Lists, Maps and Sets in Java
ArrayList vs LinkedList vs Vector
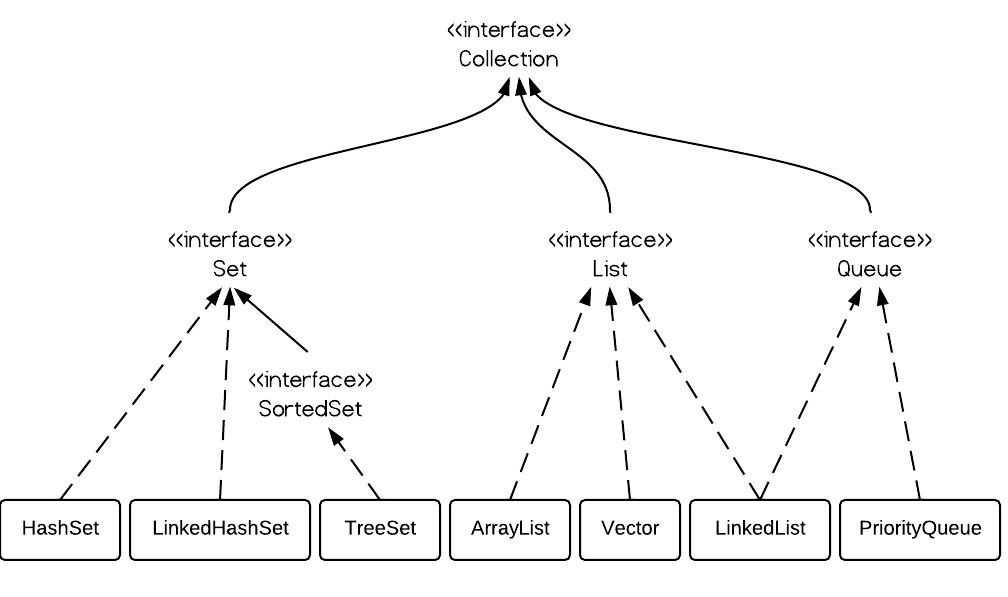
From the hierarchy diagram, they all implement List interface. They are very similar to use. Their main difference is their implementation which causes different performance for different operations.
ArrayList is implemented as a resizable array. As more elements are added to ArrayList, its size is increased dynamically. It's elements can be accessed directly by using the get and set methods, since ArrayList is essentially an array.
LinkedList is implemented as a double linked list. Its performance on add and remove is better than Arraylist, but worse on get and set methods.
Vector is similar with ArrayList, but it is synchronized. ArrayList is a better choice if your program is thread-safe. Because of this, it has an overhead than ArrayList. Normally, most Java programmers use ArrayList instead of Vector because they can synchronize explicitly by themselves.
Vector and ArrayList require space as more elements are added. Vector each time doubles its array size, while ArrayList grow 50% of its size each time.
LinkedList, however, also implements Queue interface which adds more methods than ArrayList and Vector, such as offer(), peek(), poll(), etc.
Note: The default initial capacity of an ArrayList is pretty small. It is a good habit to construct the ArrayList with a higher initial capacity. This can avoid the resizing cost.
In brief, LinkedList should be preferred if:
there are no large number of random access of element
there are a large number of add/remove operations
HashMap vs TreeMap vs LinkedHashMap

All three classes implement the Map interface and offer mostly the same functionality. The most important difference is the order in which iteration through the entries will happen:
HashMap makes absolutely no guarantees about the iteration order. It can (and will) even change completely when new elements are added.
TreeMap is a tree based mapping. Its put/get operations take O(log n) time. It requires items to have some comparison mechanism, either with Comparable or Comparator. TreeMap will iterate according to the "natural ordering" of the keys according to their compareTo() method (or an externally supplied Comparator). It also implements the SortedMap interfacer. It doesn’t use equals() and hashCode() methods for comparison of elements.
LinkedHashMap is very similar to HashMap, but it adds awareness to the order at which items are added (or accessed), so the iteration order is the same as insertion order (or access order, depending on construction parameters)
HashSet Vs TreeSet Vs LinkedHashSet In Java

HashSet is Implemented using a hash table. Elements are not ordered. The add, remove, and contains methods have constant time complexity O(1).
TreeSet is implemented using a tree structure(red-black tree in algorithm book). The elements in a set are sorted, but the add, remove, and contains methods has time complexity of O(log (n)). It offers several methods to deal with the ordered set like first(), last(), headSet(), tailSet(), etc. It doesn’t use equals() and hashCode() methods for comparision of elements.
LinkedHashSet is between HashSet and TreeSet. It is implemented as a hash table with a linked list running through it, so it provides the order of insertion. The time complexity of basic methods is O(1).
Lists, Maps and Sets in Java的更多相关文章
- 使用Maps与Sets处理集合的交差运算
import com.google.common.collect.MapDifference; import com.google.common.collect.Maps; import java.u ...
- Spring EL Lists, Maps example
In this article, we show you how to use Spring EL to get value from Map and List. Actually, the way ...
- Java Garbage Collection Basics--转载
原文地址:http://www.oracle.com/webfolder/technetwork/tutorials/obe/java/gc01/index.html Overview Purpose ...
- HIBERNATE - 符合Java习惯的关系数据库持久化(精华篇)
HIBERNATE - 符合Java习惯的关系数据库持久化 下一页 HIBERNATE - 符合Java习惯的关系数据库持久化 Hibernate参考文档 3.0.4 目录 前言 1. ...
- Guava 集合框架
在本系列中我们首先来学习一些Guava的集合框架,也就是这个package:com.google.common.collect 在这个包下面有一些通用的集合接口和一些相关的类. 集合类型: BiM ...
- G1垃圾收集器官方文档透彻解读【官方解读】
在前几次中已经对G1的理论进行了一个比较详细的了解了,对于G1垃圾收集器最权威的解读肯定得上官网,当咱们将官网的理解透了,那基本上网上对于G1的说明其实最终都是来自于官网,所以接下来会详细来解读Ora ...
- Hibernate4教程六:性能提升和二级缓存
抓取策略(fetching strategy)是指:当应用程序需要在(Hibernate实体对象图的)关联关系间进行导航的时候,Hibernate如何获取关联对象的策略.抓取策略可以在O/R映射的元数 ...
- 005-guava 集合-集合工具类-java.util.Collections中未包含的集合工具[Maps,Lists,Sets],Iterables、Multisets、Multimaps、Tables
一.概述 工具类与特定集合接口的对应关系归纳如下: 集合接口 属于JDK还是Guava 对应的Guava工具类 Collection JDK Collections2:不要和java.util.Col ...
- java基础之 GC
Java程序员在编码过程中通常不需要考虑内存问题,JVM经过高度优化的GC机制大部分情况下都能够很好地处理堆(Heap)的清理问题.以至于许多Java程序员认为,我只需要关心何时创建对象,而回收对象, ...
随机推荐
- 【转】轻应用、Web App、Native App三者分别是什么?
一.什么是Native app Native App是一种基于智能手机本地操作系统如IOS.Android.WP并使用原生程式编写运行的第三方应用程序,也叫地app.NativeApp因为位于平台 ...
- 3.Java日志框架slf4j、jcl、jul、log4j1、log4j2、logback大总结
一.slf4j.jcl.jul.log4j1.log4j2.logback JUL:JDK中的日志记录工具,也常称为JDKLog.jdk-logging. LOG4J1:一个具体的日志实现框架. LO ...
- Redis数据类型之列表List
Redis列表简介 Redis列表是简单的字符串列表,一个列表最多可以包含 232 - 1 个元素.列表按照插入顺序排序,可以从列表的头部或者尾部添加元素 上图演示了使用LPUSH向列表中插入元素,并 ...
- Felx布局(三)
flex网格布局 平均分布 最简单的网格布局,就是平均分布.在容器里面平均分配空间,跟上面的骰子布局很像,但是需要设置项目的自动缩放
- 利用_winreg模块在注册表中分析无线访问热点
_winreg.OpenKey(key, sub_key, res, sam) key是一个已经打开的键,或者是HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT.HKEY_CURRENT_USER.HKEY ...
- 打印Fibonacci数列方法汇总(前20项,每行5个)
NO.1 迭代法 标签:通俗.易懂 思路:先打印第一项.再在循环里面执行fib=fib1+fib2,把fib2赋给fib1,把fib赋给fib2,每行5个可使用if函数(循环次数对5取余). #inc ...
- zlog学习随笔
zlog1使用手册 Contents Chapter 1 zlog是什么? 1.1 兼容性说明 1.2 zlog 1.2 发布说明 Chapter 2 zlog不是什么? Chapter 3 ...
- JS实现排序
排序算法可以分为内部排序和外部排序.内部排序是数据记录在内存中进行排序,外部排序是因排序的数据很大,一次不能够容纳全部的排序记录,在排序中需要访问外存.常见的内部排序算法有插入排序,选择排序,冒泡排序 ...
- [codevs]1060搞笑世界杯
CODEVS上一道钻石题,还是DP的思想,先来题目 1060 搞笑世界杯 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目等级 : 钻石 Diamond 题解 题目描述 Description ...
- flex布局下,css设置文本不换行时,省略号不显示的解决办法
大致是有一个main容器是flex布局,左边一个logo固定宽高,右边content动态宽度. <div class="main"> <img alt=" ...
