MySQL_基本操作
sql语句
Sql语句主要用于存取数据,查询数据,更新数据和管理数据库系统。
#Sql语句分为3种类型
#1.DDL语句:数据库定义语言: 数据库、表、视图、索引、存储过程,例如CREATE DROP ALTER
#2.DML语句:数据库操纵语言: 插入数据INSERT、删除数据DELETE、更新数据UPDATE、查询数据SELECT
#3.DCL语句:数据库控制语言: 例如控制用户的访问权限GRANT、REVOKE
库操作
安装并登陆mysql后,查看数据库,发现有如下数据库:
#information_schema:虚拟库,不占用磁盘空间,存储的是数据库启动后的一些参数,如用户表信息、列信息、权限信息、字符信息等
#performance_schema:Mysql5.5开始新增一个数据库:主要用于收集数据库服务器性能参数,记录处理查询请求时发生的各种事件、锁等现象
#mysql:授权库,主要存储系统用户的权限信息
#test:Mysql数据库系统自动创建的测试数据库
创建数据库
#数据库命名规则
#可以由字母、数字、下划线、@、#、$组成
#区分大小写
#唯一性
#不能使用关键字如select、create
#不能单独使用数字
#最长128位
#数据库相关操作 #创建数据库
create database db1 charset utf8;
#查看数据库
show databases;
show create database db1;
select database();
#选择数据库
use db1;
#修改数据库
alter database db1 charset utf8;
#删除数据库
drop database db1;
表操作
表相关操作
#先切换到库下
use db1;
#创建表
#create table 表名(
字段名1 类型[(宽度) 约束条件],
字段名2 类型[(宽度)约束条件]
);
#在同一张表中,字段名不能相同;宽度和约束条件可选;字段名和类型是必须的;表中的最后一个字段不要加逗号
create table t1(id int,name char);
#查看表
show tables; #查看表
describe t1; #查看表结构,可简写为 desc t1
show create table t1\G #查看表详细结构
#修改表
alter table t1 modify name char(3);
alter table t1 change name name1 char(2);
1. 修改表名
ALTER TABLE 表名
RENAME 新表名; 2. 增加字段
ALTER TABLE 表名
ADD 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…],
ADD 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…];
ALTER TABLE 表名
ADD 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…] FIRST;
ALTER TABLE 表名
ADD 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…] AFTER 字段名; 3. 删除字段
ALTER TABLE 表名
DROP 字段名; 4. 修改字段
ALTER TABLE 表名
MODIFY 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…];
ALTER TABLE 表名
CHANGE 旧字段名 新字段名 旧数据类型 [完整性约束条件…];
ALTER TABLE 表名
CHANGE 旧字段名 新字段名 新数据类型 [完整性约束条件…];
修改表语法
#1. 修改存储引擎
alter table service engine=innodb; #2. 添加字段
alter table t1 add name varchar(20) not null; alter table t1 add stu_num varchar(10) not null after name; //添加name字段之后 alter table t1 add sex enum('male','female') default 'male' first; //添加到最前面 #3. 删除字段
alter table t1 drop sex; alter table service drop mac; #4. 修改字段类型modify
alter table t1 modify age int(3);
alter table t1 modify id int(11) not null primary key auto_increment; //修改为主键 #5. 增加约束(针对已有的主键增加auto_increment)
alter table student10 modify id int(11) not null primary key auto_increment;
#ERROR 1068 (42000): Multiple primary key defined alter table student10 modify id int(11) not null auto_increment;
#Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) #6. 对已经存在的表增加复合主键
alter table service2 add primary key(host_ip,port); #7. 增加主键
alter table student1 modify name varchar(10) not null primary key; #8. 增加主键和自动增长
alter table student1 modify id int not null primary key auto_increment; #9. 删除主键
#a. 删除自增约束
alter table student10 modify id int(11) not null; #b. 删除主键
alter table student10 drop primary key;
示例
#复制表
#复制表结构+记录
create table new_service select * from service;
#只复制表结构
create table new1_service select * from service where 1=2;
create table t4 like employees;
#删除表
drop table t1;
数据类型
表内存放的数据有不同的类型,每种数据类型都有自己的宽度,但宽度是可选的
数值类型
整数类型:TINYINT SMALLINT MEDIUMINT INT BIGINT
为该类型指定宽度时,仅仅只是指定查询结果的显示宽度,与存储范围无关,默认的显示宽度都是在最大值的基础上加1
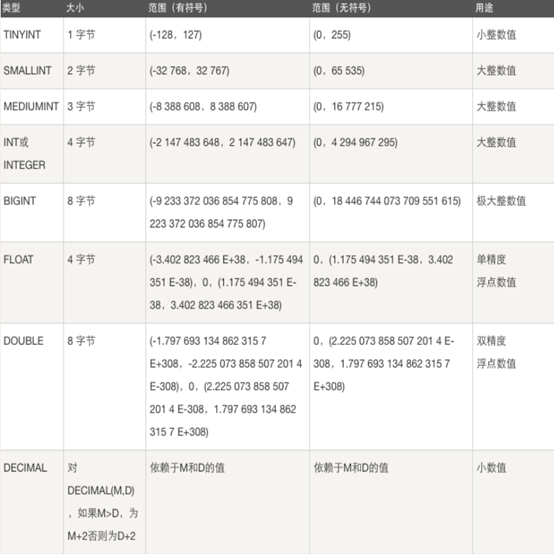
浮点型
定点数类型:DEC等同于DECIMAL,浮点类型:FLOAT DOUBLE
位类型
BIT(M)可以用来存放多位二进制数,M范围从1~64,如果不写默认为1位
#对于位字段需要使用函数读取
bin()显示为二进制
hex()显示为十六进制
日期类型:DATE TIME DATETIME TIMESTAMP YEAR
YEAR
YYYY(1901/2155) DATE
YYYY-MM-DD(1000-01-01/9999-12-31) TIME
HH:MM:SS('-838:59:59'/'838:59:59') DATETIME YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS(1000-01-01 00:00:00/9999-12-31 23:59:59 Y) TIMESTAMP YYYYMMDD HHMMSS(1970-01-01 00:00:00/2037 年某时)
字符串类型:char,varchar,
1.CHAR 和 VARCHAR 是最常使用的两种字符串类型。
2.一般来说CHAR(N)用来保存固定长度的字符串,对于 CHAR 类型,N 的范围 为 0 ~ 255
VARCHAR(N)用来保存变长字符类型,对于 VARCHAR 类型,N 的范围为 0 ~ 65 535
CHAR(N)和 VARCHAR(N) 中的 N 都代表字符长度,而非字节长度。
3. char填充空格来满足固定长度,但是在查询时却会很不要脸地删除尾部的空格(装作自己好像没有浪费过空间一样),然后修改sql_mode让其现出原形
4.虽然 CHAR 和 VARCHAR 的存储方式不太相同,但是对于两个字符串的比较,都只比 较其值,忽略 CHAR 值存在的右填充,即使将 SQL _MODE 设置为 PAD_CHAR_TO_FULL_ LENGTH 也一样,,但这不适用于like
5.虽然varchar使用起来较为灵活,但是从整个系统的性能角度来说,char数据类型的处理速度更快,有时甚至可以超出varchar处理速度的50%。因此,用户在设计数据库时应当综合考虑各方面的因素,以求达到最佳的平衡
6.#其他字符串系列(效率:char>varchar>text)
TEXT系列 TINYTEXT TEXT MEDIUMTEXT LONGTEXT
BLOB 系列 TINYBLOB BLOB MEDIUMBLOB LONGBLOB
BINARY系列 BINARY VARBINARY
text:text数据类型用于保存变长的大字符串,可以组多到65535 (2**16 − 1)个字符。
mediumtext:A TEXT column with a maximum length of 16,777,215 (2**24 − 1) characters.
longtext:A TEXT column with a maximum length of 4,294,967,295 or 4GB (2**32 − 1) characters.
枚举类型与集合类型
字段值只能在给定的范围内选一个值,enum(单选)只能在给定的范围内选一个值,set(多选)在给定的范围内可以选择一个或多个值 。
create table consumer(
name varchar(50),
sex enum('male','female'),
hobby set('play','read','study')
);
表完整性约束
约束条件与数据类型的宽度一样,都是可选参数。主要用于保证数据的完整性和一致性。
primary key (PK) #标识主键,可以唯一的标识记录
foreign key (FK) #标识外键
not null #标识字段不能为空
unique key (UK) #标识该字段唯一
auto_increment #标识该字段的值自动增长(整数类型且为主键)
default #为该字段设置默认值
unsigned #无符号
zerofill #用0填充
1. 是否允许为空,默认NULL,可设置NOT NULL,字段不允许为空,必须赋值
2. 字段是否有默认值,缺省的默认值是NULL,如果插入记录时不给字段赋值,此字段使用默认值
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male'
age int unsigned NOT NULL default 20 必须为正值(无符号) 不允许为空 默认是20
3. 是否是key
主键 primary key
外键 foreign key
索引 (index,unique...)
not null与default
not null #不可空 create table t1(id int not null);
insert into t1 values(1); #设置id字段不为空则插入记录时不能插入空 null #可空
create table t2(id int);
insert into t2 values(); #默认可以插入空 default #默认值,无论字段是null还是not null都可以插入空,插入空填入默认值
create table t3(age int not null default 18);
create table t4(hobby varchar default 'read');
unique
unique #设置唯一约束
#设置方法一
create table t1(name varchar(20) unique); #设置方法二
create table t2(
name varchar(20),
constraint uk_name unique(name)
); #联合唯一
create table t3(
name varchar(20),
host varchar(15) not null,
port int not null,
unique(host,post)
); #not null+ unique
create table t4(id int not null unique); #数据库会自动识别为primary key
primary key
主键primary key是innodb存储引擎组织数据的依据,innodb称之为索引组织表,一张表中必须有且只有一个主键
#not null + unique设置主键
create table t1(id int not null unique); #primary key 设置主键方法一
create table t2(id int primary key); #primary key 设置主键方法二
create table t2(
id int
constraint pk_name primary key(is)
); #联合主键
create table t3(
host varchar(20),
port char(15),
primary key(host,port)
);
auto_increment
约束字段为自动增长,被约束的字段必须同时被key约束
#创建完表后修改自增字段的起始值方法一
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex num('male','female') default 'male'
); alter table student auto_increment=3; #方法二
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') default 'male'
)auto_increment=3; #设置步长
sqlserver:自增步长
基于表级别
create table t1(
id int。。。
)engine=innodb,auto_increment=2 步长=2 default charset=utf8 mysql自增的步长:
show session variables like 'auto_inc%'; #基于会话级别
set session auth_increment_increment=2 #修改会话级别的步长 #基于全局级别的
set global auth_increment_increment=2 #修改全局级别的步长(所有会话都生效) 如果auto_increment_offset的值大于auto_increment_increment的值,则auto_increment_offset的值会被忽略
#不指定id,则自动增长
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') default 'male'
); #插入数据时可不指定id
insert into student(name) values('lary') #插入数据时也可以指定id
insert into student(id,name) values(3,'lily') #对于自增的字段,在用delete删除后,再插入值,该字段仍按照删除前的位置继续增长
delete from student #truncate 清空表,清空后,直接从0开始
truncate student
foreign key
#表类型必须是innodb存储引擎,且被关联的字段必须保证唯一
create table department(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20) not null
)engine=innodb; create table employee(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
dep_id int,
constraint fk_name foreign key(dep_id) references department(id)
on delete cascade # 删除父表department,子表employee中对应的记录跟着删
on update cascade #更新父表department,子表employee中对应的记录跟着改
)engine=innodb;
数据操作
插入数据
#1. 插入完整数据(顺序插入)
语法一:
INSERT INTO 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3…字段n) VALUES(值1,值2,值3…值n);
语法二:
INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES (值1,值2,值3…值n);
#2. 指定字段插入数据
语法:
INSERT INTO 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3…) VALUES (值1,值2,值3…);
#3. 插入多条记录
语法:
INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES
(值1,值2,值3…值n),
(值1,值2,值3…值n),
(值1,值2,值3…值n);
#4. 插入查询结果
语法:
INSERT INTO 表名(字段1,字段2,字段3…字段n)
SELECT (字段1,字段2,字段3…字段n) FROM 表2
WHERE …;
更新数据
update t1 set name='LARY' where id=1;
删除数据
delete from t1 where id=1
查询数据
单表查询
#语法
SELECT 字段
FROM 表名
GROUP BY field
HAVING 筛选
ORDER BY field
LIMIT 限制条数
语法
#关键字的执行优先级
from
where
group by
having
select
distinct
order by
limit
关键字的优先级
#创建表
create table student(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
name char(20) not null,
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male',
age int(3) unsigned not null default 18
); #插入记录
insert into student(name,sex) values
('lary','female'),
('lily','female'),
('jerry','male')
; #简单查询
select id,name from student; #避免重复
select distinct name from student; #定义显示格式
concat()函数用于连接字符串
select concat('编号:',id,'名字:'name) as student_info
from student #case语句
SELECT
(
CASE
WHEN NAME = 'lary' THEN
NAME
WHEN NAME = 'lily' THEN
CONCAT(name,'_hi')
ELSE
concat(NAME, 'hello')
END
) as new_name
FROM
student;
简单查询
#比较运算符
select name from student where age > 18; #between and
select * from student where age between 18 and 20; #in
select name from student where age in(18,28,30); #判断某个字段是否为空
select * from student where name is null; #like
select * from student where name like'la%'; #%表示任意多个字符 select * from student where name like'la_'; #_表示一个字符
where约束
分组查询
分组指的是将所有记录按照某个相同的字段进行归类,分组发生在where之后,即分组是基于where之后得到的记录而进行的。
多条记录之间的某个字段值相同,该字段用来作为分组的依据
分组查询
#ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY的语义就是确定select target list中的所有列的值都是明确语义,简单的说来,在ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY模式下,target list中的值要么是来自于聚集函数的结果,要么是来自于group by list中的表达式的值 #查看MySQL 5.7默认的sql_mode:
select @@global.sql_mode; #设置sql_mole如下操作(我们可以去掉ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY模式)
set global sql_mode='only_full_group_by' #设置成功后,一定要退出,然后才会生效
quit mysql> select * from user group by id;
ERROR 1055 (42000): 'db1.user.username' isn't in GROUP BY
only_full_group_by
#单独使用group by关键字分组,按照dep_id分组只能select dep_id,需要借助函数获取其他信息
select dep_id from emp group by dep_id; #group by 和group_concat()函数
select dep_id,group_concat(name) from emp group by dep_id; #按照dep_id并查看组内成员名 #group by与聚合函数一起使用
select dep_id,count(id) as count from emp group by dep_id; #按照dep_id,并查看部门人数
group by
#聚合函数聚合的是组的内容,若是没有分组,则默认一组
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee;
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee WHERE depart_id=1;
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employee;
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employee WHERE depart_id=3;
聚合函数
#having与where的区别
#执行优先级从高到低:where > group by > having
#Where 发生在分组group by之前,因而Where中可以有任意字段,但是绝对不能使用聚合函数
#Having发生在分组group by之后,因而Having中可以使用分组的字段,无法直接取到其他字段,可以使用聚合函数
having过滤
#按单列排序
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary; SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary ASC; SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC; #按多列排序:先按照age排序,如果年纪相同,则按照薪资排序
SELECT * from employee
ORDER BY age,salary DESC;
order by
#限制查询的记录数
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 3; #默认初始位置为0 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 0,5; #从第0开始,即先查询出第一条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESCLIMIT 5,5; #从第5开始,即先查询出第6条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条
limit
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP '^ale';
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'on$';
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'm{2}';
#对字符串匹配的方式
where name = 'lary';
where name like 'yuan%';
where name regexp 'on$';
正则表达式
多表查询
#多表连接查询
select 字段列表 from 表1 inner|left|right join 表2
#inner join:找两张表共有的部分
select * from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
#left join:优先显示左表所有记录
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
#right join:优先显示右表所有记录
select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
#全外连接:显示左右两个表的全部记录
#mysql不支持全外连接 full join
#mysql可以使用以下方式间接实现全外连接
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id
union
select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id=dep.id;
#union与union all的区别:union会去掉相同的记录
#示例1:以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且employee表中的age字段值必须大于25,即找出年龄大于25岁的员工以及员工所在的部门
select employee.name,department.name from employee inner join department
on employee.dep_id = department.id
where age > 25; #示例2:以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且以age字段的升序方式显示
select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,department.name from employee,department
where employee.dep_id = department.id
and age > 25
order by age asc;
符合条件连接查询
#子查询
#1:子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。
#2:内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。
#3:子查询中可以包含:IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字
#4:还可以包含比较运算符:= 、 !=、> 、<等
#查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名
select id,name
from department
where id in
(select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age) > 25);
带In关键字的子查询
#比较运算符:=、!=、>、>=、<、<=、<>
#查询大于所有人平均年龄的员工名与年龄
select name,age from emp where age > (select avg(age) from emp); select t1.name,t1.age from emp t1
inner join
(select dep_id,avg(age) avg_age from emp group by dep_id) t2
on t1.dep_id = t2.dep_id
where t1.age > t2.avg_age;
带比较运算符的子查询
#EXISTS关字键字表示存在。在使用EXISTS关键字时,内层查询语句不返回查询的记录。
而是返回一个真假值。True或False,当返回True时,外层查询语句将进行查询;当返回值为False时,外层查询语句不进行查询 select * from employee where exists(select id from department where id=12);
带exists关键字的子查询
MySQL_基本操作的更多相关文章
- Key/Value之王Memcached初探:二、Memcached在.Net中的基本操作
一.Memcached ClientLib For .Net 首先,不得不说,许多语言都实现了连接Memcached的客户端,其中以Perl.PHP为主. 仅仅memcached网站上列出的语言就有: ...
- Android Notification 详解(一)——基本操作
Android Notification 详解(一)--基本操作 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 微博:厉圣杰 源码:AndroidDemo/Notification 文中如有纰 ...
- Android Notification 详解——基本操作
Android Notification 详解 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 前几天项目中有用到 Android 通知相关的内容,索性把 Android Notificatio ...
- 三、Redis基本操作——List
小喵的唠叨话:前面我们介绍了Redis的string的数据结构的原理和操作.当时我们提到Redis的键值对不仅仅是字符串.而这次我们就要介绍Redis的第二个数据结构了,List(链表).由于List ...
- 二、Redis基本操作——String(实战篇)
小喵万万没想到,上一篇博客,居然已经被阅读600次了!!!让小喵感觉压力颇大.万一有写错的地方,岂不是会误导很多筒子们.所以,恳请大家,如果看到小喵的博客有什么不对的地方,请尽快指正!谢谢! 小喵的唠 ...
- 一、Redis基本操作——String(原理篇)
小喵的唠叨话:最近京东图书大减价,小喵手痒了就买了本<Redis设计与实现>[1]来看看.这里权当小喵看书的笔记啦.这一系列的模式,主要是先介绍Redis的实现原理(可能很大一部分会直接照 ...
- Linq查询基本操作
摘要:本文介绍Linq查询基本操作(查询关键字) - from 子句 - where 子句 - select子句 - group 子句 - into 子句 - orderby 子句 - join 子句 ...
- C++ map的基本操作和使用
原文地址:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_61533c9b0100fa7w.html Map是c++的一个标准容器,她提供了很好一对一的关系,在一些程序中建立一个map可 ...
- python之最强王者(10)———文件(File)、输入输出的基本操作
1. Python 文件I/O 本章只讲述所有基本的的I/O函数,更多函数请参考Python标准文档. 2.打印到屏幕 最简单的输出方法是用print语句,你可以给它传递零个或多个用逗号隔开的表达式. ...
随机推荐
- Golang - 异常处理
目录 Golang - 异常处理 1. 抛异常和处理异常 2. 返回异常 Golang - 异常处理 1. 抛异常和处理异常 package main import "fmt" / ...
- PAT 1080. Graduate Admission
It is said that in 2013, there were about 100 graduate schools ready to proceed over 40,000 applicat ...
- eclipse中 使用maven搭建ssh项目 思路复习(含有pom.xml)
首先在web.xml中配置监听器 在服务器启动的时候 进行bean对象的创建(只会创建单例对象 dao service 多例对象action可不会创建 每个多例对象是不同的 创建了有什么意义呢 ...
- [下载]Oracle LOB字段编辑工具
OraLobEditor 是Oracle LOB (CLOB, BLOB) 字段编辑工具. 查看.编辑LOB (CLOB, BLOB)字段(plain text, RTF, image, hex, h ...
- Adaptively handling remote atomic execution based upon contention prediction
In one embodiment, a method includes receiving an instruction for decoding in a processor core and d ...
- ReentrantLock公平锁与非公平锁lock()方法去竞争锁的不同点
- redis(四))——多实例化——实现主从配置
引言 redis是一个key-value存储系统. 和Memcached类似,它支持存储的value类型相对很多其它,包含string(字符串).list(链表).set(集合)和zset(有序集合) ...
- poj2299--归并排序求逆序数
/** \brief poj2299 * * \param date 2014/8/5 * \param state AC * \return memory 4640K time 3250ms ...
- Oracle 与 MySql 区别
一.并发性 并发性是oltp数据库最重要的特性,但并发涉及到资源的获取.共享与锁定. mysql:mysql以表级锁为主,对资源锁定的粒度很大,如果一个session对一个表加锁时间过长,会让其他se ...
- xml配置文件中的转义字符
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/14607920/the-character-breaks-passwords-that-are-stored-in-the-w ...
