SP6779 GSS7
GSS7解题报告
前言
唔,有点恶心哪,废了两个多小时debug
思路
很容易看出傻子都知道,这个是树链剖分+线段树的裸题,只不过是恶心了点,这里重点讲一下细节问题
线段树
做过GSS系列的都应该很熟悉了
线段树维护的前缀最大子段和,后缀最大子段和,和区间最大子段和
那么我们就可以很容易的写出他合并orpushup
void pushup(node &a,node x,node y) {
a.ans=max(max(x.ans,y.ans),x.rk+y.lk);
a.lk=max(x.sum+y.lk,x.lk);
a.rk=max(y.sum+x.rk,y.rk);
a.sum= x.sum +y.sum;
}
这里写成这种形式对下面的跳链比较友好
查询也是比较套路的 返回一个node,如果在mid两边,再次合并,这里就不多说了
树剖跳链
修改操作:
跳链,修改,和平常一样
查询操作:
x到y的路径是一条链子
如果我们把它伸直,捋平咯,那他就是一串数列
那我们就可以一块一块的合并喽
想一下我们是怎么跳的
是从链的两端跳,一直跳到他们相遇
那我们就维护两端的信息,也就是从起点到现在的x的区间和从现在的y到终点的区间
最后再合并起来,就是整个区间的信息喽
不过要注意合并时候的次序和l,r的交换
也许不swap而分类讨论就没这个东西了吧
我们的一条重链是从浅处到深处依次排列
我们跳的时候是从深处到浅出跳(从两端逼近中间)
所以合并就要考虑清楚了
是合并x,y还是合并y,x
文字说起来不太明白,我举个栗子吧
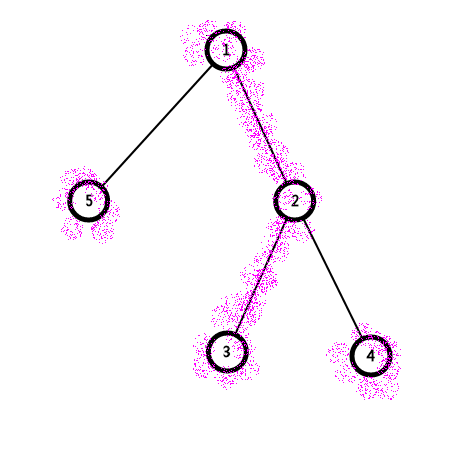
2号权值为-1,其他权值为1,要从4号到5号点
我们先从5号节点跳到1号所属重链
在跳之前我们先查询一下5号的值,得到一个node,和x
合并
我们再从4号节点跳到1号所属重链
在跳之前我们先查询一下4号的值,又得到一个node,和y合并
然后交换x,y(别问我为什么)
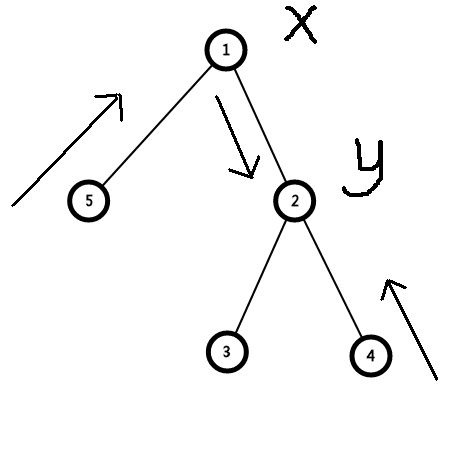
现在x,y都到了一条链子上了(注意前提)
我们考虑一下两端区间的方向
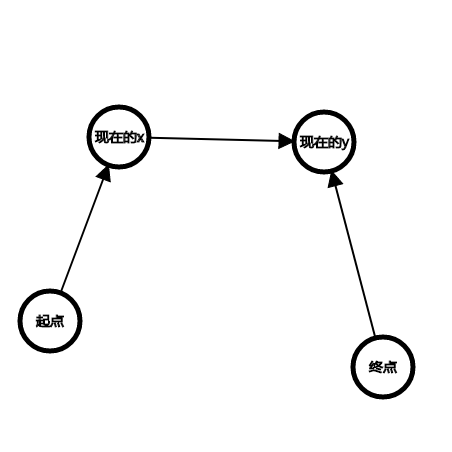
有一个是反着的,我们翻过来其中一个然后全部合并起来就好了
这里给出我的两组简单但易错数据(反正错了我好多次)
5
-1 1 1 1 1
1 5
1 2
2 3
2 4
1
1 4 5
ans=2
5
-3 -2 -1 -2 -3
1 2
2 3
1 4
4 5
2
2 3 4 2
1 2 5
ans=6
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define FOR(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;++i)
using namespace std;
const int N=6e5+7;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
inline int read() {
int x=0,f=1;char s=getchar();
for(;s>'9'||s<'0';s=getchar()) if(s=='-') f=-1;
for(;s>='0'&&s<='9';s=getchar()) x=x*10+s-'0';
return x*f;
}
vector<int> G[N];
int n,m;
int a[N],w[N],idx[N],top[N],son[N],siz[N],f[N],dep[N],cnt;
inline int max(const int &x,const int &y) {return x>y?x:y;}
void dfs1(int u,int fa) {
f[u]=fa;
siz[u]=1;
dep[u]=dep[fa]+1;
for(std::vector<int>::iterator it=G[u].begin();it!=G[u].end();++it) {
if(fa==*it) continue;
dfs1(*it,u);
siz[u]+=siz[*it];
if(siz[son[u]]<siz[*it]) son[u]=*it;
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int topf) {
idx[u]=++cnt;
a[cnt]=w[u];
top[u]=topf;
if(!son[u]) return;
dfs2(son[u],topf);
for(std::vector<int>::iterator it=G[u].begin();it!=G[u].end();++it)
if(!idx[*it]) dfs2(*it,*it);
}
namespace seg_tree {
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
struct node {
int l,r,siz,lk,rk,ans,lazy,sum;
}e[N<<2];
inline void pushup(node &a,node x,node y) {
a.ans=max(max(x.ans,y.ans),x.rk+y.lk);
a.lk=max(x.sum+y.lk,x.lk);
a.rk=max(y.sum+x.rk,y.rk);
a.sum= x.sum +y.sum;
}
void build(int l,int r,int rt) {
e[rt].l=l,e[rt].r=r,e[rt].siz=r-l+1;
e[rt].lazy=inf;
if(l==r) {
e[rt].sum=a[l];
e[rt].lk=e[rt].rk=e[rt].ans=max(a[l],0);
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(l,mid,ls);
build(mid+1,r,rs);
pushup(e[rt],e[ls],e[rs]);
}
inline void tag(int rt,int k) {
e[rt].sum=e[rt].siz*k;
if(k>=0) e[rt].lk=e[rt].rk=e[rt].ans=e[rt].sum;
else e[rt].lk=e[rt].rk=e[rt].ans=0;
e[rt].lazy=k;
}
inline void pushdown(int rt) {
if(e[rt].lazy!=inf) {
tag(ls,e[rt].lazy);
tag(rs,e[rt].lazy);
e[rt].lazy=inf;
}
}
void modify(int L,int R,int k,int rt) {
if(L<=e[rt].l&&e[rt].r<=R) {
tag(rt,k);
return;
}
pushdown(rt);
int mid=(e[rt].l+e[rt].r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) modify(L,R,k,ls);
if(R>mid) modify(L,R,k,rs);
pushup(e[rt],e[ls],e[rs]);
}
node query(int L,int R,int rt) {
if(L<=e[rt].l&&e[rt].r<=R) return e[rt];
pushdown(rt);
int mid=(e[rt].l+e[rt].r)>>1;
if(L<=mid && R>mid) {
node a=query(L,R,ls),b=query(L,R,rs),c;
pushup(c,a,b);
return c;
}
if(L<=mid) return query(L,R,ls);
if(R>mid) return query(L,R,rs);
}
}
void QQ(int x,int y) {
seg_tree::node tot_x={},tot_y={};
while(top[x]!=top[y]) {
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]]) swap(x,y),swap(tot_x,tot_y);
seg_tree::node tmp=seg_tree::query(idx[top[x]],idx[x],1);
seg_tree::pushup(tot_x,tmp,tot_x);
x=f[top[x]];
}
if(dep[x]>dep[y]) swap(x,y),swap(tot_x,tot_y);
seg_tree::node tmp=seg_tree::query(idx[x],idx[y],1);
swap(tot_x.lk,tot_x.rk);
seg_tree::pushup(tot_x,tot_x,tmp);
seg_tree::pushup(tot_y,tot_x,tot_y);
printf("%d\n",tot_y.ans);
}
void CC(int x,int y,int c) {
while(top[x]!=top[y]) {
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]]) swap(x,y);
seg_tree::modify(idx[top[x]],idx[x],c,1);
x=f[top[x]];
}
if(dep[x]>dep[y]) swap(x,y);
seg_tree::modify(idx[x],idx[y],c,1);
}
int main() {
n=read();
FOR(i,1,n) w[i]=read();
FOR(i,2,n) {
int x=read(),y=read();
G[x].push_back(y);
G[y].push_back(x);
}
dfs1(1,0);
dfs2(1,1);
seg_tree::build(1,n,1);
m=read();
FOR(i,1,m) {
int opt=read(),x=read(),y=read(),z;
if(opt==1) QQ(x,y);
else z=read(),CC(x,y,z);
}
return 0;
}
SP6779 GSS7的更多相关文章
- SP6779 GSS7 - Can you answer these queries VII
纯数据结构题,没有思维难度.直接用线段树求最大子段和的方法完成树上路径的合并.注意链上合并顺序要符合序列的前后顺序. #include <cstdio> #include <cstr ...
- SP6779 GSS7 - Can you answer these queries VII(线段树,树链剖分)
水题,只是坑点多,\(tag\)为\(0\)时可能也要\(pushdown\),所以要\(bool\)标记是否需要.最后树链剖分询问时注意线段有向!!! #include <cstring> ...
- 题解 SP6779 【GSS7 - Can you answer these queries VII】
题目传送门 题目大意 给出一个\(n\)个点的树,每个点有权值.有\(m\)次操作,每次要么查询一条链上的最大子段和,要么把一条链的权值都修改为一个常数. \(n,m\le 10^5\) 思路 如果是 ...
- GSS7 spoj 6779. Can you answer these queries VII 树链剖分+线段树
GSS7Can you answer these queries VII 给出一棵树,树的节点有权值,有两种操作: 1.询问节点x,y的路径上最大子段和,可以为空 2.把节点x,y的路径上所有节点的权 ...
- SPOJ GSS7 - Can you answer these queries VII
板的不能再板,链剖+线段树或者是LCT随便维护. 感觉唯一要注意的是跳链的时候要对$x$向上跳和$y$向上跳的情况分开讨论,而不能直接$swap$,因为只有两段接触的端点才能相互合并,而且每一次向上跳 ...
- SPOJ GSS7 Can you answer these queries VII ——树链剖分 线段树
[题目分析] 问题放到了树上,直接链剖+线段树搞一搞. 调了300行+. (还是码力不够) [代码] #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> ...
- Solution -「SP 6779」GSS7
\(\mathcal{Description}\) 给定一棵 \(n\) 个点的带点权树,\(q\) 次操作: 路径点权赋值. 询问路径最大子段和(可以为空). \(n,q\le10^5\). ...
- 激!GSS系列
#include <cstdio> ; ; inline int max(int, int); inline int getint(); inline void putint(int); ...
- OAF_文件系列4_实现OAF上传显示数据库动态图片Image(案例)
20150805 Created By BaoXinjian
随机推荐
- mybatis3 date 的处理
<if test="startTime!=null and startTime!=''"> <![CDATA[ and DATE_FORMAT(create_ti ...
- SQLSetConnectAttr
SQLSetConnectAttr 函数定义: 用法类似于SQLSetEnvAttr,该函数是设置连接的各项属性用的 SQLRETURN SQLSetConnectAttr( SQLHDBC ...
- 《大话设计模式》c++实现 代理模式
代理模式 在代理模式(Proxy Pattern)中,一个类代表另一个类的功能.这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式. 在代理模式中,我们创建具有现有对象的对象,以便向外界提供功能接口. 介绍 意图:为其 ...
- 回声状态网络(ESN)基础教程
http://jlearning.cn/2017/05/29/ESN-basic-tutorial/ 最近在看回声状态网络(Echo State Network)的内容,注意到中文搜索引擎搜不到关于有 ...
- SLAM学习笔记 - ORB_SLAM2源码运行及分析
参考资料: DBow2的理解 单目跑TUM数据集的运行和函数调用过程 跑数据集不需要ros和相机标定,进入ORB_SLAM目录,执行以下命令: ./Examples/Monocluar/mono_tu ...
- c++学习笔记(二)-指针
1. 指向数组的指针 int balance[5] = { 1000, 2, 3, 17, 50 }; int *ptr; ptr = balance; //ptr是指向数组balance的指针 // ...
- Error resolving version for plugin 'org.codehaus.mojo:tomcat-maven-plugin'
从 SNV 导入新工程后,启动工程,但 Maven 报错: Error resolving version for plugin 'org.codehaus.mojo:tomcat-maven-plu ...
- Spring NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
转http://www.baeldung.com/spring-nosuchbeandefinitionexception 1. Overview In this article, we are di ...
- Promise的简单用法
众所周知的,Javascript是一种单线程的语言,所有的代码必须按照所谓的“自上而下”的顺序来执行.本特性带来的问题就是,一些将来的.未知的操作,必须异步实现.本文将讨论一个比较常见的异步解决方案— ...
- 介绍python中运算符优先级
下面这个表给出Python的运算符优先级,从最低的优先级(最松散地结合)到最高的优先级(最紧密地结合).这意味着在一个表达式中,Python会首先计算表中较下面的运算符,然后在计算列在表上部的运算符. ...
