Java实现二叉树先序,中序,后序,层次遍历
一、以下是我要解析的一个二叉树的模型形状。本文实现了以下方式的遍历:
1、用递归的方法实现了前序、中序、后序的遍历;
2、利用队列的方法实现层次遍历;
3、用堆栈的方法实现前序、中序、后序的遍历。
。
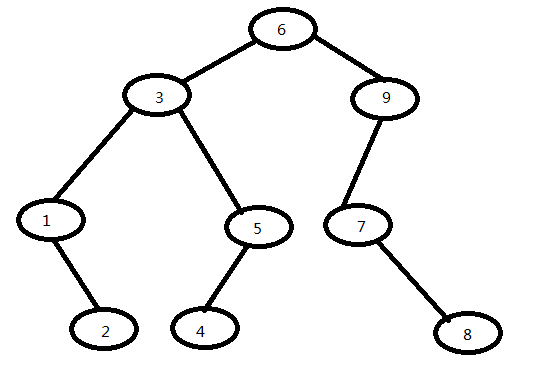
二、遍历
1、首先创建节点类
public class Node {
private int data;
private Node leftNode;
private Node rightNode;
public Node(int data, Node leftNode, Node rightNode){
this.data = data;
this.leftNode = leftNode;
this.rightNode = rightNode;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getLeftNode() {
return leftNode;
}
public void setLeftNode(Node leftNode) {
this.leftNode = leftNode;
}
public Node getRightNode() {
return rightNode;
}
public void setRightNode(Node rightNode) {
this.rightNode = rightNode;
}
}
2、递归方式实现前序、中序、后续遍历
public class BinaryTree {
/**
* @author yaobo
* 二叉树的先序中序后序排序
*/
public Node init() {//注意必须逆序建立,先建立子节点,再逆序往上建立,因为非叶子结点会使用到下面的节点,而初始化是按顺序初始化的,不逆序建立会报错
Node J = new Node(8, null, null);
Node H = new Node(4, null, null);
Node G = new Node(2, null, null);
Node F = new Node(7, null, J);
Node E = new Node(5, H, null);
Node D = new Node(1, null, G);
Node C = new Node(9, F, null);
Node B = new Node(3, D, E);
Node A = new Node(6, B, C);
return A; //返回根节点
}
public void printNode(Node node){
System.out.print(node.getData());
}
public void theFirstTraversal(Node root) { //先序遍历
printNode(root);
if (root.getLeftNode() != null) { //使用递归进行遍历左孩子
theFirstTraversal(root.getLeftNode());
}
if (root.getRightNode() != null) { //递归遍历右孩子
theFirstTraversal(root.getRightNode());
}
}
public void theInOrderTraversal(Node root) { //中序遍历
if (root.getLeftNode() != null) {
theInOrderTraversal(root.getLeftNode());
}
printNode(root);
if (root.getRightNode() != null) {
theInOrderTraversal(root.getRightNode());
}
}
public void thePostOrderTraversal(Node root) { //后序遍历
if (root.getLeftNode() != null) {
thePostOrderTraversal(root.getLeftNode());
}
if(root.getRightNode() != null) {
thePostOrderTraversal(root.getRightNode());
}
printNode(root);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
Node root = tree.init();
System.out.println("先序遍历");
tree.theFirstTraversal(root);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("中序遍历");
tree.theInOrderTraversal(root);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("后序遍历");
tree.thePostOrderTraversal(root);
System.out.println("");
}
}
3、借助队列实现层次遍历
//层次遍历
public void theLeverTraversal(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//新建一个队列,LinkedList实现了Quene接口,可以直接当作队列来用
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); Node current; //当前节点
queue.offer(root);//根节点入队列 while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
current = queue.poll(); //取出队列的头节点
System.out.print(current.val + " ");//输出队列的头节点的值
if (current.left != null) {
queue.offer(current.left); //如果当前节点的左节点不为空,则左节点入队列
}
if (current.right != null) {
queue.offer(current.right); //如果当前节点的右节点不为空,则右节点入队列
}
}
}
4、堆栈方式实现前序、中序、后续遍历
public class BinaryTree1 {
public Node init() {//注意必须逆序建立,先建立子节点,再逆序往上建立,因为非叶子结点会使用到下面的节点,而初始化是按顺序初始化的,不逆序建立会报错
Node J = new Node(8, null, null);
Node H = new Node(4, null, null);
Node G = new Node(2, null, null);
Node F = new Node(7, null, J);
Node E = new Node(5, H, null);
Node D = new Node(1, null, G);
Node C = new Node(9, F, null);
Node B = new Node(3, D, E);
Node A = new Node(6, B, C);
return A; //返回根节点
}
public void printNode(Node node){
System.out.print(node.getData());
}
public void theFirstTraversal_Stack(Node root) { //先序遍历
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node node = root;
while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) { //将所有左孩子压栈
if (node != null) { //压栈之前先访问
printNode(node);
stack.push(node);
node = node.getLeftNode();
} else {
node = stack.pop();
node = node.getRightNode();
}
}
}
public void theInOrderTraversal_Stack(Node root) { //中序遍历
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node node = root;
while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) {
if (node != null) {
stack.push(node); //直接压栈
node = node.getLeftNode();
} else {
node = stack.pop(); //出栈并访问
printNode(node);
node = node.getRightNode();
}
}
}
public void thePostOrderTraversal_Stack(Node root) { //后序遍历
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<Node> output = new Stack<Node>();//构造一个中间栈来存储逆后序遍历的结果
Node node = root;
while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) {
if (node != null) {
output.push(node);
stack.push(node);
node = node.getRightNode();
} else {
node = stack.pop();
node = node.getLeftNode();
}
}
System.out.println(output.size());
while (output.size() > 0) {
printNode(output.pop());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree1 tree = new BinaryTree1();
Node root = tree.init();
System.out.println("先序遍历");
tree.theFirstTraversal_Stack(root);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("中序遍历");
tree.theInOrderTraversal_Stack(root);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("后序遍历");
tree.thePostOrderTraversal_Stack(root);
System.out.println("");
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
参考链接:
http://www.cnblogs.com/yaobolove/p/6213936.html
二叉树遍历(前序、中序、后序、层次、深度优先、广度优先遍历):https://blog.csdn.net/yimingsilence/article/details/54783208
Java实现二叉树先序,中序,后序,层次遍历的更多相关文章
- 分别求二叉树前、中、后序的第k个节点
一.求二叉树的前序遍历中的第k个节点 //求先序遍历中的第k个节点的值 ; elemType preNode(BTNode *root,int k){ if(root==NULL) return ' ...
- [Java]算术表达式求值之二(中序表达式转后序表达式方案,支持小数)
Inlet类,入口类,这个类的主要用途是验证用户输入的算术表达式: package com.hy; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOEx ...
- [Java]算术表达式求值之一(中序表达式转后序表达式方案)
第二版请见:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiandedanteng/p/11451359.html 入口类,这个类的主要用途是粗筛用户输入的算术表达式: package com.h ...
- 前、中、后序遍历随意两种是否能确定一个二叉树?理由? && 栈和队列的特点和区别
前序和后序不能确定二叉树理由:前序和后序在本质上都是将父节点与子结点进行分离,但并没有指明左子树和右子树的能力,因此得到这两个序列只能明确父子关系,而不能确定一个二叉树. 由二叉树的中序和前序遍历序列 ...
- 已知树的前序、中序,求后序的java实现&已知树的后序、中序,求前序的java实现
public class Order { int findPosInInOrder(String str,String in,int position){ char c = str.charAt(po ...
- DS Tree 已知先序、中序 => 建树 => 求后序
参考:二叉树--前序和中序得到后序 思路历程: 在最初敲的时候,经常会弄混preorder和midorder的元素位置.大体的思路就是在preorder中找到根节点(根节点在序列的左边),然后在mid ...
- TZOJ 3209 后序遍历(已知中序前序求后序)
描述 在数据结构中,遍历是二叉树最重要的操作之一.所谓遍历(Traversal)是指沿着某条搜索路线,依次对树中每个结点均做一次且仅做一次访问. 这里给出三种遍历算法. 1.中序遍历的递归算法定义: ...
- java 根据二叉树前序 ,中序求后续
在一棵二叉树总,前序遍历结果为:ABDGCEFH,中序遍历结果为:DGBAECHF,求后序遍历结果. 我们知道: 前序遍历方式为:根节点->左子树->右子树 中序遍历方式为:左子树-> ...
- hdu1710-Binary Tree Traversals (由二叉树的先序序列和中序序列求后序序列)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java ...
- LeetCode:二叉树的前、中、后序遍历
描述: ------------------------------------------------------- 前序遍历: Given a binary tree, return the pr ...
随机推荐
- matlab柱面图
f=@(x,y)log(y); % ln(x)函数,平行于x轴ezsurf(f,[-pi*2,pi*2,0,20])
- Win7 VS2015环境使用SDL2-2.0.4
之前在VS中使用SDL2,如果只链接SDL2.lib,会提示 error LNK2019: unresolved external symbol _main referenced in functio ...
- openstack之安全组管理
命令概览 (nova-api)[root@cc07 /]# nova help|grep secgroup add-secgroup Add a Security Group to a server. ...
- MySQL/Oracle视图的创建与使用
1.什么是视图? 视图是一个虚拟的表,是一个表中的数据经过某种筛选后的显示方式,视图由一个预定义的查询select语句组成. 2.视图的特点. 视图中的数据并不属于视图本身,而是属于基本的表,对视 ...
- 第08章:MongoDB-CRUD操作--文档--删除
①语法 remove() [2.6以后方法过时] deleteOne() [2.6以后官方推荐] deleteMany() [2.6以后官方推荐] db.collection.remove( < ...
- Ng第九课:神经网络的学习(Neural Networks: Learning)
9.1 代价函数 9.2 反向传播算法 9.3 反向传播算法的直观理解 9.4 实现注意:展开参数 9.5 梯度检验 9.6 随机初始化 9.7 综合起来 9.8 自主驾驶 9.1 ...
- bat文件命令
- Properties类、序列化流与反序列化流、打印流、commons-IO
Properties类 特点: 1.Hashtable的子类,map集合中的方法都可以用: 2.该集合没有泛型,键值都是字符串: 3.是一个可以持久化的属性集,键值可以存到集合中,也可存到持久化的设备 ...
- Circles and Pi
Circles and Pi Introduction id: intro-1 For as long as human beings exist, we have looked to the sky ...
- yum改成网易的源
用网易的源会快很多,步骤如下:http://mirrors.163.com/.help/centos.html 1.首先备份/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo mv / ...
