设计模式(十)Strategy模式
Strategy模式,就是用来整体地替换算法,可以轻松地以不同的算法解决同一个问题。
还是根据一个示例程序来理解这种设计模式吧。先看一下示例程序的类图。
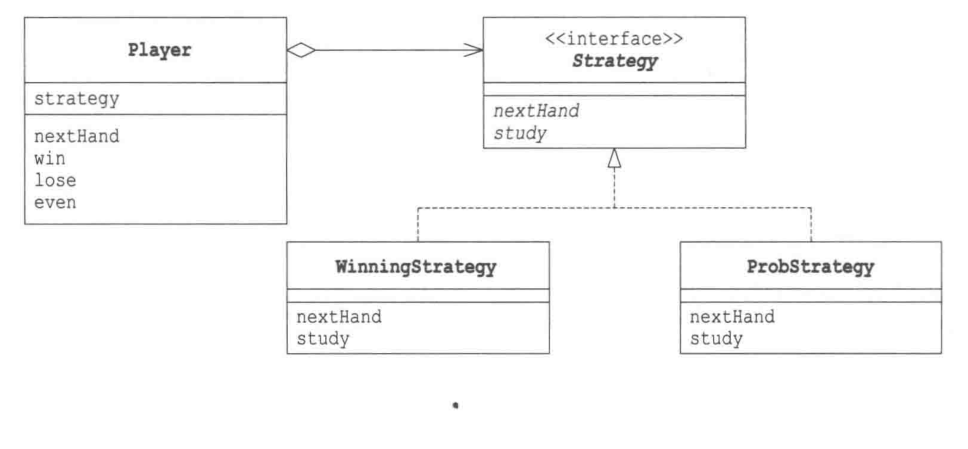
然后看示例程序代码。
package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy;
public class Hand {
public static final int HANDVALUE_GUU = 0; // 表示石头的值
public static final int HANDVALUE_CHO = 1; // 表示剪刀的值
public static final int HANDVALUE_PAA = 2; // 表示布的值
public static final Hand[] hand = { // 表示猜拳中3种手势的实例
new Hand(HANDVALUE_GUU),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_CHO),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_PAA),
};
private static final String[] name = { // 表示猜拳中手势所对应的字符串
"石头", "剪刀", "布",
};
private int handvalue; // 表示猜拳中出的手势的值
private Hand(int handvalue) {
this.handvalue = handvalue;
}
public static Hand getHand(int handvalue) { // 根据手势的值获取其对应的实例
return hand[handvalue];
}
public boolean isStrongerThan(Hand h) { // 如果this胜了h则返回true
return fight(h) == 1;
}
public boolean isWeakerThan(Hand h) { // 如果this输给了h则返回true
return fight(h) == -1;
}
private int fight(Hand h) { // 计分:平0, 胜1, 负-1
if (this == h) {
return 0;
} else if ((this.handvalue + 1) % 3 == h.handvalue) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
public String toString() { // 转换为手势值所对应的字符串
return name[handvalue];
}
}
Hand类是用来表示猜拳中“手势”的类,首先创建了Hand类的实例,并将它们保存在hand数组中。getHand方法的作用是,将手势的值作为参数传递给getHand方法,它就会将手势的值对应的Hand类的实例返回。判断猜拳结果比较有意思,如果hand1赢了hand2,那么可以用hand1.isStrongerThan(hand2)来表示,反之如果hand1输了hand2,那么可以用hand1.isWeakerThan(hand2)来表示。fight方法是用来比较this和h的,如果this的手势值加1后是h的手势值,那么this获胜。例如this是石头(0),h是剪刀(1);或者this是剪刀(1)而h是布(2);或者this是布(2)而h是石头(0)。这里的取余是因为2加上1后除以3的余数正好是0,也就是石头。这里的Hand类被其他类使用,但是它不是strategy模式的一部分。
package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy;
public interface Strategy {
public abstract Hand nextHand();
public abstract void study(boolean win);
}
Strategy接口定义了猜拳策略的抽象方法接口。nextHand方法的作用是“获取下一局要出的手势”,study方法是学习“上一局的手势是否获胜了”。
package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy;
import java.util.Random;
public class WinningStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private boolean won = false;
private Hand prevHand;
public WinningStrategy(int seed) {
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand() {
if (!won) {
prevHand = Hand.getHand(random.nextInt(3));
}
return prevHand;
}
public void study(boolean win) {
won = win;
}
}
WinningStrategy类实现了Strategy接口。这种猜拳策略是,如果上一局的手势赢了,则下一局的手势就与上局相同;如果上一局手势输了,那下一局就随机出手势。won字段中保存的是上一局猜拳的输赢结果,如果上一局赢了,那么won值为true,然后nextHand方法直接返回prevHand,study方法调用study(True)。
package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy;
import java.util.Random;
public class ProbStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private int prevHandValue = 0;
private int currentHandValue = 0;
private int[][] history = {
{ 1, 1, 1, },
{ 1, 1, 1, },
{ 1, 1, 1, },
};
public ProbStrategy(int seed) {
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand() {
int bet = random.nextInt(getSum(currentHandValue));
int handvalue = 0;
if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0]) {
handvalue = 0;
} else if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0] + history[currentHandValue][1]) {
handvalue = 1;
} else {
handvalue = 2;
}
prevHandValue = currentHandValue;
currentHandValue = handvalue;
return Hand.getHand(handvalue);
}
private int getSum(int hv) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
sum += history[hv][i];
}
return sum;
}
public void study(boolean win) {
if (win) {
history[prevHandValue][currentHandValue]++;
} else {
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 1) % 3]++;
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 2) % 3]++;
}
}
}
ProbStrategy类是随机出手势,但是每种手势出现的概率会根据以前的猜拳结果而改变。这里的理解就是,假如上一局出的是石头,那么history【0】【0】表示两局分别出石头和石头时胜了的次数,同理history【0】【1】表示两局分别出石头和剪刀时胜了的次数,history【0】【2】表示两局分别出石头和布时胜了的次数。这三个的值假如是3/5/7的情况下,下一局就会以石头、剪刀和布的比率为3:5:7来决定,在0到15之间取一个随机数,如果随机数是0 1 2那么出石头,如果随机数在3 4 5 6 7 那么出剪刀,如果随机数是9 10 11 12 13 14 15那么出布。
package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy;
public class Player {
private String name;
private Strategy strategy;
private int wincount;
private int losecount;
private int gamecount;
public Player(String name, Strategy strategy) { // 赋予姓名和策略
this.name = name;
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public Hand nextHand() { // 策略决定下一局要出的手势
return strategy.nextHand();
}
public void win() { // 胜
strategy.study(true);
wincount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void lose() { // 负
strategy.study(false);
losecount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void even() { // 平
gamecount++;
}
public String toString() {
return "[" + name + ":" + gamecount + " games, " + wincount + " win, " + losecount + " lose" + "]";
}
}
Player类表示进猜拳游戏选手的类。nextHand方法的返回值就是策略的nextHand方法的返回值,也就是将自己的工作委托给了strategy。
package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.out.println("Usage: java Main randomseed1 randomseed2");
System.out.println("Example: java Main 314 15");
System.exit(0);
}
int seed1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int seed2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
Player player1 = new Player("Lianjiang", new WinningStrategy(seed1));
Player player2 = new Player("Qiaoye", new ProbStrategy(seed2));
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
Hand nextHand1 = player1.nextHand();
Hand nextHand2 = player2.nextHand();
if (nextHand1.isStrongerThan(nextHand2)) {
System.out.println("Winner:" + player1);
player1.win();
player2.lose();
} else if (nextHand2.isStrongerThan(nextHand1)) {
System.out.println("Winner:" + player2);
player1.lose();
player2.win();
} else {
System.out.println("Even...");
player1.even();
player2.even();
}
}
System.out.println("Total result:");
System.out.println(player1.toString());
System.out.println(player2.toString());
}
}
main类负责让电脑进行猜拳游戏。Lianjiang和Qiaoye分别使用不同的策略进行了100局比赛。这里必须输入两个数作为随机数的种子,关于这一方面,目前还是不太理解,等到理解了再来解释。
Even...
Winner:[Qiaoye:1 games, 0 win, 0 lose]
Winner:[Lianjiang:2 games, 0 win, 1 lose]
Even...
Winner:[Qiaoye:4 games, 1 win, 1 lose]
Winner:[Lianjiang:5 games, 1 win, 2 lose]
Even...
Even...
Winner:[Lianjiang:8 games, 2 win, 2 lose]
Winner:[Lianjiang:9 games, 3 win, 2 lose]
Winner:[Lianjiang:10 games, 4 win, 2 lose]
Even...
Winner:[Qiaoye:12 games, 2 win, 5 lose]
Even...
Winner:[Lianjiang:14 games, 5 win, 3 lose]
Winner:[Qiaoye:15 games, 3 win, 6 lose]
Winner:[Qiaoye:16 games, 4 win, 6 lose]
Winner:[Lianjiang:17 games, 6 win, 5 lose]
Winner:[Qiaoye:18 games, 5 win, 7 lose]
Even...
Total result:
[Lianjiang:20 games, 7 win, 6 lose]
[Qiaoye:20 games, 6 win, 7 lose]
输出结果如上,进行了20局的结果。
Strategy模式类图如下:
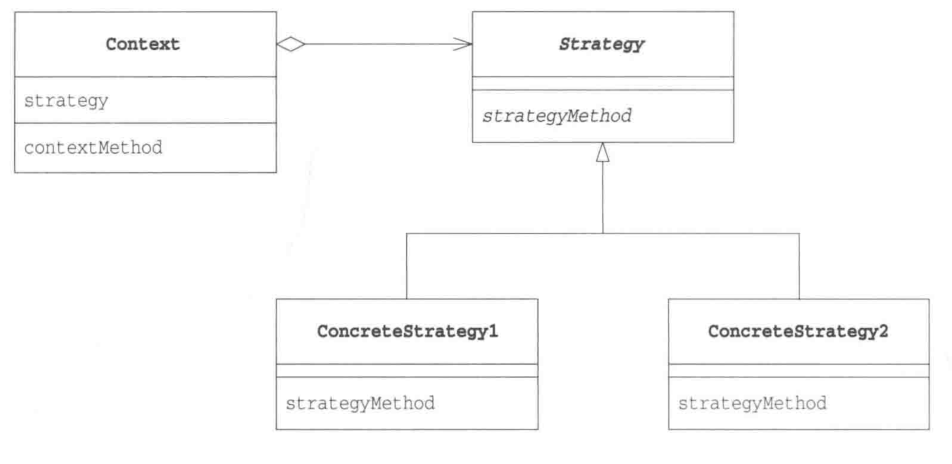
Strategy模式主要思想就是将算法与其他部分分离开,只定义了与算法相关的接口,然后在程序中以委托的方式来使用算法。使用委托这种弱关联关系可以很方便地整体替换算法,或者选择更好的算法在不同的环境下运行。
设计模式(十)Strategy模式的更多相关文章
- 设计模式之Strategy模式
策略模式属于对象的行为模式.其用意是针对一组算法,将每一个算法封装到具体的共同接口的独立类中,从而使得他们可以互相替换. 策略模式使得算法可以在不影响客户端的情况下发生变化. all in one “ ...
- 设计模式十: 生成器模式(Builder Pattern)
简介 生成器模式属于创建型模式的一种, 又叫建造者模式. 生成器模式涉及4个关键角色:产品(Product),抽象生成器(builder),具体生成器(ConcreteBuilder),指挥者(Dir ...
- 设计模式:strategy模式
思想:将算法进行抽象,然后使用桥接的模式使用算法的抽象接口,达到算法整体替换的目的 理解:和桥接模式相同,只是桥接的两边分开的思想不同 例子: class Algrithm //算法的抽象 { pub ...
- 【转】设计模式 ( 十八 ) 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型)
设计模式 ( 十八 ) 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型) 1.概述 在软件开发中也常常遇到类似的情况,实现某一个功能有多种算法或者策略,我们可以根据环境或者条件的不同选择不同的算法或者策略来完成 ...
- 设计模式 ( 十八 ) 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型)
设计模式 ( 十八 ) 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型) 1.概述 在软件开发中也经常遇到类似的情况,实现某一个功能有多种算法或者策略,我们能够依据环境或者条件的不同选择不同的算法或者策略来完毕 ...
- 设计模式 ( 十九 ) 模板方法模式Template method(类行为型)
设计模式 ( 十九 ) 模板方法模式Template method(类行为型) 1.概述 在面向对象开发过程中,通常我们会遇到这样的一个问题:我们知道一个算法所需的关键步骤,并确定了这些步骤的执行 ...
- 【转】设计模式 ( 十五 ) 中介者模式Mediator(对象行为型)
设计模式 ( 十五 ) 中介者模式Mediator(对象行为型) 1.概述 在面向对象的软件设计与开发过程中,根据"单一职责原则",我们应该尽量将对象细化,使其只负责或呈现单一的职 ...
- 设计模式:Strategy 策略模式 -- 行为型
设计模式 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型) 这是几年前写的文字(转载做的笔记更准确些),发觉还是废话多了点. 其实,核心就是5.结构中的UML图 5.1 和 5.2(新增).现在看这张图就觉得一 ...
- 设计模式 ( 十八 ):State状态模式 -- 行为型
1.概述 在软件开发过程中,应用程序可能会根据不同的情况作出不同的处理.最直接的解决方案是将这些所有可能发生的情况全都考虑到.然后使用if... ellse语句来做状态判断来进行不同情况的处理.但是对 ...
随机推荐
- java-newInstance()和new()
public <T> T genericMethod(Class<T> tClass)throws InstantiationException , IllegalAccess ...
- JAVA面试题 (一)
java作用域public private protected 不写-friendly的区别? public:可以被任何类引用. protected:除了其他包不能使用,当前类,子孙类,同一包下的所有 ...
- SpringBoot -> @Import使用
@Import 注解出自spring-context包中 package org.springframework.context.annotation; import java.lang.annota ...
- python爬虫遇到会话存储sessionStorage
记录一次爬虫生成链接过程中遇到的sessionStorage存储数据 1.简介 sessionStorage 是HTML5新增的一个会话存储对象,用于临时保存同一窗口(或标签页)的数据,在关闭窗口或标 ...
- Docker实战笔记命令篇
拉取一个镜像 docker pull ubuntu:14.04 查看系统中的镜像 docker images 运行镜像并进入 docker run -it ubuntu:14.04 查看运行的容器 d ...
- centos7.x 部署主、从DNS服务器
1.准备 例:两台192.168.219.146(主), 192.168.219.147(从), 域名www.panyangduola.com 主.从DNS服务器均需要安装bind.bind-chro ...
- java第3天:Scanner,Random,ArrayList
第一章:Scanner从入门到放弃 1 API的概述和使用步骤 API简称应用程序编程接口,是JDK给我们提供好的可以直接使用的类和方法,是程序员随手使用的字典. *** 2 Scanner的概述 2 ...
- Redis面试篇 -- Redis主从复制原理
Redis一般是用来支撑读高并发的,为了分担读压力,Redis支持主从复制.架构是主从架构,一主多从, 主负责写,并且将数据复制到其它的 slave 节点,从节点负责读. 所有的读请求全部走从 ...
- mysql引号与esc键下方键
navicat导出数据表发现建表语句如下: create table `product_category` ( `category_id` int not null auto_increment, ` ...
- Linux入门(服务)
LInux入门之 服务 服务介绍 常驻在内存中的程序,且可以提供一些系统或网络功能,那就是服务.比如: apache提供web服务 ftp提供文件下载上传服务 ssh提供了远程连接服务 防火墙提供了安 ...
