[LeetCode] 883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes 三维物体的投影面积
On a `N * N` grid, we place some `1 * 1 * 1 `cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes.
Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cubes placed on top of grid cell (i, j).
Now we view the projection of these cubes onto the xy, yz, and zx planes.
A projection is like a shadow, that maps our 3 dimensional figure to a 2 dimensional plane.
Here, we are viewing the "shadow" when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side.
Return the total area of all three projections.
Example 1:
Input: [[2]]
Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: 17
Explanation:
Here are the three projections ("shadows") of the shape made with each axis-aligned plane.
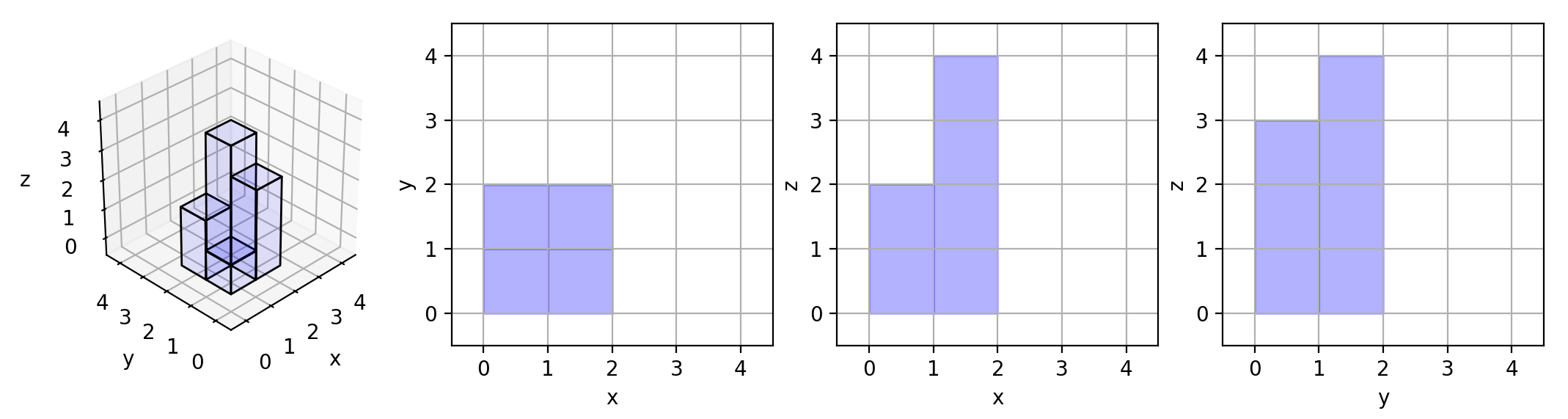
Example 3:
Input: [[1,0],[0,2]]
Output: 8
Example 4:
Input: [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Output: 14
Example 5:
Input: [[2,2,2],[2,1,2],[2,2,2]]
Output: 21
Note:
1 <= grid.length = grid[0].length <= 500 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
这道题给了我们一个二维数组 grid,用来表示一个 3D 物体形状,表示方法是 grid[i][j] 表示在 (i, j) 位置上的高度,就像垒积木一样,累出了一个三维物体。然后让我们计算三个方向的投影面积之和,所谓的三个方向分别是上方 Top,前方 Front,和侧方 Side。用过一些三维建模软件(例如 Maya, 3DMax)的同学,对这个应该不陌生。我们先来考虑正上方投影面积如何计算,由于题目中说了 grid 数组的宽和高相等,那么上方投影就是一个正方形,前提是每个 grid[i][j] 的值都大于0的话。因为若 grid 数组中有0存在,则表示正方形投影会缺少了一块。由于这个大的正方形投影是由 nxn 个小的正方形组成,那么实际上我们只要统计出小正方形的个数,那么大正方形投影的面积也就知道了(是不有点微积分的感觉)。所以我们在遍历的过程中,只要判断若 grid[i][j] 大于0,则结果 res 自增1即可。下面再来考虑另外两个方向的投影怎么计算,另两个方向的投影的可能是不规则图形,参见题目中给的那个图,如果仔细观察的话,其投影图像的每个阶段的高其实就是各行或各列中的最大值,这也不难理解,就像城市中耸立的高度不同的大楼,若要描出城市的轮廓,那么描出来的肯定都是每个位置上最高建筑物的轮廓。那么问题就变成了累加各行各列的最大值。我们实际上在一次遍历中就能完成,使用了一个小 trick,那就是在第二层 for 循环中,行最大值 rowMax 就是不断用 grid[i][j] 来更新,而列最大值 colMax 就是不断用 grid[j][i] 来更新,巧妙的交换i和j,实现了目标。然后分别把更新出来的行列最大值加到结果 res 中即可,参见代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int projectionArea(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid[0].size(), res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int rowMax = 0, colMax = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] > 0) ++res;
rowMax = max(rowMax, grid[i][j]);
colMax = max(colMax, grid[j][i]);
}
res += rowMax + colMax;
}
return res;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/883
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/projection-area-of-3d-shapes/
[LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)](https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4606334.html)
[LeetCode] 883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes 三维物体的投影面积的更多相关文章
- LeetCode 883 Projection Area of 3D Shapes 解题报告
题目要求 On a N * N grid, we place some 1 * 1 * 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes. ...
- Leetcode883.Projection Area of 3D Shapes三维形体投影面积
在 N * N 的网格中,我们放置了一些与 x,y,z 三轴对齐的 1 * 1 * 1 立方体. 每个值 v = grid[i][j] 表示 v 个正方体叠放在单元格 (i, j) 上. 现在,我们查 ...
- 【Leetcode_easy】883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes
problem 883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes 参考 1. Leetcode_easy_883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes; 完
- [LeetCode] 892. Surface Area of 3D Shapes 三维物体的表面积
On a N * N grid, we place some 1 * 1 * 1 cubes. Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cu ...
- 883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes
问题 NxN个格子中,用1x1x1的立方体堆叠,grid[i][j]表示坐标格上堆叠的立方体个数,求三视图面积. Input: [[1,2],[3,4]] Output: 17 Explanation ...
- 【LeetCode】883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes 解题报告(Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 数学计算 日期 题目地址:https://leetc ...
- [LeetCode&Python] Problem 883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes
On a N * N grid, we place some 1 * 1 * 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes. Each ...
- 【leetcode】883. Projection Area of 3D Shapes
题目如下: 解题思路:分别求出所有立方体的个数,各行的最大值之和,各列的最大值之和.三者相加即为答案. 代码如下: class Solution(object): def projectionArea ...
- [Swift]LeetCode883. 三维形体投影面积 | Projection Area of 3D Shapes
On a N * N grid, we place some 1 * 1 * 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes. Each ...
随机推荐
- C语言中的scanf与scanf_s 以及循环输入的问题解决
Scanf 在标准C中,scanf提供了键盘输入功能. scanf函数是一个标准库函数,它的函数原型在头文件“stdio.h”中.与printf函数相同,C语言也允许在使用scanf函数之前不必包含s ...
- 此贴告诉你:为啥shell脚本人,不建议学python
py很强大,我承认.但在运维方面,py不但不强大,还有硬伤.正因为有下述硬伤,所以我们运维,还是用shell多,用py极少.我看到用shell的人很多,你建议人用python,人说py是很好,但下一秒 ...
- 移动端rem布局,用户调整手机字体大小或浏览器字体大小后导致页面布局出错问题
一.用户修改手机字体设置大小,影响App里打开的web页面. 手机字体设置大小,影响App的页面.Android的可以通过webview配置webview.getSettings().setTextZ ...
- zabbix 自定义mysql监控
一.配置zabbix-agent 编辑 /etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.conf文件 增加如下两个配置 1.vim /etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.conf ...
- kali渗透综合靶机(十五)--Breach-1.0靶机
kali渗透综合靶机(十五)--Breach-1.0靶机 靶机下载地址:https://download.vulnhub.com/breach/Breach-1.0.zip 一.主机发现 1.netd ...
- jakarta-oro-2.0.8.jar-----------JAVA FTP相关
资源不好找,找到了就和大家分享一下! 链接:https://share.weiyun.com/51kBB0y 密码:2hcxcu
- 1-HTTPS之SNI介绍
原文:https://blog.51cto.com/zengestudy/2170245 介绍 早期的SSLv2根据经典的公钥基础设施PKI(Public Key Infrastructure)设计, ...
- 咕咕咕-HLPP算法
hlpp(欢乐婆婆)算法总结 突然发现咕了好久(X) emm先大概说一下,hlpp是针对网络流算法的一种复杂度更优的算法,基于预流推进(即模拟) 复杂度上界为 n2根号m 且跑不满 (所以学会了它,可 ...
- VSCode搭建django项目
之前我们使用VSCode搭建C#项目,今天写一篇关于django项目的搭建,其实以其说是搭建django框架,不如说是如何通过vscode开发django项目:django官网:https://www ...
- Linux管道及重定向
Linux管道及重定向 对shell有一定了解的人都知道,管道和重定向是 Linux 中非常实用的 IPC 机制.在shell中,我们通常使用符合'|'来表示管道,符号'>'和'<'表示重 ...
