Looper Handler MessageQueue Message 探究
Android消息处理的大致的原理如下:
1.有一个消息队列,可以往队列中添加消息
2.有一个消息循环,可以从消息队列中取出消息
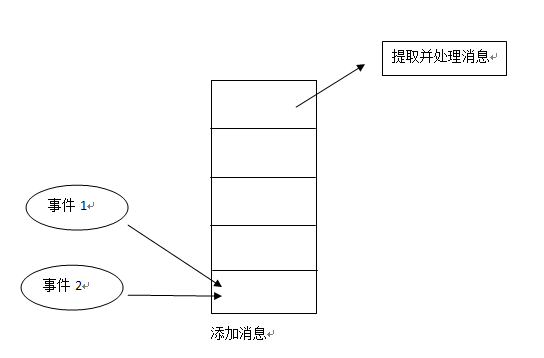
Android系统中这些工作主要由Looper和Handler两个类来实现:
Looper类: 有一个消息队列,封装消息循环
Handler类: 消息的投递、消息的处理
Looper类:
Looper的使用需先调用 Looper.prepare(),然后调用Looper.loop()开启消息循环。
public static void prepare() {
prepare(true);
}
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();
prepare会在调用线程的局部变量中设置一个Looper对象;
ThreadLocal是java中线程局部变量类,有两个关键函数:
set: 设置调用线程的局部变量
get: 获取调用线程的局部变量
Looper的构造函数:
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
创建了一个消息队列,用于存放消息。
Looper.loop(), myLooper()通过ThreadLocal对象获取了prepare时创建的Looper对象。loop里面是一个循环,循环从MessageQueue中取消息,然后通过Handler去处理。
(msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); target是一个Handler对象,后面会提到)
public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() {
return sThreadLocal.get();
}
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block 可能会阻塞
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
}
// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
}
msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
Looper的作用:
封装一个消息队列
prepare()方法把Looper对象和调用的线程绑定起来
通过loop()方法处理消息队列中的消息
Hander类:
Handler有多个构造函数,常用的就下面几个:
public Handler() {
this(null, false);
}
public Handler(Looper looper) {
this(looper, null, false);
}
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = looper;
mQueue = looper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
无参构造函数,通过Looper.myLooper()获取调用线程的Looper对象; Handler提供了一个Callback的接口,参数里面的Callback在处理消息的时候会用到,如果设置了全局Callback,消息会通过这个Callback处理,如果未设置,则需重重载handlerMessage()方法来处理消息。
public interface Callback {
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg);
}
(1) Handler和Message ----> Handler把Message插入Looper的消息队列。
Handler有一系列的处理消息的函数,比如:
public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg)
{
return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);
} public final boolean sendEmptyMessage(int what)
{
return sendEmptyMessageDelayed(what, 0);
} public final boolean sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what, long delayMillis) {
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
return sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMillis);
} public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis)
{
if (delayMillis < 0) {
delayMillis = 0;
}
return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
} public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
} public final boolean sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(Message msg) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, 0);
}
这些都是将消息插入到Looper的消息队列,sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue()是将消息插入到消息队列的队列头,所以优先级很高。所有方法最后都是通过enqueueMessage()方法插入消息。
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
msg.target = this,前面有提到,target是Handler对象,消息的处理最后都需通过这个。
(2)Handler的消息处理
上面的Looper.loop()方法中,不断从消息队列中提取消息,然后通过Handler的dispatchMessage()方法处理消息。
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
如果Message设置了callback,则通过这个callback处理,如果Message没设置callback则先通过全局callback来处理,如果都没设置,则通过handlerMessage()方法来处理。
简单总结一下:
Looper中有一个MessageQueue,里面存储一个个待处理的Message。
Message中有一个Handler,这个Handler处理Message。
转载还望注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaojianli/p/5642380.html
Looper Handler MessageQueue Message 探究的更多相关文章
- Android开发之漫漫长途 ⅥI——Android消息机制(Looper Handler MessageQueue Message)
该文章是一个系列文章,是本人在Android开发的漫漫长途上的一点感想和记录,我会尽量按照先易后难的顺序进行编写该系列.该系列引用了<Android开发艺术探索>以及<深入理解And ...
- Android开发之漫漫长途 Ⅶ——Android消息机制(Looper Handler MessageQueue Message)
该文章是一个系列文章,是本人在Android开发的漫漫长途上的一点感想和记录,我会尽量按照先易后难的顺序进行编写该系列.该系列引用了<Android开发艺术探索>以及<深入理解And ...
- android的消息处理有三个核心类:Looper,Handler和Message。
android的消息处理机制(图+源码分析)——Looper,Handler,Message 作为 一名android程序员,我学习android的一大乐趣是可以通过源码学习google大牛们的设 ...
- Looper: Looper,Handler,MessageQueue三者之间的联系
在Android中每个应用的UI线程是被保护的,不能在UI线程中进行耗时的操作,其他的子线程也不能直接进行UI操作.为了达到这个目的Android设计了handler Looper这个系统框架,And ...
- Looper,Handler, MessageQueue
Looper Looper是线程用来运行消息循环(message loop)的类.默认情况下,线程并没有与之关联的Looper,可以通过在线程中调用Looper.prepare() 方法来获取,并通过 ...
- android的消息处理机制——Looper,Handler,Message
在开始讨论android的消息处理机制前,先来谈谈一些基本相关的术语. 通信的同步(Synchronous):指向客户端发送请求后,必须要在服务端有回应后客户端才继续发送其它的请求,所以这时所有请求将 ...
- 转 Android的消息处理机制(图+源码分析)——Looper,Handler,Message
作为一个大三的预备程序员,我学习android的一大乐趣是可以通过源码学习google大牛们的设计思想.android源码中包含了大量的设计模式,除此以外,android sdk还精心为我们设计了各种 ...
- 【转】android的消息处理机制(图+源码分析)——Looper,Handler,Message
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/codingmyworld/archive/2011/09/12/2174255.html#!comments 作为一个大三的预备程序员,我学习 ...
- android的消息处理机制(图+源码分析)——Looper,Handler,Message
android源码中包含了大量的设计模式,除此以外,android sdk还精心为我们设计了各种helper类,对于和我一样渴望水平得到进阶的人来说,都太值得一读了.这不,前几天为了了解android ...
随机推荐
- Netty版本升级血泪史之线程篇
1. 背景 1.1. Netty 3.X系列版本现状 根据对Netty社区部分用户的调查,结合Netty在其它开源项目中的使用情况,我们可以看出目前Netty商用的主流版本集中在3.X和4.X上,其中 ...
- Jetty实战之 安装 运行 部署
本文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/kongxx/article/details/7218767 1. 首先从Jetty的官方网站http://wiki.eclipse.org/Jet ...
- 大整数相乘的C实现
//之前有个测试这个题没做完,现在把它做完,通过这个程序可以对乘法了解更深刻.分析:运用整数乘法,当然进制越高越好,考虑到乘法不要越界,故考虑进制底数N应该满 //足,N^2<2^32次方.所以 ...
- 《STL源码剖析》chapter2空间配置器allocator
为什么不说allocator是内存配置器而说是空间配置器,因为空间不一定是内存,也可以是磁盘或其他辅助介质.是的,你可以写一个allocator,直接向硬盘取空间.sgi stl提供的配置器,配置的对 ...
- Android基础之响应Menu键弹出菜单Demo
对于Android我也不是很熟悉,只是学习一些基本内容就OK.所以写的内容也很简单.本Demo要实现的效果就点击Menu键将弹出一个菜单并响应点击菜单项事件. 一.废话少说直接上代码.其实就是重写两个 ...
- 执行计划之CONCATENATION
CREATE TABLE T_CONCAT (ID NUMBER, NAME VARCHAR2(30), TYPE VARCHAR2(30)); INSERT INTO T_CONCAT SELECT ...
- 【转】模拟器上安装googleplay apk
原文网址:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_9fc2ff230101gv57.html 1.进入到sdk\android-sdk-windows\tools>目录下: ...
- HDU 5926 Mr. Frog's Game 【模拟】 (2016CCPC东北地区大学生程序设计竞赛)
Mr. Frog's Game Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)T ...
- 利用腾讯企业邮箱开放API获取账户未读邮件数初探
公司一直使用腾讯提供的免费企业邮箱服务,今天用管理员帐户登录后发现,原来现在腾讯的企业邮箱也开放了部分API 你可以通过开放接口实现以下功能: 数据同步 数据同步可以帮助你同步部门成员信息,你还可以创 ...
- Unity Skin Shader Optimized
Shader "Skin Shader" { Properties { _MainTex ("Diffuse (RGB)", 2D) = "white ...
