Codeforces 690 C3. Brain Network (hard) LCA
Breaking news from zombie neurology! It turns out that – contrary to previous beliefs – every zombie is born with a single brain, and only later it evolves into a complicated brain structure. In fact, whenever a zombie consumes a brain, a new brain appears in its nervous system and gets immediately connected to one of the already existing brains using a single brain connector. Researchers are now interested in monitoring the brain latency of a zombie. Your task is to write a program which, given a history of evolution of a zombie's nervous system, computes its brain latency at every stage.
The first line of the input contains one number n – the number of brains in the final nervous system (2 ≤ n ≤ 200000). In the second line a history of zombie's nervous system evolution is given. For convenience, we number all the brains by 1, 2, ..., n in the same order as they appear in the nervous system (the zombie is born with a single brain, number 1, and subsequently brains 2, 3, ..., n are added). The second line contains n - 1 space-separated numbers p2, p3, ..., pn, meaning that after a new brain k is added to the system, it gets connected to a parent-brain 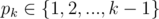 .
.
Output n - 1 space-separated numbers – the brain latencies after the brain number k is added, for k = 2, 3, ..., n.
6
1
2
2
1
5
1 2 2 3 4
题意:
给你一个根节点1,之后每次加一条边,结点的父结点是树中已经得到的结点,问你加完边之后每一次的直径
题解:
新直径与加边之前的直径的关系,假设未加边之前是由X,Y这两点组成的链最长,那么答案必然是 max(dis(i,X),dis(i,Y),dis(X,Y));
这个画图作作假设就看得出
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=4e5+,mods=,inf=2e9+; int fa[N][],dep[N],n,f[N];
vector<int > G[N];
void Lca_dfs(int u,int p,int d) {
fa[u][] = p, dep[u] = d;
for(int i = ; i < G[u].size(); ++i) {
int to = G[u][i];
if(to == p) continue;
Lca_dfs(to,u,d+);
}
}
void Lca_init() {
Lca_dfs(,,);
for(int i = ; i <= ; ++i) {
for(int j = ; j <= n; ++j) {
if(fa[j][i-]) {
fa[j][i] = fa[fa[j][i-]][i-];
} else {
fa[j][i] = ;
}
}
}
}
int Lca(int x,int y) {
if(dep[x] > dep[y]) swap(x,y);
for(int k = ; k < ; ++k) {
if((dep[y] - dep[x])>>k&)
y = fa[y][k];
}
if(x == y) return x;
for(int k = ; k >= ; --k) {
if(fa[x][k] != fa[y][k]) {
x = fa[x][k];
y = fa[y][k];
}
}
return fa[x][];
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&f[i]);
G[f[i]].push_back(i);
}
Lca_init();
int ans = ,x = ,y = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
int ux = Lca(i,x);
int uy = Lca(i,y);
int nowx,nowy;
if(x == ux) {
if(ans < dep[i] - dep[x]) {
ans = dep[i] - dep[x];
nowx = i;nowy = x;
}
}else {
if(dep[i] + dep[x] - *dep[ux] > ans) {
ans = dep[i] + dep[x] - *dep[ux];
nowx = i;
nowy = x;
}
}
if(y == uy) {
if(ans < dep[i] - dep[y]) {
ans = dep[i] - dep[y];
nowx = i;nowy = y;
}
}
else {
if(dep[i] + dep[y] - *dep[uy] > ans) {
ans = dep[i] + dep[y] - *dep[uy];
nowx = i;
nowy = y;
}
}
x= nowx;
y = nowy;
cout<<ans<<" ";
}
return ;
}
Codeforces 690 C3. Brain Network (hard) LCA的更多相关文章
- codeforces 690C3 C3. Brain Network (hard)(lca)
题目链接: C3. Brain Network (hard) time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- codeforces 690C2 C2. Brain Network (medium)(bfs+树的直径)
题目链接: C2. Brain Network (medium) time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes i ...
- codeforces 690C1 C1. Brain Network (easy)(水题)
题目链接: C1. Brain Network (easy) time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- CF 690C3. Brain Network (hard) from Helvetic Coding Contest 2016 online mirror (teams, unrated)
题目描述 Brain Network (hard) 这个问题就是给出一个不断加边的树,保证每一次加边之后都只有一个连通块(每一次连的点都是之前出现过的),问每一次加边之后树的直径. 算法 每一次增加一 ...
- Brain Network (medium)(DFS)
H - Brain Network (medium) Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:262144KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d &am ...
- Brain Network (easy)(并查集水题)
G - Brain Network (easy) Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:262144KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & ...
- Brain Network (medium)
Brain Network (medium) Further research on zombie thought processes yielded interesting results. As ...
- Brain Network (easy)
Brain Network (easy) One particularly well-known fact about zombies is that they move and think terr ...
- poj 3417 Network(tarjan lca)
poj 3417 Network(tarjan lca) 先给出一棵无根树,然后下面再给出m条边,把这m条边连上,然后每次你能毁掉两条边,规定一条是树边,一条是新边,问有多少种方案能使树断裂. 我们设 ...
随机推荐
- 启发式合并 CodeForces - 600E
启发式合并最重要的思想就是指的是每次将小集合拷贝合并至大集合.考虑每个元素的合并开销.对于合并次数最多的那个元素来说,它每合并一次,所在集合的规模扩大两倍,最多只会合并 logN 次,因而对于所有元素 ...
- PermGen space OOM 记录
前些天线上除出了个OOM问题,今天闲下来记录下: OOM的提示信息是-PermGen space,说明问题出在方法区,方法区存的是什么东西?:类的加载信息.常量.静态变量. 按照方法区的定义:类加载的 ...
- 微信小程序 video组件----真机测试position:fixed无效 且有黑底
1.问题描述 video组件fixed后,视频随页面滚动,且有个黑色底停留在页面. 页面滚动前 滚动后 这里贴一下修改前代码,在微信开发者工具看是没有任何问题的.在手机端测试就有以上的问题 <v ...
- wepy 编译警告去除办法
如果你用过wepy打包小程序的话,那么你一定碰到了很多坑,(什么也不用说,抱一下吧)下面记录的是本人遇到的一个小坑, 编译的时候出现了黄色警告 如果你出现了上图这样的话,相信你一定也知道什么意思,就是 ...
- Python基础知识点总结
Python基础知识与常用数据类型 一.Python概述: 1.1.Python的特点: 1.Python是一门面向对象的语言,在Python中一切皆对象 2.Python是一门解释性语言 3.Pyt ...
- LeetCode(53) Maximum Subarray
题目 Find the contiguous subarray within an array (containing at least one number) which has the large ...
- 对于BFC(block format context)理解
目录 前言 Box: CSS布局的基本单位&盒模型 什么是BFC?(Block formatting contexts) 元素与盒 正常流 块级与行内级 产生垂直外边距合并的必备条件 前言 什 ...
- FPGA学习笔记(八)—— 状态机设计实例之独立按键消抖
###### [该随笔中部分内容转载自小梅哥] ######### 独立按键消抖自古以来在单片机和FPGA中都是个不可避免的问题,首先,解释一下什么叫做按键抖动,如图,按键在按下和松开的那个瞬间存在大 ...
- 【裸的并查集】POJ 1611 The Suspects
http://poj.org/problem?id=1611 [Accepted] #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include&l ...
- web文件管理系统和日志实时监控工具
https://blog.csdn.net/xuesong123/article/details/52752384
