Bash基本功能
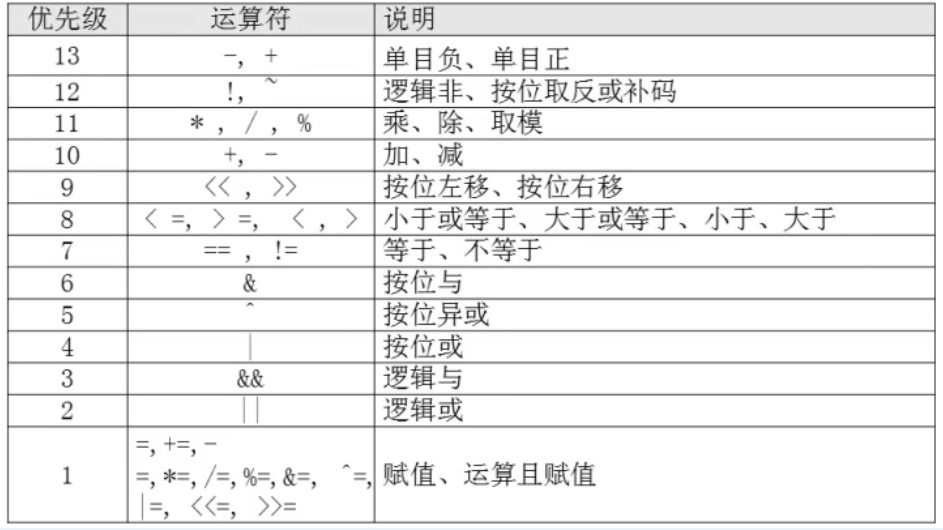
SHELL脚本编程的运算符
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
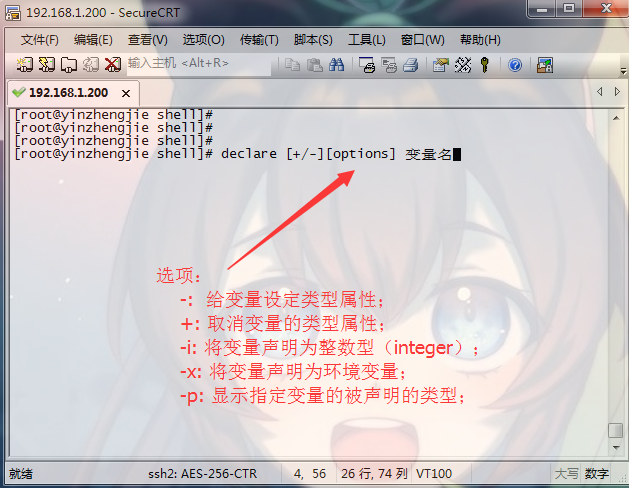
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# help let
let: let arg [arg ...]
Evaluate arithmetic expressions. Evaluate each ARG as an arithmetic expression. Evaluation is done in
fixed-width integers with no check for overflow, though division by
is trapped and flagged as an error. The following list of operators is
grouped into levels of equal-precedence operators. The levels are listed
in order of decreasing precedence. id++, id-- variable post-increment, post-decrement
++id, --id variable pre-increment, pre-decrement
-, + unary minus, plus
!, ~ logical and bitwise negation
** exponentiation
*, /, % multiplication, division, remainder
+, - addition, subtraction
<<, >> left and right bitwise shifts
<=, >=, <, > comparison
==, != equality, inequality
& bitwise AND
^ bitwise XOR
| bitwise OR
&& logical AND
|| logical OR
expr ? expr : expr
conditional operator
=, *=, /=, %=,
+=, -=, <<=, >>=,
&=, ^=, |= assignment Shell variables are allowed as operands. The name of the variable
is replaced by its value (coerced to a fixed-width integer) within
an expression. The variable need not have its integer attribute
turned on to be used in an expression. Operators are evaluated in order of precedence. Sub-expressions in
parentheses are evaluated first and may override the precedence
rules above. Exit Status:
If the last ARG evaluates to , let returns ; let returns otherwise.
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
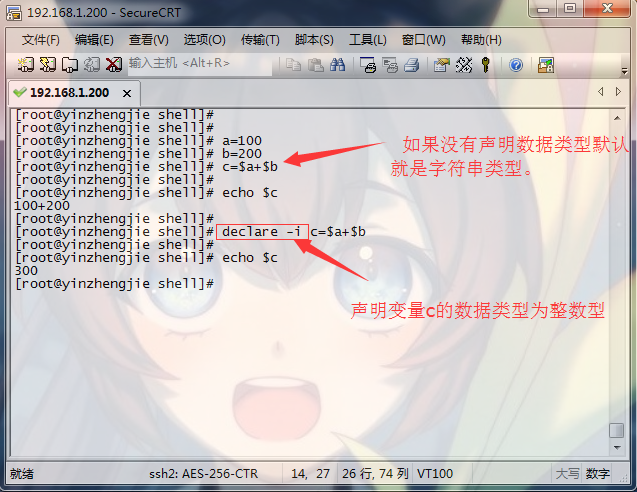
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# help let
+, -, *, /, %取模(取余), **(乘方),乘法符号有些场景中需要转义。 实现算术运算:
() let var=算术表达式
() var=$[算术表达式]
() var=$((算术表达式))
() var=$(expr arg1 arg2 arg3 ...)
() declare –i var = 数值
() echo ‘算术表达式’ | bc 增强型赋值:
+=, -=, *=, /=, %= let varOPERvalue
例如:let count+=
自加3后自赋值 自增,自减:
let var+=
let var++
let var-=
let var--
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# x=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# y=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# let num=$x*$y
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $num
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# let num=x*y
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $num
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $[x-y]
-
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $[x**y]
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $[y%x]
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# i=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $i [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# ((i++)) #等价于i=i+,表示要先使用i变量后,在对其进行加1操作。
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $i [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# unset i
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# m=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# let ++m #在循环中使用会需要先对m变量进行加1在使用它。
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $m [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $x [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $y [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# expr $x \* $y [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# declare -i m=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# declare -i n=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# declare -i num=m+n
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $num [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo "100 * 2" | bc [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# x=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# let x+=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $x [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# let x-=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $x [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# let x/= #不支持浮点数,因此除等得到的值只能取整数。
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $x [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
算术运算符测试案例
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# man bash #保存了BASH中默认存在的变量,RANDOM只是其中之一。
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $RANDOM [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $RANDOM [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $RANDOM #默认生成 - 之间随机数 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $[$RANDOM%] #生成 - 之间随机数 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $[$RANDOM%] [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $[$RANDOM%] [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#


()编写脚本 sumid.sh,计算/etc/passwd文件中的第10个用户和第20用户的UID之和
()编写脚本 sumspace.sh,传递两个文件路径作为参数给脚本,计算这两个文件中所有空白行之和
()编写脚本 sumfile.sh,统计/etc, /var, /usr 目录中共有多少个一级子目录和文件
与运算只能是二进制的操作,任何数和0相与,结果为0,任何数和1相与,保留原值。 举例,请将十进制的12和8进行与运算。
首先将12和8转换成二进制,如下所示:
------> 0b0000
------> 0b0000
得到的最终结果为:0b0000 ,即12&=。
与运算只能是二进制的操作,两个数字只要有1,结果为1,两个书数字都为0,结果才为0。 举例,请将十进制的12和8进行或运算。
首先将12和8转换成二进制,如下所示:
------> 0b0000
------> 0b0000
得到的最终结果为:0b0000 ,即12|=。
非操作就是取反,如:
!1 = 0,即1(true)的非为0(false)。
!0 = 1,即0(false)的非为1(true)。
短路与(&&):
举例:我们将0表示为假,1表示为真,则有以下关系:
假与真=假(&&=)
假与假=假(&&=)
真与真=真(&&=)
真与假=假(&&=)
总结:
CMD1 && CMD2
如果与前面的CMD1执行是假,结果必定是假,没有必要执行与后的操作CMD2。反之,则CMD2要参加运算。 短路或(||):
举例:我们将0表示为假,1表示为真,则有以下关系:
真或真=真(||=)
真或假=真(||=)
假或真=真(||=)
假或假=假(||=) 总结:
CMD1 || CMD2
如果或前面的CMD1执行结果是真,结果必定是真,没有必要执行或后的操作CMD2。反正,则CMD2要参与运算。
举例:我们将0表示为假,1表示为真,则有以下关系:
假异或假=假(^=)
假异或真=真(^=)
真异或假=真(^=)
真异或真=假(^=) 总结:
异或的两个值,相同为假,不同为真。 小试牛刀:请将十进制的12和8进行异或运算。
首先将12和8转换成二进制,如下所示:
------> 0b0000
------> 0b0000
得到的最终结果为:0b0000 0,即12^=4。由此可迅速推断出4^8=12,4^12=8。
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# x=;y=;tmp=$x;x=$y;y=$tmp;echo x=$x,y=$y #借助于中间变量
x=,y=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# x=;y=;x=$[x^y];y=$[x^y];x=$[x^y];echo x=$x,y=$y #借助于异或运算,效率更好,因为是基于二进制的。
x=,y=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
变量互换案例(将x=100,y=200变为y=100,x=200)
Bash基本功能的更多相关文章
- 鸟哥的私房菜:Bash shell(一)-Bash shell功能简介
Bash shell系列里,由变量谈起,先讲到环境变量的功能与修改的问题, 然后会继续提到历史指令的运用.接下来,就会谈一下『数据流重导向』这个重要概念, 最后就是管线命令的利用! 一 Bash s ...
- 6.Bash的功能
6.Bash的功能本章介绍 Bash 的特色功能.6.1 Bash的启动 bash [长选项] [-ir] [-abefhkmnptuvxdBCDHP] [-o 选项] [-O shopt 选项] [ ...
- Linux学习笔记(15)shell基础之Bash基本功能
1 shell概述 shell是一个命令解释器,为用户提供了一个向Linux内核发送请求以便运行程序的界面系统级程序.用户可以用shell启动.挂起.停止甚至是编写一些程序. shell是一个功能强大 ...
- Linux系列教程(二十一)——Linux的bash基本功能
上篇博客我们介绍了什么是shell,以及编写shell脚本的两种执行方式.我们知道在敲命令的时候,有很多快捷键,比如tab键能补全命令,在比如为什么我们直接敲 ll 命令能显示目录的长格式,其实这是b ...
- bash 基本功能
1 shell概述 shell是一个命令解释器,为用户提供了一个向Linux内核发送请求以便运行程序的界面系统级程序.用户可以用shell启动.挂起.停止甚至是编写一些程序. shell是一个功能强大 ...
- 『忘了再学』Shell基础 — 4、Bash基本功能(history命令)
目录 1.history历史命令 2.设置命令历史记录的条数 3.清空历史命令 4.历史命令的调用 5.命令与文件的补全 在Linux系统中默认的Shell就是Bourne-AgainShell(简称 ...
- linux笔记:shell基础-bash基本功能
历史命令的调用: 命令和文件补全(如果当前有多个可选的补全,则按2次tab键,可以列出所有的可选项): 命令别名: 让别名永久生效: 删除别名: bash常用快捷键: 标准输入输出: 输出重定向: 输 ...
- Linux学习 -- Shell基础 -- Bash基本功能
历史命令 history -c clear -w 写入 ~/.bash_history 默认保存1000条, 可在/etc/profile中修改 调用 Tab补全 命令.目录.文件 命令别名 ...
- Shell基础 - Bash基础功能
历史命令 history选项: -c 清空历史命令 -w 立即保存历史命令Linux 下输入过的历史命令,都会保存在根目录下的:~/root/.bash_history 文件中默认保存 1000 条, ...
随机推荐
- Find Amir CodeForces - 805C (贪心+思维)
A few years ago Sajjad left his school and register to another one due to security reasons. Now he w ...
- 变更RHEL(Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.8)更新源使之自动更新
HP 4411s Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.8) pick up from http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-423637-id- ...
- PS(光影魔术手)
完成
- pandas获取当前时间
datetime.now()用于获取当前的日期和时间 print pd.datetime.now() #encoding:utf8 import pandas as pd print("(p ...
- WPF将数据库和GridView绑定并更改GridView模板
首先来看一下如何使用GridView,在前台的话代码如下:这里仅仅举出一个例子,GridView是作为子项嵌套在ListView中的,这里的数据源是通过绑定的方式来绑定到GridView中的. < ...
- python之小应用:读取csv文件并处理01数据串
目的:读取csv文件内容,把0和1的数据串取出来,统计出现1的连续次数和各次数出现的频率次数 先读取csv文件内容: import csv def csv_read(file): list = [] ...
- Django-website 程序案例系列-9 分页
分页例子程序: LIST = [] #全局列表 for i in range(103): #1:100的列表 LIST.append(i) def user_list(request): curren ...
- BZOJ1045 HAOI2008糖果传递(贪心)
显然最后每个小朋友所拥有的糖果数就是糖果数总和的平均数.设该平均数为t. 环的问题一般断成链,但这个题似乎没有什么很好的办法在枚举断点的时候快速算出答案(我甚至不知道会不会有断点) 于是我们假装把他断 ...
- MT【216】韦达定理
设$n$为正整数,$a_1,a_2,\cdots,a_n;b_1,b_2,\cdots,b_n;A,B$都是正数, 满足$a_i\le b_i,a_i\le A,i=1,2,\cdots,n$ 且$\ ...
- MT【38】与砝码有关的两个题
此题只适合1%的优秀学生阅读: 北京大学2017中学生数学奖个人能力挑战赛第四题(最后一题) 解析:第一问: 第二问,略,答案也是147. 类似的: 评:1.北大的题用了2进制,后面的这题用了三进制, ...
