C语言 链表的创建--打印--逆置--新增--删除--排序--释放
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h> //定义结构体
typedef struct _student{
int num;
struct _student *pNext;
}Student; //创建链表(顺序创建链表)
Student * SList_Create(int *len/*out*/);
//创建链表(逆序创建链表)
Student * SList_Create2(int *len/*out*/);
//打印链表
int PrintfAll(Student *pin/*in*/);
//链表排序
int Sort(Student *pin/*in*/, int *len/*in*/);
//插入指定位置节点
int InsertOption(int numx/*in*/, Student *pin/*in*/, int *len/*out*/);
//链表顺序逆置
int NoSort(Student *pin/*in*/, Student **pout/*out*/);
//链表顺序逆置2
int NoSort2(Student **pin/*in*/);
//删除指定节点
int RemoveNode(int numx/*in*/, Student *pin/*in*/, int *len/*out*/);
//释放内存
int FreeAll(Student **pin/*in*/); void main(){
Student *s1 = NULL, *s2 = NULL;
//定义链表长度
int len = ;
//初始化链表
s1 = SList_Create(&len);
int res = ;
//打印链表
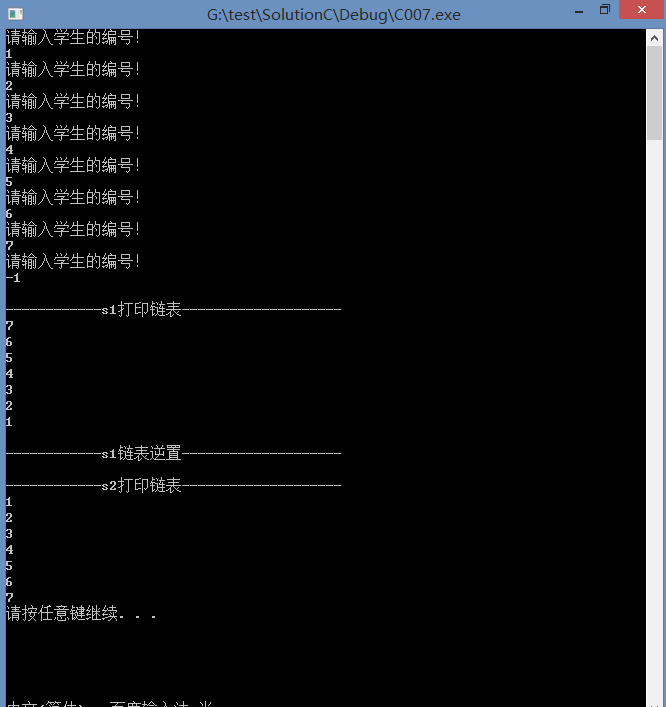
printf("\n------------s1打印链表--------------------\n");
res = PrintfAll(s1);
if (res != )
{
printf("s1打印链表程序出现错误!\n");
goto END;
}
//删除链表中指定节点
printf("\n------------s1链表逆置--------------------\n");
res = NoSort2(&s1);
if (res != )
{
printf("链表逆置程序出现错误!\n");
goto END;
}
//打印链表
printf("\n------------s1打印链表--------------------\n");
res = PrintfAll(s1);
if (res != )
{
printf("s2打印链表程序出现错误!\n");
goto END;
} END:
//释放链表内存
if (s1 != NULL)
{
FreeAll(&s1);
}
if (s2 != NULL)
{
FreeAll(&s2);
} system("pause");
} //创建链表(顺序创建链表)
Student * SList_Create(int *len/*in*/){
if (len == NULL)
{
printf("不可以为NULL\n");
return NULL;
}
//定义链表头结点指针
Student * pHead = NULL, *pMalloc = NULL, *pCurrent = NULL, *pPrior = NULL;
int numx = , index = ;
while (){
printf("请输入学生的编号!\n");
scanf("%d", &numx);
if (numx == -)
{
break;
}
pCurrent = (Student *)malloc(sizeof(Student));
//注意这部分的内存释放
if (pCurrent==NULL)
{
printf("创建链表分配内存失败,释放已创建内存!\n");
FreeAll(&pHead);
}
memset(pCurrent, , sizeof(Student));
pCurrent->num = numx;
pCurrent->pNext = NULL;
if (pPrior != NULL)
{
pPrior->pNext = pCurrent;
pPrior = pCurrent;
}
else{
pHead = pPrior = pCurrent;
}
index++;
}
*len = index;
return pHead;
} //创建链表(逆序创建链表)
Student * SList_Create2(int *len/*in*/){
if (len == NULL)
{
printf("链表的长度不可以为NULL\n");
return NULL;
}
//定义链表头结点指针
Student * pHead = NULL, *pMalloc = NULL, *pCurrent = NULL, *pNext = NULL;
int numx = , index = ;
while (){
printf("请输入学生的编号!\n");
scanf("%d", &numx);
if (numx == -)
{
break;
}
pCurrent = (Student *)malloc(sizeof(Student));
if (pCurrent == NULL)
{
printf("创建链表分配内存失败,释放已创建内存!\n");
FreeAll(&pHead);
}
memset(pCurrent, , sizeof(Student));
pCurrent->num = numx;
pCurrent->pNext = pNext;
pNext = pCurrent;
index++;
}
pHead = pCurrent;
*len = index;
return pHead;
} //打印链表
int PrintfAll(Student *pin/*in*/){
int ERRO_MSG = ;
if (pin == NULL)
{
ERRO_MSG = ;
printf("pin==NULL erro msg:%d\n", ERRO_MSG);
return ERRO_MSG;
}
Student *pHead = NULL, *pCurrent = NULL;
pHead = pCurrent = pin;
while (pCurrent != NULL){
printf("%d\n", pCurrent->num);
pCurrent = pCurrent->pNext;
}
return ERRO_MSG;
} //链表排序
int Sort(Student *pin/*in*/, int *len/*in*/){
int ERRO_MSG = ;
if (pin == NULL || len == NULL)
{
ERRO_MSG = ;
printf("pin==NULL|| len==NULL erro msg :%d\n", ERRO_MSG);
return ERRO_MSG;
}
//定义链表变量
Student *pHead = NULL, *pPrior = NULL, *pCurrent = NULL, *pNext = NULL;
//接收链表变量
pCurrent = pin;
//冒泡排序
//分析:两种方案①是调换链表元素的指针,但是操作复杂,理解麻烦,而且这个环境里,结构体并不是很大(如果结构体比较大,那么推荐使用指针替换),复杂的逻辑不适合
//②调换链表元素的值,这个方案比较简单
//链表一般使用while,因为不知道链表的个数
//获取链表中实际元素的个数,方便冒泡排序,(冒泡排序循环的次数和元素的个数有关)
int numx = *len;
while (numx){
//将最大的元素扔到末尾
//重置pCurrent
pPrior = pCurrent = pin;
while (pCurrent != NULL){
if (pPrior != pCurrent)
{
if (pPrior->num>pCurrent->num)
{
numx = pPrior->num;
pPrior->num = pCurrent->num;
pCurrent->num = numx;
}
}
pPrior = pCurrent;
pCurrent = pCurrent->pNext;
}
numx--;
} return ERRO_MSG;
} //插入指定位置节点
int InsertOption(int numx/*in*/, Student *pin/*in*/, int *len/*out*/){
int ERRO_MSG = ;
if (pin == NULL || len == NULL)
{
ERRO_MSG = ;
printf("pin == NULL || len==NULL erro msg:%d\n", ERRO_MSG);
return ERRO_MSG;
}
Student *pHead = NULL, *pPrior = NULL, *pCurrent = NULL, *pMalloc = NULL;
//创建指定元素
pMalloc = (Student *)malloc(sizeof(Student));
if (pMalloc == NULL)
{
ERRO_MSG = ;
printf("创建链表分配内存失败! erro msg:%d\n", ERRO_MSG);
return ERRO_MSG;
}
pMalloc->num = numx;
pMalloc->pNext = NULL;
pCurrent = pPrior = pin;
//思路:找到目标节点的当前节点和前一个节点,比较指定元素是否比连表中元素大
//先比较第一个元素和指定元素的大小
if (pCurrent->num>pMalloc->num)
{
pMalloc->pNext = pCurrent;
pin = pMalloc;
}
else{
//遍历链表
while (pCurrent != NULL){
if (pPrior != pCurrent)
{
if (pMalloc->num<pCurrent->num)
{
//把这个节点插入到链表中
pPrior->pNext = pMalloc;
pMalloc->pNext = pCurrent;
break;
}
}
pPrior = pCurrent;
pCurrent = pCurrent->pNext;
}
}
*len++;
return ERRO_MSG;
} //链表顺序逆置
int NoSort(Student *pin/*in*/, Student **pout/*out*/){
int ERRO_MSG = ;
if (pin == NULL || pout == NULL)
{
ERRO_MSG = ;
printf("pin == NULL || pout==NULL erro msg:%d\n", ERRO_MSG);
return ERRO_MSG;
}
Student *pCurrent = NULL;
Student *pHead2 = NULL, *pCurrent2 = NULL, *pNext2 = NULL;
pCurrent = pin;;
while (pCurrent != NULL){
pCurrent2 = (Student *)malloc(sizeof(Student));
pCurrent2->num = pCurrent->num;
pCurrent2->pNext = pNext2;
pNext2 = pCurrent2;
pCurrent = pCurrent->pNext;
}
pHead2 = pCurrent2;
*pout = pHead2;
return ERRO_MSG;
} //链表顺序逆置2
int NoSort2(Student **pin/*in*/){
int ERRO_MSG = ;
if (pin == NULL)
{
ERRO_MSG = ;
printf("pin == NULL erro msg:%d\n", ERRO_MSG);
return ERRO_MSG;
}
Student *pHead = NULL, *pCurrent = NULL, *pNext = NULL, *pPrior = NULL;
pCurrent = pPrior = *pin;
pNext = pCurrent->pNext;
pPrior->pNext = NULL;
if (pCurrent->pNext=NULL)
{
return ERRO_MSG;
}
while (pCurrent){
if (pCurrent != pPrior)
{
//下一个节点
pNext = pCurrent->pNext;
pCurrent->pNext = pPrior;
}
pPrior = pCurrent;
pCurrent = pNext;
}
pHead = pPrior;
*pin = pHead;
return ERRO_MSG;
} //删除指定节点
int RemoveNode(int numx/*in*/, Student *pin/*in*/, int *len/*out*/){
int ERRO_MSG = ;
if (pin == NULL || len == NULL)
{
ERRO_MSG = ;
printf("pin == NULL || len==NULL erro msg:%d\n", ERRO_MSG);
return ERRO_MSG;
}
//定义链表变量
Student *pHead = NULL, *pCurrent = NULL, *pNext = NULL, *pPrior = NULL;
pPrior = pCurrent = pin;
//判断第一个节点
if (pCurrent->num == numx)
{
pHead = pCurrent->pNext;
//释放该节点
free(pCurrent);
}
else{
//遍历链表
while (pCurrent != NULL){
if (pCurrent != pPrior)
{
if (pCurrent->num == numx)
{
pPrior->pNext = pCurrent->pNext;
//释放该节点
free(pCurrent);
pCurrent = NULL;
pCurrent = pPrior->pNext;
continue;
}
}
pPrior = pCurrent;
pCurrent = pCurrent->pNext;
}
}
*len = *len - ;
return ERRO_MSG;
} //释放内存
int FreeAll(Student **pin/*in*/){
int ERRO_MSG = ;
if (pin == NULL)
{
ERRO_MSG = ;
printf("pin==NULL erro msg:%d\n", ERRO_MSG);
return ERRO_MSG;
}
Student *pHead = NULL, *pCurrent = NULL, *pNext = NULL;
pHead = *pin;
pCurrent = pHead;
if (pCurrent != NULL)
{
while (pCurrent != NULL){
pNext = pCurrent->pNext;
//释放内存
free(pCurrent);
pCurrent = pNext;
}
}
//避免野指针
*pin = NULL;
return ERRO_MSG;
}
C语言 链表的创建--打印--逆置--新增--删除--排序--释放的更多相关文章
- C语言strrev()函数:字符串逆置(倒序、逆序)
头文件:#include<string.h> strrev()函数将字符串逆置,其原型为: char *strrev(char *str); [参数说明]str为要逆置的字符串. s ...
- C语言实现整数数组的逆置算法
读入100个整数到一个数组中,写出实现该数组进行逆置的算法. 方法一: 假设100个整数读入到数组a中,算法f1的思想是分别从数组两端依次将对应数进行交换,即a[i]与a[100 - i - 1]进行 ...
- leetcode 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 及 82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 问题描述 给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次. 示例 1: 输入: 1->1->2 输出: 1->2 示例 2: 输入: ...
- C语言链表总结(创建,排序,增加,删除)
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h> typedef struct NODE{ int data ; struct NODE * pNex ...
- Leetcode:Swap Nodes in Pairs 单链表相邻两节点逆置
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. For example, Given 1->2-& ...
- 如何在时间复杂度为O(n)空间复杂度为O(1)的情况下完成链表的逆置
问题如题目,首先分析,链表的反转的空间复杂度如果为常数级,那么不可能完成从堆中申请数据来完成链表的反转工作,所以问题就转化为了如何将原链表修改/拆解为逆置的链表: 函数形式假定如下 void Inv ...
- YTU 2991: 链表节点逆置(线性表)
2991: 链表节点逆置(线性表) 时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB 提交: 14 解决: 6 题目描述 设计一个算法,将一个带头节点的数据域依次为a1,a2,-,an(n> ...
- SDUT OJ 数据结构实验之链表三:链表的逆置
数据结构实验之链表三:链表的逆置 Time Limit: 1000 ms Memory Limit: 65536 KiB Submit Statistic Discuss Problem Descri ...
- SDUT-2118_数据结构实验之链表三:链表的逆置
数据结构实验之链表三:链表的逆置 Time Limit: 1000 ms Memory Limit: 65536 KiB Problem Description 输入多个整数,以-1作为结束标志,顺序 ...
随机推荐
- 异步get请求之代理方法
#import "ViewController.h" #import "Header.h" @interface ViewController ()<NS ...
- 【原】训练自己haar-like特征分类器并识别物体(1)
本系列文章旨在学习如何在opencv中基于haar-like特征训练自己的分类器,并且用该分类器用于模式识别.该过程大致可以分为一下几个大步骤: 1.准备训练样本图片,包括正例及反例样本 2.生成样本 ...
- 小波说雨燕 第三季 构建 swift UI 之 UI组件集-视图集(五)Image View视图 学习笔记
留下两个问题:1.后面涉及到的异常不知道原因.2.动态图片到了程序里面就不动了. 然后: 上面是有问题的,下面是没有问题的了. 代码(另外简单写的代码,纠正了那个错误): imp ...
- debian和ubuntu的sh dash bash
Ubuntu和debian 的 shell 默认安装的是 dash,而不是 bash.运行以下命令查看 sh 的详细信息,确认 shell 对应的程序是哪个:$ls -al /bin/sh dash ...
- Entity Framework做IN查询
开发中遇到的Too high level of nesting for select错误 项目使用了Entity Framework结合Mysql, 遇到了一个非常奇怪的性能问题,一个看起来非常简单的 ...
- Effective Java 31 Use instance fields instead of ordinals
Principle Never derive a value associated with an enum from its ordinal; store it in an instance fie ...
- 问题解决——WSAAsyncSelect模型 不触发 FD_CLOSE
==================================声明================================== 本文原创,转载在正文中显要的注明作者和出处,并保证文章的完 ...
- oracle向in语句传入参数查不出数据
在oracle字符串中使用了in,但是查不出数据 string getModel = "select * from TB_YBSH where ID in :ids"; Oracl ...
- javascript特效实现(4)——当前时间和倒计时效果
这个效果的实现关键是对Date对象和setTimeout的使用. 一共有三个例子,HTML结构如下,就不添加CSS样式了. <body> 当前时间:<p id="p1&qu ...
- JS高级程序设计2nd部分知识要点6
DOM nodeType属性 所有类型节点都有的两个方法 1. cloneNode()用于创建调用这个方法的节点的一个完全相同的副本.
