EasyPR--开发详解(8)文字定位
今天我们来介绍车牌定位中的一种新方法--文字定位方法(MSER),包括其主要设计思想与实现。接着我们会介绍一下EasyPR v1.5-beta版本中带来的几项改动。
一. 文字定位法
在EasyPR前面几个版本中,最为人所诟病的就是定位效果不佳,尤其是在面对生活场景(例如手机拍摄)时。由于EasyPR最早的数据来源于卡口,因此对卡口数据进行了优化,而并没有对生活场景中图片有较好处理的策略。后来一个版本(v1.3)增加了颜色定位方法,改善了这种现象,但是对分辨率较大的图片处理仍然不好。再加上颜色定位在面对低光照,低对比度的图像时处理效果大幅度下降,颜色本身也是一个不稳定的特征。因此EasyPR的车牌定位的整体鲁棒性仍然不足。
针对这种现象,EasyPR v1.5增加了一种新的定位方法,文字定位方法,大幅度改善了这些问题。下面几幅图可以说明文字定位法的效果。
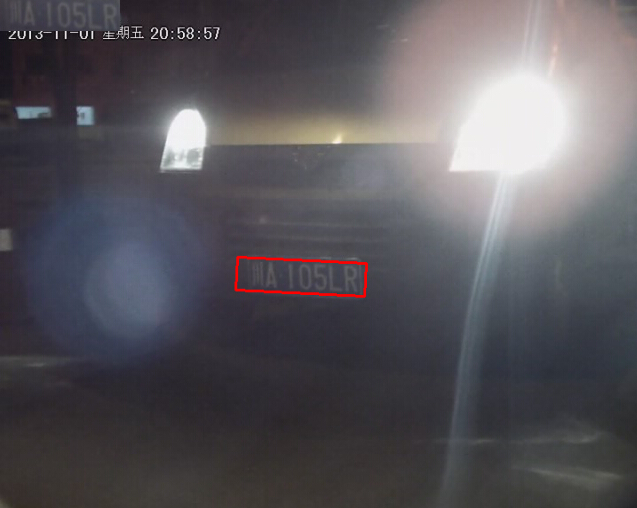
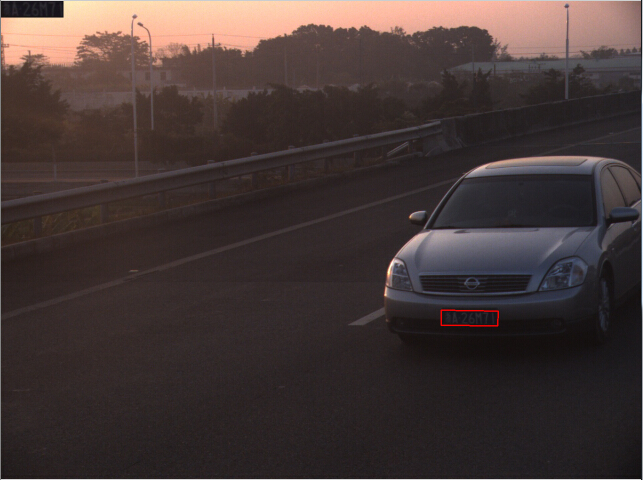


图1 夜间的车牌图像(左) , 图2 对比度非常低的图像(右)

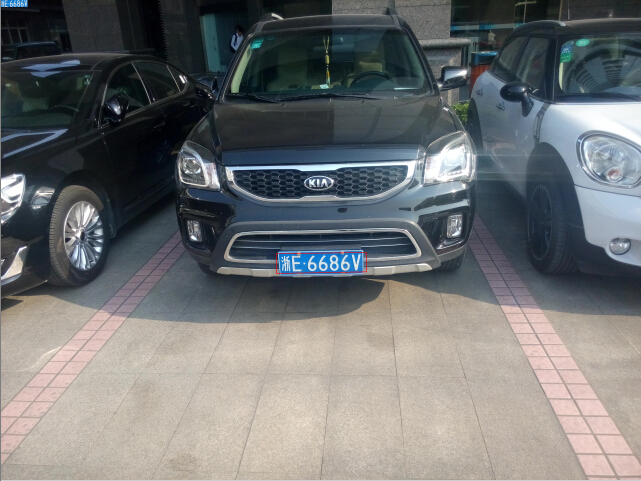
图3 近距离的图像(左) , 图4 高分辨率的图像(右)
图1是夜间的车牌图像,图2是对比度非常低的图像,图3是非常近距离拍摄的图像,图4则是高分辨率(3200宽)的图像。
文字定位方法是采用了低级过滤器提取文字,然后再将其组合的一种定位方法。原先是利用在场景中定位文字,在这里利用其定位车牌。与在扫描文档中的文字不同,自然场景中的文字具有低对比度,背景各异,光亮干扰较多等情况,因此需要一个极为鲁棒的方法去提取出来。目前业界用的较多的是MSER(最大稳定极值区域)方法。EasyPR使用的是MSER的一个改良方法,专门针对文字进行了优化。在文字定位出来以后,一般需要用一个分类器将其中大部分的定位错误的文字去掉,例如ANN模型。为了获得最终的车牌,这些文字需要组合起来。由于实际情况的复杂,简单的使用普通的聚类效果往往不好,因此EasyPR使用了一种鲁棒性较强的种子生长方法(seed growing)去组合。
我在这里简单介绍一下具体的实现。关于方法的细节可以看代码,有很多的注释(代码可能较长)。关于方法的思想可以看附录的两篇论文。
//! use verify size to first generate char candidates
void mserCharMatch(const Mat &src, std::vector<Mat> &match, std::vector<CPlate>& out_plateVec_blue, std::vector<CPlate>& out_plateVec_yellow,
bool usePlateMser, std::vector<RotatedRect>& out_plateRRect_blue, std::vector<RotatedRect>& out_plateRRect_yellow, int img_index,
bool showDebug) {
Mat image = src; std::vector<std::vector<std::vector<Point>>> all_contours;
std::vector<std::vector<Rect>> all_boxes;
all_contours.resize();
all_contours.at().reserve();
all_contours.at().reserve();
all_boxes.resize();
all_boxes.at().reserve();
all_boxes.at().reserve(); match.resize(); std::vector<Color> flags;
flags.push_back(BLUE);
flags.push_back(YELLOW); const int imageArea = image.rows * image.cols;
const int delta = ;
//const int delta = CParams::instance()->getParam2i();;
const int minArea = ;
const double maxAreaRatio = 0.05; Ptr<MSER2> mser;
mser = MSER2::create(delta, minArea, int(maxAreaRatio * imageArea));
mser->detectRegions(image, all_contours.at(), all_boxes.at(), all_contours.at(), all_boxes.at()); // mser detect
// color_index = 0 : mser-, detect white characters, which is in blue plate.
// color_index = 1 : mser+, detect dark characters, which is in yellow plate. #pragma omp parallel for
for (int color_index = ; color_index < ; color_index++) {
Color the_color = flags.at(color_index); std::vector<CCharacter> charVec;
charVec.reserve(); match.at(color_index) = Mat::zeros(image.rows, image.cols, image.type()); Mat result = image.clone();
cvtColor(result, result, COLOR_GRAY2BGR); size_t size = all_contours.at(color_index).size(); int char_index = ;
int char_size = ; // Chinese plate has max 7 characters.
const int char_max_count = ; // verify char size and output to rects;
for (size_t index = ; index < size; index++) {
Rect rect = all_boxes.at(color_index)[index];
std::vector<Point>& contour = all_contours.at(color_index)[index]; // sometimes a plate could be a mser rect, so we could
// also use mser algorithm to find plate
if (usePlateMser) {
RotatedRect rrect = minAreaRect(Mat(contour));
if (verifyRotatedPlateSizes(rrect)) {
//rotatedRectangle(result, rrect, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2);
if (the_color == BLUE) out_plateRRect_blue.push_back(rrect);
if (the_color == YELLOW) out_plateRRect_yellow.push_back(rrect);
}
} // find character
if (verifyCharSizes(rect)) {
Mat mserMat = adaptive_image_from_points(contour, rect, Size(char_size, char_size));
Mat charInput = preprocessChar(mserMat, char_size);
Rect charRect = rect; Point center(charRect.tl().x + charRect.width / , charRect.tl().y + charRect.height / );
Mat tmpMat;
double ostu_level = cv::threshold(image(charRect), tmpMat, , , CV_THRESH_BINARY | CV_THRESH_OTSU); //cv::circle(result, center, 3, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); // use judegMDOratio2 function to
// remove the small lines in character like "zh-cuan"
if (judegMDOratio2(image, rect, contour, result)) {
CCharacter charCandidate;
charCandidate.setCharacterPos(charRect);
charCandidate.setCharacterMat(charInput);
charCandidate.setOstuLevel(ostu_level);
charCandidate.setCenterPoint(center);
charCandidate.setIsChinese(false);
charVec.push_back(charCandidate);
}
}
} // improtant, use matrix multiplication to acclerate the
// classification of many samples. use the character
// score, we can use non-maximum superssion (nms) to
// reduce the characters which are not likely to be true
// charaters, and use the score to select the strong seed
// of which the score is larger than 0.9
CharsIdentify::instance()->classify(charVec); // use nms to remove the character are not likely to be true.
double overlapThresh = 0.6;
//double overlapThresh = CParams::instance()->getParam1f();
NMStoCharacter(charVec, overlapThresh);
charVec.shrink_to_fit(); std::vector<CCharacter> strongSeedVec;
strongSeedVec.reserve();
std::vector<CCharacter> weakSeedVec;
weakSeedVec.reserve();
std::vector<CCharacter> littleSeedVec;
littleSeedVec.reserve(); //size_t charCan_size = charVec.size();
for (auto charCandidate : charVec) {
//CCharacter& charCandidate = charVec[char_index];
Rect rect = charCandidate.getCharacterPos();
double score = charCandidate.getCharacterScore();
if (charCandidate.getIsStrong()) {
strongSeedVec.push_back(charCandidate);
}
else if (charCandidate.getIsWeak()) {
weakSeedVec.push_back(charCandidate);
//cv::rectangle(result, rect, Scalar(255, 0, 255));
}
else if (charCandidate.getIsLittle()) {
littleSeedVec.push_back(charCandidate);
//cv::rectangle(result, rect, Scalar(255, 0, 255));
}
} std::vector<CCharacter> searchCandidate = charVec; // nms to srong seed, only leave the strongest one
overlapThresh = 0.3;
NMStoCharacter(strongSeedVec, overlapThresh); // merge chars to group
std::vector<std::vector<CCharacter>> charGroupVec;
charGroupVec.reserve();
mergeCharToGroup(strongSeedVec, charGroupVec); // genenrate the line of the group
// based on the assumptions , the mser rects which are
// given high socre by character classifier could be no doubtly
// be the characters in one plate, and we can use these characeters
// to fit a line which is the middle line of the plate.
std::vector<CPlate> plateVec;
plateVec.reserve();
for (auto charGroup : charGroupVec) {
Rect plateResult = charGroup[].getCharacterPos();
std::vector<Point> points;
points.reserve(); Vec4f line;
int maxarea = ;
Rect maxrect;
double ostu_level_sum = ; int leftx = image.cols;
Point leftPoint(leftx, );
int rightx = ;
Point rightPoint(rightx, ); std::vector<CCharacter> mserCharVec;
mserCharVec.reserve(); // remove outlier CharGroup
std::vector<CCharacter> roCharGroup;
roCharGroup.reserve(); removeRightOutliers(charGroup, roCharGroup, 0.2, 0.5, result);
//roCharGroup = charGroup; for (auto character : roCharGroup) {
Rect charRect = character.getCharacterPos();
cv::rectangle(result, charRect, Scalar(, , ), );
plateResult |= charRect; Point center(charRect.tl().x + charRect.width / , charRect.tl().y + charRect.height / );
points.push_back(center);
mserCharVec.push_back(character);
//cv::circle(result, center, 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2); ostu_level_sum += character.getOstuLevel(); if (charRect.area() > maxarea) {
maxrect = charRect;
maxarea = charRect.area();
}
if (center.x < leftPoint.x) {
leftPoint = center;
}
if (center.x > rightPoint.x) {
rightPoint = center;
}
} double ostu_level_avg = ostu_level_sum / (double)roCharGroup.size();
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "ostu_level_avg:" << ostu_level_avg << std::endl;
}
float ratio_maxrect = (float)maxrect.width / (float)maxrect.height; if (points.size() >= && ratio_maxrect >= 0.3) {
fitLine(Mat(points), line, CV_DIST_L2, , 0.01, 0.01); float k = line[] / line[];
//float angle = atan(k) * 180 / (float)CV_PI;
//std::cout << "k:" << k << std::endl;
//std::cout << "angle:" << angle << std::endl;
//std::cout << "cos:" << 0.3 * cos(k) << std::endl;
//std::cout << "ratio_maxrect:" << ratio_maxrect << std::endl; std::sort(mserCharVec.begin(), mserCharVec.end(),
[](const CCharacter& r1, const CCharacter& r2) {
return r1.getCharacterPos().tl().x < r2.getCharacterPos().tl().x;
}); CCharacter midChar = mserCharVec.at(int(mserCharVec.size() / .f));
Rect midRect = midChar.getCharacterPos();
Point midCenter(midRect.tl().x + midRect.width / , midRect.tl().y + midRect.height / ); int mindist = * maxrect.width;
std::vector<Vec2i> distVecVec;
distVecVec.reserve(); Vec2i mindistVec;
Vec2i avgdistVec; // computer the dist which is the distacne between
// two near characters in the plate, use dist we can
// judege how to computer the max search range, and choose the
// best location of the sliding window in the next steps.
for (size_t mser_i = ; mser_i + < mserCharVec.size(); mser_i++) {
Rect charRect = mserCharVec.at(mser_i).getCharacterPos();
Point center(charRect.tl().x + charRect.width / , charRect.tl().y + charRect.height / ); Rect charRectCompare = mserCharVec.at(mser_i + ).getCharacterPos();
Point centerCompare(charRectCompare.tl().x + charRectCompare.width / ,
charRectCompare.tl().y + charRectCompare.height / ); int dist = charRectCompare.x - charRect.x;
Vec2i distVec(charRectCompare.x - charRect.x, charRectCompare.y - charRect.y);
distVecVec.push_back(distVec); //if (dist < mindist) {
// mindist = dist;
// mindistVec = distVec;
//}
} std::sort(distVecVec.begin(), distVecVec.end(),
[](const Vec2i& r1, const Vec2i& r2) {
return r1[] < r2[];
}); avgdistVec = distVecVec.at(int((distVecVec.size() - ) / .f)); //float step = 10.f * (float)maxrect.width;
//float step = (float)mindistVec[0];
float step = (float)avgdistVec[]; //cv::line(result, Point2f(line[2] - step, line[3] - k*step), Point2f(line[2] + step, k*step + line[3]), Scalar(255, 255, 255));
cv::line(result, Point2f(midCenter.x - step, midCenter.y - k*step), Point2f(midCenter.x + step, k*step + midCenter.y), Scalar(, , ));
//cv::circle(result, leftPoint, 3, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); CPlate plate;
plate.setPlateLeftPoint(leftPoint);
plate.setPlateRightPoint(rightPoint); plate.setPlateLine(line);
plate.setPlatDistVec(avgdistVec);
plate.setOstuLevel(ostu_level_avg); plate.setPlateMergeCharRect(plateResult);
plate.setPlateMaxCharRect(maxrect);
plate.setMserCharacter(mserCharVec);
plateVec.push_back(plate);
}
} // use strong seed to construct the first shape of the plate,
// then we need to find characters which are the weak seed.
// because we use strong seed to build the middle lines of the plate,
// we can simply use this to consider weak seeds only lie in the
// near place of the middle line
for (auto plate : plateVec) {
Vec4f line = plate.getPlateLine();
Point leftPoint = plate.getPlateLeftPoint();
Point rightPoint = plate.getPlateRightPoint(); Rect plateResult = plate.getPlateMergeCharRect();
Rect maxrect = plate.getPlateMaxCharRect();
Vec2i dist = plate.getPlateDistVec();
double ostu_level = plate.getOstuLevel(); std::vector<CCharacter> mserCharacter = plate.getCopyOfMserCharacters();
mserCharacter.reserve(); float k = line[] / line[];
float x_1 = line[];
float y_1 = line[]; std::vector<CCharacter> searchWeakSeedVec;
searchWeakSeedVec.reserve(); std::vector<CCharacter> searchRightWeakSeed;
searchRightWeakSeed.reserve();
std::vector<CCharacter> searchLeftWeakSeed;
searchLeftWeakSeed.reserve(); std::vector<CCharacter> slideRightWindow;
slideRightWindow.reserve();
std::vector<CCharacter> slideLeftWindow;
slideLeftWindow.reserve(); // draw weak seed and little seed from line;
// search for mser rect
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "search for mser rect:" << std::endl;
} if ( && showDebug) {
std::stringstream ss(std::stringstream::in | std::stringstream::out);
ss << "resources/image/tmp/" << img_index << "_1_" << "searcgMserRect.jpg";
imwrite(ss.str(), result);
}
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "mserCharacter:" << mserCharacter.size() << std::endl;
} // if the count of strong seed is larger than max count, we dont need
// all the next steps, if not, we first need to search the weak seed in
// the same line as the strong seed. The judge condition contains the distance
// between strong seed and weak seed , and the rect simily of each other to improve
// the roubustnedd of the seed growing algorithm.
if (mserCharacter.size() < char_max_count) {
double thresh1 = 0.15;
double thresh2 = 2.0;
searchWeakSeed(searchCandidate, searchRightWeakSeed, thresh1, thresh2, line, rightPoint,
maxrect, plateResult, result, CharSearchDirection::RIGHT);
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "searchRightWeakSeed:" << searchRightWeakSeed.size() << std::endl;
}
for (auto seed : searchRightWeakSeed) {
cv::rectangle(result, seed.getCharacterPos(), Scalar(, , ), );
mserCharacter.push_back(seed);
} searchWeakSeed(searchCandidate, searchLeftWeakSeed, thresh1, thresh2, line, leftPoint,
maxrect, plateResult, result, CharSearchDirection::LEFT);
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "searchLeftWeakSeed:" << searchLeftWeakSeed.size() << std::endl;
}
for (auto seed : searchLeftWeakSeed) {
cv::rectangle(result, seed.getCharacterPos(), Scalar(, , ), );
mserCharacter.push_back(seed);
}
} // sometimes the weak seed is in the middle of the strong seed.
// and sometimes two strong seed are actually the two parts of one character.
// because we only consider the weak seed in the left and right direction of strong seed.
// now we examine all the strong seed and weak seed. not only to find the seed in the middle,
// but also to combine two seed which are parts of one character to one seed.
// only by this process, we could use the seed count as the condition to judge if or not to use slide window.
float min_thresh = 0.3f;
float max_thresh = 2.5f;
reFoundAndCombineRect(mserCharacter, min_thresh, max_thresh, dist, maxrect, result); // if the characters count is less than max count
// this means the mser rect in the lines are not enough.
// sometimes there are still some characters could not be captured by mser algorithm,
// such as blur, low light ,and some chinese characters like zh-cuan.
// to handle this ,we use a simple slide window method to find them.
if (mserCharacter.size() < char_max_count) {
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "search chinese:" << std::endl;
std::cout << "judege the left is chinese:" << std::endl;
} // if the left most character is chinese, this means
// that must be the first character in chinese plate,
// and we need not to do a slide window to left. So,
// the first thing is to judge the left charcater is
// or not the chinese.
bool leftIsChinese = false;
if () {
std::sort(mserCharacter.begin(), mserCharacter.end(),
[](const CCharacter& r1, const CCharacter& r2) {
return r1.getCharacterPos().tl().x < r2.getCharacterPos().tl().x;
}); CCharacter leftChar = mserCharacter[]; //Rect theRect = adaptive_charrect_from_rect(leftChar.getCharacterPos(), image.cols, image.rows);
Rect theRect = leftChar.getCharacterPos();
//cv::rectangle(result, theRect, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1); Mat region = image(theRect);
Mat binary_region; ostu_level = cv::threshold(region, binary_region, , , CV_THRESH_BINARY | CV_THRESH_OTSU);
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "left : ostu_level:" << ostu_level << std::endl;
}
//plate.setOstuLevel(ostu_level); Mat charInput = preprocessChar(binary_region, char_size);
if ( /*&& showDebug*/) {
imshow("charInput", charInput);
waitKey();
destroyWindow("charInput");
} std::string label = "";
float maxVal = -.f;
leftIsChinese = CharsIdentify::instance()->isCharacter(charInput, label, maxVal, true);
//auto character = CharsIdentify::instance()->identifyChinese(charInput, maxVal, leftIsChinese);
//label = character.second;
if ( /* && showDebug*/) {
std::cout << "isChinese:" << leftIsChinese << std::endl;
std::cout << "chinese:" << label;
std::cout << "__score:" << maxVal << std::endl;
}
} // if the left most character is not a chinese,
// this means we meed to slide a window to find the missed mser rect.
// search for sliding window
float ratioWindow = 0.4f;
//float ratioWindow = CParams::instance()->getParam3f();
float threshIsCharacter = 0.8f;
//float threshIsCharacter = CParams::instance()->getParam3f();
if (!leftIsChinese) {
slideWindowSearch(image, slideLeftWindow, line, leftPoint, dist, ostu_level, ratioWindow, threshIsCharacter,
maxrect, plateResult, CharSearchDirection::LEFT, true, result);
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "slideLeftWindow:" << slideLeftWindow.size() << std::endl;
}
for (auto window : slideLeftWindow) {
cv::rectangle(result, window.getCharacterPos(), Scalar(, , ), );
mserCharacter.push_back(window);
}
}
} // if we still have less than max count characters,
// we need to slide a window to right to search for the missed mser rect.
if (mserCharacter.size() < char_max_count) {
// change ostu_level
float ratioWindow = 0.4f;
//float ratioWindow = CParams::instance()->getParam3f();
float threshIsCharacter = 0.8f;
//float threshIsCharacter = CParams::instance()->getParam3f();
slideWindowSearch(image, slideRightWindow, line, rightPoint, dist, plate.getOstuLevel(), ratioWindow, threshIsCharacter,
maxrect, plateResult, CharSearchDirection::RIGHT, false, result);
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "slideRightWindow:" << slideRightWindow.size() << std::endl;
}
for (auto window : slideRightWindow) {
cv::rectangle(result, window.getCharacterPos(), Scalar(, , ), );
mserCharacter.push_back(window);
}
} // computer the plate angle
float angle = atan(k) * / (float)CV_PI;
if ( && showDebug) {
std::cout << "k:" << k << std::endl;
std::cout << "angle:" << angle << std::endl;
} // the plateResult rect need to be enlarge to contains all the plate,
// not only the character area.
float widthEnlargeRatio = 1.15f;
float heightEnlargeRatio = 1.25f;
RotatedRect platePos(Point2f((float)plateResult.x + plateResult.width / .f, (float)plateResult.y + plateResult.height / .f),
Size2f(plateResult.width * widthEnlargeRatio, maxrect.height * heightEnlargeRatio), angle); // justify the size is likely to be a plate size.
if (verifyRotatedPlateSizes(platePos)) {
rotatedRectangle(result, platePos, Scalar(, , ), ); plate.setPlatePos(platePos);
plate.setPlateColor(the_color);
plate.setPlateLocateType(CMSER); if (the_color == BLUE) out_plateVec_blue.push_back(plate);
if (the_color == YELLOW) out_plateVec_yellow.push_back(plate);
} // use deskew to rotate the image, so we need the binary image.
if () {
for (auto mserChar : mserCharacter) {
Rect rect = mserChar.getCharacterPos();
match.at(color_index)(rect) = ;
}
cv::line(match.at(color_index), rightPoint, leftPoint, Scalar());
}
} if ( /*&& showDebug*/) {
imshow("result", result);
waitKey();
destroyWindow("result");
} if () {
imshow("match", match.at(color_index));
waitKey();
destroyWindow("match");
} if () {
std::stringstream ss(std::stringstream::in | std::stringstream::out);
ss << "resources/image/tmp/plateDetect/plate_" << img_index << "_" << the_color << ".jpg";
imwrite(ss.str(), result);
}
} }
首先通过MSER提取区域,提取出的区域进行一个尺寸判断,滤除明显不符合车牌文字尺寸的。接下来使用一个文字分类器,将分类结果概率大于0.9的设为强种子(下图的绿色方框)。靠近的强种子进行聚合,划出一条线穿过它们的中心(图中白色的线)。一般来说,这条线就是车牌的中间轴线,斜率什么都相同。之后,就在这条线的附近寻找那些概率低于0.9的弱种子(蓝色方框)。由于车牌的特征,这些蓝色方框应该跟绿色方框距离不太远,同时尺寸也不会相差太大。蓝色方框实在绿色方框的左右查找的,有时候,几个绿色方框中间可能存在着一个方库,这可以通过每个方框之间的距离差推出来,这就是橙色的方框。全部找完以后。绿色方框加上蓝色与橙色方框的总数代表着目前在车牌区域中发现的文字数。有时这个数会低于7(中文车牌的文字数),这是因为有些区域即便通过MSER也提取不到(例如非常不稳定或光照变化大的),另外很多中文也无法通过MSER提取到(中文大多是不连通的,MSER提取的区域基本都是连通的)。所以下面需要再增加一个滑动窗口(红色方框)来寻找这些缺失的文字或者中文,如果分类器概率大于某个阈值,就可以将其加入到最终的结果中。最后,把所有文字的位置用一个方框框起来,就是车牌的区域。
想要通过中间图片进行调试程序的话,首先依次根据函数调用关系plateMserLocate->mserSearch->mserCharMatch在core_func.cpp找到位置。在函数的最后,把图片输出的判断符改为1。然后在resources/image下面依次新建tmp与plateDetect目录(跟代码中的一致),接下来再运行时在新目录里就可以看到这些调试图片。(EasyPR里还有很多其他类似的输出代码,只要按照代码的写法创建文件夹就可以看到输出结果了)。
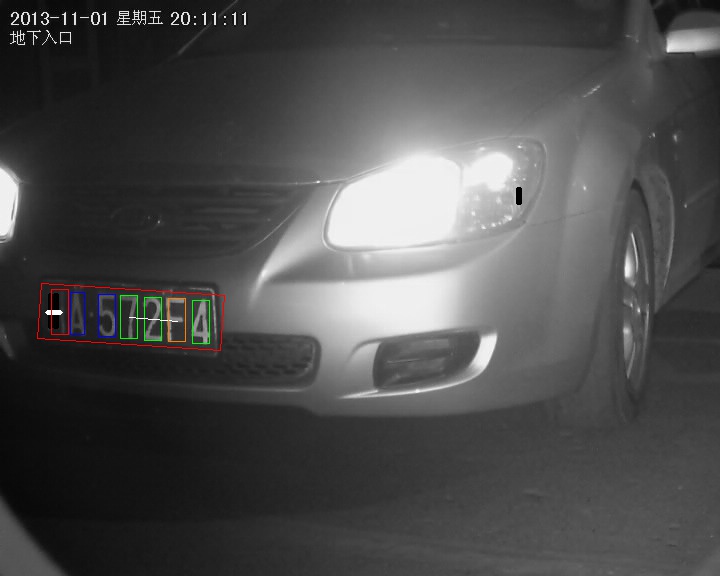

图5 文字定位的中间结果(调试图像)
二. 更加合理准确的评价指标
原先的EasyPR的评价标准中有很多不合理的地方。例如一张图片中找到了一个疑似的区域,就认为是定位成功了。或者如果一张图片中定位到了几个车牌,就用差距率最小的那个作为定位结果。这些地方不合理的地方在于,有可能找到的疑似区域根本不是车牌区域。另外一个包含几个车牌的图片仅仅用最大的一个作为结果,明显不合理。
因此新评价指标需要考虑定位区域和车牌区域的位置差异,只有当两者接近时才能认为是定位成功。另外,一张图片如果有几个车牌,对应的就有几个定位区域,每个区域与车牌做比对,综合起来才能作为定位效果。因此需要加入一个GroundTruth,标记各个车牌的位置信息。新版本中,我们标记了251张图片,其中共250个车牌的位置信息。为了衡量定位区域与车牌区域的位置差的比例,又引入了ICDAR2003的评价协议,来最终计算出定位的recall,precise与fscore值。
车牌定位评价中做了大改动。字符识别模块则做了小改动。首先是去除了“平均字符差距”这个意义较小的指标。转而用零字符差距,一字符差距,中文字符正确替代,这三者都是比率。零字符差距(0-error)指的是识别结果与车牌没有任何差异,跟原先的评价协议中的“完全正确率”指代一样。一字符差距(1-error)指的是错别仅仅只有1个字符或以下的,包括零字符差距。注意,中文一般是两个字符。中文字符正确(Chinese-precise)指代中文字符识别正确的比率。这三个指标,都是越大越好,100%最高。
为了实际看出这些指标的效果,拿通用测试集里增加的50张复杂图片做对此测试,文字定位方法在这些数据上的表现的差异与原先的SOBEL,COLOR定位方法的区别可以看下面的结果。
SOBEL+COLOR:
总图片数:50, Plates count:52, 定位率:51.9231%
Recall:46.1696%, Precise:26.3273%, Fscore:33.533%.
0-error:12.5%, 1-error:12.5%, Chinese-precise:37.5%
CMSER:
总图片数:50, Plates count:52, 定位率:78.8462%
Recall:70.6192%, Precise:70.1825%, Fscore:70.4002%.
0-error:59.4595%, 1-error:70.2703%, Chinese-precise:70.2703%
可以看出定位率提升了接近27个百分点,定位Fscore与中文识别正确率则提升了接近1倍。
三. 非极大值抑制
新版本中另一个较大的改动就是大量的使用了非极大值抑制(Non-maximum suppression)。使用非极大值抑制有几个好处:1.当有几个定位区域重叠时,可以根据它们的置信度(也是SVM车牌判断模型得出的值)来取出其中最大概率准确的一个,移除其他几个。这样,不同定位方法,例如Sobel与Color定位的同一个区域,只有一个可以保留。因此,EasyPR新版本中,最终定位出的一个车牌区域,不再会有几个框了。2.结合滑动窗口,可以用其来准确定位文字的位置,例如在车牌定位模块中找到概率最大的文字位置,或者在文字识别模块中,更准确的找到中文文字的位置。
非极大值抑制的使用使得EasyPR的定位方法与后面的识别模块解耦了。以前,每增加定位方法,可能会对最终输出产生影响。现在,无论多少定位方法定位出的车牌都会通过非极大值抑制取出最大概率的一个,对后面的方法没有一点影响。
另外,如今setMaxPlates()这个函数可以确实的作用了。以前可以设置,但没效果。现在,设置这个值为n以后,当在一副图像中检测到大于n个车牌区域(注意,这个是经过非极大值抑制后的)时,EasyPR只会输出n个可能性最高的车牌区域。
四. 字符分割与识别部分的强化
新版本中字符分割与识别部分都添加了新算法。例如使用了spatial-ostu替代普通的ostu算法,增加了图像分割在面对光照不均匀的图像上的二值化效果。


图6 车牌图像(左),普通大津阈值结果(中),空间大津阈值结果(右)
同时,识别部分针对中文增加了一种adaptive threshold方法。这种方法在二值化“川”字时有比ostu更好的效果。通过将两者一并使用,并选择其中字符识别概率最大的一个,显著提升了中文字符的识别准确率。在识别中文时,增加了一个小型的滑动窗口,以此来弥补通过省份字符直接查找中文字符时的定位不精等现象。
五. 新的特征与SVM模型,新的中文识别ANN模型
为了强化车牌判断的鲁棒性,新版本中更改了SVM模型的特征,使用LBP特征的模型在面对低对比度与光照的车牌图像中也有很好的判断效果。为了强化中文识别的准确率,现在单独为31类中文文字训练了一个ANN模型ann_chinese,使用这个模型在分类中文是的效果,相对原先的通用模型可以提升近10个百分点。
六. 其他
几天前EasyPR发布了1.5-alpha版本。今天发布的beta版本相对于alpha版本,增加了Grid Search功能, 对文字定位方法的参数又进行了部分调优,同时去除了一些中文注释以提高window下的兼容性,除此之外,在速度方面,此版本首次使用了多线程编程技术(OpenMP)来提高算法整体的效率等,使得最终的速度有了2倍左右的提升。
下面说一点新版本的不足:目前来看,文字定位方法的鲁棒性确实很高,不过遗憾的速度跟颜色定位方法相比,还是慢了接近一倍(与Sobel定位效率相当)。后面的改善中,考虑对其进行优化。另外,字符分割的效果实际上还是可以有更多的优化算法选择的,未来的版本可以考虑对其做一个较大的尝试与改进。
对EasyPR做下说明:EasyPR,一个开源的中文车牌识别系统,代码托管在github和gitosc。其次,在前面的博客文章中,包含EasyPR至今的开发文档与介绍。
版权说明:
本文中的所有文字,图片,代码的版权都是属于作者和博客园共同所有。欢迎转载,但是务必注明作者与出处。任何未经允许的剽窃以及爬虫抓取都属于侵权,作者和博客园保留所有权利。
参考文献:
1.Character-MSER : Scene Text Detection with Robust Character Candidate Extraction Method, ICDAR2015
2.Seed-growing : A robust hierarchical detection method for scene text based on convolutional neural networks, ICME2015
EasyPR--开发详解(8)文字定位的更多相关文章
- EasyPR--开发详解(6)SVM开发详解
在前面的几篇文章中,我们介绍了EasyPR中车牌定位模块的相关内容.本文开始分析车牌定位模块后续步骤的车牌判断模块.车牌判断模块是EasyPR中的基于机器学习模型的一个模块,这个模型就是作者前文中从机 ...
- javaCV开发详解之4:转流器实现(也可作为本地收流器、推流器,新增添加图片及文字水印,视频图像帧保存),实现rtsp/rtmp/本地文件转发到rtmp流媒体服务器(基于javaCV-FFMPEG)
javaCV系列文章: javacv开发详解之1:调用本机摄像头视频 javaCV开发详解之2:推流器实现,推本地摄像头视频到流媒体服务器以及摄像头录制视频功能实现(基于javaCV-FFMPEG.j ...
- 【转发】NPAPI开发详解,Windows版
NPAPI开发详解,Windows版 9 jiaofeng601, +479 9人支持,来自Meteor.猪爪.hanyuxinting更多 .是非黑白 .Yuan Xulei.hyolin.Andy ...
- iOS原生地图开发详解
在上一篇博客中:http://my.oschina.net/u/2340880/blog/414760.对iOS中的定位服务进行了详细的介绍与参数说明,在开发中,地位服务往往与地图框架结合使用,这篇博 ...
- wpf 客户端【JDAgent桌面助手】开发详解(四) popup控件的win8.0的bug
目录区域: 业余开发的wpf 客户端终于完工了..晒晒截图 wpf 客户端[JDAgent桌面助手]开发详解-开篇 wpf 客户端[JDAgent桌面助手]详解(一)主窗口 圆形菜单... wpf 客 ...
- iOS应用开发详解
<iOS应用开发详解> 基本信息 作者: 郭宏志 出版社:电子工业出版社 ISBN:9787121207075 上架时间:2013-6-28 出版日期:2013 年7月 开本:16开 ...
- javaCV开发详解之技术杂烩:javaCV能帮我们做什么?能实现什么功能?ffmpeg和openCV能实现功能,javaCV如何做到更快、更简单的实现相应的功能?等等一堆实用话题
前言: 该篇文章旨在帮助刚接触javaCV的盆友系统的认识音视频.javaCV.图像处理相关的体系知识和一些实用的知识. 序: javaCV早期因为内置了openCV库,所以常用来做图像识别应用,现在 ...
- javaCV开发详解之7:让音频转换更加简单,实现通用音频编码格式转换、重采样等音频参数的转换功能(以pcm16le编码的wav转mp3为例)
javaCV系列文章: javacv开发详解之1:调用本机摄像头视频 javaCV开发详解之2:推流器实现,推本地摄像头视频到流媒体服务器以及摄像头录制视频功能实现(基于javaCV-FFMPEG.j ...
- javaCV开发详解之6:本地音频(话筒设备)和视频(摄像头)抓取、混合并推送(录制)到服务器(本地)
javaCV系列文章: javacv开发详解之1:调用本机摄像头视频 javaCV开发详解之2:推流器实现,推本地摄像头视频到流媒体服务器以及摄像头录制视频功能实现(基于javaCV-FFMPEG.j ...
- javaCV开发详解之5:录制音频(录制麦克风)到本地文件/流媒体服务器(基于javax.sound、javaCV-FFMPEG)
javaCV系列文章: javacv开发详解之1:调用本机摄像头视频 javaCV开发详解之2:推流器实现,推本地摄像头视频到流媒体服务器以及摄像头录制视频功能实现(基于javaCV-FFMPEG.j ...
随机推荐
- iOS可视化动态绘制连通图
上篇博客<iOS可视化动态绘制八种排序过程>可视化了一下一些排序的过程,本篇博客就来聊聊图的东西.在之前的博客中详细的讲过图的相关内容,比如<图的物理存储结构与深搜.广搜>.当 ...
- 微信企业号 获取AccessToken
目录 1. AccessToken介绍 2. 示例代码 1. AccessToken介绍 1.1 什么是AccessToken AccessToken即访问凭证,业务服务器每次主动调用企业号接口时需要 ...
- 前端框架 EasyUI (1)熟悉一下EasyUI
jQuery EasyUI 官方网站 http://www.jeasyui.com/ .去年新开了个中文网 http://www.jeasyui.net/,不知道是不是官方的,不过看着挺像样.但是,广 ...
- 一步一步教你用CSS画爱心
今天小颖给大家分享一个用CSS画的爱心,底下有代码和制作过程,希望对大家有所帮助. 第一步: 先画一个正方形.如图: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <he ...
- Tesseract-OCR字符识别简介
OCR(Optical Character Recognition):光学字符识别,是指对图片文件中的文字进行分析识别,获取的过程.Tesseract:开源的OCR识别引擎,初期Tesseract引擎 ...
- 用javascript 写个函数返回一个页面里共使用了多少种HTML 标签
今天我无意间看到一个面试题: 如何用javascript 写个函数返回一个页面里共使用了多少种HTML 标签? 不知你看到 是否蒙B了,如果是我 面试,肯定脑子嗡嗡的响.... 网上搜了搜也没有找到答 ...
- javascript 笔记!
1.通过javascript向文档中输出文本 document是javascript的内置对象,代表浏览器的文档部分 document.write("Hello Javascript&quo ...
- Android(安卓)-------CardView
1.activity_main.xml <android.support.v7.widget.CardView android:id="@+id/cardView" andr ...
- iOS 自定义方法 - 不完整边框
示例代码 ///////////////////////////OC.h////////////////////////// //// UIView+FreeBorder.h// BHBFreeB ...
- Jquery 获得当前标签的名称和标签属性
得到标签的名称 $("#name").prop("tagName"); 或者 $("#name")[0].tagName; 注意:1.得到的 ...
