torch.cat()和torch.stack()
torch.cat() 和 torch.stack()略有不同
torch.cat(tensors,dim=0,out=None)→ Tensor
torch.cat()对tensors沿指定维度拼接,但返回的Tensor的维数不会变,可理解为续接;
torch.stack(tensors,dim=0,out=None)→ Tensor
torch.stack()同样是对tensors沿指定维度拼接,但返回的Tensor会多一维,可理解为叠加;
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「进阶媛小吴」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/wuli_xin/article/details/118972316
torch.cat((a,b),dim=1)和torch.cat((a,b)axis=1)一样。
同理:torch.stack((a,b),dim=1)和torch.stack((a,b)axis=1)一样。
zz=torch.rand(100)#默认zz是列向量。而非行向量。
上述3行的情况,自己已经实际实验过。

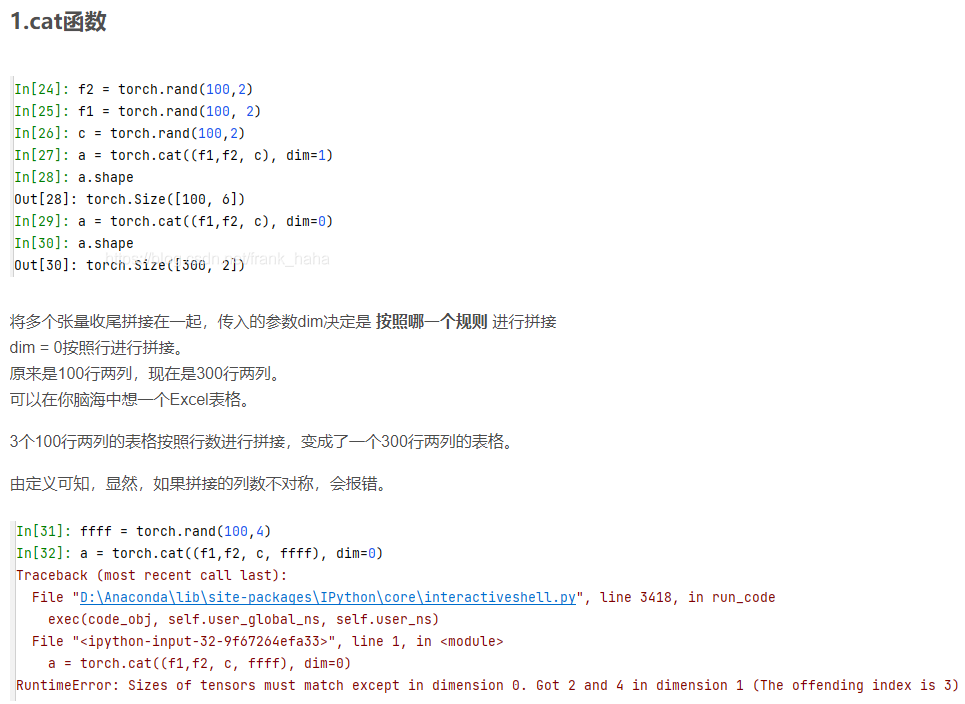

结果为:

上述行数相同d,c,在第一维度也即列上拼接时,能拼接成100行六列的tensor.

import torch
a=torch.rand(100)
b=torch.rand(100)
c=torch.rand((100,2))
d=torch.rand((100,2))
e=torch.rand((100,2)) ab,ab1,cd,cd1,cd2,cd3=torch.stack((a,b)),torch.stack((a,b),dim=0),torch.stack((c,d),dim=0),torch.stack((c,d),dim=1),torch.stack((c,d,e),axis=1),torch.stack((c,d,e),dim=-1)
'a.shape',a.shape,"b.shape",b.shape,"ab.shape",ab.shape,"ab1.shape",ab1.shape,'cd.shape',cd.shape,'cd1.shape',cd1.shape,'cd2.shape',cd2.shape,cd3.shape
此处需注意的是:torch.stack((c,d,e),dim=-1)和torch.stack((c,d,e),dim=2)结果是一样的;
('a.shape',
torch.Size([100]),
'b.shape',
torch.Size([100]),
'ab.shape',
torch.Size([2, 100]),
'ab1.shape',
torch.Size([2, 100]),
'cd.shape',
torch.Size([2, 100, 2]),
'cd1.shape',
torch.Size([100, 2, 2]),
'cd2.shape',
torch.Size([100, 3, 2]),
torch.Size([100, 2, 3]))

import torch
# t1=torch.tensor([1,1,1])
# t2=torch.tensor([2,2,2])
# t3=torch.tensor([3,3,3]) f1=torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
f2=torch.tensor([[7,8,9],[10,11,12]])
c=torch.tensor([[13,14,15],[16,17,18]]) # a=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),dim=0)
# b=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),1)
# print(a.shape,b.shape,sep='\n')
# d=torch.rand(100,4)
# e=torch.cat((d,c),1)
# print(e.shape)
g=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),0)
g1=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),1)
print(f1.shape,f2.shape,c.shape)
print('g: ',g.shape,g,sep='\n')
print('g1: ',g1.shape,g1,sep='\n') 输出结果为: torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3])
g:
torch.Size([3, 2, 3])#本来3个,就3个;本来2行3列就两行三列;只不过把他们放到一起,变成了3维的,多了一个维度;个人理解,可能有误。
tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]], [[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]], [[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]]])
g1:
torch.Size([2, 3, 3])#把本来的三个中,每个的第一列拼在一块;第二列拼在一块;再把拼过后的第一列和第二列分别作为一个二维矩阵; 个人理解,可能有误。 tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 7, 8, 9],
[13, 14, 15]], [[ 4, 5, 6],
[10, 11, 12],
[16, 17, 18]]])
import torch
# t1=torch.tensor([1,1,1])
# t2=torch.tensor([2,2,2])
# t3=torch.tensor([3,3,3]) f1=torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
f2=torch.tensor([[7,8,9],[10,11,12]])
c=torch.tensor([[13,14,15],[16,17,18]]) # a=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),dim=0)
# b=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),1)
# print(a.shape,b.shape,sep='\n')
# d=torch.rand(100,4)
# e=torch.cat((d,c),1)
# print(e.shape)
g=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),0)
g1=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),2)
print(f1.shape,f2.shape,c.shape)
print('g: ',g.shape,g,sep='\n')
print('g1: ',g1.shape,g1,sep='\n') 输出结果:
torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3])
g:
torch.Size([3, 2, 3])
tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]],
[[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]]])
g1:
torch.Size([2, 3, 3])
tensor([[[ 1, 7, 13],
[ 2, 8, 14],
[ 3, 9, 15]],
[[ 4, 10, 16],
[ 5, 11, 17],
[ 6, 12, 18]]])
import torch
# t1=torch.tensor([1,1,1])
# t2=torch.tensor([2,2,2])
# t3=torch.tensor([3,3,3]) f1=torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
f2=torch.tensor([[7,8,9],[10,11,12]])
c=torch.tensor([[13,14,15],[16,17,18]]) # a=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),dim=0)
# b=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),1)
# print(a.shape,b.shape,sep='\n')
# d=torch.rand(100,4)
# e=torch.cat((d,c),1)
# print(e.shape)
g=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),0)
g1=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),3)#此处dim=3,或比3大的任何正数,都是如下报错结果。
print(f1.shape,f2.shape,c.shape)
print('g: ',g.shape,g,sep='\n')
print('g1: ',g1.shape,g1,sep='\n') 输出结果:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<input>", line 17, in <module>
IndexError: Dimension out of range (expected to be in range of [-3, 2], but got 3)
此外:
如果,torch.stack()的维度dim输入的是-1,-2,-3,也都可以正确输出结果。但是如果输入比-3小的任何数则会报错;具体如下:
import torch
# t1=torch.tensor([1,1,1])
# t2=torch.tensor([2,2,2])
# t3=torch.tensor([3,3,3]) f1=torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
f2=torch.tensor([[7,8,9],[10,11,12]])
c=torch.tensor([[13,14,15],[16,17,18]]) # a=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),dim=0)
# b=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),1)
# print(a.shape,b.shape,sep='\n')
# d=torch.rand(100,4)
# e=torch.cat((d,c),1)
# print(e.shape)
g=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),0)
g1=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),-1) #此时,维度是-1
print(f1.shape,f2.shape,c.shape)
print('g: ',g.shape,g,sep='\n')
print('g1: ',g1.shape,g1,sep='\n') 输出结果为:
torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3])
g:
torch.Size([3, 2, 3])
tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]], [[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]], [[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]]])
g1:
torch.Size([2, 3, 3])
tensor([[[ 1, 7, 13],
[ 2, 8, 14],
[ 3, 9, 15]], [[ 4, 10, 16],
[ 5, 11, 17],
[ 6, 12, 18]]])
torch.stack()的维度dim输入的是--2;
输出结果为:
torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3])
g:
torch.Size([3, 2, 3])
tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]], [[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]], [[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]]])
g1:
torch.Size([2, 3, 3])
tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 7, 8, 9],
[13, 14, 15]], [[ 4, 5, 6],
[10, 11, 12],
[16, 17, 18]]])
torch.stack()的维度dim输入的是-3;
torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3])
g:
torch.Size([3, 2, 3])
tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]], [[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]], [[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]]])
g1:
torch.Size([3, 2, 3])
tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]], [[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]], [[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]]])
import torch
# t1=torch.tensor([1,1,1])
# t2=torch.tensor([2,2,2])
# t3=torch.tensor([3,3,3]) f1=torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
f2=torch.tensor([[7,8,9],[10,11,12]])
c=torch.tensor([[13,14,15],[16,17,18]]) # a=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),dim=0)
# b=torch.cat((f1,f2,c),1)
# print(a.shape,b.shape,sep='\n')
# d=torch.rand(100,4)
# e=torch.cat((d,c),1)
# print(e.shape)
g=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),0)
g1=torch.stack((f1,f2,c),-4)#此处是dim=-4,小于-4的任何负数,输出类似的结果。
print(f1.shape,f2.shape,c.shape)
print('g: ',g.shape,g,sep='\n')
print('g1: ',g1.shape,g1,sep='\n') 输出结果为:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<input>", line 17, in <module>
IndexError: Dimension out of range (expected to be in range of [-3, 2], but got -4)
import torch
a=torch.rand(100)
b=torch.rand(100) c=torch.stack((a,b))
d=torch.stack((a,b),dim=0)
e=torch.stack((a,b),dim=1) f=torch.cat((a,b))
f1=torch.cat((a,b),dim=0)
# f2=torch.cat((a,b),dim=1)#错误提示:Dimension out of range (expected to be in range of [-1, 0], but got 1)
c.size,c.size(),c.shape,d.shape,e.shape,f.shape,f.size(),f1.shape
#从输出结果可看出,torch.rand(100)生成的是100行1列的数据,也即是一个列向量;concat沿着已有的维度拼接,stack在新创建的维度上拼接;
#输出:
(<function Tensor.size>,
torch.Size([2, 100]),
torch.Size([2, 100]),
torch.Size([2, 100]),
torch.Size([100, 2]),
torch.Size([200]),
torch.Size([200]),
torch.Size([200]))
torch.cat()和torch.stack()的更多相关文章
- torch.stack()与torch.cat()
torch.stack():http://www.45fan.com/article.php?aid=1D8JGDik5G49DE1X torch.stack()个人理解:属于先变形再cat的操作,所 ...
- torch.cat拼接 stack拼接 分块chunk
torch.cat拼接 stack拼接 分块chunk 待办 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39709535/article/details/80803003 stack dim理 ...
- Pytorch中的torch.cat()函数
cat是concatnate的意思:拼接,联系在一起. 先说cat( )的普通用法 如果我们有两个tensor是A和B,想把他们拼接在一起,需要如下操作: C = torch.cat( (A,B),0 ...
- Pytorch的torch.cat实例
import torch 通过 help((torch.cat)) 可以查看 cat 的用法 cat(seq,dim,out=None) 其中 seq表示要连接的两个序列,以元组的形式给出,例如:se ...
- 从 relu 的多种实现来看 torch.nn 与 torch.nn.functional 的区别与联系
从 relu 的多种实现来看 torch.nn 与 torch.nn.functional 的区别与联系 relu多种实现之间的关系 relu 函数在 pytorch 中总共有 3 次出现: torc ...
- 【Pytorch】关于torch.matmul和torch.bmm的输出tensor数值不一致问题
发现 对于torch.matmul和torch.bmm,都能实现对于batch的矩阵乘法: a = torch.rand((2,3,10))b = torch.rand((2,2,10))### ma ...
- [pytorch笔记] torch.nn vs torch.nn.functional; model.eval() vs torch.no_grad(); nn.Sequential() vs nn.moduleList
1. torch.nn与torch.nn.functional之间的区别和联系 https://blog.csdn.net/GZHermit/article/details/78730856 nn和n ...
- Pytorch本人疑问(1) torch.nn和torch.nn.functional之间的区别
在写代码时发现我们在定义Model时,有两种定义方法: torch.nn.Conv2d()和torch.nn.functional.conv2d() 那么这两种方法到底有什么区别呢,我们通过下述代码看 ...
- torch.rand、torch.randn、torch.normal、torch.linespace
torch.rand(*size, *, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False) # ...
随机推荐
- Exchange 2013 清空邮箱
在某些应用场景中,需要清空用户邮箱的所有数据.如果使用Outlook web app或者Outlook 的邮件删除方式,对数以千计的邮件来说,实在不是一个好办法.exchange管理员可以使用&quo ...
- webpack 4.0 配置方法以及错误解决
选取一个空目录来试验 全局安装webpack4.1之后 创建目录 mkdir webpacktest && cd webpacktes 初始化package.json npm init ...
- nodejs全局对象简析
Global:全局变量 定时器.控制台输出.事件 模块化相关的一些全局变量 path/url相关的一些全局变量 编码相关的 buffer:缓存(简单介绍) Process:进程(重点解析) 一.Glo ...
- 【UWP】实现一个波浪进度条
好久没写 blog 了,一个是忙,另外一个是觉得没啥好写.废话不多说,直接上效果图: 可能看到这波浪线你觉得会很难,但看完这篇 blog 后应该你也会像我一样恍然大悟.图上的图形,我们可以考虑是由 3 ...
- oracle查看impdp进度
当数据量比较大的时候,当你导入,导出的时候,在数据库中查看运行的情况,可以利用下面的视图查看: //这里由于导表空间时出现问题,所以再次执行导入任务.但是已有任务在执行,查看执行中的任务方法. ora ...
- jquery版本的ajax请求
首先引入 <script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.js"></script> $ 和 jqu ...
- perf性能分析工具使用分享
@ 目录 前言 perf的介绍和安装 perf基本使用 perf list使用,可以列出所有的采样事件 perf stat 概览程序的运行情况 perf top实时显示当前系统的性能统计信息 perf ...
- 可怕!CPU暗藏了这些未公开的指令!
大家好,我是轩辕. 我们知道,我们平时编程写的高级语言,是经过编译器编译以后,变成了CPU可以执行的机器指令: 而CPU能支持的指令,都在它的指令集里面了. 很久以来,我都在思考一个问题: CPU有没 ...
- Blazor Bootstrap 组件库地理定位/移动距离追踪组件介绍
地理定位/移动距离追踪组件 通过浏览器 API 获取定位信息 DEMO https://www.blazor.zone/geolocations 小提示 注意: 出于安全考虑,当网页请求获取用户位置信 ...
- JS_Window-三种消息框:警告框、确认框、提示框、页面显示时间-计时-延时
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="U ...
