4 关于word2vec的skip-gram模型使用负例采样nce_loss损失函数的源码剖析
tf.nn.nce_loss是word2vec的skip-gram模型的负例采样方式的函数,下面分析其源代码。
1 上下文代码
loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.nce_loss(weights=nce_weights,
biases=nce_biases,
labels=train_labels,
inputs=embed,
num_sampled=num_sampled,
num_classes=vocabulary_size))
其中,
train_inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size])
train_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size, 1])
embeddings = tf.Variable(
tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0))
embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, train_inputs)
train_inputs中的就是中心词,train_label中的就是语料库中该中心词在滑动窗口内的上下文词。
所以,train_inputs中会有连续n-1(n为滑动窗口大小)个元素是相同的。即同一中心词。
embddings是词嵌入,就是要学习的词向量的存储矩阵。共有词汇表大小的行数,每一行对应一个词的向量。
# Construct the variables for the NCE loss
nce_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, embedding_size],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(embedding_size)))
nce_biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([vocabulary_size]))
nce_weights就是用来存储如下负例采样公式中的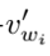
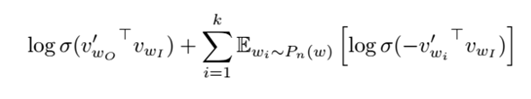 、
、
sigmoid函数有一个对称特性:

故而上面的公式中,就没有出现1-XX的形式。用1-XX的形式,可能会更好理解。
具体解释如下:
- l #train_inputs中是中心词的单词编号,就是词汇表中对该单词的一个编号,一般按词频排列,用顺序进行编号。
- l #train_labels中是中心词的上下文中的单次编号,这些都算是正样本,注意和机器学习中的正样本的意思不一样,这里是做正确答案的意思。
- l #embedding_lookup就是取出某一行。下标从0开始。
- l #tf.truncated_normal从截断的正态分布中输出随机值。#生成的值服从具有指定平均值和标准偏差的正态分布,如果生成的值大于平均值2个标准偏差的值则丢弃重新选择。#标准差就是标准偏差,是方差的算术平均根。而上面的代码中对标准方差进行了限制的原因就是为了防止神经网络的参数过大。为什么embeddings中的参数没有进行限制呢?是因为最初初始化的时候,所有的词的词向量之间要保证一定的距离。然后通过学习,才能拉近某些词的关系,使得某些词的词向量更加接近。
- l #因为是单层神经网络,所以要限制参数过大。如果是深层神经网络,就不需要标准差除一一个embedding_size的平方根了。深层神经网络虽然也要进行参数的正则化限制,防止过拟合和梯度爆炸问题,但是很少看见,有直接对stddev进行限制的。
2 nce_loss源码
def nce_loss(weights,
biases,
labels,
inputs,
num_sampled,
num_classes,
num_true=1,
sampled_values=None,
remove_accidental_hits=False,
partition_strategy="mod",
name="nce_loss"):
logits, labels = _compute_sampled_logits(
weights=weights,
biases=biases,
labels=labels,
inputs=inputs,
num_sampled=num_sampled,
num_classes=num_classes,
num_true=num_true,
sampled_values=sampled_values,
subtract_log_q=True,
remove_accidental_hits=remove_accidental_hits,
partition_strategy=partition_strategy,
name=name)
sampled_losses = sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=labels, logits=logits, name="sampled_losses")
# sampled_losses is batch_size x {true_loss, sampled_losses...}
# We sum out true and sampled losses.
return _sum_rows(sampled_losses)
可以看出核心就在于传入sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits的参数。对于任何一个输出节点只有一个的二分类神经网络,用sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits是最好理解的。logits的维度是batch_size,1。labels的维度就是batch_size,元素取值为0或者1,
来看一下sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits函数
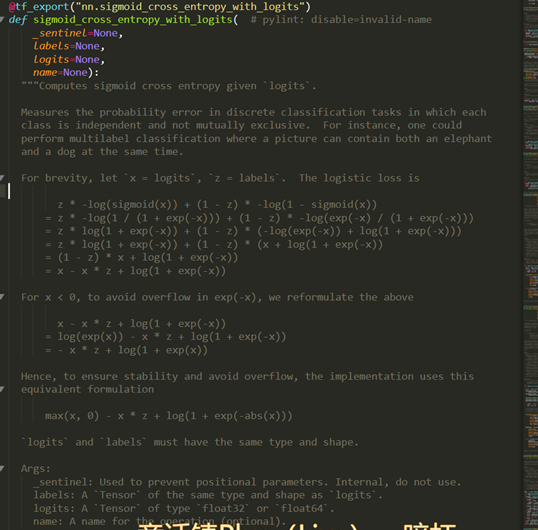
sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits的返回值是:
Returns:
A `Tensor` of the same shape as `logits` with the componentwise
logistic losses.
也就是说:logits的维度是batch_size,1,其返回的维度也是batch_size,1。这个位置的元素就是用这个公式计算的loss:

但是在负例采样中,传入的logits的维度不是batch_size,1,而是[batch_size, num_true + num_sampled]`。主要观察一下_compute_sampled_logits函数的输出。其输出如下:
Returns:
out_logits: `Tensor` object with shape
`[batch_size, num_true + num_sampled]`, for passing to either
`nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits` (NCE) or
`nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits` (sampled softmax).
out_labels: A Tensor object with the same shape as `out_logits`.
"""
其传入参数的解释是:
labels: A `Tensor` of type `int64` and shape `[batch_size,
num_true]`. The target classes. Note that this format differs from
the `labels` argument of `nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits`.
inputs: A `Tensor` of shape `[batch_size, dim]`. The forward
activations of the input network.
weights: A `Tensor` of shape `[num_classes, dim]`, or a list of `Tensor`
objects whose concatenation along dimension 0 has shape
`[num_classes, dim]`. The (possibly-partitioned) class embeddings.
可以看出_compute_sampled_logits完成的是一个什么过程呢。就是对于每一个样本,计算出一个维度为[batch_size, num_true + num_sampled]的向量,向量的每个元素都同之前logits的每个元素的意义一样,是输出值。同时,返回一个维度为[batch_size, num_true + num_sampled]的向量labels。这个labels中只有一个元素为1。于是再看一下如下公式:
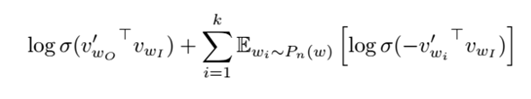
其实,此时的out_logits中对应(label位置为0)的元素就是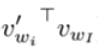 ,对应label位置为1)的元素就是
,对应label位置为1)的元素就是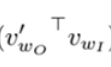 。
。
然后再传给sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits,同样是对于每个元素位置的计算使用下面的公式:

所以,nce_loss中调用sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits后返回的是:[batch_size, num_true + num_sampled]的向量,其中每个元素都是一个用上述公式计算出loss。
nce_loss的最后一步是_sum_rows:
def _sum_rows(x):
"""Returns a vector summing up each row of the matrix x."""
# _sum_rows(x) is equivalent to math_ops.reduce_sum(x, 1) when x is
# a matrix. The gradient of _sum_rows(x) is more efficient than
# reduce_sum(x, 1)'s gradient in today's implementation. Therefore,
# we use _sum_rows(x) in the nce_loss() computation since the loss
# is mostly used for training.
cols = array_ops.shape(x)[1]
ones_shape = array_ops.stack([cols, 1])
ones = array_ops.ones(ones_shape, x.dtype)
return array_ops.reshape(math_ops.matmul(x, ones), [-1])
最后,再对nce_loss的返回结果用reduce_mean即可计算一个batch的平均损失。
关于_compute_sampled_logits中如何采样,如何计算的,这里就不再阐述,同文字理论是一样的。
我们将_compute_sampled_logits函数中的
# Construct output logits and labels. The true labels/logits start at col 0.
out_logits = array_ops.concat([true_logits, sampled_logits], 1) # true_logits is a float tensor, ones_like(true_logits) is a float
# tensor of ones. We then divide by num_true to ensure the per-example
# labels sum to 1.0, i.e. form a proper probability distribution.
out_labels = array_ops.concat([
array_ops.ones_like(true_logits) / num_true,
array_ops.zeros_like(sampled_logits)
], 1)
改为
out_logits = array_ops.concat([true_logits, sampled_logits], 1,name="xiaojie_logits")
# true_logits is a float tensor, ones_like(true_logits) is a float
# tensor of ones. We then divide by num_true to ensure the per-example
# labels sum to 1.0, i.e. form a proper probability distribution.
out_labels = array_ops.concat([
array_ops.ones_like(true_logits) / num_true,
array_ops.zeros_like(sampled_logits)
], 1,name="xiaojie_labels")
然后由于这些代码位于:
with ops.name_scope(name, "compute_sampled_logits",
weights + [biases, inputs, labels]):
ops指定的name下,name为“nce_loss”
我们在word2vec的程序训练迭代的过程中添加如下代码:
for step in range(num_steps):
batch_inputs, batch_labels = generate_batch(
batch_size, num_skips, skip_window)
feed_dict = {train_inputs : batch_inputs, train_labels : batch_labels}
print ("xiaojie Debug:")
xiaojie_logits= session.graph.get_tensor_by_name("nce_loss/xiaojie_logits:0")
xiaojie_labels = session.graph.get_tensor_by_name("nce_loss/xiaojie_labels:0")
xiaojie_logits_value,xiaojie_labels_value=session.run([xiaojie_logits,xiaojie_labels],feed_dict=feed_dict)
print (xiaojie_logits_value,xiaojie_labels_value)
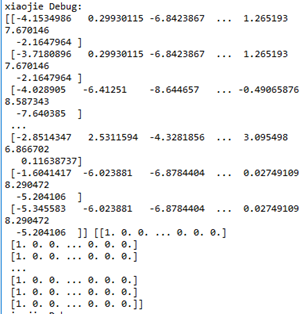
可以看出输出结果中传递给sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits函数的就是这么个玩意。
4 关于word2vec的skip-gram模型使用负例采样nce_loss损失函数的源码剖析的更多相关文章
- petite-vue源码剖析-沙箱模型
在解析v-if和v-for等指令时我们会看到通过evaluate执行指令值中的JavaScript表达式,而且能够读取当前作用域上的属性.而evaluate的实现如下: const evalCache ...
- Linux设备驱动模型简述(源码剖析)
1. Linux设备驱动模型和sysfs文件系统 Linux内核在2.6版本中引入设备驱动模型,简化了驱动程序的编写.Linux设备驱动模型包含设备(device).总线(bus).类(class)和 ...
- memcached源码剖析4:并发模型
memcached是一个典型的单进程系统.虽然是单进程,但是memcached内部通过多线程实现了master-worker模型,这也是服务端最常见的一种并发模型.实际上,除了master线程和wor ...
- PHP用抛物线的模型实现微信红包生成算法的程序源码
<?php /* *Author:Kermit *Time:2015-8-26 *Note:红包生成随机算法 */ header("Content-type:text/html;cha ...
- memcached源码剖析5:并发模型
网络连接建立与分发 前面分析了worker线程的初始化,以及主线程创建socket并监听的过程.本节会分析连接如何建立与分发. 初始状态 A,可以摸清楚master线程的大致逻辑: 1)初始化各个wo ...
- word2vec的Java源码【转】
一.核心代码 word2vec.java package com.ansj.vec; import java.io.*; import java.lang.reflect.Array; import ...
- [源码解析] 模型并行分布式训练 Megatron (3) ---模型并行实现
[源码解析] 模型并行分布式训练 Megatron (3) ---模型并行实现 目录 [源码解析] 模型并行分布式训练 Megatron (3) ---模型并行实现 0x00 摘要 0x01 并行Tr ...
- jQuery源码解析对象实例化与jQuery原型及整体构建模型分析(一)
//源码剖析都基于jQuery-2.0.3版本,主要考虑到兼容IE 一.关于jQuery对象实例化的逻辑: 整个jQuery程序被包裹在一个匿名自执行行数内: (function(window,und ...
- 谷歌BERT预训练源码解析(二):模型构建
目录前言源码解析模型配置参数BertModelword embeddingembedding_postprocessorTransformerself_attention模型应用前言BERT的模型主要 ...
随机推荐
- C# 连接Oracle 11g 无需安装Oracle客户端
1.首先到Oracle网站上下载ODAC 下载地址1:http://download.csdn.net/detail/easyboot/9456476 下载地址2:http://www.oracle. ...
- vue-cli 启动过项目步骤
一. 安装 node.js 安装完成后,可以命令行工具中输入 node -v 和 npm -v,如果能显示出版本号,就说明安装成功. 二.安装webpack npm install webpack - ...
- Hangfire项目
什么是Hangfire Hangfire 是一个开源的.NET任务调度框架,目前1.6+版本已支持.NET Core.个人认为它最大特点在于内置提供集成化的控制台,方便后台查看及监控: 另外,Hang ...
- rocketmq的消息过滤-sql方式
通常我们会使用Tag过滤 特殊情况下我们也可以使用userproperties+TAGS过滤 , sql92定义 这两种都是在服务器端完成过滤, 对于超大数据量的场景(1小时4000W+)不要在客流端 ...
- 第十次 Scrum Meeting
第十次 Scrum Meeting 写在前面 会议时间 会议时长 会议地点 2019/4/16 14:30 30min 新主楼F座2F 附Github仓库:WEDO 例会照片 工作情况总结 人员 上阶 ...
- SpringBoot 整合 slf4j 日志打印
划水时间,记录一下用到的相关slf4j 日志打印,如何实现配置输出.本地保存log日志文件... 我使用的是SpringBoot框架,slf4j 类库已经包含到了 SpringBoot 框架中,所有, ...
- 关于typedef的用法
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/csyisong/archive/2009/01/09/1372363.html https://wenda.so.com/q/1471668835 ...
- Vector bit-select and part-select addressing verilog片选写法
大端 m m[ a +: b ] == m[ (a+b-1) : a ] m[ a -: b ] == m[ a : (a-b+1) ] 小端 n n[ a +: b ] == n[ a : (a+b ...
- MySQL PRIMARY KEY 和 UNIQUE的区别
primary key = unique + not null unique 就是唯一,当你需要限定你的某个表字段每个值都唯一,没有重复值时使用.比如说,如果你有一个person 表,并且表中有个身 ...
- java多线程开发之CyclicBarrier,CountDownLatch
最近研究了一个别人的源码,其中用到多个线程并行操作一个文件,并且在所有线程全部结束后才进行主线程后面的处理. 其用到java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier 这个类. Cy ...
