Flask源码解读--所有可扩展点
一、前言
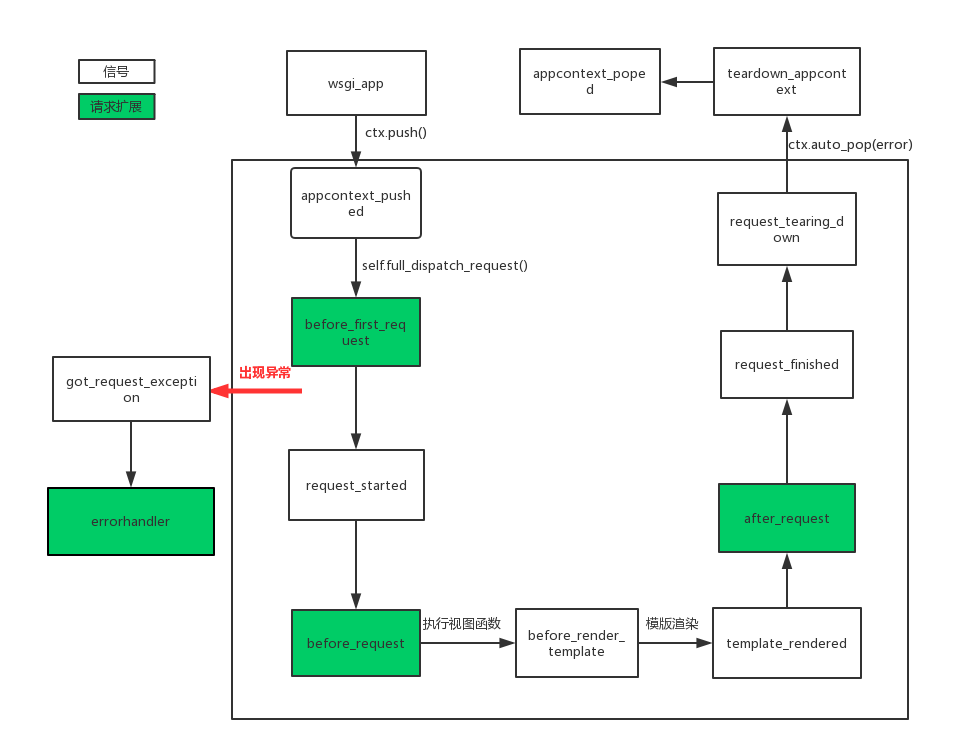
flask中有很多可扩展点(笔者这样称呼),其中包含了信号和请求钩子,这些信号和钩子有什么用呢?其主要作用用于帮助我们进行程序的耦合性,当然还可以让我们自定义一些行为。话不多说,通过阅读源码,笔者将这些所有的可扩展点的执行顺序进行总结(如下图),这样我们更能清楚的知道flask的内部请求流程,后面将对信号以及源码流程做说明,最后以下所有内容都是基于flask版本为1.0.2。重要:信号的触发可以在任何时候,以下流程只是源码的触发顺序。
二、信号
在django中同样也有信号,但django中是内置的,而Flask框架中的信号基于blinker,所以我们在使用flask信号时候需安装blinker。
pip3 install blinker
flask中所有的信号在其源码中都有定义:
request_started = _signals.signal('request-started') # 请求到来前执行
request_finished = _signals.signal('request-finished') # 请求结束后执行
before_render_template = _signals.signal('before-render-template') # 模板渲染前执行
template_rendered = _signals.signal('template-rendered') # 模板渲染后执行
got_request_exception = _signals.signal('got-request-exception') # 请求执行出现异常时执行
request_tearing_down = _signals.signal('request-tearing-down') # 请求执行完毕后自动执行(无论成功与否)
appcontext_tearing_down = _signals.signal('appcontext-tearing-down')# 应用上下文执行完毕后自动执行(无论成功与否)
appcontext_pushed = _signals.signal('appcontext-pushed') # 应用上下文push时执行
appcontext_popped = _signals.signal('appcontext-popped') # 应用上下文pop时执行
message_flashed = _signals.signal('message-flashed') # 调用消息闪现时,自动触发
如何使用
使用信号的 connect() 方法订阅该信号,该方法的第一个参数是当信号发出时所调用的函数。第二个参数是可选参数,定义一个发送者。使用 disconnect() 方法可以退订信号。
示例:
from flask import Flask, signals, request app = Flask(import_name=__name__) def check_host(app, *args):
print(app.config['DEBUG'])
print("host is :", request.host) signals.request_started.connect(receiver=check_host) # 请求之前发送信号检查请求的host @app.route("/")
def index():
return 'index' if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run() #结果
False
host is : 127.0.0.1:5000
在新的版本中还可以使用connect_via信号装饰器来订阅信号,以下代码可以修改为:
from flask import Flask, signals, request app = Flask(import_name=__name__) @signals.request_started.connect_via(app)
def check_host(app, *args):
print(app.config['DEBUG'])
print("host is :", request.host) @app.route("/")
def index():
return 'index' if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
自定义信号
自定义信号允许我们能跟多进行自定义操作,在自定义信号步骤:
- 定义信号
- 订阅信号
- 触发信号
示例:
rom flask import Flask
from blinker import Namespace app = Flask(import_name=__name__)
model_signals=Namespace() # 定义信号 model_update = model_signals.signal(name='model_update') #触发信号是对应的操作
def logging(arg):
print(arg)
print('write log..') #订阅信号
model_update.connect(logging) @app.route("/")
def index():
# 触发信号
model_update.send('save model')
return 'index' if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
结果:
save model
write log..
三、源码流程
在熟悉源码之前,你需要了解下flask的上线文管理,请移步这里, 之前在请求上下文源码中就介绍了请求进来会到wsgi_app,以下是源码定义:
def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response):
"""The actual WSGI application. This is not implemented in
:meth:`__call__` so that middlewares can be applied without
losing a reference to the app object. Instead of doing this:: app = MyMiddleware(app) It's a better idea to do this instead:: app.wsgi_app = MyMiddleware(app.wsgi_app) Then you still have the original application object around and
can continue to call methods on it. .. versionchanged:: 0.7
Teardown events for the request and app contexts are called
even if an unhandled error occurs. Other events may not be
called depending on when an error occurs during dispatch.
See :ref:`callbacks-and-errors`. :param environ: A WSGI environment.
:param start_response: A callable accepting a status code,
a list of headers, and an optional exception context to
start the response.
"""
ctx = self.request_context(environ)
error = None
try:
try:
ctx.push() #存储请求上下文
response = self.full_dispatch_request() #处理请求,执行视图函数,返回响应
except Exception as e:
error = e
response = self.handle_exception(e) # 处理异常
except:
error = sys.exc_info()[1]
raise
return response(environ, start_response) #返回给客户端
finally:
if self.should_ignore_error(error):
error = None
ctx.auto_pop(error) #删除栈中的请求上下文
在wsgi_app中会执行ctx.push方法将上线问push到栈中,此时触发1.appcontext_pushed,以下是源码部分:
def push(self):
"""Binds the app context to the current context."""
self._refcnt += 1
if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'):
sys.exc_clear()
_app_ctx_stack.push(self)
appcontext_pushed.send(self.app) #触发appcontext_pushed信号
接着执行self.full_dispatch_request(),在改方法中主要是用于请求预处理、以及更具路由匹配执行视图函数,下面其源码:
def full_dispatch_request(self):
"""Dispatches the request and on top of that performs request
pre and postprocessing as well as HTTP exception catching and
error handling. .. versionadded:: 0.7
"""
self.try_trigger_before_first_request_functions() #执行请求扩展before_first_request
try:
request_started.send(self) #触发request_started信号
rv = self.preprocess_request()
if rv is None:
rv = self.dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
rv = self.handle_user_exception(e) #处理异常
return self.finalize_request(rv) #最后对请求进行最后的处理
这里面执行请求扩展2.before_first_request,然后触发信号3.request_started信号,接着执行self.preprocess_request()进行请求预处理,源码:
bp = _request_ctx_stack.top.request.blueprint funcs = self.url_value_preprocessors.get(None, ())
if bp is not None and bp in self.url_value_preprocessors:
funcs = chain(funcs, self.url_value_preprocessors[bp])
for func in funcs:
func(request.endpoint, request.view_args) funcs = self.before_request_funcs.get(None, ()) #执行请求扩展before_request
if bp is not None and bp in self.before_request_funcs:
funcs = chain(funcs, self.before_request_funcs[bp])
for func in funcs:
rv = func()
if rv is not None:
return rv
在视图函数中如果使用了render_template(模版渲染),我们来看下其渲染方法:
def _render(template, context, app):
"""Renders the template and fires the signal""" before_render_template.send(app, template=template, context=context) # 触发before_render_template信号
rv = template.render(context) # 模版渲染
template_rendered.send(app, template=template, context=context) ## 触发template_rendered信号
return rv
渲染模版时候分别触发5.before_render_template以及6.template_rendered信号,在执行wsgi_app中的self.finalize_request(rv)对请求做最后的处理,源码:
def finalize_request(self, rv, from_error_handler=False):
"""Given the return value from a view function this finalizes
the request by converting it into a response and invoking the
postprocessing functions. This is invoked for both normal
request dispatching as well as error handlers. Because this means that it might be called as a result of a
failure a special safe mode is available which can be enabled
with the `from_error_handler` flag. If enabled, failures in
response processing will be logged and otherwise ignored. :internal:
"""
response = self.make_response(rv)
try:
response = self.process_response(response) #处理响应
request_finished.send(self, response=response) # 触发request_finished信号
except Exception:
if not from_error_handler:
raise
self.logger.exception('Request finalizing failed with an '
'error while handling an error')
return response
在触发request_finished之前会执行self.process_response,源码:
def process_response(self, response):
"""Can be overridden in order to modify the response object
before it's sent to the WSGI server. By default this will
call all the :meth:`after_request` decorated functions. .. versionchanged:: 0.5
As of Flask 0.5 the functions registered for after request
execution are called in reverse order of registration. :param response: a :attr:`response_class` object.
:return: a new response object or the same, has to be an
instance of :attr:`response_class`.
"""
ctx = _request_ctx_stack.top #获取请求上下文
bp = ctx.request.blueprint # 获取蓝图
funcs = ctx._after_request_functions
if bp is not None and bp in self.after_request_funcs:
funcs = chain(funcs, reversed(self.after_request_funcs[bp]))#执行请求扩张after_request
if None in self.after_request_funcs:
funcs = chain(funcs, reversed(self.after_request_funcs[None]))
for handler in funcs:
response = handler(response)
if not self.session_interface.is_null_session(ctx.session):
self.session_interface.save_session(self, ctx.session, response) # 保存session
return response
所以这里先执行了请求扩展7.after_request然后触发信号8.request_finished信号,当在处理请求时候出现异常则会执行self.handle_exception(e),源码:
def handle_exception(self, e):
"""Default exception handling that kicks in when an exception
occurs that is not caught. In debug mode the exception will
be re-raised immediately, otherwise it is logged and the handler
for a 500 internal server error is used. If no such handler
exists, a default 500 internal server error message is displayed. .. versionadded:: 0.3
"""
exc_type, exc_value, tb = sys.exc_info() got_request_exception.send(self, exception=e) #触发got_request_exception信号
handler = self._find_error_handler(InternalServerError()) if self.propagate_exceptions:
# if we want to repropagate the exception, we can attempt to
# raise it with the whole traceback in case we can do that
# (the function was actually called from the except part)
# otherwise, we just raise the error again
if exc_value is e:
reraise(exc_type, exc_value, tb)
else:
raise e self.log_exception((exc_type, exc_value, tb))
if handler is None:
return InternalServerError()
return self.finalize_request(handler(e), from_error_handler=True)
def pop(self, exc=_sentinel):
"""Pops the request context and unbinds it by doing that. This will
also trigger the execution of functions registered by the
:meth:`~flask.Flask.teardown_request` decorator. .. versionchanged:: 0.9
Added the `exc` argument.
"""
app_ctx = self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.pop() try:
clear_request = False
if not self._implicit_app_ctx_stack:
self.preserved = False
self._preserved_exc = None
if exc is _sentinel:
exc = sys.exc_info()[1]
self.app.do_teardown_request(exc) # 触发request_tearing_down信号 # If this interpreter supports clearing the exception information
# we do that now. This will only go into effect on Python 2.x,
# on 3.x it disappears automatically at the end of the exception
# stack.
if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'):
sys.exc_clear() request_close = getattr(self.request, 'close', None)
if request_close is not None:
request_close()
clear_request = True
finally:
rv = _request_ctx_stack.pop() # get rid of circular dependencies at the end of the request
# so that we don't require the GC to be active.
if clear_request:
rv.request.environ['werkzeug.request'] = None # Get rid of the app as well if necessary.
if app_ctx is not None:
app_ctx.pop(exc) #触发teardown_appcontext信号 assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong request context. ' \
'(%r instead of %r)' % (rv, self)
此时会触发9.request_tearing_down信号,然后执行到app_ctx.pop(exc):
def pop(self, exc=_sentinel):
"""Pops the app context."""
try:
self._refcnt -= 1
if self._refcnt <= 0:
if exc is _sentinel:
exc = sys.exc_info()[1]
self.app.do_teardown_appcontext(exc) #触发teardown_appcontext信号
finally:
rv = _app_ctx_stack.pop()
assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong app context. (%r instead of %r)' \
% (rv, self)
appcontext_popped.send(self.app) # 触发appcontext_poped信号
到pop app_ctx是先触发了10.teardown_appcontext信号再触发11.appcontext_poped信号,到此整个flask的所有信号以及所有可扩展点的所有顺序执行完毕。
最后,整体的执行顺序的流程图我已经在最开始放上了。
Flask源码解读--所有可扩展点的更多相关文章
- Python Web Flask源码解读(一)——启动流程
关于我 一个有思想的程序猿,终身学习实践者,目前在一个创业团队任team lead,技术栈涉及Android.Python.Java和Go,这个也是我们团队的主要技术栈. Github:https:/ ...
- Python Web Flask源码解读(二)——路由原理
关于我 一个有思想的程序猿,终身学习实践者,目前在一个创业团队任team lead,技术栈涉及Android.Python.Java和Go,这个也是我们团队的主要技术栈. Github:https:/ ...
- Python Web Flask源码解读(三)——模板渲染过程
关于我 一个有思想的程序猿,终身学习实践者,目前在一个创业团队任team lead,技术栈涉及Android.Python.Java和Go,这个也是我们团队的主要技术栈. Github:https:/ ...
- Python Web Flask源码解读(四)——全局变量
关于我 一个有思想的程序猿,终身学习实践者,目前在一个创业团队任team lead,技术栈涉及Android.Python.Java和Go,这个也是我们团队的主要技术栈. Github:https:/ ...
- 【mybatis源码学习】mybtias扩展点
[1]org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ReflectorFactory 该扩展点,主要是对javaBean对象,进行反射操作. org.apache.ibatis.refle ...
- Flask源码解读(一)
Flask是一个使用 Python 编写的轻量级 Web 应用框架.Flask 本身只是 Werkezug 和 Jinja2 的之间的桥梁,前者实现一个合适的 WSGI 应用,后者处理模板. 当然, ...
- flask 源码专题(九):flask扩展点
1. 信号(源码) 信号,是在flask框架中为我们预留的钩子,让我们可以进行一些自定义操作. pip3 install blinker 2. 根据flask项目的请求流程来进行设置扩展点 中间件 # ...
- Flask(4)- flask请求上下文源码解读、http聊天室单聊/群聊(基于gevent-websocket)
一.flask请求上下文源码解读 通过上篇源码分析,我们知道了有请求发来的时候就执行了app(Flask的实例化对象)的__call__方法,而__call__方法返回了app的wsgi_app(en ...
- flask的请求上下文源码解读
一.flask请求上下文源码解读 通过上篇源码分析( ---Flask中的CBV和上下文管理--- ),我们知道了有请求发来的时候就执行了app(Flask的实例化对象)的__call__方法,而__ ...
随机推荐
- WebGL学习笔记(一)
作者:朱金灿 来源:http://blog.csdn.net/clever101 (一)WebGL是什么? WebGL是一门在网页上显示三维图形的技术,你可以把它理解为把OpenGL从C/S端搬到了B ...
- 安装VMwareTool
对于刚刚学习Linux的小白来说,安装VMwareTool工具是一个比较迫切需要,又是些难度的活,下面就做一个简单的介绍. 第一步:点击虚拟机.或者选中需要安装的虚拟机,右键虚拟机,选中安装VMwar ...
- DB2表被锁,如何解锁
原因与解决方案 1.原因:修改表结构表结构发生变化后再对表进行任何操作都不被允许,SQLState为57016(因为表不活动,所以不能对其进行访问),由于修改了表字段权限,导致表处于不可用状态 2.解 ...
- Bash On Windows上安装JDK
1. 引言 由于实习生转正,公司给配了一台新电脑,配置不用多说,16G内存,i7-7700的CPU,128SSD的系统盘,1T的机械硬盘,虽然只有一个破核显.对于我个人而言,最重要的是系统从Windo ...
- 手机上的m3u8视频(缓存)怎么转成MP4?
一.下载M3u8合并APK,自定义扫描手机中的m3u8文件目录.选择导出的目录,可以多个同时进行m3u8的合并任务. 合并后的文件可以完整播放,但是视频时间只有前十来秒,进度无法拖动. 二.将合并好的 ...
- EasyUI DataGrid自适应高度
我的页面分为上下两部分,但发现下面有DataGrid的高度总是自动改,数据根本显示不出来. 后来在博客园里看到这个:http://www.cnblogs.com/xienb/archive/2013/ ...
- 控件_ImageView
ImageView(图片视图)的基本概念:就是将一张图片放在一个Activity中显示出来,就是一个放图片的容器 import android.app.Activity; import android ...
- 【SDOI2009】Bill的挑战
Description Sheng bill不仅有惊人的心算能力,还可以轻松地完成各种统计.在昨天的比赛中,你凭借优秀的程序与他打成了平局,这导致Sheng bill极度的不满.于是他再次挑战你.这次 ...
- 【洛谷】【动态规划/01背包】P2925 [USACO08DEC]干草出售Hay For Sale
[题目描述:] 约翰遭受了重大的损失:蟑螂吃掉了他所有的干草,留下一群饥饿的牛.他乘着容量为C(1≤C≤50000)个单位的马车,去顿因家买一些干草. 顿因有H(1≤H≤5000)包干草,每一包都有它 ...
- SSM 搭建精美实用的管理系统
课程介绍 SSM 框架即 SpringMVC+Spring+Mybatis,相信各位朋友在投递简历时已直观感受到它的重要性,JavaWeb 相关工作的招聘要求中基本都包括了这三项技术能力. 由于其轻量 ...
