SVM实现邮件分类
首先学习一下svm分类的使用。
主要有以下步骤:
- Loading and Visualizing Dataj
- Training Linear SVM
- Implementing Gaussian Kernel
- Training SVM with RBF Kernel
- 选择最优的C, sigma参数
- 画出边界线
线性keneral实现
C = 1;
model = svmTrain(X, y, C, @linearKernel, 1e-3, 20);
visualizeBoundaryLinear(X, y, model);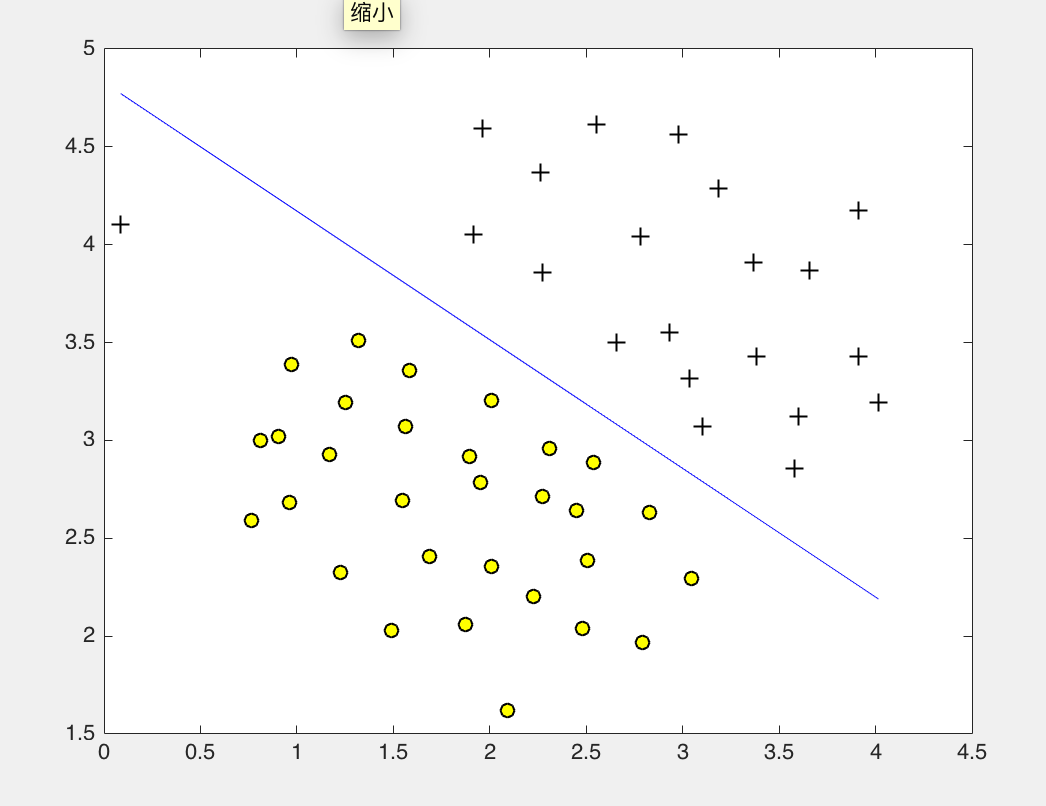
高斯keneral实现
function sim = gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma)
x1 = x1(:); x2 = x2(:);
sim = 0;
sim = exp( - (x1-x2)'* (x1-x2) / (2 * sigma *sigma ) );
end
load('ex6data2.mat');
% SVM Parameters
C = 1; sigma = 0.1;
% We set the tolerance and max_passes lower here so that the code will run
% faster. However, in practice, you will want to run the training to
% convergence.
model= svmTrain(X, y, C, @(x1, x2) gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma));
visualizeBoundary(X, y, model);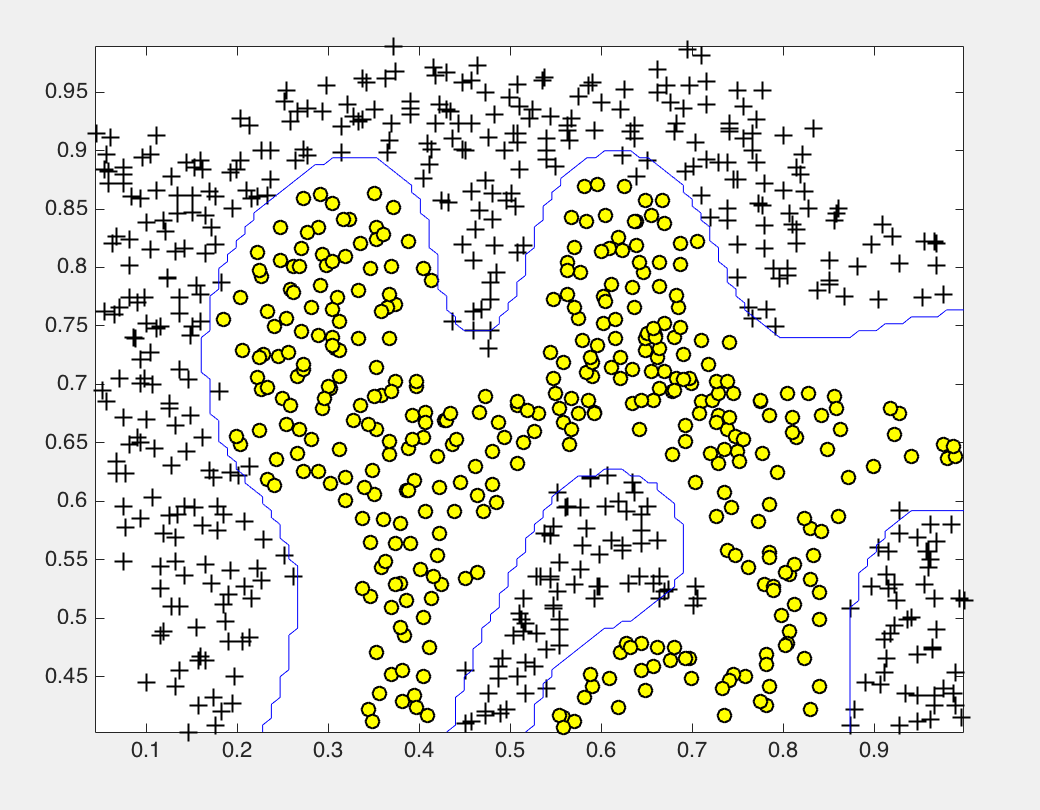
选择合适的参数
function [C, sigma] = dataset3Params(X, y, Xval, yval)
C = 1;
sigma = 0.3;
C_vec = [0.01 0.03 0.1 0.3 1 3 10 30]';
sigma_vec = [0.01 0.03 0.1 0.3 1 3 10 30]';
error_val = zeros(length(C_vec),length(sigma_vec));
error_train = zeros(length(C_vec),length(sigma_vec));
for i = 1:length(C_vec)
for j = 1:length(sigma_vec)
model= svmTrain(X, y, C_vec(i), @(x1, x2) gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma_vec(j)));
predictions = svmPredict(model, Xval);
error_val(i,j) = mean(double(predictions ~= yval));
end
end
% figure
% error_val
% surf(C_vec,sigma_vec,error_val) % 画出三维图找最低点
[minval,ind] = min(error_val(:)); % 0.03
[I,J] = ind2sub([size(error_val,1) size(error_val,2)],ind);
C = C_vec(I) % 1
sigma = sigma_vec(J) % 0.100
% [I,J]=find(error_val == min(error_val(:)) ); % 另一种方式找最小元素位子
% C = C_vec(I) % 1
% sigma = sigma_vec(J) % 0.100
end
[C, sigma] = dataset3Params(X, y, Xval, yval);
% Train the SVM
model= svmTrain(X, y, C, @(x1, x2) gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma));
visualizeBoundary(X, y, model);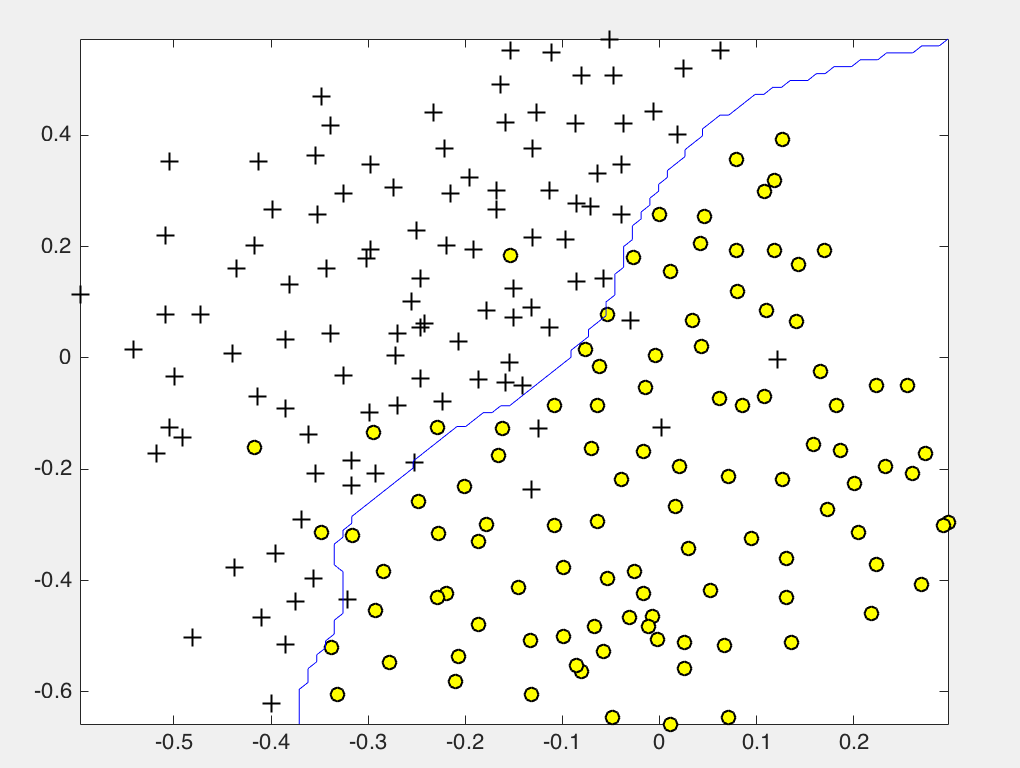
邮件分类
主要步骤如下:
- 邮件数据归一化处理
- 特征提取
- Train Linear SVM for Spam Classification
- Test Spam Classification
- Top Predictors of Spam
- 测试自己的email
归一化处理
In processEmail.m, we have implemented the following email prepro- cessing and normalization steps:
- Lower-casing: The entire email is converted into lower case, so that captialization is ignored (e.g., IndIcaTE is treated the same as Indicate).
- Stripping HTML: All HTML tags are removed from the emails. Many emails often come with HTML formatting; we remove all the HTML tags, so that only the content remains.
- Normalizing URLs: All URLs are replaced with the text “httpaddr”.
- Normalizing Email Addresses: All email addresses are replaced
with the text “emailaddr”. - Normalizing Numbers: All numbers are replaced with the text
“number”. - Normalizing Dollars: All dollar signs ($) are replaced with the text
“dollar”. - Word Stemming: Words are reduced to their stemmed form. For ex- ample, “discount”, “discounts”, “discounted” and “discounting” are all replaced with “discount”. Sometimes, the Stemmer actually strips off additional characters from the end, so “include”, “includes”, “included”, and “including” are all replaced with “includ”.
- Removal of non-words: Non-words and punctuation have been re- moved. All white spaces (tabs, newlines, spaces) have all been trimmed to a single space character.
处理之后效果如下:
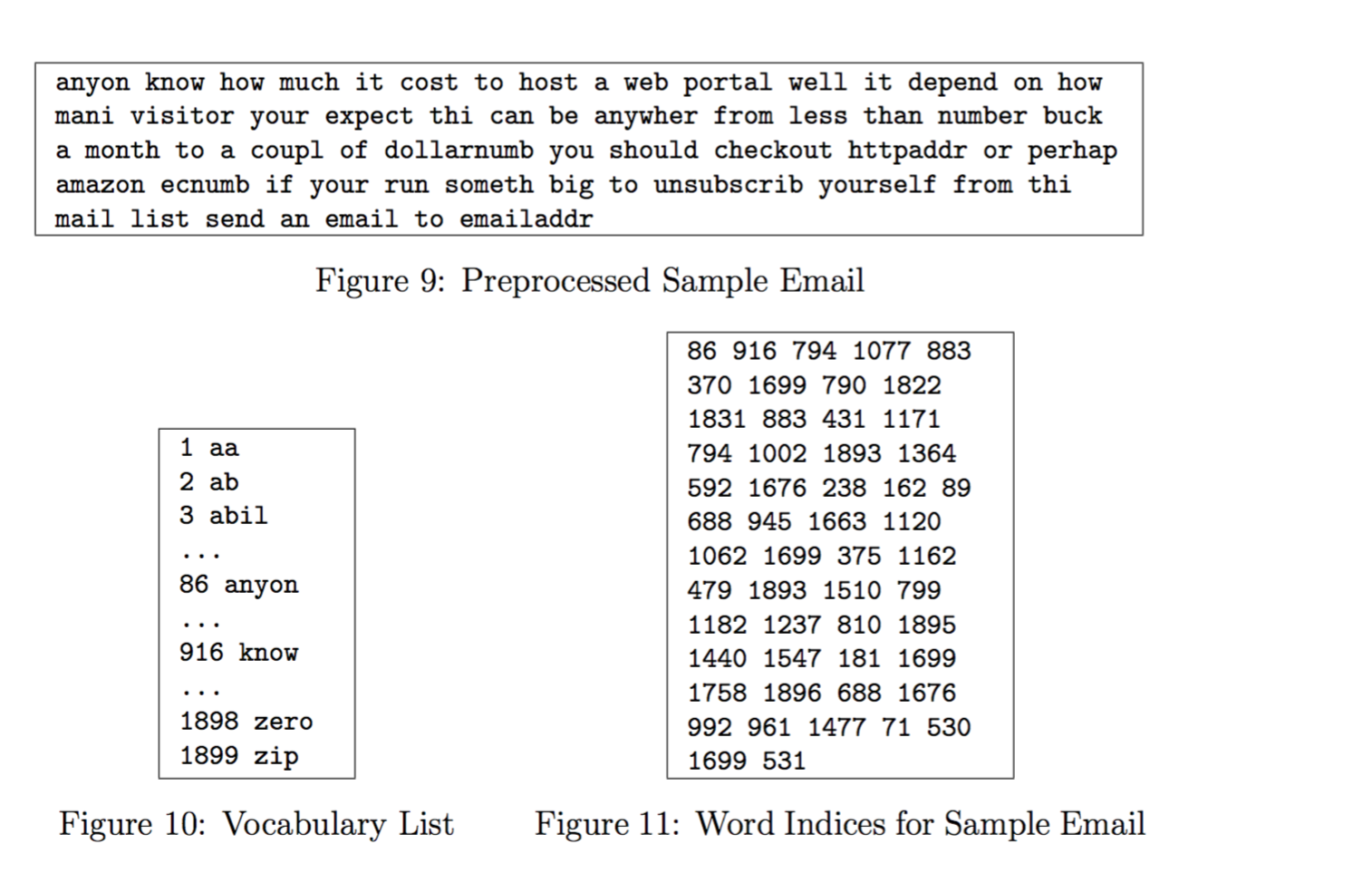
Vocabulary List
我们取垃圾邮件中最常见的单词放入单词表中。
Our vocabulary list was selected by choosing all words which occur at least a 100 times in the spam corpus, resulting in a list of 1899 words. In practice, a vocabulary list with about 10,000 to 50,000 words is often used.
将我们邮件中有的单词在单词表中的id存储在word_indices中
for i=1:length(vocabList)
if( strcmp(vocabList{i}, str) )
word_indices = [word_indices;i];
end
endExtracting Features from Emails
然后查找我们的邮件中的单词在单词表中的位置,有则置1,无则跳过。
You should look up the word in the vocabulary list vocabList and find if the word exists in the vocabulary list. If the word exists, you should add the index of the word into the word indices variable. If the word does not exist, and is therefore not in the vocabulary, you can skip the word.
function x = emailFeatures(word_indices)
% Total number of words in the dictionary
n = 1899;
% You need to return the following variables correctly.
x = zeros(n, 1);
x(word_indices) = 1;
endTraining SVM for Spam Classification
load('spamTrain.mat');
fprintf('\nTraining Linear SVM (Spam Classification)\n')
fprintf('(this may take 1 to 2 minutes) ...\n')
C = 0.1;
model = svmTrain(X, y, C, @linearKernel);
p = svmPredict(model, X);
fprintf('Training Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
%% =================== Part 4: Test Spam Classification ================
load('spamTest.mat');
fprintf('\nEvaluating the trained Linear SVM on a test set ...\n')
p = svmPredict(model, Xtest);
fprintf('Test Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == ytest)) * 100);After loading the dataset, ex6 spam.m will proceed to train a SVM to classify between spam (y = 1) and non-spam (y = 0) emails. Once the training completes, you should see that the classifier gets a training accuracy of about 99.8% and a test accuracy of about 98.5%.
Top Predictors for Spam
找出最易被判断为垃圾邮件的单词。
[weight, idx] = sort(model.w, 'descend');
vocabList = getVocabList();
fprintf('\nTop predictors of spam: \n');
for i = 1:15
fprintf(' %-15s (%f) \n', vocabList{idx(i)}, weight(i));
end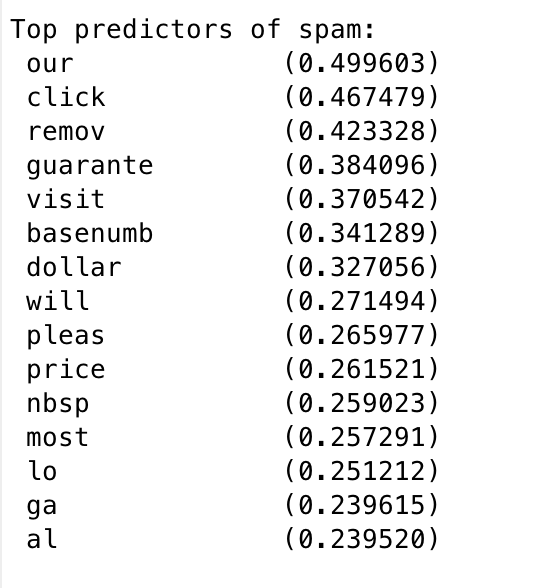
Try your own emails
filename = 'spamSample1.txt';
% Read and predict
file_contents = readFile(filename);
word_indices = processEmail(file_contents);
x = emailFeatures(word_indices);
p = svmPredict(model, x);
fprintf('\nProcessed %s\n\nSpam Classification: %d\n', filename, p);
fprintf('(1 indicates spam, 0 indicates not spam)\n\n');可以看出我们的邮件判断准确率大概在98%左右。
SVM实现邮件分类的更多相关文章
- 基于SKLearn的SVM模型垃圾邮件分类——代码实现及优化
一. 前言 由于最近有一个邮件分类的工作需要完成,研究了一下基于SVM的垃圾邮件分类模型.参照这位作者的思路(https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40186809/article/det ...
- Bert模型实现垃圾邮件分类
近日,对近些年在NLP领域很火的BERT模型进行了学习,并进行实践.今天在这里做一下笔记. 本篇博客包含下列内容: BERT模型简介 概览 BERT模型结构 BERT项目学习及代码走读 项目基本特性介 ...
- Atitit 贝叶斯算法的原理以及垃圾邮件分类的原理
Atitit 贝叶斯算法的原理以及垃圾邮件分类的原理 1.1. 最开始的垃圾邮件判断方法,使用contain包含判断,只能一个关键词,而且100%概率判断1 1.2. 元件部件串联定律1 1.3. 垃 ...
- CNN实现垃圾邮件分类(行大小不一致要补全)
以下是利用卷积神经网络对某一个句子的处理结构图 我们从上图可知,将一句话转化成一个矩阵.我们看到该句话有6个单词和一个标点符号,所以我们可以将该矩阵设置为7行,对于列的话每个单词可以用什么样的数值表示 ...
- Python之机器学习-朴素贝叶斯(垃圾邮件分类)
目录 朴素贝叶斯(垃圾邮件分类) 邮箱训练集下载地址 模块导入 文本预处理 遍历邮件 训练模型 测试模型 朴素贝叶斯(垃圾邮件分类) 邮箱训练集下载地址 邮箱训练集可以加我微信:nickchen121 ...
- 利用朴素贝叶斯(Navie Bayes)进行垃圾邮件分类
贝叶斯公式描写叙述的是一组条件概率之间相互转化的关系. 在机器学习中.贝叶斯公式能够应用在分类问题上. 这篇文章是基于自己的学习所整理.并利用一个垃圾邮件分类的样例来加深对于理论的理解. 这里我们来解 ...
- 垃圾邮件分类实战(SVM)
1. 数据集说明 trec06c是一个公开的垃圾邮件语料库,由国际文本检索会议提供,分为英文数据集(trec06p)和中文数据集(trec06c),其中所含的邮件均来源于真实邮件保留了邮件的原有格式和 ...
- 8.SVM用于多分类
从前面SVM学习中可以看出来,SVM是一种典型的两类分类器.而现实中要解决的问题,往往是多类的问题.如何由两类分类器得到多类分类器,就是一个值得研究的问题. 以文本分类为例,现成的方法有很多,其中一劳 ...
- SVM实现多分类的三种方案
SVM本身是一个二值分类器 SVM算法最初是为二值分类问题设计的,当处理多类问题时,就需要构造合适的多类分类器. 目前,构造SVM多类分类器的方法主要有两类 (1)直接法,直接在目标函数上进行修改,将 ...
随机推荐
- [转]Eclipse Debug不为人知的秘密
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/mgoann/article/details/7239492 Debug视图 认识debug视图,红色部分框为线程堆栈视图,黄色部分框为表达式.断点 ...
- C#-WinForm-MDI窗体容器、权限设置
MDI窗体容器 - 放窗体的容器 窗体时顶级控件,是不允许放到其他的控件或窗体中的 (李献策lxc) 窗体属性中有一个属性:IsMdiContainer - 确定该窗体是否是MDI容器 在窗体中放一个 ...
- Python学习笔记 之 递归、二维数组顺时针旋转90°、正则表达式
递归.二维数组顺时针旋转90°.正则表达式 1. 递归算法是一种直接或间接调用自身算法的过程. 特点: 递归就是在过程或函数里调用自身 明确的递归结束条件,即递归出口 简洁,但是不提倡 递归次数多 ...
- 移动端浏览器和微信浏览器上禁止body的滚动条
一般禁止body滚动的做法就是设置overflow:hidden. 但是很奇怪的发现在移动端浏览器和微信浏览器上这个不起作用,然后我分析了我的写法,就是在body上加了一个class去定义属性,然后改 ...
- poj1006Biorhythms(同余定理)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/dongfengkuayue/article/details/6461298 本文转自head for better博客,版权归其所有,代码系本人自己编 ...
- WEKA使用
参考 http://bbs.middleware123.com/thread-24052-1-1.html 使用Weka进行数据挖掘 http://quweiprotoss.blog.163.com ...
- java 判断String 是否为空
StringUtils.isBlank(null) = true StringUtils.isBlank("") = true StringUtils.isBlank(" ...
- android md5加密与rsa加解密实现代码
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;import java.security.MessageDigest;import java.security. ...
- QQ等级表
什么是QQ等级呢? 2003年,腾讯公司推出了QQ等级制度 . 最早是以小时,来计算的,那段时间,绝大部分QQ用户都在挂QQ,之后就有不少媒体指责其浪费能源,在有关部门的介入下,腾讯公司将QQ等级变为 ...
- Windows中创建桌面快捷方式
Windows中创建桌面快捷方式 -------------- -------------- -------------- --------------
