codeforces round #427 div2
A:读懂题,乘一下判断大小就行了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int s, v1, v2, t1, t2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &s, &v1, &v2, &t1, &t2);
int ans1 = v1 * s + t1 * , ans2 = v2 * s + t2 * ;
if(ans1 == ans2) puts("Friendship");
else if(ans1 < ans2) puts("First");
else puts("Second");
return ;
}
B:又是桶。。。cf怎么这么喜欢桶,当然把最小的位换成9是最好的,那么10个数字开10个桶,暴力删除每位改成9就行了,只是while要放在前面枚举pos
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tot[], sum, ans;
char s[];
int main()
{
int k;
scanf("%d%s", &k, s);
int len = strlen(s);
for(int i = ; i < len; ++i) ++tot[s[i] - ''], sum += s[i] - '';
int pos = ;
while(sum < k)
{
while(tot[pos] == ) ++pos;
sum += - pos;
--tot[pos];
++ans;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return ;
}
C:很明显不能暴力每次把所有星星+1,这是做不到的,但是看见c很小,那么我们预处理出c+1种情况就行了,可以用二维前缀和或二维bit,注意星星的位置可以重叠,考试的时候脑子坏了重新写了一遍,skip罚时爆炸,30min没了。。。
二维前缀和
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[][][], mark[][];
vector<int> b[][][];
int main()
{
int n, q, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &q, &c);
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i)
{
int x, y, s;
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &s);
mark[x][y] = ;
b[][x][y].push_back(s);
}
for(int k = ; k <= ; ++k)
for(int i = ; i <= ; ++i)
for(int j = ; j <= ; ++j)
{
int delta = ;
if(k > )
{
for(int l = ; l < b[k - ][i][j].size(); ++l)
{
b[k][i][j].push_back((b[k - ][i][j][l] + ) % (c + ));
delta += b[k][i][j][l];
}
}
else
{
for(int l = ; l < b[k][i][j].size(); ++l)
delta += b[k][i][j][l];
}
a[k][i][j] = a[k][i][j - ] + a[k][i - ][j] - a[k][i - ][j - ] + delta;
}
for(int i = ; i <= q; ++i)
{
int t, x1, y1, x2, y2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &t, &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
int sum = a[t % (c + )][x2][y2] - a[t % (c + )][x2][y1 - ] - a[t % (c + )][x1 - ][y2] + a[t % (c + )][x1 - ][y1 - ];
printf("%d\n", sum);
}
return ;
}
二维bit
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[][][], mark[][];
int tree[][][], x[], y[], s[][];
int lowbit(int i)
{
return i & (-i);
}
void update(int k, int x, int y, int delta)
{
for(int i = x; i <= ; i += lowbit(i))
for(int j = y; j <= ; j += lowbit(j))
tree[k][i][j] += delta;
}
int query(int k, int x, int y)
{
int ret = ;
for(int i = x; i; i -= lowbit(i))
for(int j = y; j; j -= lowbit(j)) ret += tree[k][i][j];
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int n, q, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &q, &c);
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i)
scanf("%d%d%d", &x[i], &y[i], &s[i][]);
for(int k = ; k <= ; ++k)
for(int l = ; l <= n; ++l)
{
if(k == ) update(k, x[l], y[l], s[l][]);
else
{
s[l][k] = (s[l][k - ] + ) % (c + );
update(k, x[l], y[l], s[l][k]);
}
}
for(int i = ; i <= q; ++i)
{
int t, x1, y1, x2, y2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &t, &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
int sum = query(t % (c + ), x2, y2) - query(t % (c + ), x2, y1 - ) - query(t % (c + ), x1 - , y2) + query(t % (c + ), x1 - , y1 - );
printf("%d\n", sum);
}
return ;
}
bit常数真是小,跑的跟前缀和一样快
D:怎么出原题,和7D有什么区别,直接拉板子。。。dp[i]表示第i位结束的串是多少palindrome,如果是回文,dp[i]=dp[i/2]+1,否则是0,判断回文用前后哈希,就是维护一个串正反的哈希,每次O(1)维护,然后枚举起点跑dp就行了。。。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = ;
char s[N];
int dp[N], ans[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%s", s + );
int n = strlen(s + );
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i)
{
memset(dp, , sizeof(dp));
ll p = , pre = , bak = ;
for(int j = i; j <= n; ++j)
{
pre = pre * 1234567ll + s[j];
bak = s[j] * p + bak;
p *= 1234567ll;
if(pre == bak) dp[j - i + ] = dp[(j - i + ) / ] + ;
++ans[dp[j - i + ]];
}
}
for(int i = n; i; --i) ans[i] += ans[i + ];
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) printf("%d ", ans[i]);
return ;
}
F:比较套路没想出来。。。zz。。。看见基环树,我们就要把环展开,具体方式是cycle存了环上每个点,最后push_back(cycle[0]),这样就首尾相接了,然后对于环上每个点维护max_d,挂在这个点下的最长链,pre_dia,从1->i这段环,包括环上点挂着的链的直径,pre_len,1->i这段环到1的最长路径,bak也一样
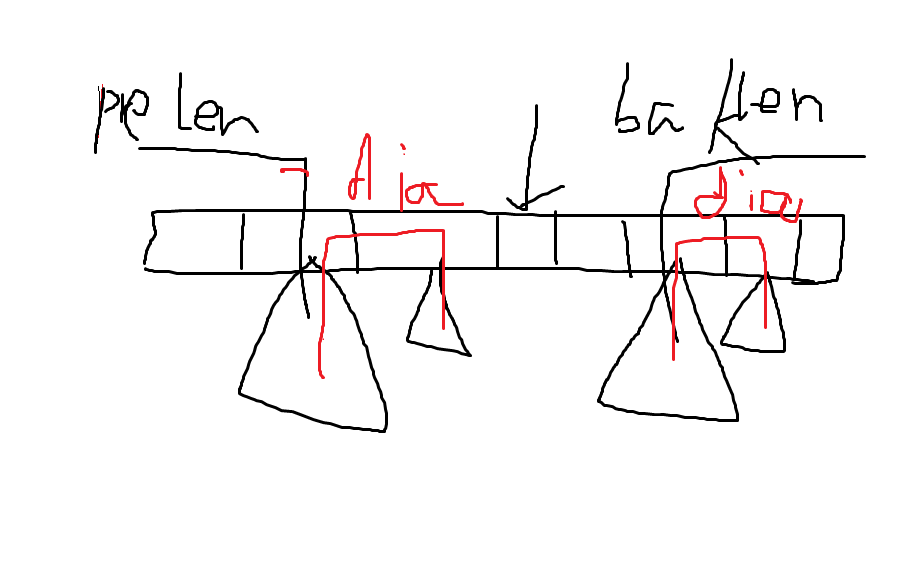
具体是这个样子的,然后枚举分割点,把环分割成两段后,mn=min(mn,max(pre_len+bak_len,max(pre_dia,bak_dia)),两段len相加构成了一条完全的链,两个dia分别是这两段的直径。
ans=max(ans,mn) ans先预处理不在环上的最长距离,就是子树内的直径,环上分割不影响这一段,所以和mn取max。注意最后push的cycle[0] max_d要取0,否则可能cycle在第一段和第二段都取了cycle[0],这样就不对了,但是后面一段的dia要加上max_d,因为两段dia是分别互不影响的,这个东西坑了我们长时间,又没办法对拍。。。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = ;
inline int read()
{
int x = , f = ; char c = getchar();
while(c < '' || c > '') { if(c == '-') f = -; c = getchar(); }
while(c >= '' && c <= '') { x = x * + c - ''; c = getchar(); }
return x * f;
}
struct edge {
int to, w;
edge(int to = , int w = ) : to(to), w(w) {}
};
ll ans = -;
int n, dfn_clock, tar;
vector<edge> G[N];
vector<int> cycle;
int dfn[N], mark[N];
ll w[N], pre_len[N], bak_len[N], pre_dia[N], bak_dia[N], max_d[N];
bool dfs(int u, int last)
{
if(dfn[u])
{
tar = u;
return true;
}
dfn[u] = ++dfn_clock;
for(int i = ; i < G[u].size(); ++i)
{
edge e = G[u][i];
if(e.to == last) continue;
if(dfs(e.to, u))
{
if(dfn[u] >= dfn[tar])
{
cycle.push_back(u);
mark[u] = ;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
ll Dfs(int u, int last)
{
ll max_d = ;
for(int i = ; i < G[u].size(); ++i)
{
edge e = G[u][i];
if(e.to == last || mark[e.to]) continue;
ll dep = Dfs(e.to, u);
ans = max(ans, dep + max_d + (ll)e.w);
max_d = max(max_d, dep + (ll)e.w);
}
return max_d;
}
int main()
{
n = read();
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i)
{
int u = read(), v = read(), w = read();
G[u].push_back(edge(v, w));
G[v].push_back(edge(u, w));
}
dfs(, );
reverse(cycle.begin(), cycle.end());
cycle.push_back(cycle[]);
for(int i = ; i < cycle.size() - ; ++i)
{
int u = cycle[i], v = cycle[i + ];
for(int j = ; j < G[u].size(); ++j)
{
edge e = G[u][j];
if(e.to == v)
{
w[i] = e.w;
break;
}
}
max_d[i] = Dfs(u, );
}
max_d[cycle.size() - ] = max_d[];
ll cur_len = , cur_dia = max_d[];
pre_len[] = pre_dia[] = max_d[];
for(int i = ; i < cycle.size(); ++i)
{
cur_len += w[i - ];
cur_dia += w[i - ];
pre_len[i] = max(pre_len[i - ], cur_len + max_d[i]);
pre_dia[i] = max(pre_dia[i - ], cur_dia + max_d[i]);
cur_dia = max(cur_dia, max_d[i]);
}
cur_len = ;
cur_dia = max_d[cycle.size() - ];
bak_dia[cycle.size() - ] = max_d[cycle.size() - ];
for(int i = cycle.size() - ; i >= ; --i)
{
cur_len += w[i];
cur_dia += w[i];
bak_len[i] = max(bak_len[i + ], cur_len + max_d[i]);
bak_dia[i] = max(bak_dia[i + ], cur_dia + max_d[i]);
cur_dia = max(cur_dia, max_d[i]);
}
ll mn = 1000000000000000ll;
for(int i = ; i < cycle.size() - ; ++i)
{
mn = min(mn, max(pre_len[i] + bak_len[i + ], max(pre_dia[i], bak_dia[i + ])));
// ans = min(ans, pre_len[i] + bak_len[i + 1]);
}
printf("%lld\n", max(ans, mn));
return ;
}
codeforces round #427 div2的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #539 div2
Codeforces Round #539 div2 abstract I 离散化三连 sort(pos.begin(), pos.end()); pos.erase(unique(pos.begin ...
- 【前行】◇第3站◇ Codeforces Round #512 Div2
[第3站]Codeforces Round #512 Div2 第三题莫名卡半天……一堆细节没处理,改一个发现还有一个……然后就炸了,罚了一啪啦时间 Rating又掉了……但是没什么,比上一次好多了: ...
- Codeforces Round#320 Div2 解题报告
Codeforces Round#320 Div2 先做个标题党,骗骗访问量,结束后再来写咯. codeforces 579A Raising Bacteria codeforces 579B Fin ...
- CodeForces 835C - Star sky | Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2)
s <= c是最骚的,数组在那一维开了10,第八组样例直接爆了- - /* CodeForces 835C - Star sky [ 前缀和,容斥 ] | Codeforces Round #4 ...
- CodeForces 835D - Palindromic characteristics | Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2)
证明在Tutorial的评论版里 /* CodeForces 835D - Palindromic characteristics [ 分析,DP ] | Codeforces Round #427 ...
- Codeforces Round #564(div2)
Codeforces Round #564(div2) 本来以为是送分场,结果成了送命场. 菜是原罪 A SB题,上来读不懂题就交WA了一发,代码就不粘了 B 简单构造 很明显,\(n*n\)的矩阵可 ...
- Codeforces Round #361 div2
ProblemA(Codeforces Round 689A): 题意: 给一个手势, 问这个手势是否是唯一. 思路: 暴力, 模拟将这个手势上下左右移动一次看是否还在键盘上即可. 代码: #incl ...
- Codeforces Round #626 Div2 D,E
比赛链接: Codeforces Round #626 (Div. 2, based on Moscow Open Olympiad in Informatics) D.Present 题意: 给定大 ...
- CodeForces Round 192 Div2
This is the first time I took part in Codeforces Competition.The only felt is that my IQ was contemp ...
随机推荐
- impdp and docker install oracleXE
docker oracle https://hub.docker.com/r/sath89/oracle-xe-11g/ docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -p 1521:1521 ...
- wpf 自定义Button按钮
创建ButtonEx类 public class ButtonEx : Button { static ButtonEx() { DefaultStyleKeyProperty.OverrideMet ...
- static private 与 final 的用法总结
1.static表示静态.他是属于类的.可以在本身类里直接调用,或在其它类里用类名.方法名调用.不加static表示是实例的方法,必须用实例来调用.在本类里也一样,必须用实例调用 2.private是 ...
- MySQL异常:com.mysql.jdbc.PacketTooBigException: Packet for query is too large
### Cause: com.mysql.jdbc.PacketTooBigException: Packet for query is too large (1169 > 1024). You ...
- 以gnome-terminal为例,修改gnome3 的默认配置
gnome连续几个版本的terminal默认配置文件都是同一个配置文件“b1dcc9dd-5262-4d8d-a863-c897e6d979b9”.这是因为gnome的developers编辑了这个配 ...
- python json、 pickle 、shelve 模块
json 模块 用于序列化的模块 json,用于字符串 和 python数据类型间进行转换 Json模块提供了四个功能:dumps.dump.loads.load #!/usr/bin/env pyt ...
- Django DTL模板语法中的过滤器
template_filter_demo 过滤器相关: 一.形式:小写{{ name | lower }} 二.串联:先转义文本到HTML,再转换每行到 <p> 标签{{ my_text| ...
- Django-Rest framework中文翻译-generic-views
通用视图 Django的通用视图......被开发为常见用法模式的快捷方式......它们采用视图开发中的某些常见习语和模式并对其进行抽象,以便您可以快速编写数据的常用视图,而无需重复自己. - Dj ...
- Ajax_数据格式_XML
[XML] 优点: --XML是一种通用的数据格式. --不必把数据强加到已经定义好的格式中,而是要为数据自定义合适的标记. --利用DOM可以完全掌控文档. 缺点: --如果文档来自于服务器,就必须 ...
- Java基础学习总结(85)——Java中四种线程安全的单例模式实现方式
