Apache Hadoop YARN – NodeManager--转载
原文地址:http://zh.hortonworks.com/blog/apache-hadoop-yarn-nodemanager/
The NodeManager (NM) is YARN’s per-node agent, and takes care of the individual compute nodes in a Hadoop cluster. This includes keeping up-to date with the ResourceManager (RM), overseeing containers’ life-cycle management; monitoring resource usage (memory, CPU) of individual containers, tracking node-health, log’s management and auxiliary services which may be exploited by different YARN applications.
NodeManager Components
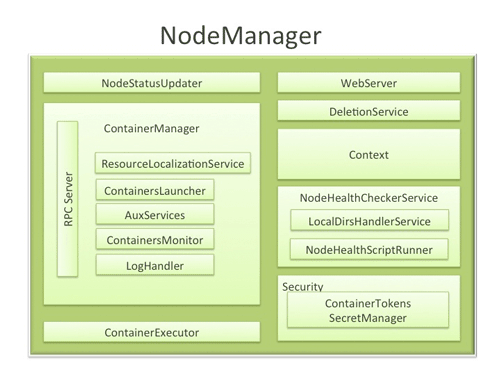
- NodeStatusUpdater
On startup, this component registers with the RM and sends information about the resources available on the nodes. Subsequent NM-RM communication is to provide updates on container statuses – new containers running on the node, completed containers, etc.
In addition the RM may signal the NodeStatusUpdater to potentially kill already running containers.
- ContainerManager
This is the core of the NodeManager. It is composed of the following sub-components, each of which performs a subset of the functionality that is needed to manage containers running on the node.
- RPC server: ContainerManager accepts requests from Application Masters (AMs) to start new containers, or to stop running ones. It works with ContainerTokenSecretManager (described below) to authorize all requests. All the operations performed on containers running on this node are written to an audit-log which can be post-processed by security tools.
- ResourceLocalizationService: Responsible for securely downloading and organizing various file resources needed by containers. It tries its best to distribute the files across all the available disks. It also enforces access control restrictions of the downloaded files and puts appropriate usage limits on them.
- ContainersLauncher: Maintains a pool of threads to prepare and launch containers as quickly as possible. Also cleans up the containers’ processes when such a request is sent by the RM or the ApplicationMasters (AMs).
- AuxServices: The NM provides a framework for extending its functionality by configuring auxiliary services. This allows per-node custom services that specific frameworks may require, and still sandbox them from the rest of the NM. These services have to be configured before NM starts. Auxiliary services are notified when an application’s first container starts on the node, and when the application is considered to be complete.
- ContainersMonitor: After a container is launched, this component starts observing its resource utilization while the container is running. To enforce isolation and fair sharing of resources like memory, each container is allocated some amount of such a resource by the RM. The ContainersMonitor monitors each container’s usage continuously and if a container exceeds its allocation, it signals the container to be killed. This is done to prevent any runaway container from adversely affecting other well-behaved containers running on the same node.
- LogHandler: A pluggable component with the option of either keeping the containers’ logs on the local disks or zipping them together and uploading them onto a file-system.
- ContainerExecutor
Interacts with the underlying operating system to securely place files and directories needed by containers and subsequently to launch and clean up processes corresponding to containers in a secure manner.
- NodeHealthCheckerService
Provides functionality of checking the health of the node by running a configured script frequently. It also monitors the health of the disks specifically by creating temporary files on the disks every so often. Any changes in the health of the system are notified to NodeStatusUpdater (described above) which in turn passes on the information to the RM.
- Security
- ApplicationACLsManagerNM needs to gate the user facing APIs like container-logs’ display on the web-UI to be accessible only to authorized users. This component maintains the ACLs lists per application and enforces them whenever such a request is received.
- ContainerTokenSecretManager: verifies various incoming requests to ensure that all the incoming operations are indeed properly authorized by the RM.
- WebServer
Exposes the list of applications, containers running on the node at a given point of time, node-health related information and the logs produced by the containers.
Spotlight on Key Functionality
- Container Launch
To facilitate container launch, the NM expects to receive detailed information about a container’s runtime as part of the container-specifications. This includes the container’s command line, environment variables, a list of (file) resources required by the container and any security tokens.
On receiving a container-launch request – the NM first verifies this request, if security is enabled, to authorize the user, correct resources assignment, etc. The NM then performs the following set of steps to launch the container.
- A local copy of all the specified resources is created (Distributed Cache).
- Isolated work directories are created for the container, and the local resources are made available in these directories.
- The launch environment and command line is used to start the actual container.
- Log Aggregation
Handling user-logs has been one of the big pain-points for Hadoop installations in the past. Instead of truncating user-logs, and leaving them on individual nodes like the TaskTracker, the NM addresses the logs’ management issue by providing the option to move these logs securely onto a file-system (FS), for e.g. HDFS, after the application completes.
Logs for all the containers belonging to a single Application and that ran on this NM are aggregated and written out to a single (possibly compressed) log file at a configured location in the FS. Users have access to these logs via YARN command line tools, the web-UI or directly from the FS.
- How MapReduce shuffle takes advantage of NM’s Auxiliary-services
The Shuffle functionality required to run a MapReduce (MR) application is implemented as an Auxiliary Service. This service starts up a Netty Web Server, and knows how to handle MR specific shuffle requests from Reduce tasks. The MR AM specifies the service id for the shuffle service, along with security tokens that may be required. The NM provides the AM with the port on which the shuffle service is running which is passed onto the Reduce tasks.
Conclusion
In YARN, the NodeManager is primarily limited to managing abstract containers i.e. only processes corresponding to a container and not concerning itself with per-application state management like MapReduce tasks. It also does away with the notion of named slots like map and reduce slots. Because of this clear separation of responsibilities coupled with the modular architecture described above, NM can scale much more easily and its code is much more maintainable.
Apache Hadoop YARN – NodeManager--转载的更多相关文章
- Apache Hadoop YARN: 背景及概述
从2012年8月开始Apache Hadoop YARN(YARN = Yet Another Resource Negotiator)成了Apache Hadoop的一项子工程.自此Apache H ...
- hadoop错误org.apache.hadoop.yarn.exceptions.YarnException Unauthorized request to start container
错误: 14/04/29 02:45:07 INFO mapreduce.Job: Job job_1398704073313_0021 failed with state FAILED due to ...
- spark on yarn 动态资源分配报错的解决:org.apache.hadoop.yarn.exceptions.InvalidAuxServiceException: The auxService:spark_shuffle does not exist
组件:cdh5.14.0 spark是自己编译的spark2.1.0-cdh5.14.0 第一步:确认spark-defaults.conf中添加了如下配置: spark.shuffle.servic ...
- org.apache.hadoop.yarn.exceptions.InvalidAuxServiceException: The auxService: mapreduce_shuffle do
在yarn-site.xml 配置文件中增加: <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name> < ...
- Hadoop - YARN NodeManager 剖析
一 概述 NodeManager是执行在单个节点上的代理,它管理Hadoop集群中单个计算节点,功能包含与ResourceManager保持通信,管理Container的生命周期.监控 ...
- spark 笔记 4:Apache Hadoop YARN: Yet Another Resource Negotiator
spark支持YARN做资源调度器,所以YARN的原理还是应该知道的:http://www.socc2013.org/home/program/a5-vavilapalli.pdf 但总体来说, ...
- Apache Hadoop YARN – ResourceManager--转载
原文地址:http://zh.hortonworks.com/blog/apache-hadoop-yarn-resourcemanager/ ResourceManager (RM) is the ...
- Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/hadoop/yarn/exceptions/YarnException
这个是Flink 1.11.1 使用yarn-session 出现的错误:原因是在Flink1.11 之后不再提供flink-shaded-hadoop-*” jars 需要在yarn-sessio ...
- Caused by:java.lang.ClassNotFoundException:org.apache.hadoop.yarn.util.Apps
错误原因 缺少hadoop-yarn.jar包. 导入jar包就好了~-~
随机推荐
- 20155328 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》 第一周学习总结
20155328 2016-2017-2 <Java程序设计> 第一周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 本周学习目标是浏览<Java学习笔记>中的十八章,其中第一章和第二章认真学习, ...
- day6 网络 HTML模板
1.HTML模板 HTML模板 baidu一下 http://www.cssmoban.com/ http://www.cnblogs.com/web-d/archive/2010/04/16/171 ...
- 手撕一个 Galgame 神器——Shub-Niggurath Project
一.想法 Galgame 我们大概可以分为好用的 Galgame 和好玩的 Galgame,但是如果你把好玩的 Galgame 拿来用的话,有时候会十分让人着急.如果你躺在床上,一只手还在按压键盘实际 ...
- 对posintion属性的简单认识,对于还在纠结的同学们,有一定的帮助
position的四个属性值: relative ,absolute ,fixed,static 下面分别讲述这四个属性,以简单代码表示 <div id="parent" ...
- Maven学习(十一)-----使用Maven创建Web应用程序项目
使用Maven创建Web应用程序项目 用到的技术/工具: Maven 3.3.3 Eclipse 4.3 JDK 8 Spring 4.1.1.RELEASED Tomcat 7 Logback 1. ...
- Maven学习(一)-----Maven安装配置总结
想要安装 Apache Maven 在Windows 系统上, 需要下载 Maven 的 zip 文件,并将其解压到你想安装的目录,并配置 Windows 环境变量. 所需工具 : JDK 1.8 M ...
- Zigbee系列(网络)
Zigbee设备类型 Coordinator:形成网络,选择信道.PANID.允许其他设备加入等. Router: 作为路由节点,转发报文. End Device: 终端节点,不转发报文. Zigbe ...
- 使用GitLab创建项目
- linux 下 python 安装 Django
安装 setuptools 使用easy_install命令 easy_install django
- 用EC5/EC6自定义class的区别及用法 -- Phaser3网页游戏框架
custom class EC6 自定义class class Brain extends Phaser.GameObjects.Sprite { constructor (scene, x, y ...
