MySQL Cursor
MySQL Cursor
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL cursor in stored procedures to iterate through a result set returned by a SELECT statement.
Introduction to MySQL cursor
To handle a result set inside a stored procedure, you use a cursor. A cursor allows you to iteratea set of rows returned by a query and process each row accordingly.
MySQL cursor is read-only, non-scrollable and asensitive.
- Read only: you cannot update data in the underlying table through the cursor.
- Non-scrollable: you can only fetch rows in the order determined by the SELECT statement. You cannot fetch rows in the reversed order. In addition, you cannot skip rows or jump to a specific row in the result set.
- Asensitive: there are two kinds of cursors: asensitive cursor and insensitive cursor. An asensitive cursor points to the actual data, whereas an insensitive cursor uses a temporary copy of the data. An asensitive cursor performs faster than an insensitive cursor because it does not have to make a temporary copy of data. However, any change that made to the data from other connections will affect the data that is being used by an asensitive cursor, therefore, it is safer if you don’t update the data that is being used by an asensitive cursor. MySQL cursor is asensitive.
You can use MySQL cursors in stored procedures, stored functions, and triggers.
Working with MySQL cursor
First, you have to declare a cursor by using the DECLARE statement:
|
1
|
DECLARE cursor_name CURSOR FOR SELECT_statement;
|
The cursor declaration must be after any variabledeclaration. If you declare a cursor before variables declaration, MySQL will issue an error. A cursor must always be associated with aSELECT statement.
Next, you open the cursor by using the OPEN statement. The OPEN statement initializes the result set for the cursor, therefore, you must call the OPEN statement before fetching rows from the result set.
|
1
|
OPEN cursor_name;
|
Then, you use the FETCH statement to retrieve the next row pointed by the cursor and move the cursor to the next row in the result set.
|
1
|
FETCH cursor_name INTO variables list;
|
After that, you can check to see if there is any row available before fetching it.
Finally, you call the CLOSE statement to deactivate the cursor and release the memory associated with it as follows:
|
1
|
CLOSE cursor_name;
|
When the cursor is no longer used, you should close it.
When working with MySQL cursor, you must also declare a NOT FOUND handler to handle the situation when the cursor could not find any row. Because each time you call the FETCHstatement, the cursor attempts to read the next row in the result set. When the cursor reaches the end of the result set, it will not be able to get the data, and a condition is raised. The handler is used to handle this condition.
To declare a NOT FOUND handler, you use the following syntax:
|
1
|
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET finished = 1;
|
Where finished is a variable to indicate that the cursor has reached the end of the result set. Notice that the handler declaration must appear after variable and cursor declaration inside the stored procedures.
The following diagram illustrates how MySQL cursor works.
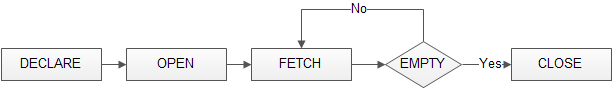
MySQL Cursor Example
We are going to develop a stored procedure that builds an email list of all employees in theemployees table in the MySQL sample database.
First, we declare some variables, a cursor for looping over the emails of employees, and a NOT FOUND handler:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
DECLARE finished INTEGER DEFAULT 0;
DECLARE email varchar(255) DEFAULT "";
-- declare cursor for employee email
DEClARE email_cursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT email FROM employees;
-- declare NOT FOUND handler
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER
FOR NOT FOUND SET finished = 1;
|
Next, we open the email_cursor by using the OPEN statement:
|
1
|
OPEN email_cursor;
|
Then, we iterate the email list, and concatenate all emails where each email is separated by a semicolon(;):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
get_email: LOOP
FETCH email_cursor INTO v_email;
IF v_finished = 1 THEN
LEAVE get_email;
END IF;
-- build email list
SET email_list = CONCAT(v_email,";",email_list);
END LOOP get_email;
|
After that, inside the loop we used the v_finished variable to check if there is any email in the list to terminate the loop.
Finally, we close the cursor using the CLOSE statement:
|
1
|
CLOSE email_cursor;
|
The build_email_list stored procedure is as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE build_email_list (INOUT email_list varchar(4000))
BEGIN
DECLARE v_finished INTEGER DEFAULT 0;
DECLARE v_email varchar(100) DEFAULT "";
-- declare cursor for employee email
DEClARE email_cursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT email FROM employees;
-- declare NOT FOUND handler
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER
FOR NOT FOUND SET v_finished = 1;
OPEN email_cursor;
get_email: LOOP
FETCH email_cursor INTO v_email;
IF v_finished = 1 THEN
LEAVE get_email;
END IF;
-- build email list
SET email_list = CONCAT(v_email,";",email_list);
END LOOP get_email;
CLOSE email_cursor;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
|
You can test the build_email_list stored procedure using the following script:
|
1
2
3
|
SET @email_list = "";
CALL build_email_list(@email_list);
SELECT @email_list;
|
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to use MySQL cursor to iterate a result set and process each row accordingly.
MySQL Cursor的更多相关文章
- mysql cursor游标的使用,实例
mysql被oracle收购后,从mysql-5.5开始,将InnoDB作为默认存储引擎,是一次比较重大的突破.InnoDB作为支持事务的存储引擎,拥有相关的RDBMS特性:包括ACID事务支持,数据 ...
- MySQL Cursor Demo
-- 使用cursor的demo -- ==============================## -- 删除存储过程 DROP PROCEDURE USP_TestCursor; DELIMI ...
- cursor游标(mysql)
/* 游标 cursor 什么是游标?为什么需要游标 使用存储过程对sql进行编程的时候,我们查询的语句可能是数据是多个,它总是一口气全部执行,我们无法针对每一条进行判断.也就是说,我们无法控制程序的 ...
- Mysql游标的简明写法
-- cursor 游标/*declare 声明; declare 游标名 cursor for select_statement;open 找开; open 游标名fetch 取值; fetch 游 ...
- C API向MySQL插入批量数据的快速方法——关于mysql_autocommit
MySQL默认的数据提交操作模式是自动提交模式(autocommit).这就表示除非显式地开始一个事务,否则每个查询都被当做一个单独的事务自动执行.我们可以通过设置autocommit的值改变是否是自 ...
- python操作MongoDB、MySQL、Postgres、Sqlite、redis实例
总结:除了MongoDB.redis,其他三个数据库用python来操作其实是差不多的.所有例子都很简单,实际生产环境中的数据库操作远比这复杂得多,命令也比我例子中的多得多,我这里高级一点的用法就是批 ...
- MySQL数据库再回首
前言: 数据库是程序员的数据源泉,加上近期 要开发DB可视化.性能分析的功能 重新回顾一下MySQL知识,以下是笔记: MySQL架构 MySQL基础理论 1.什么是关系型数据库? 关系型数据库,这个 ...
- python mysql数据库操作
一.pymysql 模块安装(本文博客推荐:https://www.cnblogs.com/clschao/articles/10023248.html) pip3 install pymysql 二 ...
- 自定义 Mysql 类 与 自定义 异常类
import MySQLdb class MyExcept(Exception): ''' 常见做法定义异常基类,然后在派生不同类型的异常 ''' def __init__(self, *args): ...
随机推荐
- SpringMVC自定义注入controller变量
springmvc config the controller parameter injection 问题描述 在SpringMVC中默认可以注入Model,ModelAndView,@Reques ...
- IOS Socket 02-Socket基础知识
1. 简介 Socket就是为网络服务提供的一种机制 通信的两端都是Socket 网络通信其实就是Socket间的通信 数据在两个Socket间通过IO传输 2. Socket通信流程图 3. 模拟Q ...
- Objective-C实现发短信和接电话
发短信: [[UIApplication sharedApplication]openURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"sms://10000"]]; 打电话: ...
- 缓存篇(Cache)~第二回 使用static静态成员实现服务器端缓存(导航面包屑)~续
返回目录 在写完首篇cache文章后,有些朋友给我来信,希望可以使用JS的方法来实现这个导航功能,所以,才有了这篇文章,JS与C#不同,它虽然有引用类型,但它不具备一些引用类型的特性,如它的方法参数为 ...
- 第十六回 IoC组件Unity续~批量动态为Unity添加类型和行为
回到目录 之前的一篇Unity的文章主要是基本的实现,并没有什么特别的地方,使用Unity可以方便的实现应用程序的IoC控制反转,这给我们的应用程序在耦合度上变得高了,同时可测试性加强了,当然,这些的 ...
- Android上dip、dp、px、sp等单位说明
Android上dip.dp.px.sp等单位说明 dip device independent pixels(设备独立像素). 不同设备不同的显示效果,这个和设备硬件有关,一般我们为了支持WVGA ...
- SQLServer数据库还原提示 数据库正在使用,无法获得独占访问权
还原数据库的时候提示下图的错误:
- CSS字体
字体系列 [1]5种通用字体系列:拥有相似外观的字体系列 serif字体:字体成比例,且有上下短线,包括Times\Georgia\New century Schoolbook sans-serif字 ...
- SQL*Loader之CASE7
CASE7 1. SQL脚本 case7包含两个SQL脚本,一个是删除脚本ulcase7e.sql,一个是创建脚本ulcase7s.sql [oracle@node3 ulcase]$ cat ulc ...
- Unity3D 游戏前端开发技能树(思维导图)
如果做游戏也是一种游戏,那么这个游戏的自由度实在是太高了.(导图源文件链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1eSHpH5o 密码:qzl5) 最近要用思维导图软件Xmind把自己的思路 ...
