Codeforces 932.D Tree
2 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given a node of the tree with index 1 and with weight 0. Let cnt be the number of nodes in the tree at any instant (initially, cnt is set to 1). Support Q queries of following two types:
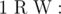 Add a new node (index cnt + 1) with weight W and add edge between node R and this node.
Add a new node (index cnt + 1) with weight W and add edge between node R and this node.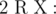 Output the maximum length of sequence of nodes which
Output the maximum length of sequence of nodes which
- starts with R.
- Every node in the sequence is an ancestor of its predecessor.
- Sum of weight of nodes in sequence does not exceed X.
- For some nodes i, j that are consecutive in the sequence if i is an ancestor of j then w[i] ≥ w[j] and there should not exist a node k on simple path from i to j such that w[k] ≥ w[j]
The tree is rooted at node 1 at any instant.
Note that the queries are given in a modified way.
First line containing the number of queries Q (1 ≤ Q ≤ 400000).
Let last be the answer for previous query of type 2 (initially last equals 0).
Each of the next Q lines contains a query of following form:
- 1 p q (1 ≤ p, q ≤ 1018): This is query of first type where
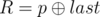 and
and 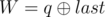 . It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cnt and0 ≤ W ≤ 109.
. It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cnt and0 ≤ W ≤ 109. - 2 p q (1 ≤ p, q ≤ 1018): This is query of second type where
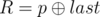 and
and 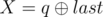 . It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cntand 0 ≤ X ≤ 1015.
. It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cntand 0 ≤ X ≤ 1015.
 denotes bitwise XOR of a and b.
denotes bitwise XOR of a and b.
It is guaranteed that at least one query of type 2 exists.
Output the answer to each query of second type in separate line.
6
1 1 1
2 2 0
2 2 1
1 3 0
2 2 0
2 2 2
0
1
1
2
6
1 1 0
2 2 0
2 0 3
1 0 2
2 1 3
2 1 6
2
2
3
2
7
1 1 2
1 2 3
2 3 3
1 0 0
1 5 1
2 5 0
2 4 0
1
1
2
7
1 1 3
1 2 3
2 3 4
1 2 0
1 5 3
2 5 5
2 7 22
1
2
3
In the first example,
last = 0
- Query 1: 1 1 1, Node 2 with weight 1 is added to node 1.
- Query 2: 2 2 0, No sequence of nodes starting at 2 has weight less than or equal to 0. last = 0
- Query 3: 2 2 1, Answer is 1 as sequence will be {2}. last = 1
- Query 4: 1 2 1, Node 3 with weight 1 is added to node 2.
- Query 5: 2 3 1, Answer is 1 as sequence will be {3}. Node 2 cannot be added as sum of weights cannot be greater than 1. last = 1
- Query 6: 2 3 3, Answer is 2 as sequence will be {3, 2}. last = 2
题目大意:一棵树,每个点有点权,两种操作:1.新加一个点连接r,权值为w. 2.从一个点r开始往祖先上跳,每次跳到第一个值≥自身的祖先,将跳到的点的和加起来,不能大于w,问能跳几次.
分析:挺有意思的一道题.
暴力算法就是一个一个往上跳着找喽,在树上往上跳有一种常用的优化方法--倍增.在这道题里面可以倍增地跳到≥自身权值的点.
考虑怎么实现,fa数组就不能记录第2^i个祖先了,而要记录比自身权值大的第2^i个祖先.在加点的时候处理.可以发现,一旦处理出fa[i][0],就能够根据祖先节点的信息推出fa[i][j].
如何处理fa[i][0]?如果r的权值比新加的点i的权值大或相等,则fa[i][0] = r,否则从r开始往上跳,如果w[fa[r][j]] < w[i],则往上跳,最后fa[i][0] = fa[r][0].
因为最后要求和嘛,可以顺便维护一个sum数组,表示从i这个点跳到比i权值大的第2^j个祖先跳到的点的权值和为多少. 求出了这两个数组以后查询就很好办了,sum[i][j]是否≤w,是的话就往上跳,并且w -= sum[i][j].倍增的基础应用嘛.
想清楚如何加速往祖先跳的过程,以及倍增应该维护什么东西这道题就能解决了.
一些边界的值需要特殊考虑!
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn = ,inf = 1e18;
ll q,lastans,cnt = ,w[maxn];
ll fa[maxn][],sum[maxn][]; void add(ll x,ll v)
{
w[++cnt] = v;
if (w[cnt] <= w[x])
fa[cnt][] = x;
else
{
int y = x;
for (int i = ; i >= ; i--)
{
if (w[fa[y][i]] < w[cnt])
y = fa[y][i];
}
fa[cnt][] = fa[y][];
}
if (fa[cnt][] == )
sum[cnt][] = inf;
else
sum[cnt][] = w[fa[cnt][]];
for (int i = ; i <= ; i++)
{
fa[cnt][i] = fa[fa[cnt][i - ]][i - ];
if (fa[cnt][i] == )
sum[cnt][i] = inf;
else
sum[cnt][i] = sum[cnt][i - ] + sum[fa[cnt][i - ]][i - ];
}
} ll query(ll x,ll v)
{
if (w[x] > v)
return ;
v -= w[x];
ll res = ;
for (int i = ; i >= ; i--)
{
if (v >= sum[x][i])
{
v -= sum[x][i];
res += ( << i);
x = fa[x][i];
}
}
return res;
} int main()
{
w[] = inf;
for (int i = ; i <= ; i++)
sum[][i] = inf;
scanf("%I64d",&q);
while (q--)
{
int id;
ll a,b;
scanf("%d",&id);
scanf("%I64d%I64d",&a,&b);
a ^= lastans;
b ^= lastans;
if (id == )
add(a,b);
else
printf("%I64d\n",lastans = query(a,b));
}
}
Codeforces 932.D Tree的更多相关文章
- Problem - D - Codeforces Fix a Tree
Problem - D - Codeforces Fix a Tree 看完第一名的代码,顿然醒悟... 我可以把所有单独的点全部当成线,那么只有线和环. 如果全是线的话,直接线的条数-1,便是操作 ...
- Codeforces 765 E. Tree Folding
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/765/E $DFS子$树进行$DP$ 大概分以下几种情况: 1.为叶子,直接返回. 2.长度不同的路径长度 ...
- Codeforces 932 E. Team Work(组合数学)
http://codeforces.com/contest/932/problem/E 题意: 可以看做 有n种小球,每种小球有无限个,先从中选出x种,再在这x种小球中任选k个小球的方案数 选出的 ...
- codeforces 570 D. Tree Requests 树状数组+dfs搜索序
链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/570/D D. Tree Requests time limit per test 2 seconds mem ...
- CodeForces 383C Propagating tree
Propagating tree Time Limit: 2000ms Memory Limit: 262144KB This problem will be judged on CodeForces ...
- 【19.77%】【codeforces 570D】Tree Requests
time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outputstandard o ...
- CodeForces - 274B Zero Tree
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/274/B 题目大意: 给定你一颗树,每个点上有权值. 现在你每次取出这颗树的一颗子树(即点集和边集均是原图的子集的连 ...
- Codeforces 343D Water Tree(DFS序 + 线段树)
题目大概说给一棵树,进行以下3个操作:把某结点为根的子树中各个结点值设为1.把某结点以及其各个祖先值设为0.询问某结点的值. 对于第一个操作就是经典的DFS序+线段树了.而对于第二个操作,考虑再维护一 ...
- codeforces 375D:Tree and Queries
Description You have a rooted tree consisting of n vertices. Each vertex of the tree has some color. ...
随机推荐
- POJ-3122(二分算法)
//题意:这是一个分蛋糕的游戏, t个测试数据,输入n, f n代表的是n块蛋糕,蛋糕的高为1, f代表的是f个人朋友,然后输入每份蛋糕的半径 // 将n块蛋糕分成 f+1 份 每一份都是完成的一块蛋 ...
- NO.04--我的使用心得之使用vue绑定class名
今天聊一聊这个话题,其实方式有很多种,我今天介绍几种我使用到的,各位看官耐心看: 一.用 变量形式 绑定单个 Class 名 在 vue 中绑定单个 class 名还好说,直接写就可以了 <te ...
- 001----Mysql隔离级别
一:事务隔离级别 mysql数据库的隔离界别如下: 1, READ UNCOMMITTED(未提交读) 事务中的修改,即使没有提交,对其它事务也是可见的. 这样会造成脏读(Dirty Read)的问 ...
- 算法笔记(c++)--关于01背包的滚动数组
算法笔记(c++)--关于01背包的滚动数组 关于01背包问题:基本方法我这篇写过了. https://www.cnblogs.com/DJC-BLOG/p/9416799.html 但是这里数组是N ...
- PKI(Public Key Infrastucture)介绍
PKI(Public Key Infrastucture)介绍 根据Wikipedia PKI词条整理. PKI(Public Key Infrastucture)是一系列的规则.策略以及过程,可以用 ...
- 关于JavaScript定时器我的一些小理解
因为自己在平时工作中,有些功能需要用到定时器,但是定时器并不像我们表边上看到的那样,所以这周末我看看书查查资料,深入研究了一下JavaScript中的定时器,那么废话不多说,下面进入我们今天的正题. ...
- ZOJ 3946 Highway Project 贪心+最短路
题目链接: http://www.icpc.moe/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=3946 题解: 用dijkstra跑单元最短路径,如果对于顶点v,存 ...
- 3dContactPointAnnotationTool开发日志(三三)
添加背景图片后发现Runtime Transform Gizmo无法选中物体了: 于是改了一下EditorObjectSelection.cs中的WereAnyUIElementsHovere ...
- vue-cli脚手架搭建
我们使用vue-cli来搭建整个项目,vue-cli就是一个脚手架,步骤很简单,输入几个命令之后就会生成整个项目,里面包括了webpack.ESLint.babel很多配置等等,省了很多事 Vue+ ...
- Kotlin在处理GET和POST请求的数据问题
1.网络请求获取到的数据流处理 java写法 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in, "utf-8& ...
