win32 - 匿名管道的使用
目标: 创建一个父进程和子进程,在子进程的控制台窗口输入数据,数据通过管道发送给父进程,父进程的控制台窗口读取数据,最后将数据打印出来。
Parent.cpp
//CMD.exe
#include <windows.h>
#include <tchar.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <strsafe.h> #define BUFSIZE 4096 HANDLE g_hChildStd_Rd = NULL;
HANDLE g_hChildStd_Wr = NULL; HANDLE g_hInputFile = NULL; void CreateChildProcess(void);
void ReadFromPipe(void);
void ErrorExit(LPCWSTR); int _tmain(int argc, TCHAR* argv[])
{
SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES saAttr; printf("\n->Start of parent execution.\n"); // Set the bInheritHandle flag so pipe handles are inherited. saAttr.nLength = sizeof(SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES);
saAttr.bInheritHandle = TRUE;
saAttr.lpSecurityDescriptor = NULL; // Create a pipe for the child process's STDOUT. if (!CreatePipe(&g_hChildStd_Rd, &g_hChildStd_Wr, &saAttr, 0))
ErrorExit(L"StdoutRd CreatePipe"); // Ensure the read handle to the pipe for STDOUT is not inherited. if (!SetHandleInformation(g_hChildStd_Rd, HANDLE_FLAG_INHERIT, 0))
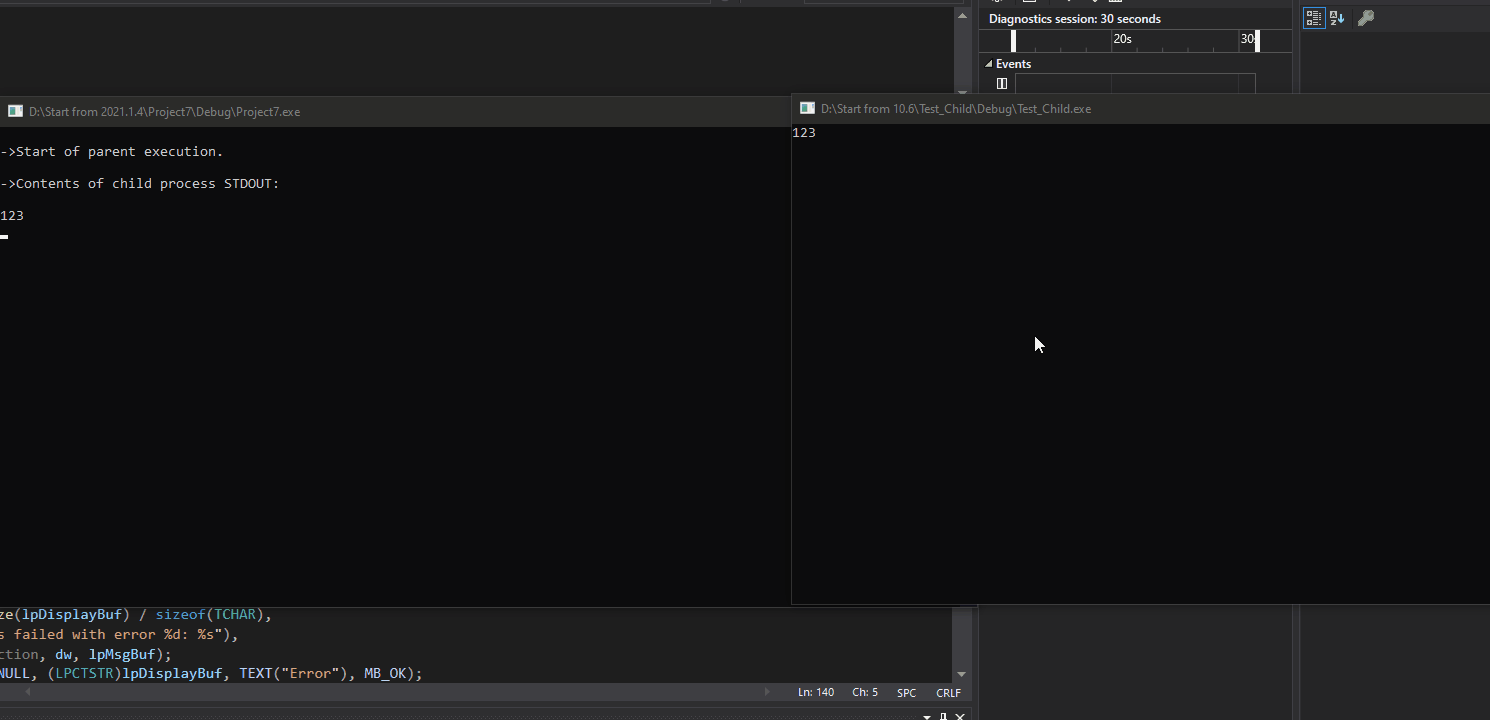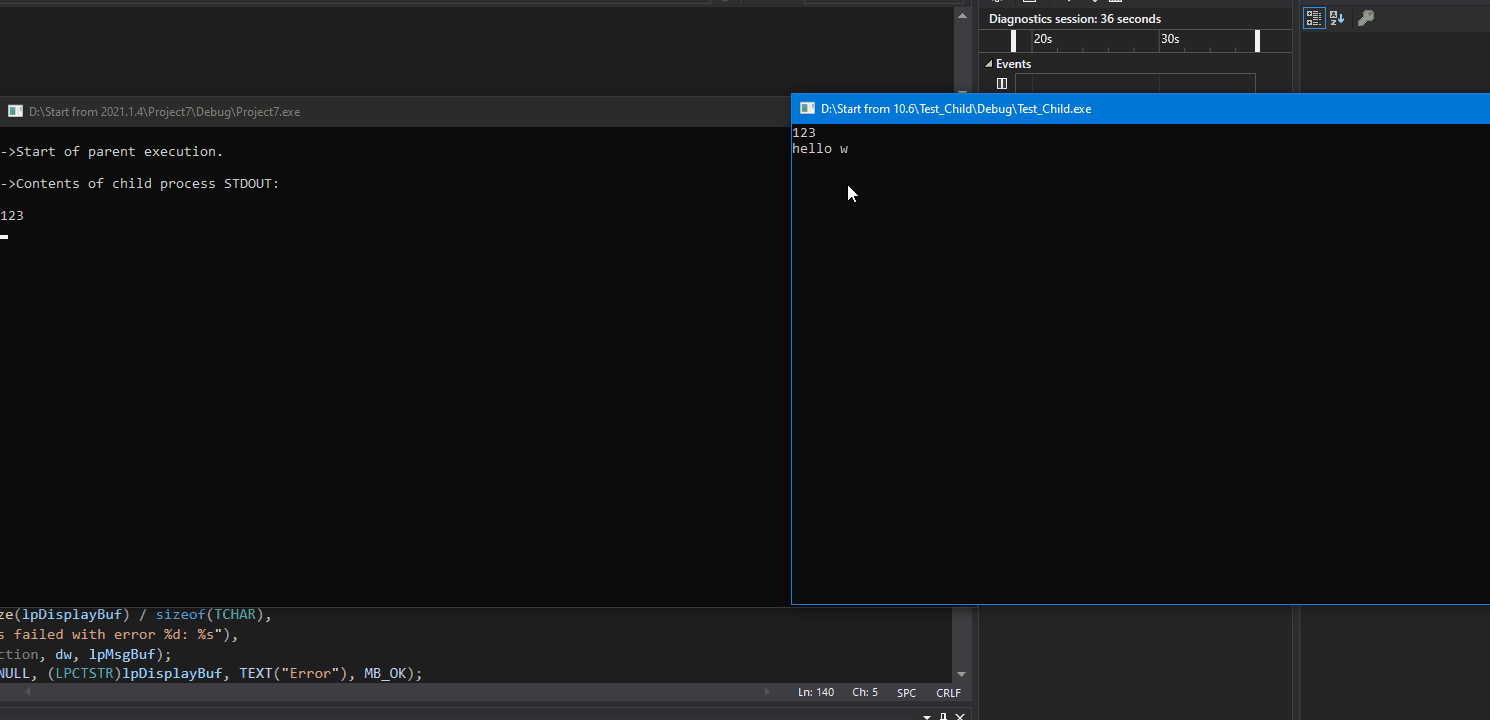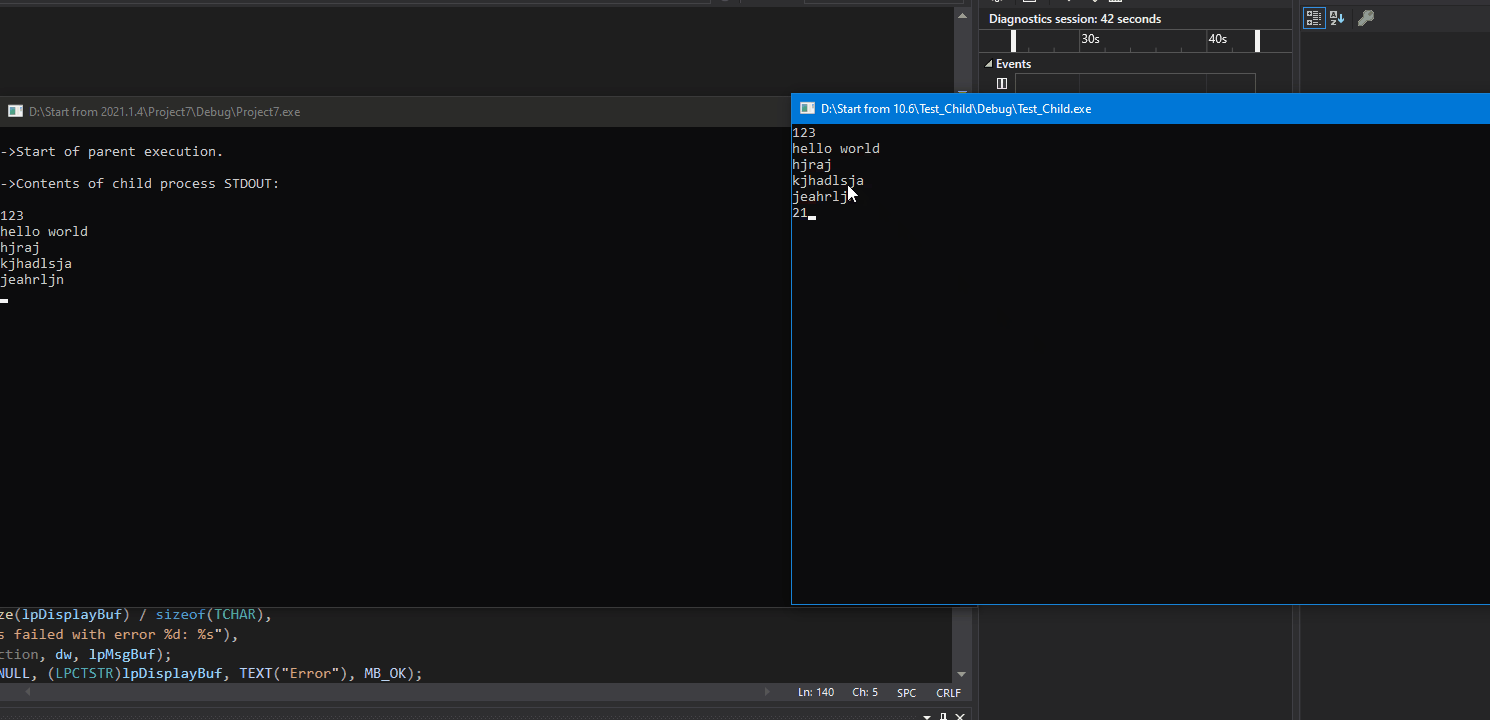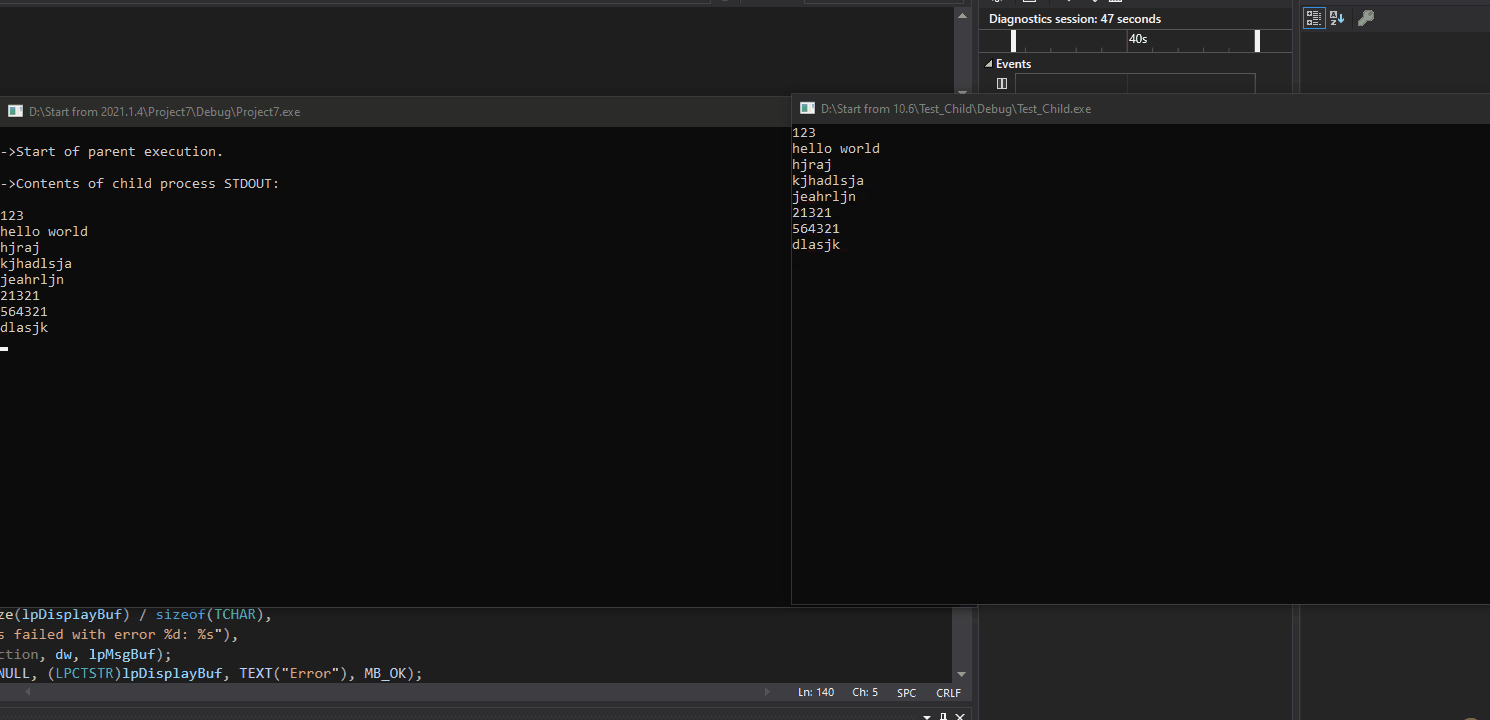
ErrorExit(L"Stdout SetHandleInformation"); CreateChildProcess(); // Read from pipe that is the standard output for child process. printf("\n->Contents of child process STDOUT:\n\n");
ReadFromPipe(); printf("\n->End of parent execution.\n"); return 0;
} void CreateChildProcess()
{
TCHAR szCmdline[] = TEXT("Child.exe");
PROCESS_INFORMATION piProcInfo;
STARTUPINFO siStartInfo;
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE; // Set up members of the PROCESS_INFORMATION structure. ZeroMemory(&piProcInfo, sizeof(PROCESS_INFORMATION)); ZeroMemory(&siStartInfo, sizeof(STARTUPINFO));
siStartInfo.cb = sizeof(STARTUPINFO);
siStartInfo.hStdError = g_hChildStd_Wr;
siStartInfo.hStdOutput = g_hChildStd_Wr;
siStartInfo.dwFlags |= STARTF_USESTDHANDLES; // Create the child process. bSuccess = CreateProcess(NULL,
szCmdline, // command line
NULL, // process security attributes
NULL, // primary thread security attributes
TRUE, // handles are inherited
CREATE_NEW_CONSOLE, // creation flags
NULL, // use parent's environment
NULL, // use parent's current directory
&siStartInfo, // STARTUPINFO pointer
&piProcInfo); // receives PROCESS_INFORMATION // If an error occurs, exit the application.
if (!bSuccess)
ErrorExit(L"CreateProcess");
else
{
CloseHandle(piProcInfo.hProcess);
CloseHandle(piProcInfo.hThread); CloseHandle(g_hChildStd_Wr);
}
} void ReadFromPipe(void)
// Read output from the child process's pipe for STDOUT
// and write to the parent process's pipe for STDOUT.
// Stop when there is no more data.
{
DWORD dwRead, dwWritten;
CHAR chBuf[BUFSIZE];
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE;
HANDLE hParentStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE); for (;;)
{
bSuccess = ReadFile(g_hChildStd_Rd, chBuf, BUFSIZE, &dwRead, NULL);
if (!bSuccess || dwRead == 0) break; bSuccess = WriteFile(hParentStdOut, chBuf,
dwRead, &dwWritten, NULL);
if (!bSuccess) break;
}
} void ErrorExit(LPCWSTR lpszFunction)
// Format a readable error message, display a message box,
// and exit from the application.
{
LPVOID lpMsgBuf;
LPVOID lpDisplayBuf;
DWORD dw = GetLastError(); FormatMessage(
FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER |
FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM |
FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS,
NULL,
dw,
MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT),
(LPTSTR)&lpMsgBuf,
0, NULL); lpDisplayBuf = (LPVOID)LocalAlloc(LMEM_ZEROINIT,
(lstrlen((LPCTSTR)lpMsgBuf) + lstrlen((LPCTSTR)lpszFunction) + 40) * sizeof(TCHAR));
StringCchPrintf((LPTSTR)lpDisplayBuf,
LocalSize(lpDisplayBuf) / sizeof(TCHAR),
TEXT("%s failed with error %d: %s"),
lpszFunction, dw, lpMsgBuf);
MessageBox(NULL, (LPCTSTR)lpDisplayBuf, TEXT("Error"), MB_OK); LocalFree(lpMsgBuf);
LocalFree(lpDisplayBuf);
ExitProcess(1);
}
Child.cpp
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h> #define BUFSIZE 4096
#pragma warning(disable:4996) int main(void)
{
CHAR chBuf[BUFSIZE] = {};
DWORD dwRead, dwWritten;
HANDLE hStdin, hStdout;
BOOL bSuccess; hStdout = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
hStdin = GetStdHandle(STD_INPUT_HANDLE);
if (
(hStdout == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) ||
(hStdin == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
)
ExitProcess(1); // Send something to this process's stdout using printf.
printf("\n ** This is child process. ** \n"); // This simple algorithm uses the existence of the pipes to control execution.
// It relies on the pipe buffers to ensure that no data is lost.
// Larger applications would use more advanced process control. for (;;)
{
ReadFile(hStdin, chBuf, strlen(chBuf) + 2, &dwRead, NULL);
// Write to standard output and stop on error.
bSuccess = WriteFile(hStdout, chBuf, strlen(chBuf)+2, &dwWritten, NULL);
memset(chBuf, NULL, BUFSIZE);
if (!bSuccess)
break;
}
return 0;
}
效果:
win32 - 匿名管道的使用的更多相关文章
- Linux学习笔记(12)-进程间通信|匿名管道
Linux的进程间通信有几种方式,包括,管道,信号,信号灯,共享内存,消息队列和套接字等-- 现在一个个的开始学习! ----------------------------------------- ...
- Linux进程间通信(三):匿名管道 popen()、pclose()、pipe()、close()、dup()、dup2()
在前面,介绍了一种进程间的通信方式:使用信号,我们创建通知事件,并通过它引起响应,但传递的信息只是一个信号值.这里将介绍另一种进程间通信的方式——匿名管道,通过它进程间可以交换更多有用的数据. 一.什 ...
- linux进程通信之使用匿名管道进行父子进程通信
管道:是指用于连接一个读进程和一个写进程,以实现它们之间通信的共享文件,又称pipe文件. 管道是单向的.先进先出的.无结构的.固定大小的字节流,它把一个进程的标准输出和另一个进程的标准输入连接在一起 ...
- [C++] socket -9[匿名管道]
::怎么弄都不能读取信息....先把代码放着.... #include<windows.h> #include<stdio.h> int main() { HANDLE rea ...
- 匿名管道读取CMD回显信息
之前用了很坑爹的做法去读取了cmd命令的回显信息,现在发现了用匿名管道的实现方法,由于楼主没有学过Windows核心编程,找了一个代码来凑数 存下来以后研究 #include <windows. ...
- Windows下 C++ 实现匿名管道的读写操作
由于刚弄C++没多久,部分还不熟练,最近又由于开发需求要求实现与其他程序进行通信,瞬间就感觉想到了匿名通信.于是自己查阅了一下资料,实现了一个可读可写的匿名管道: 源代码大部分都有注释: Pipe.h ...
- Linux进程间通信-匿名管道
前面我们讲了进程间通信的一种方式,共享内存.下面看一看另一种机制,匿名管道.1.什么是管道管道是一个进程的数据流到另一个进程的通道,即一个进程的数据输出作为另一个进程的数据输入,管道起到了桥梁的作用. ...
- IPC——匿名管道
Linux进程间通信——使用匿名管道 在前面,介绍了一种进程间的通信方式:使用信号,我们创建通知事件,并通过它引起响应,但传递的信息只是一个信号值.这里将介绍另一种进程间通信的方式——匿名管道,通过它 ...
- 使用匿名管道在进程间通信 (System.IO.Pipes使用)(转)
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yukaizhao/archive/2011/08/04/system-io-pipes.html 管道的用途是在同一台机器上的进程之间通信,也 ...
- Linux进程通信----匿名管道
Linux进程通信中最为简单的方式是匿名管道 匿名管道的创建需要用到pipe函数,pipe函数参数为一个数组表示的文件描述字.这个数组有两个文件描 述字,第一个是用于读数据的文件描述符第二个是用于写数 ...
随机推荐
- [转帖]没 K8s 用不了 Chaos Mesh?试试 Chaosd
https://cn.pingcap.com/blog/cannot-use-chaosmesh-without-k8s-then-try-chaosd Chaosd 是什么? 相信大家对 Chaos ...
- [转帖]人大金仓和PG的关系
作者:山抹微云链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/582960448/answer/2997151260来源:知乎著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转 ...
- [转帖]MySQL InnoDB存储引擎大观
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1709263187856706948&wfr=spider&for=pc MySQL InnoDB 引擎现在广为 ...
- [转帖]基于 Skywalking 部署应用性能监控
https://www.jianshu.com/p/50627b9ab0be 今天我们就着重讲一讲如何基于 Skywalking 来快速搭建一套应用性能监控平台 walkingfunny.com. ...
- [转帖]总结:Springboot监控Actuator相关
一.介绍 由于项目中使用的仍然是比较老旧的1.5.6版本,所以本文是基于此版本进行描述. 二.Actuator使用 ActuatorActuator是Spring Boot提供的对应用系统的监控和管理 ...
- git日志输出相关命令
git log 默认输出所有的日志 git log 默认输出所有的日志 git 日志输出--只看最近的两条或者三条 有些时候我们可能只需要看最近的2或者3条日志 git log -2 日志输出--只看 ...
- vue在render函数中如何实现v-model和事件绑定(4)
1.h函数的三个参数 第一个参数是必须的. 类型:{String | Object | Function} 一个 HTML 标签名.一个组件.一个异步组件.或一个函数式组件. 是要渲染的html标签. ...
- net core部署iis执行此操作时出错web.config
页面访问会报服务器内部错误,你点对应的IIS下的默认页面或模块会出现下面的错语. 请到官网下载对应的运行时:https://www.microsoft.com/net/download 如果是服务器, ...
- 策略模式学习,使用go实现策略模式
策略模式 定义 优点 缺点 使用场景 代码实现 策略模式和工厂模式的区别 参考 策略模式 定义 策略模式定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让他们之间可以相互替换,此模式让算法的变化,不会影响到客户端的使用 ...
- 码云gitee创建仓库并用git上传文件
相关文章链接: 码云(gitee)配置SSH密钥 码云gitee创建仓库并用git上传文件 git 上传错误This oplation equires one of the flowi vrsions ...
