Calculate CAN bit timing parameters -- STM32
Calculate CAN bit timing parameters
Calculate CAN bit timing parameters
typedef struct
{
//char name[ 16 ]; // Name of the CAN controller hardware
//uint32_t ref_clk; // CAN system clock frequency in Hz
//uint32_t sjw_max; // Synchronisation jump width
uint32_t brp_min; // Bit-rate prescaler
uint32_t brp_max;
uint32_t brp_inc;
uint32_t tseg1_min; // Time segement 1 = prop_seg + phase_seg1
uint32_t tseg1_max;
uint32_t tseg2_min; // Time segement 2 = phase_seg2
uint32_t tseg2_max;
} CAN_BitTimingConst_TypeDef; typedef struct
{
uint32_t ref_clk; // CAN system clock frequency in Hz
uint32_t bitrate; // Bit-rate in bits/second
uint32_t sample_point; // Sample point in one-tenth of a percent
uint32_t brp; // Bit-rate prescaler
uint32_t tq; // Time quanta (TQ) in nanoseconds
uint32_t tseg1; // Time segement 1 = prop_seg + phase_seg1
uint32_t tseg2; // Time segement 2 = phase_seg2
uint32_t sjw; // Synchronisation jump width in TQs
//uint32_t prop_seg; // Propagation segment in TQs
//uint32_t phase_seg1; // Phase buffer segment 1 in TQs
//uint32_t phase_seg2; // Phase buffer segment 2 in TQs
} CAN_BitTiming_TypeDef;
#define CAN_CALC_MAX_ERROR 50 // in one-tenth of a percent int32_t CAN_UpdateSamplePoint( CAN_BitTimingConst_TypeDef *btc,
int32_t sampl_pt, int32_t tseg, int32_t *tseg1, int32_t *tseg2 )
{
*tseg2 = tseg + - ( sampl_pt * ( tseg + ) ) / ; if ( *tseg2 < btc->tseg2_min )
*tseg2 = btc->tseg2_min; if ( *tseg2 > btc->tseg2_max )
*tseg2 = btc->tseg2_max; *tseg1 = tseg - *tseg2; if ( *tseg1 > btc->tseg1_max )
{
*tseg1 = btc->tseg1_max;
*tseg2 = tseg - *tseg1;
} return * ( tseg + - *tseg2 ) / ( tseg + );
} // CIA Sample Point : 75.0% : Speed > 800000
// CIA Sample Point : 80.0% : Speed > 500000
// CIA Sample Point : 87.5% : Speed <= 500000
uint32_t CAN_CIA_SamplePoint( uint32_t bitrate )
{
uint32_t sampl_pt; if ( bitrate > )
sampl_pt = ;
else if ( bitrate > )
sampl_pt = ;
else
sampl_pt = ; return sampl_pt;
} int32_t CAN_CalcBitTiming( CAN_BitTimingConst_TypeDef *btc,
CAN_BitTiming_TypeDef *bt )
{
uint64_t v64;
int32_t rate = ;
int32_t best_error = , error = ;
int32_t best_tseg = , best_brp = , brp = ;
int32_t tsegall, tseg = , tseg1 = , tseg2 = ;
int32_t spt_error = , spt = , sampl_pt; // Use gived sample points
if ( bt->sample_point )
sampl_pt = bt->sample_point;
else
// Use CIA recommended sample points
sampl_pt = CAN_CIA_SamplePoint( bt->bitrate ); // tseg even = round down, odd = round up
for ( tseg = ( btc->tseg1_max + btc->tseg2_max ) * + ;
tseg >= ( btc->tseg1_min + btc->tseg2_min ) * ; tseg-- )
{
tsegall = + tseg / ; // Compute all possible tseg choices (tseg=tseg1+tseg2)
brp = bt->ref_clk / ( tsegall * bt->bitrate ) + tseg % ; // chose brp step which is possible in system
brp = ( brp / btc->brp_inc ) * btc->brp_inc;
if ( ( brp < btc->brp_min ) || ( brp > btc->brp_max ) )
continue; rate = bt->ref_clk / ( brp * tsegall );
error = bt->bitrate - rate; // tseg brp biterror
if ( error < )
error = -error; if ( error > best_error )
continue; best_error = error;
if ( error == )
{
spt = CAN_UpdateSamplePoint( btc, sampl_pt, tseg / , &tseg1, &tseg2 );
error = sampl_pt - spt;
if ( error < )
error = -error;
if ( error > spt_error )
continue; spt_error = error;
} best_tseg = tseg / ;
best_brp = brp;
if ( error == )
break;
} if ( best_error )
{
/* Error in one-tenth of a percent */
error = ( best_error * ) / bt->bitrate;
if ( error > CAN_CALC_MAX_ERROR )
{
// error ( "bitrate error %ld.%ld%% too high\n", error / 10, error % 10 );
return DRIVER_ERROR_PARAMETER;
}
else
{
// warn( "bitrate error %ld.%ld%%\n", error / 10, error % 10 );
}
} v64 = ( (uint64_t) best_brp * 1000000000UL ) / bt->ref_clk; bt->tq = (uint32_t) v64;
bt->brp = best_brp;
bt->tseg2 = tseg2;
bt->tseg1 = tseg1;
bt->sjw = ;
// bt->prop_seg = tseg1 / 2;
// bt->phase_seg1 = tseg1 - bt->prop_seg;
// bt->phase_seg2 = tseg2; // real bit-rate
bt->bitrate = bt->ref_clk / ( bt->brp * ( tseg1 + tseg2 + ) );
// real sample point bt->sample_point = CAN_UpdateSamplePoint( btc, sampl_pt, best_tseg, &tseg1,
&tseg2 ); return DRIVER_OK;
}
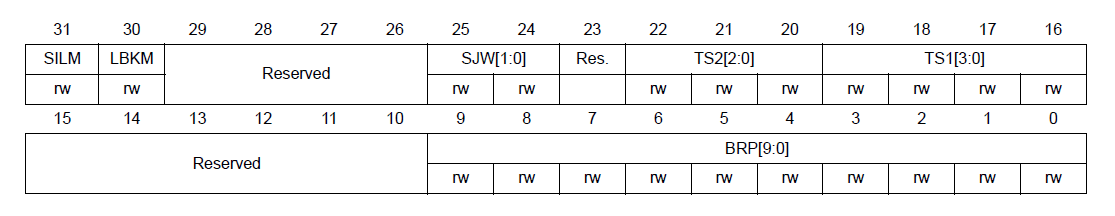
SJW[1:0]: Resynchronization jump width
These bits define the maximum number of time quanta the CAN hardware
is allowed to lengthen or shorten a bit to perform the resynchronization.
tRJW = tq x (SJW[1:0] + 1)
TS2[2:0]: Time segment 2
These bits define the number of time quanta in Time Segment 2.
tBS2 = tq x (TS2[2:0] + 1)
TS1[3:0]: Time segment 1
These bits define the number of time quanta in Time Segment 1
tBS1 = tq x (TS1[3:0] + 1)
BRP[9:0]: Baud rate prescaler
These bits define the length of a time quanta.
tq = (BRP[9:0]+1) x tPCLK
const CAN_BitTimingConst_TypeDef CAN_BitTimingConst =
{ , // Bit-rate prescaler Min
, // Bit-rate prescaler Max
, // Bit-rate prescaler Inc
, // Time segement 1 = prop_seg + phase_seg1 Min
, // Time segement 1 = prop_seg + phase_seg1 Max
, // Time segement 2 = phase_seg2 Min
, // Time segement 2 = phase_seg2 Max
}; static int32_t CAN_SetSpeed( CAN_Controller_TypeDef *can, uint32_t speed )
{
int32_t RetValue = CAN_EnterInit( can );
if ( RetValue != DRIVER_OK )
return RetValue; uint32_t Freq = can->freq( );
CAN_BitTiming_TypeDef CAN_BitTiming;
CAN_BitTiming.ref_clk = Freq;
CAN_BitTiming.bitrate = speed; // be updated to real speed
CAN_BitTiming.sample_point = 0; // be updated to real spt RetValue = CAN_CalcBitTiming( &CAN_BitTimingConst, &CAN_BitTiming );
if ( RetValue == DRIVER_OK )
{
can->info->speed = CAN_BitTiming.bitrate; // updated
uint32_t BTR = can->reg->BTR & 0xC0000000; // SILM|LBKM
BTR |= ( ( CAN_BitTiming.brp - ) << ) // BRP
| ( ( CAN_BitTiming.tseg1 ) << ) // TS1
| ( ( CAN_BitTiming.tseg2 - ) << ) // TS2
| ( ( CAN_BitTiming.sjw - ) << ); // SJW
can->reg->BTR = BTR;
} return CAN_LeaveInit( can );
/* BPR TSEG1 TSEG2 */
/* 36 MHz 1 Mbps */ { , , }, // 75%
/* 36 MHz 800 Kbps */ { , , }, // 80%
/* 36 MHz 500 Kbps */ { , , }, // 83.3%
/* 36 MHz 250 Kbps */ { , , }, // 87.5%
/* 36 MHz 125 Kbps */ {, , }, // 87.5%
/* 36 MHz 100 Kbps */ {, , }, // 86.6%
/* 36 MHz 83.3 Kbps */ {, , }, // 83.3%
/* 36 MHz 62.5 Kbps */ {, , }, // 87.5%
/* 36 MHz 50 Kbps */ {, , }, // 87.5%
/* 36 MHz 20 Kbps */ {,, }, // 86.6%
/* 36 MHz 10 Kbps */ {,, }, // 87.5%
/* 36 MHz 500 Kbps */ { , , } // 83.3%
Calculate CAN bit timing parameters -- STM32的更多相关文章
- Calculate CAN bit timing parameters
Calculate CAN bit timing parameters TSYNC_SEG === 1 TSEG1 = Prop_Seg + Phase_Seg1 TSEG2 = Phase_Seg2 ...
- 0xWS2812 STM32 driver for WS2812(B) RGB LEDs
0xWS2812 STM32 driver for WS2812(B) RGB LEDs 0xWS2812 pronounced "hex-WS2812" This code ai ...
- CRT/LCD/VGA Information and Timing
彩色阴极射线管的剖面图: 1. 电子QIANG Three Electron guns (for red, green, and blue phosphor dots)2. 电子束 Electron ...
- CRT/LCD/VGA Information and Timing【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/shangdawei/p/4760933.html 彩色阴极射线管的剖面图: 1. 电子QIANG Three Electron guns (for ...
- CALayer之 customizing timing of an animation
customizing timing of an animation Timing is an important part of animations, and with Core Animatio ...
- RFID 读写器 Reader Writer Cloner
RFID读写器的工作原理 RFID的数据采集以读写器为主导,RFID读写器是一种通过无线通信,实现对标签识别和内存数据的读出和写入操作的装置. 读写器又称为阅读器或读头(Reader).查询器(Int ...
- RFID Reader 线路图收集
This 125 kHz RFID reader http://www.serasidis.gr/circuits/RFID_reader/125kHz_RFID_reader.htm http:// ...
- BlackArch-Tools
BlackArch-Tools 简介 安装在ArchLinux之上添加存储库从blackarch存储库安装工具替代安装方法BlackArch Linux Complete Tools List 简介 ...
- Timequest静态时序分析(STA)基础
Setup Slack Hold Slack Recovery&Removal Recovery: The minimum time an asynchronous signal must b ...
随机推荐
- nmap - 网络扫描
NMap,Network Mapper 最早是Linux下的网络扫描和嗅探工具包 网络链接扫描; nmap -PT 192.168.1.1-111 # 先ping在扫描主机开放端口 nmap -O 1 ...
- CUDA性能优化----warp深度解析
本文转自:http://blog.163.com/wujiaxing009@126/blog/static/71988399201701224540201/ 1.引言 CUDA性能优化----sp, ...
- 6 个 Linux 运维典型问题,大牛的分析解决思路在这里 【转】
作为一名合格的 Linux 运维工程师,一定要有一套清晰.明确的解决故障思路,当问题出现时,才能迅速定位.解决问题,这里给出一个处理问题的一般思路: 重视报错提示信息:每个错误的出现,都是给出错误提示 ...
- phantomjs 长图截屏
var page = require('webpage').create(); var url = 'http://cardloan9.hateblo.jp/'; page.settings = { ...
- trove远程连接mongodb
创建数据库 <pre> [root@a581c7388dca /]# trove database-create e50f3b40-5165-4ccc-af9f-c121089fd902 ...
- centos6.5环境通过shell脚本备份php的web及mysql数据库并做远程备份容灾
centos6.5环境通过shell脚本备份php的web及mysql数据库并做远程备份容灾 系统:centos6.5 1.创建脚本目录 mkdir -p /usr/local/sh/ 创建备份web ...
- 初始ASP.NET数据控件【续 ListView】
ListView控件 ListView控件可以用来显示数据,它还提供编辑,删除,插入,分页与排序等功能.ListView是GridView与DataList的融合体,它具有GridView控件编辑 ...
- jenkins的svn路径中文问题
今天弄Jenkins,我们的SVN代码路径是中文的,他娘的坑死我了,很没面子弄了俩点,网上方案试了好多,说装插件,修改Tomcat server.xml,基本没用,后来看到一个帖子写的方案蛮实用的,分 ...
- Orchard学习 02、orchard 路由
Orchard对mvc路由重新做了包装,重写了asp.net的路由模块 一.路由模块类图 1.路由 Descriptor RouteDescriptor是对常规mvc路由的包装类,它的Route属性就 ...
- python selenium-webdriver 环境搭建(一)
selenium 虽然过了这么多年,但是到目前为止依然是比较流行的自动化框架了,还有很多的初学者在学习,所以根据自己的时间将把相关的资料汇总一下,下面首先我们需要搭建一下基础环境. 首先自己本身比较笨 ...
