cs224d 作业 problem set2 (一) 用tensorflow纯手写实现sofmax 函数,线性判别分析,命名实体识别
Hi Dear
Today we will use tensorflow to implement the softmax regression and linear classifier algorithm.
not using the library of tensorflow (like tf.nn.softmax),
but using tensorflow simple function to implement the softmax.
The whole structure of the network is the shown blow:
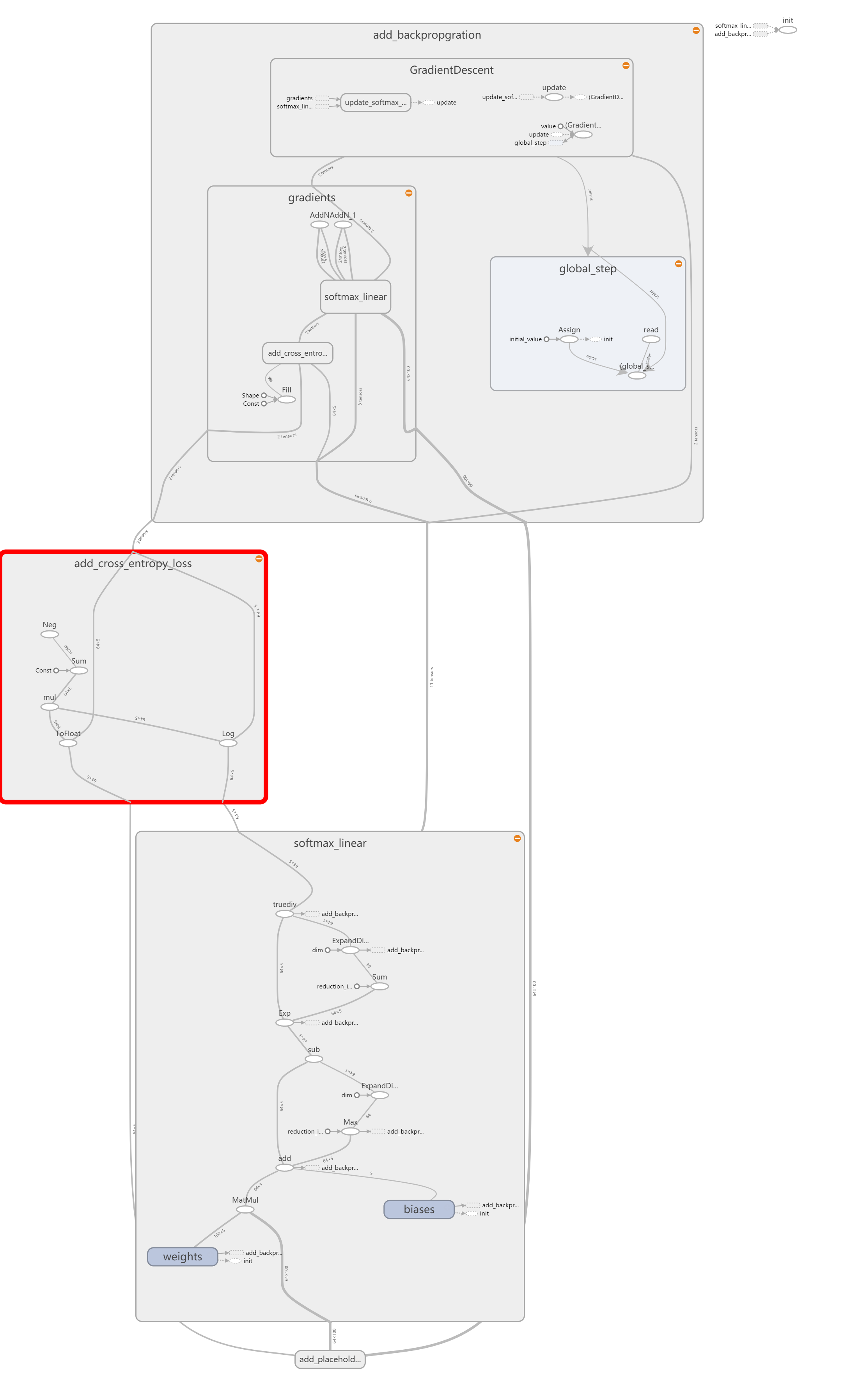
so first let us take a look at the softmax function.I think it's so easy.
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def softmax(x):
"""
tensorflow 版本的softmax函数
compute the softmax function in tensorflow
interal functions may be used:
tf.exp,tf.reduce_max,tf.reduce_sum,tf.expend_dims
Args:
x:tf.Tensor with shape (n_samples,n_features)
feature vectors are represented by row-vectors (no need to handle 1-d
input as in the previous homework)
Returns:
out:tf.Tensor with shape (n_sample,n_features). You need to construct
this tensor in this problem
""" # tf.reduce_max沿着tensorflow的某一维度计算元素的最大值
# tf.reduce_sum沿着tensorflow的某一维度计算元素的和
# tf.expand_dims在tensorflow的某一维度插入一个tensor
maxes = tf.expand_dims(tf.reduce_max(x, reduction_indices=[1]), 1)
x_red = x - maxes
x_exp = tf.exp(x_red)
sums = tf.expand_dims(tf.reduce_sum(x_exp, reduction_indices=[1]), 1)
out = x_exp / sums return out
Then here goes the cross-entropy to calculate the loss
def cross_entropy_loss(y, yhat):
"""
计算交叉熵在tensorflow中
y是一个one-hot tensor 大小是(n_samples,n_classes)这么大,类型是tf.int32
yhat是一个tensor 大小是(n_samples,n_classes) 类型是 tf.float32
function:
tf.to_float,tf.reduce_sum,tf.log可能会用到
参数:
y:tf.Tensor with shape(n_samples,n_classes) One-hot encoded
yhat: tf.Tensorwith shape (n_samples,n_classes) Each row encodes a
probability distribution and should sum to 1
返回:
out: tf.Tensor with shape(1,) (Scalar output).You need to construct
this tensor in the problem.
"""
y = tf.to_float(y)
out = -tf.reduce_sum(y * tf.log(yhat))
return out
after the two previous implementation,we will test our function in the following code
def test_softmax_basic():
"""
Some simple tests to get you started.
Warning: these are not exhaustive
"""
print("Running basic tests...")
test1 = softmax(tf.convert_to_tensor(np.array([[1001, 1002], [3, 4]]), dtype=tf.float32))
with tf.Session():
test1 = test1.eval()
assert np.amax(np.fabs(test1 - np.array([0.26894142, 0.73105858]))) <= 1e-6
test2 = softmax(tf.convert_to_tensor(np.array([[-1001, -1002]]), dtype=tf.float32))
with tf.Session():
test2 = test2.eval()
assert np.amax(np.fabs(test2 - np.array([0.73105858, 0.26894142]))) <= 1e-6
print("Basic (non-exhaustive) softmax tests pass\n") def test_cross_entropy_loss_basic():
"""
Some simple tests to get you started
Warning: these are not exhaustive.
"""
y = np.array([[0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 0]])
yhat = np.array([[.5, .5], [.5, .5], [.5, .5]]) test1 = cross_entropy_loss(tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32),
tf.convert_to_tensor(yhat, dtype=tf.float32))
with tf.Session():
test1 = test1.eval()
result = -3 * np.log(.5)
assert np.amax(np.fabs(test1 - result)) <= 1e-6
print("Basic (non-exhaustive) cross-entropy tests pass\n") if __name__ == "__main__":
test_softmax_basic()
test_cross_entropy_loss_basic()
in the end let's take a look at the log
Running basic tests...
2017-09-21 20:41:46.031587: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 20:41:46.032109: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE2 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 20:41:46.032409: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE3 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 20:41:46.033081: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE4.1 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 20:41:46.033489: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE4.2 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 20:41:46.033870: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use AVX instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 20:41:46.034304: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use AVX2 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 20:41:46.034710: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use FMA instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 20:41:46.759599: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:887] Found device 0 with properties:
name: GeForce 940MX
major: 5 minor: 0 memoryClockRate (GHz) 1.189
pciBusID 0000:01:00.0
Total memory: 2.00GiB
Free memory: 1.66GiB
2017-09-21 20:41:46.760018: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:908] DMA: 0
2017-09-21 20:41:46.760183: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:918] 0: Y
2017-09-21 20:41:46.760640: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:977] Creating TensorFlow device (/gpu:0) -> (device: 0, name: GeForce 940MX, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0)
2017-09-21 20:41:46.944591: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:977] Creating TensorFlow device (/gpu:0) -> (device: 0, name: GeForce 940MX, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0)
Basic (non-exhaustive) softmax tests pass 2017-09-21 20:41:46.977580: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:977] Creating TensorFlow device (/gpu:0) -> (device: 0, name: GeForce 940MX, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0)
Basic (non-exhaustive) cross-entropy tests pass
you see the function successfully pass the test.
Second we comes to the linear classifier function
1、we defined a basic config of the training parameter
import time from model import Model
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tf_softmax import cross_entropy_loss
from tf_softmax import softmax
from utils import data_iterator class Config(object):
"""
Holds model hyperparams and data information
The config class is used to store various hyperparameters and dataset
information parameters.
Model objects are passed a Config() object at instantiation.
"""
batch_size = 64 #how many data we train in one forward and backward process
n_samples = 1024 #the total number of our data
n_features = 100 #one data can have 100 dimension feature
n_classes = 5 #total there are 5 classes in deed for us to classified
#You may adjust the max_epochs to ensure Convergence
max_epochs = 50
#You may adjust this learning rate to ensure convergence.
lr = 1e-4
2、then we defined our a class called softmax for us to train,which include functions of
load_data, :load the trainning data
add_placeholders,:define the input and output data
create_feed_dict,:receive the input and output data
add_training_op,:set the goal of our trainning and select the optimizer function
add_model, :do forward calculation
add_loss_op, :add cross-entropy function to our model
run_epoch, :how many times we run our model forward and backward each time with batch_size of data
fit, :in this function we evaluate our model and calculate the total loss
__init__ :the construction of our class in this function we call the above function in correct order.to construct the model
load_data
class SoftmaxModel(Model):
"""实现一个softmax 交叉熵分类器"""
def load_data(self):
"""创建一个预测数据集,并且在内存中储存它"""
np.random.seed(1234)
self.input_data = np.random.rand(self.config.n_samples,self.config.n_features)
self.input_labels = np.ones((self.config.n_samples,), dtype=np.int32)
add_placeholders
def add_placeholders(self):
"""生成 placeholder 变量来呈现输入的 tensor
这些 placeholders 是被用做输入,
在建立别的模型的时候还可以用到,
在训练的过程中可以对其填入数据
input_placeholder:Input placeholder :tensor of shape (batch_size,n_features),type tf.float32
labels_placeholder:Labels placeholder tensor of shape (batch_size,n_classes),type tf.int32
Add these placeholders to self as the instance variables
self.input_placeholder
self.labels_placeholder
(Don't change the variable names)
"""
self.input_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(self.config.batch_size,self.config.n_features))
self.labels_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=(self.config.batch_size,self.config.n_classes))
create_feed_dict
def create_feed_dict(self,input_batch,label_batch):
"""为softmax classifier创建feed_dict"""
feed_dict={
self.input_placeholder:input_batch,
self.labels_placeholder:label_batch,
}
return feed_dict
add_training_op
def add_training_op(self,loss):
"""设置训练目标,创建一个优化器,应用梯度下降到所有的训练变量上面
Args:
loss:Loss tensor,from cross_entropy_loss
Returns:
train_op:The Op for training
"""
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(self.config.lr)
global_step = tf.Variable(0,name='global_step',trainable=False)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss,global_step=global_step)
return train_op
add_model
def add_model(self,input_data):
"""添加一个线性层,增加一个softmax变换
y = softmax(xW+b)
Hint:make sure to create tf.Variables as needed
also make sure to use tf.name_scope to ensure that your name
spaces are clean
Hint:For this simple use-case, it's sufficient to initialize both
weights W and biases b with zeros
Args:
input_data:A tensor of shape (batch_size,n_features)
Returns:
out: A tensor of shape (batch_size,n_classes)
"""
n_features,n_classes = self.config.n_features,self.config.n_classes
with tf.name_scope('softmax_linear'):
weights = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n_features,n_classes]),name='weights')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n_classes]),name='biases')
#矩阵乘法,不是内积
logits = tf.matmul(input_data,weights)+biases
out = softmax(logits)
return out
add_loss_op
def add_loss_op(self,pred):
"""将交叉熵损失添加到目标的损失函数上
Hint: use the cross_entropy_loss function we defined. This should be a very
short function.
Args:
pred: A tensor of shape (batch_size,n_classes)
Returns:
loss: A 0-d tensor (scalar)
"""
loss = cross_entropy_loss(self.labels_placeholder, pred)
return loss
run_epoch
def run_epoch(self,sess,input_data,input_labels):
"""运行一段epoch大小数据的训练
Trains the model for one-epoch
Args:
sess:tf.Session() object
input_data : np.ndarray of shape (n_samples,n_features)
input_labels : np.ndarray of shape (n_samples,n_classes)
Returns:
average_loss : scalar . Average minibatch loss of model on epoch
"""
#And then after everything is built , start the training loop.
average_loss = 0
for step,(input_batch,label_batch) in enumerate(
data_iterator(input_data,input_labels,
batch_size=self.config.batch_size,
label_size=self.config.n_classes)):
#Fill a feed dictionary with the actual set of images and labels
#for this particular training step
feed_dict = self.create_feed_dict(input_batch, label_batch) #Run one step of the model. The return values are the activations
#from the 'self.train_op' (which is discard) and the 'loss' Op.
#To inspect the values of your Ops or variables, you may include then
#in the list passed to sess.run() and the value tensors will be
#returned in the tuple from the call.
_,loss_value = sess.run([self.train_op,self.loss],feed_dict=feed_dict)
average_loss += loss_value
average_loss = average_loss / step
return average_loss
fit
def fit(self,sess,input_data,input_labels):
"""Fit model on provided data
Args:
sess:tf.Session()
input_data : np.ndarray of shape (n_samples,n_features)
input_labels : np.ndarray of shape (n_samples,n_classes)
Returns:
losses: list of loss per epoch
"""
losses = []
for epoch in range(self.config.max_epochs):
start_time = time.time()
average_loss = self.run_epoch(sess, input_data, input_labels)
duration = time.time() - start_time
#Print status to stdout
print('Epoch %d: loss = %.2f (%3.f sec)'%(epoch,average_loss,duration))
losses.append(average_loss)
return losses
__init__
def __init__(self,config):
"""Initializes the model.
Args:
config:A model configuration object of type Config
"""
self.config = config
#Generate placeholders for the images and labels
self.load_data()
self.add_placeholders()
self.pred = self.add_model(self.input_placeholder)
self.loss = self.add_loss_op(self.pred)
self.train_op = self.add_training_op(self.loss)
test_SoftmaxModel 测试softmax模型
def test_SoftmaxModel():
"""Train softmax model for a number of steps."""
config = Config()
with tf.Graph().as_default():
model = SoftmaxModel(config) #create a session for running Ops on the Graph
sess = tf.Session() #Run the Op to initialize the variables
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init) losses = model.fit(sess, model.input_data, model.input_labels)
#If ops are implemented correctly, the average loss should fall close to zero
#repidly
assert losses[-1]<.5
print("Basic (non-exhaustive) classifier tests pass\n")
最后是程序入口
if __name__=="__main__":
test_SoftmaxModel()
下面是训练的log
2017-09-21 21:42:00.292713: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 21:42:00.293137: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE2 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 21:42:00.293493: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE3 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 21:42:00.293854: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE4.1 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 21:42:00.294870: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use SSE4.2 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 21:42:00.295880: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use AVX instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 21:42:00.296193: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use AVX2 instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 21:42:00.296527: W c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:45] The TensorFlow library wasn't compiled to use FMA instructions, but these are available on your machine and could speed up CPU computations.
2017-09-21 21:42:01.016620: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:887] Found device 0 with properties:
name: GeForce 940MX
major: 5 minor: 0 memoryClockRate (GHz) 1.189
pciBusID 0000:01:00.0
Total memory: 2.00GiB
Free memory: 1.66GiB
2017-09-21 21:42:01.017317: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:908] DMA: 0
2017-09-21 21:42:01.017652: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:918] 0: Y
2017-09-21 21:42:01.018251: I c:\tf_jenkins\home\workspace\release-win\device\gpu\os\windows\tensorflow\core\common_runtime\gpu\gpu_device.cc:977] Creating TensorFlow device (/gpu:0) -> (device: 0, name: GeForce 940MX, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0)
WARNING:tensorflow:From C:\Users\weizhen\workspace\TflinearClassifier\tf_classifier.py:181: initialize_all_variables (from tensorflow.python.ops.variables) is deprecated and will be removed after 2017-03-02.
Instructions for updating:
Use `tf.global_variables_initializer` instead.
Epoch 0: loss = 63.15 ( 1 sec)
Epoch 1: loss = 21.69 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 2: loss = 11.66 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 3: loss = 7.79 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 4: loss = 5.80 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 5: loss = 4.61 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 6: loss = 3.82 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 7: loss = 3.25 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 8: loss = 2.83 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 9: loss = 2.51 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 10: loss = 2.25 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 11: loss = 2.04 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 12: loss = 1.86 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 13: loss = 1.71 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 14: loss = 1.59 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 15: loss = 1.48 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 16: loss = 1.38 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 17: loss = 1.30 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 18: loss = 1.23 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 19: loss = 1.16 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 20: loss = 1.10 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 21: loss = 1.05 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 22: loss = 1.00 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 23: loss = 0.95 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 24: loss = 0.91 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 25: loss = 0.88 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 26: loss = 0.84 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 27: loss = 0.81 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 28: loss = 0.78 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 29: loss = 0.75 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 30: loss = 0.73 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 31: loss = 0.70 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 32: loss = 0.68 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 33: loss = 0.66 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 34: loss = 0.64 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 35: loss = 0.62 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 36: loss = 0.60 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 37: loss = 0.59 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 38: loss = 0.57 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 39: loss = 0.56 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 40: loss = 0.54 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 41: loss = 0.53 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 42: loss = 0.52 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 43: loss = 0.50 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 44: loss = 0.49 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 45: loss = 0.48 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 46: loss = 0.47 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 47: loss = 0.46 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 48: loss = 0.45 ( 0 sec)
Epoch 49: loss = 0.44 ( 0 sec)
Basic (non-exhaustive) classifier tests pass
Thanks
WeiZhen
cs224d 作业 problem set2 (一) 用tensorflow纯手写实现sofmax 函数,线性判别分析,命名实体识别的更多相关文章
- cs224d 作业 problem set2 (二) TensorFlow 实现命名实体识别
神经网络在命名实体识别中的应用 所有的这些包括之前的两篇都可以通过tensorflow 模型的托管部署到 google cloud 上面,发布成restful接口,从而与任何的ERP,CRM系统集成. ...
- cs224d 作业 problem set2 (三) 用RNNLM模型实现Language Model,来预测下一个单词的出现
今天将的还是cs224d 的problem set2 的第三部分习题, 原来国外大学的系统难度真的如此之大,相比之下还是默默地再天朝继续搬砖吧 下面讲述一下RNN语言建模的数学公式: 给出一串连续 ...
- cs224d 作业 problem set1 (一) 主要是实现word2vector模型,SGD,CBOW,Softmax,算法
''' Created on 2017年9月13日 @author: weizhen ''' import numpy as np def sigmoid(x): return 1 / (1 + np ...
- CS224d 单隐层全连接网络处理英文命名实体识别tensorflow
什么是NER? 命名实体识别(NER)是指识别文本中具有特定意义的实体,主要包括人名.地名.机构名.专有名词等.命名实体识别是信息提取.问答系统.句法分析.机器翻译等应用领域的重要基础工具,作为结构化 ...
- springmvc 动态代理 JDK实现与模拟JDK纯手写实现。
首先明白 动态代理和静态代理的区别: 静态代理:①持有被代理类的引用 ② 代理类一开始就被加载到内存中了(非常重要) 动态代理:JDK中的动态代理中的代理类是动态生成的.并且生成的动态代理类为$Pr ...
- 简易-五星评分-jQuery纯手写
超级简单的评分功能,分为四个步骤轻松搞定: 第一步: 引入jquery文件:这里我用百度CDN的jquery: <script src="http://apps.bdimg.com/l ...
- vue10行代码实现上拉翻页加载更多数据,纯手写js实现下拉刷新上拉翻页不引用任何第三方插件
vue10行代码实现上拉翻页加载更多数据,纯手写js实现下拉刷新上拉翻页不引用任何第三方插件/库 一提到移动端的下拉刷新上拉翻页,你可能就会想到iScroll插件,没错iScroll是一个高性能,资源 ...
- TensorFlow 之 手写数字识别MNIST
官方文档: MNIST For ML Beginners - https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/mnist/beginners Deep MNIST for ...
- 超级简单的jQuery纯手写五星评分效果
超级简单的评分功能,分为四个步骤轻松搞定: 第一步: 引入jquery文件:这里我用百度CDN的jquery: <script src="http://apps.bdimg.com/l ...
随机推荐
- Mac上VMWare Fusion配置多台cent os
一.创建虚拟机(准备工作) 1.使用VMWare Fusion 创建第一台虚拟机 2.选择操作系统(本次使用的是使用cent os 6.5 64bit 系统) 3.选择磁盘大小(楼主mac上的磁盘大小 ...
- Where should I put <script> tags in HTML markup?
Where should I put <script> tags in HTML markup? When embedding JavaScript in an HTML document ...
- VS2015 编写C++的DLL,并防止DLL导出的函数名出现乱码(以串口通信为例,实现串口通信)
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/songyi160/article/details/50754705 1.新建项目 建立好的项目界面如下: 接着在解决方案中找到[头文件]然后右击 ...
- Flink容错机制(checkpoint)
checkpoint是Flink容错的核心机制.它可以定期地将各个Operator处理的数据进行快照存储( Snapshot ).如果Flink程序出现宕机,可以重新从这些快照中恢复数据. 1. ch ...
- H5rem
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1,maximum-scale=1, ...
- P3375 【模板】KMP字符串匹配——kmp算法
先上一波题目 https://www.luogu.org/problem/P3375 kmp模板 看了好久才想起来是个什么东西qwq #include<cstdio> #include&l ...
- docker安装中遇到的问题
错误一 提示:Segmentation Fault or Critical Error encountered. Dumping core and aborting. Aborted 解答:安装错误安 ...
- docker--container的port映射
使用nginx为例 先运行nginx [root@localhost ~]# docker run --name web -d nginx Unable to find image 'nginx:la ...
- docker--container
[root@localhost docker_test]# docker run bigni/test3 #运行 docker so easy ! [root@localhost docker_tes ...
- wireshark抓取本地回环及其问题 转摘:http://www.cnblogs.com/luminji/p/3503464.html
一:The NPF driver isn’t running 这个错误是因为没有开启NPF服务造成的. NPF即网络数据包过滤器(Netgroup Packet Filter,NPF)是Winpcap ...
