
if prev_cost:
if prev_cost - cost <= self.threhold:
break
if loop_num>1000:
break prev_cost = cost self.theta = theta
print (theta,loop_num) def predict(self,X):
return self.sigmoid(X.dot(self.theta))
『科学计算』通过代码理解线性回归&Logistic回归模型的更多相关文章
- 『科学计算』通过代码理解SoftMax多分类
SoftMax实际上是Logistic的推广,当分类数为2的时候会退化为Logistic分类 其计算公式和损失函数如下, 梯度如下, 1{条件} 表示True为1,False为0,在下图中亦即对于每个 ...
- 『科学计算』L0、L1与L2范数_理解
『教程』L0.L1与L2范数 一.L0范数.L1范数.参数稀疏 L0范数是指向量中非0的元素的个数.如果我们用L0范数来规则化一个参数矩阵W的话,就是希望W的大部分元素都是0,换句话说,让参数W是稀 ...
- 『科学计算』可视化二元正态分布&3D科学可视化实战
二元正态分布可视化本体 由于近来一直再看kaggle的入门书(sklearn入门手册的感觉233),感觉对机器学习的理解加深了不少(实际上就只是调包能力加强了),联想到假期在python科学计算上也算 ...
- 『科学计算』科学绘图库matplotlib学习之绘制动画
基础 1.matplotlib绘图函数接收两个等长list,第一个作为集合x坐标,第二个作为集合y坐标 2.基本函数: animation.FuncAnimation(fig, update_poin ...
- 『科学计算』图像检测微型demo
这里是课上老师给出的一个示例程序,演示图像检测的过程,本来以为是传统的滑窗检测,但实际上引入了selectivesearch来选择候选窗,所以看思路应该是RCNN的范畴,蛮有意思的,由于老师的注释写的 ...
- 『科学计算』科学绘图库matplotlib练习
思想:万物皆对象 作业 第一题: import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = [1, 2, 3, 1] y = [1, 3, 0, 1 ...
- 『TensorFlow』通过代码理解gan网络_中
『cs231n』通过代码理解gan网络&tensorflow共享变量机制_上 上篇是一个尝试生成minist手写体数据的简单GAN网络,之前有介绍过,图片维度是28*28*1,生成器的上采样使 ...
- 机器学习之线性回归---logistic回归---softmax回归
在本节中,我们介绍Softmax回归模型,该模型是logistic回归模型在多分类问题上的推广,在多分类问题中,类标签 可以取两个以上的值. Softmax回归模型对于诸如MNIST手写数字分类等问题 ...
- 『cs231n』通过代码理解gan网络&tensorflow共享变量机制_上
GAN网络架构分析 上图即为GAN的逻辑架构,其中的noise vector就是特征向量z,real images就是输入变量x,标签的标准比较简单(二分类么),real的就是tf.ones,fake ...
随机推荐
- javashop技术培训总结,架构介绍,Eop核心机制
javashop技术培训一.架构介绍1.Eop核心机制,基于spring的模板引擎.组件机制.上下文管理.数据库操作模板引擎负责站点页面的解析与展示组件机制使得可以在不改变核心代码的情况下实现对应用核 ...
- Shell脚本实现检测某ip网络畅通情况,实战用例
Shell脚本实现检测某ip网络畅通情况,实战用例 环境准备,linux shell 发送email 邮件:1.安装sendmailyum -y install sendmail安装好sendmail ...
- java模拟表单上传文件,java通过模拟post方式提交表单实现图片上传功能实例
java模拟表单上传文件,java通过模拟post方式提交表单实现图片上传功能实例HttpClient 测试类,提供get post方法实例 package com.zdz.httpclient; i ...
- Q_DECLARE_PRIVATE与Q_DECLARE_PUBLIC
Q_DECLARE_PRIVATE与Q_DECLARE_PUBLIC 这两个宏在Qt的源码中随处可见,重要性不言而喻.在 部落格的 Inside Qt Series 系列文章中,他用了3篇文章来讲这个 ...
- [转载]C#操作符??和?:
先看如下代码: string strParam = Request.Params["param"]; if ( strParam== null ) { strParam= ...
- web前端----Bootstrap框架补充
一.一个小知识点 1.截取长屏的操作 2.设置默认格式 3.md,sm, xs 4.空格和没有空格的选择器 二.响应式介绍 - 响应式布局是什么? 同一个网页在不同的终端上呈现不同的布局等- 响应式怎 ...
- Python之路----迭代器与生成器
一.迭代器 L=[1,,2,3,4,5,] 取值:索引.循环for 循环for的取值:list列表 dic字典 str字符串 tuple元组 set f=open()句柄 range() enumer ...
- java使用反射给对象属性赋值的两种方法
java反射无所不能,辣么,怎么通过反射设置一个属性的值呢? 主程序: /** * @author tengqingya * @create 2017-03-05 15:54 */ public cl ...
- 20165310_获奖感想与Java阶段性学习总结
获奖感想与Java阶段性学习总结 一.Learning By Doing 在此之前,其实我并没有想到能够成为小黄杉的第一批成员之一,喜悦之余,也感受到了许多的压力.小黄杉一方面代表了老师对于我这一 ...
- Wireshark过滤总结
Wireshark提供了两种过滤器:捕获过滤器:在抓包之前就设定好过滤条件,然后只抓取符合条件的数据包.显示过滤器:在已捕获的数据包集合中设置过滤条件,隐藏不想显示的数据包,只显示符合条件的数据包.需 ...
