用10张图来看机器学习Machine learning in 10 pictures
I find myself coming back to the same few pictures when explaining basic machine learning concepts. Below is a list I find most illuminating.
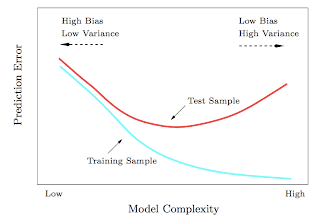
1. Test and training error: Why lower training error is not always a good thing: ESL Figure 2.11. Test and training error as a function of model complexity.
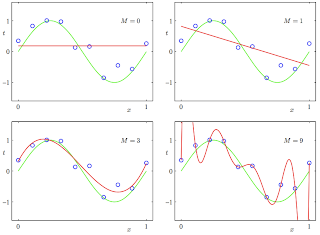
2. Under and overfitting: PRML Figure 1.4. Plots of polynomials having various orders M, shown as red curves, fitted to the data set generated by the green curve.
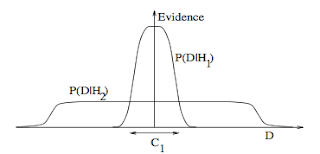
3. Occam's razor: ITILA Figure 28.3. Why Bayesian inference embodies Occam’s razor. This figure gives the basic intuition for why complex models can turn out to be less probable. The horizontal axis represents the space of possible data sets D. Bayes’ theorem rewards models in proportion to how much they predicted the data that occurred. These predictions are quantified by a normalized probability distribution on D. This probability of the data given model Hi, P (D | Hi), is called the evidence for Hi. A simple model H1 makes only a limited range of predictions, shown by P(D|H1); a more powerful model H2, that has, for example, more free parameters than H1, is able to predict a greater variety of data sets. This means, however, that H2 does not predict the data sets in region C1 as strongly as H1. Suppose that equal prior probabilities have been assigned to the two models. Then, if the data set falls in region C1, the less powerful model H1 will be the more probable model.
4. Feature combinations: (1) Why collectively relevant features may look individually irrelevant, and also (2) Why linear methods may fail. From Isabelle Guyon's feature extraction slides.
.png)
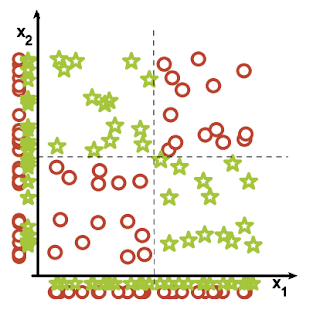
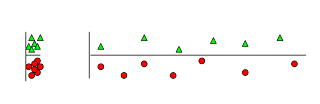
5. Irrelevant features: Why irrelevant features hurt kNN, clustering, and other similarity based methods. The figure on the left shows two classes well separated on the vertical axis. The figure on the right adds an irrelevant horizontal axis which destroys the grouping and makes many points nearest neighbors of the opposite class.
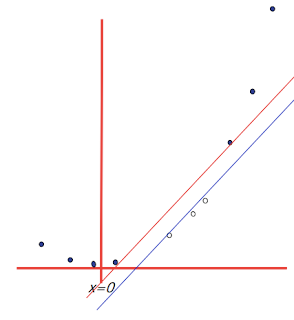
6. Basis functions: How non-linear basis functions turn a low dimensional classification problem without a linear boundary into a high dimensional problem with a linear boundary. From SVM tutorial slides by Andrew Moore: a one dimensional non-linear classification problem with input x is turned into a 2-D problem z=(x, x^2) that is linearly separable.
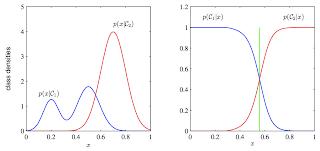
7. Discriminative vs. Generative: Why discriminative learning may be easier than generative: PRML Figure 1.27. Example of the class-conditional densities for two classes having a single input variable x (left plot) together with the corresponding posterior probabilities (right plot). Note that the left-hand mode of the class-conditional density p(x|C1), shown in blue on the left plot, has no effect on the posterior probabilities. The vertical green line in the right plot shows the decision boundary in x that gives the minimum misclassification rate.
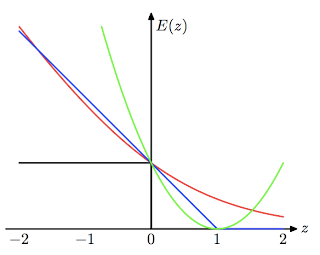
8. Loss functions: Learning algorithms can be viewed as optimizing different loss functions: PRML Figure 7.5. Plot of the ‘hinge’ error function used in support vector machines, shown in blue, along with the error function for logistic regression, rescaled by a factor of 1/ln(2) so that it passes through the point (0, 1), shown in red. Also shown are the misclassification error in black and the squared error in green.
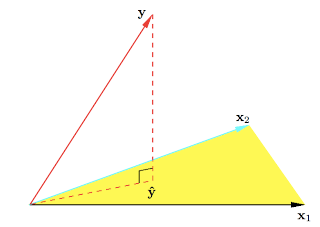
9. Geometry of least squares: ESL Figure 3.2. The N-dimensional geometry of least squares regression with two predictors. The outcome vector y is orthogonally projected onto the hyperplane spanned by the input vectors x1 and x2. The projection yˆ represents the vector of the least squares predictions.
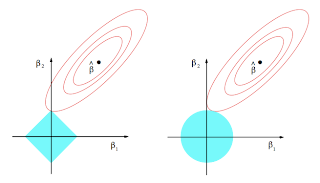
10. Sparsity: Why Lasso (L1 regularization or Laplacian prior) gives sparse solutions (i.e. weight vectors with more zeros): ESL Figure 3.11. Estimation picture for the lasso (left) and ridge regression (right). Shown are contours of the error and constraint functions. The solid blue areas are the constraint regions |β1| + |β2| ≤ t and β12 + β22 ≤ t2, respectively, while the red ellipses are the contours of the least squares error function.
from: http://www.denizyuret.com/2014/02/machine-learning-in-5-pictures.html
用10张图来看机器学习Machine learning in 10 pictures的更多相关文章
- 【机器学习Machine Learning】资料大全
昨天总结了深度学习的资料,今天把机器学习的资料也总结一下(友情提示:有些网站需要"科学上网"^_^) 推荐几本好书: 1.Pattern Recognition and Machi ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料
<Brief History of Machine Learning> 介绍:这是一篇介绍机器学习历史的文章,介绍很全面,从感知机.神经网络.决策树.SVM.Adaboost到随机森林.D ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)&深入学习(Deep Learning)资料
<Brief History of Machine Learning> 介绍:这是一篇介绍机器学习历史的文章,介绍很全面,从感知机.神经网络.决策树.SVM.Adaboost 到随机森林. ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料【转】
转自:机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料 <Brief History of Machine Learning> 介绍:这是一 ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料汇总 (上)
转载:http://dataunion.org/8463.html?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral <Brief History of Ma ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料
机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料 機器學習.深度學習方面不錯的資料,轉載. 原作:https://github.com/ty4z2008 ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)与深度学习(Deep Learning)资料汇总
<Brief History of Machine Learning> 介绍:这是一篇介绍机器学习历史的文章,介绍很全面,从感知机.神经网络.决策树.SVM.Adaboost到随机森林.D ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料(Chapter 2)
##机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料(Chapter 2)---#####注:机器学习资料[篇目一](https://github.co ...
- 数据挖掘(data mining),机器学习(machine learning),和人工智能(AI)的区别是什么? 数据科学(data science)和商业分析(business analytics)之间有什么关系?
本来我以为不需要解释这个问题的,到底数据挖掘(data mining),机器学习(machine learning),和人工智能(AI)有什么区别,但是前几天因为有个学弟问我,我想了想发现我竟然也回答 ...
随机推荐
- 495. Teemo Attacking
In LOL world, there is a hero called Teemo and his attacking can make his enemy Ashe be in poisoned ...
- list列表常用方法
列表是Python中常用的功能,我们知道,列表可以用来存储很多信息,掌握列表的功能有助于我们处理更多的问题,下面来看看列表都具有那些属性: 1.append(self,p_object) de ...
- React.js学习之理解JSX和组件
在开启JSX的学习旅程前,我们先了解一下React的基本原理.React本质上是一个"状态机",它只关心两件事:更新DOM和响应事件,React不处理Ajax.路由和数据存储,也不 ...
- 查找无序数组中第K大的数
思路: 利用快速排序的划分思想 可以找出前k大数,然后不断划分 直到找到第K大元素 代码: #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> # ...
- thinkjs项目中使用mongoose需要注意的地方
原文链接thinkjs项目中使用mongoose需要注意的地方 由于thinkjs不支持mongodb的关联模型查询,所以我不得不使用mongoose这个第三方odm. 我有两个选择,一是像我在exp ...
- Codeforces 722C(并查集 + 思维)
本文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/Ash-ly/p/5932712.html 题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/722/ ...
- CPPUNIT_TEST
(1) CPPUNIT_ASSERT(condition):判断condition的值是否为真,如果为假则生成错误信息. (2)CPPUNIT_ASSERT_MESSAGE(message, cond ...
- laravel框架安装过程中遇到的问题
1.安装laravel框架之前的必要环境 php环境:网上有集成好的服务器,例如wamp,phpstudy.当然你可以自己搭建属于自己的环境.其中php必须是7.1版本以上: compose:php的 ...
- ssm demo,用户角色权限管理
SSM框架整合 Spring SpringMVC MyBatis 导包: 1, spring 2, MyBatis 3, mybatis-spring 4, fastjson 5, aspectwea ...
- arm Linux 驱动LED子系统 测试
Linux内核在3.0以上引入了设备树概念(具体哪个版本不清楚)在编译内核后需要将与之对应的dtb文件也下载人板子上才能使内核与硬件关联起来. dtb文件是有dts文件编译后生成的:例如 /* * C ...
