MLE vs MAP: the connection between Maximum Likelihood and Maximum A Posteriori Estimation
Reference:MLE vs MAP.
Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) and Maximum A Posteriori (MAP), are both a method for estimating some variable in the setting of probability distributions or graphical models. They are similar, as they compute a single estimate, instead of a full distribution.
MLE, as we, who have already indulge ourselves in Machine Learning, would be familiar with this method. Sometimes, we even use it without knowing it. Take for example, when fitting a Gaussian to our dataset, we immediately take the sample mean and sample variance, and use it as the parameter of our Gaussian. This is MLE, as, if we take the derivative of the Gaussian function with respect to the mean and variance, and maximizing it (i.e. setting the derivative to zero), what we get is functions that are calculating sample mean and sample variance. Another example, most of the optimization in Machine Learning and Deep Learning (neural net, etc), could be interpreted as MLE.
Speaking in more abstract term, let’s say we have a likelihood function P(X|θ)P(X|θ). Then, the MLE for θ , the parameter we want to infer, is:
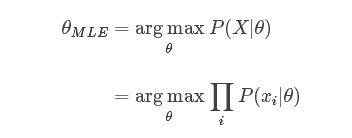
As taking a product of some numbers less than 1 would approaching 0 as the number of those numbers goes to infinity, it would be not practical to compute, because of computation underflow. Hence, we will instead work in the log space, as logarithm is monotonically increasing, so maximizing a function is equal to maximizing the log of that function.

To use this framework, we just need to derive the log likelihood of our model, then maximizing it with regard of θ using our favorite optimization algorithm like Gradient Descent.
Up to this point, we now understand what does MLE do. From here, we could draw a parallel line with MAP estimation.
MAP usually comes up in Bayesian setting. Because, as the name suggests, it works on a posterior distribution, not only the likelihood.
Recall, with Bayes’ rule, we could get the posterior as a product of likelihood and prior:

We are ignoring the normalizing constant as we are strictly speaking about optimization here, so proportionality is sufficient.
If we replace the likelihood in the MLE formula above with the posterior, we get:
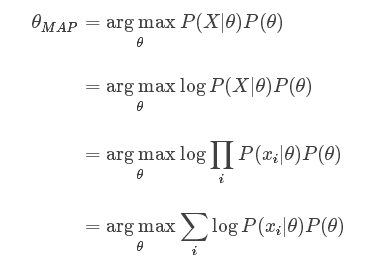
Comparing both MLE and MAP equation, the only thing differs is the inclusion of prior P(θ) in MAP, otherwise they are identical. What it means is that, the likelihood is now weighted with some weight coming from the prior.
Let’s consider what if we use the simplest prior in our MAP estimation, i.e. uniform prior. This means, we assign equal weights everywhere, on all possible values of the θ. The implication is that the likelihood equivalently weighted by some constants. Being constant, we could be ignored from our MAP equation, as it will not contribute to the maximization.
Let’s be more concrete, let’s say we could assign six possible values into θ . Now, our prior P(θ) is 1/6 everywhere in the distribution. And consequently, we could ignore that constant in our MAP estimation.

We are back at MLE equation again!
If we use different prior, say, a Gaussian, then our prior is not constant anymore, as depending on the region of the distribution, the probability is high or low, never always the same.
What we could conclude then, is that MLE is a special case of MAP, where the prior is uniform!
MLE vs MAP: the connection between Maximum Likelihood and Maximum A Posteriori Estimation的更多相关文章
- Maximum Likelihood及Maximum Likelihood Estimation
1.What is Maximum Likelihood? 极大似然是一种找到最可能解释一组观测数据的函数的方法. Maximum Likelihood is a way to find the mo ...
- 最大似然估计实例 | Fitting a Model by Maximum Likelihood (MLE)
参考:Fitting a Model by Maximum Likelihood 最大似然估计是用于估计模型参数的,首先我们必须选定一个模型,然后比对有给定的数据集,然后构建一个联合概率函数,因为给定 ...
- 机器学习的MLE和MAP:最大似然估计和最大后验估计
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32480810 TLDR (or the take away) 频率学派 - Frequentist - Maximum Likelihoo ...
- Linear Regression and Maximum Likelihood Estimation
Imagination is an outcome of what you learned. If you can imagine the world, that means you have lea ...
- 似然函数 | 最大似然估计 | likelihood | maximum likelihood estimation | R代码
学贝叶斯方法时绕不过去的一个问题,现在系统地总结一下. 之前过于纠结字眼,似然和概率到底有什么区别?以及这一个奇妙的对等关系(其实连续才是f,离散就是p). 似然函数 | 似然值 wiki:在数理统计 ...
- [Bayes] Maximum Likelihood estimates for text classification
Naïve Bayes Classifier. We will use, specifically, the Bernoulli-Dirichlet model for text classifica ...
- 最大似然估计(Maximum Likelihood,ML)
先不要想其他的,首先要在大脑里形成概念! 最大似然估计是什么意思?呵呵,完全不懂字面意思,似然是个啥啊?其实似然是likelihood的文言翻译,就是可能性的意思,所以Maximum Likeliho ...
- MLE、MAP、贝叶斯三种估计框架
三个不同的估计框架. MLE最大似然估计:根据训练数据,选取最优模型,预测.观测值D,training data:先验为P(θ). MAP最大后验估计:后验概率. Bayesian贝叶斯估计:综合模型 ...
- Maximum Likelihood Method最大似然法
最大似然法,英文名称是Maximum Likelihood Method,在统计中应用很广.这个方法的思想最早由高斯提出来,后来由菲舍加以推广并命名. 最大似然法是要解决这样一个问题:给定一组数据和一 ...
随机推荐
- C++进阶笔记
思想原则: 以类为例,类最终要处理的是数据,方法只是过程,最终要改变的是private中的数据成员状态.程序设计也是如此,要的是数据. 一.const的作用 const定义变量:定义了一个不可修改的常 ...
- java 重写的 几大注意点
Single Dispatch class Parent { void print(String a) { log.info("Parent - String"); } void ...
- 基于SpringBoot从零构建博客网站 - 整合ehcache和开发注册登录功能
对于程序中一些字典信息.配置信息应该在程序启动时加载到缓存中,用时先到缓存中取,如果没有命中,再到数据库中获取同时放到缓存中,这样做可以减轻数据库层的压力.目前暂时先整合ehcache缓存,同时预留了 ...
- 批量删除redis的数据
批量删除redis的数据 # redis-cli -h 192.168.1.17 -p 6379 keys "xiaolang_*"|xargs redis-cli -h 192. ...
- Spring系列三:IoC 与 DI
水晶帘动微风起,满架蔷薇一院香. 概述 在软件工程中,控制反转(IoC)是一种设计思想,对象之间耦合在一起,在运行时自动绑定,并且它们编译时对所需要引用的对象是不确定的.在这个spring教程中,通过 ...
- 【NOIP2015普及组】 推销员(纪中数据-标准)
题目 [题目描述] 阿明是一名推销员,他奉命到螺丝街推销他们公司的产品.螺丝街是一条死胡同,出口与入口是同一个,街道的一侧是围墙,另一侧是住户.螺丝街一共有 N 家住户,第 i 家住户到入口的距离为 ...
- Tesseract机器识别
1.合并图片打开jtessboxeditor,点击Tools->Merge Tiff ,按住shift键选择前文提到的101个tif文件,并把生成的tif合并到新目录d:\python\lnyp ...
- Lazy的SDL教程 翻译----Lesson 22 Timing
原文:http://lazyfoo.net/tutorials/SDL/22_timing/index.php Timing 计时 Last Updated 3/10/14 Another impor ...
- Scala学习十二——高阶函数
一.本章要点 在Scala中函数是”头等公民“(可以作为参数,返回值,赋值给其他); 可以创建匿名函数,通常还会交给其他函数; 函数参数可以给出需要稍后执行的行为; 许多集合方法都接受函数参数,将函数 ...
- 三、maven学习-高级
maven父子工程
