secure boot (一)fit image
前言
secure boot 和FIT Image是前段时间接触到的,其实早就该总结下了,奈何懒癌犯了,拖了好久才写出来。
之前也有人问我,工作后最大的感受是什么?我的回答是:“快速学习”。
就嵌入式来讲,大多数应届生在校期间可能都没做过完整的项目,仅凭在校期间学习的内容很难胜任公司的要求。
就底层驱动来讲,虽然我之前也学习过韦东山老师的上s3c2440的课程,但是到了公司才发现,这些内容其实都已经过时了。
但并不是说这些内容都没有必要去学习了。在学习的过程中,认为最重要的是培养我们的自学能力。
很多初学者在刚开始学习时,可能就败在了搭建环境上。搭建环境时遇到问题不知道怎么办?
我们日常开发中遇到的90%的问题,在网上都有人遇到过,也有相应的解决办法。学会利用bing,google,stackoverflow等搜索工具是一项很重要的技能。
如果遇到了网上没有的问题怎么办?软件问题要先搞清楚原理,再去看代码逻辑。硬件问题看官方手册。像Linux kernel,ARM等都提供了完善的手册,大部分问题在手册中都有相应说明。
好了,扯远了。下面回归正题。
本文主要介绍了FIT Image起源,制作方法,its的语法结构,bootm 启动FIT Image的方式。
本文这篇文章是对后面介绍的secure boot做铺垫。ARMv8 secure boot一种实现的方式就是利用了FIT Image的特性。
zImage,uImage, Legacy uImage 和 FIT uImage
内核经过编译后,会生成一个elf的可执行程序,叫vmlinux,这个就是原始的未经任何处理加工的原版内核elf文件。不过,最终烧写在嵌入式设备上的并不是这个文件。而是经过objcopy工具加工后的专门用于烧录的镜像格式Image。
原则上Image就可以直接被烧录到Flash上进行启动执行,但linux的内核开发者觉得Image还是太大了,因此对Image进行了压缩,并且在Image压缩后的文件的前端附加了一部分解压缩代码,构成了一个压缩格式的镜像文件就叫zImage。
解压的时候,通过zImage镜像头部的解压缩代码进行自解压,然后执行解压出来的内核镜像。
Uboot要正确启动Linux内核,就需要知道内核的一些信息,比如镜像的类型(kernel image,dtb,ramdisk image),镜像在内存的位置,镜像的链接地址,镜像文件是否有压缩等等。
Uboot为了拿到这些信息,发明了一种内核格式叫uImage,也叫Legacy uImage。uImage是由zImage加工得到的,uboot中有一个工具mkimage,该工具会给zImage加一个64字节的header,将启动内核所需的信息存储在header中。uboot启动后,从header中读取所需的信息,按照指示,进行相应的动作即可。
header格式可以参考:include/image.h。mkimage源码在tools/mkimage
FIT image的来源
有了Legacy uImage后,为什么又搞出来一个FIT uImage呢?
在Linus Torvalds 看来,内核中arch/arm/mach-xxx充斥着大量的垃圾代码。因为内核并不关心板级细节,比如板上的platform设备、resource、i2c_board_info、spi_board_info等等。大家有兴趣可以看下s3c2410的板级目录,代码量在数万行。
因此,ARM社区引入了Device Tree,使用Device Tree后,许多硬件的细节可以直接透过它传递给Linux,而不再需要在kernel中进行大量的冗余编码。
为了更好的支持单个固件的通用性,Uboot也需要对这种uImage固件进行支持。FIT uImage中加入多个dtb文件 和ramdisk文件,当然如果需要的话,同样可以支持多个kernel文件。
内核中的FDT全程为flattened device tree,FIT全称叫flattened image tree。FIT利用了Device Tree Source files(DTS)的语法,生成的Image文件也和dtb文件类似(称作itb)。
这样的目的就是能够使同一个uImage能够在Uboot中选择特定的kernel/dtb和ramdisk进行启动了,达成一个uImage可以通用多个板型的目的。
制作FIT Image
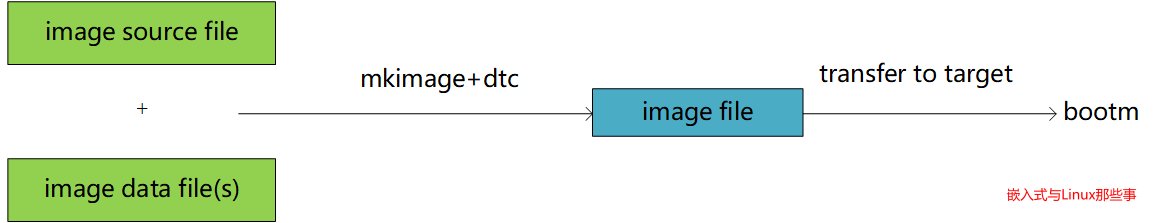
制作FIT Image需要用到两个工具,mkimage和的dtc。dtc要导入到环境变量$PATH中,mkimage会调用dtc。
mkimage的输入为 image source file,它定义了启动过程中image的各种属性,扩展名为.its。its只是描述了Image的属性,实际的Image data 是在uImage中,具体路径由its指定。
如下是kernel 的its文件,后面会介绍各项内容的含义。
/*
* Simple U-Boot uImage source file containing a single kernel
*/
/dts-v1/;
/ {
description = "Simple image with single Linux kernel";
#address-cells = <1>;
images {
kernel@1 {
description = "Vanilla Linux kernel";
data = /incbin/("./vmlinux.bin.gz"); # Image data 具体路径
type = "kernel";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash@1 {
algo = "crc32";
};
hash@2 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
};
configurations {
default = "config@1";
config@1 {
description = "Boot Linux kernel";
kernel = "kernel@1";
};
};
};
mkimage的输出是一个后缀为.itb的二进制文件,包含了所有需要的数据(kernel,dtb,ramdisk)。itb文件制作好之后,就可以直接加载到嵌入式设备上,通过bootm命令启动。
总结下制作FIT Image的4个必要文件:
- mkimage,
- dtc
- its(image source file (*.its))
- image data file(s)。
its语法结构
uImage Tree 的根节点结构
/ o image-tree
|- description = "image description"
|- timestamp = <12399321>
|- #address-cells = <1>
|
o images
| |
| o image@1 {...}
| o image@2 {...}
| ...
|
o configurations
|- default = "conf@1"
|
o conf@1 {...}
o conf@2 {...}
...
description:描述uImage的文本。
timestamp:修改Image镜像的时间,由mkimage工具自动生成。在security boot中,timestamp不同也会被认为是不同的Image。
images:子镜像,如kernel Image,ramdisk Image。
configurations:配置项节点,可以将不同类型的二进制文件,根据不同的场景,组合起来,形成一个个的配置项。u-boot在boot的时候,以配置项为单位加载、执行,这样就可以根据不同的场景,方便的选择不同的配置。
'/images' node
该节点中描述了Image镜像必要的信息.
o image@1
|- description = "component sub-image description"
|- data = /incbin/("path/to/data/file.bin")
|- type = "sub-image type name"
|- arch = "ARCH name"
|- os = "OS name"
|- compression = "compression name"
|- load = <00000000>
|- entry = <00000000>
|
o hash@1 {...}
o hash@2 {...}
...
description:子镜像的文本描述,可以随便写。
type:子镜像的类型,比如standalone,kernel,ramdisk,firmware等等。
data:包含该节点二进制文件的路径。
compression:压缩方式,比如none,gzip,bzip2。
os:操作系统的名称,如solaris,uboot,qnx等。
arch:平台架构,如arm,mips,i386等。
entry:二进制文件入口地址,即链接地址。
load:二进制文件的加载位置。
hash@1:镜像使用的校验算法,如sha256,crc32等。
Hash nodes
o hash@1
|- algo = "hash or checksum algorithm name"
|- value = [hash or checksum value]
algo:算法名称,如crc32,md5,sha256等。
value:算法校验值,即algo计算后的数值。
'/configurations' node
o configurations
|- default = "default configuration sub-node unit name"
|
o config@1 {...}
o config@2 {...}
...
default:默认的子节点的配置
config@1: 该配置具体使用那些kernel Image,ramdisk Image等。
Configuration nodes
o config@1
|- description = "configuration description"
|- kernel = "kernel sub-node unit name"
|- ramdisk = "ramdisk sub-node unit name"
|- fdt = "fdt sub-node unit-name" [, "fdt overlay sub-node unit-name", ...]
|- fpga = "fpga sub-node unit-name"
|- loadables = "loadables sub-node unit-name"
description:该配置的名称。
kernel:镜像类型为kernel的单元的名称。
ramdisk:镜像类型为ramdisk的单元的名称。
fdt:镜像类型为fdt的单元的名称。
loadables:额外的可加载的二进制文件的列表,U-Boot将在给定的起始地址加载每个二进制文件。
举例
如下是一个有多种kernels, ramdisks and FDT blobs镜像多套配置的its文件。它包含了3种配置,每种配置使用了不同的kernel、ramdisk和fdt,默认配置项由“default”指定,当然也可以在运行时指定。
/*
* U-Boot uImage source file with multiple kernels, ramdisks and FDT blobs
*/
/dts-v1/;
/ {
description = "Various kernels, ramdisks and FDT blobs";
#address-cells = <1>;
images {
kernel@1 {
description = "vanilla-2.6.23";
data = /incbin/("./vmlinux.bin.gz");
type = "kernel";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash@1 {
algo = "md5";
};
hash@2 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
kernel@2 {
description = "2.6.23-denx";
data = /incbin/("./2.6.23-denx.bin.gz");
type = "kernel";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash@1 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
kernel@3 {
description = "2.4.25-denx";
data = /incbin/("./2.4.25-denx.bin.gz");
type = "kernel";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash@1 {
algo = "md5";
};
};
ramdisk@1 {
description = "eldk-4.2-ramdisk";
data = /incbin/("./eldk-4.2-ramdisk");
type = "ramdisk";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash@1 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
ramdisk@2 {
description = "eldk-3.1-ramdisk";
data = /incbin/("./eldk-3.1-ramdisk");
type = "ramdisk";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash@1 {
algo = "crc32";
};
};
fdt@1 {
description = "tqm5200-fdt";
data = /incbin/("./tqm5200.dtb");
type = "flat_dt";
arch = "ppc";
compression = "none";
hash@1 {
algo = "crc32";
};
};
fdt@2 {
description = "tqm5200s-fdt";
data = /incbin/("./tqm5200s.dtb");
type = "flat_dt";
arch = "ppc";
compression = "none";
load = <00700000>;
hash@1 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
};
configurations {
default = "config@1";
config@1 {
description = "tqm5200 vanilla-2.6.23 configuration";
kernel = "kernel@1";
ramdisk = "ramdisk@1";
fdt = "fdt@1";
};
config@2 {
description = "tqm5200s denx-2.6.23 configuration";
kernel = "kernel@2";
ramdisk = "ramdisk@1";
fdt = "fdt@2";
};
config@3 {
description = "tqm5200s denx-2.4.25 configuration";
kernel = "kernel@3";
ramdisk = "ramdisk@2";
};
};
};
FIT Image的编译和启动
在服务器上,可以使用mkimage工具制作 FIT Image。
如下是kernel_fdt.its,下面将使用该文件制作itb。
/*
* Simple U-Boot uImage source file containing a single kernel and FDT blob
*/
/dts-v1/;
/ {
description = "Simple image with single Linux kernel and FDT blob";
#address-cells = <1>;
images {
kernel@1 {
description = "Vanilla Linux kernel";
data = /incbin/("./vmlinux.bin.gz");
type = "kernel";
arch = "ppc";
os = "linux";
compression = "gzip";
load = <00000000>;
entry = <00000000>;
hash@1 {
algo = "crc32";
};
hash@2 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
fdt@1 {
description = "Flattened Device Tree blob";
data = /incbin/("./target.dtb");
type = "flat_dt";
arch = "ppc";
compression = "none";
hash@1 {
algo = "crc32";
};
hash@2 {
algo = "sha1";
};
};
};
configurations {
default = "conf@1";
conf@1 {
description = "Boot Linux kernel with FDT blob";
kernel = "kernel@1";
fdt = "fdt@1";
};
};
};
$ mkimage -f kernel_fdt.its kernel_fdt.itb
DTC: dts->dtb on file "kernel_fdt.its"
$
$ mkimage -l kernel_fdt.itb
FIT description: Simple image with single Linux kernel and FDT blob
Created: Tue Mar 11 16:29:22 2008
Image 0 (kernel@1)
Description: Vanilla Linux kernel
Type: Kernel Image
Compression: gzip compressed
Data Size: 1092037 Bytes = 1066.44 kB = 1.04 MB
Architecture: PowerPC
OS: Linux
Load Address: 0x00000000
Entry Point: 0x00000000
Hash algo: crc32
Hash value: 2c0cc807
Hash algo: sha1
Hash value: 264b59935470e42c418744f83935d44cdf59a3bb
Image 1 (fdt@1)
Description: Flattened Device Tree blob
Type: Flat Device Tree
Compression: uncompressed
Data Size: 16384 Bytes = 16.00 kB = 0.02 MB
Architecture: PowerPC
Hash algo: crc32
Hash value: 0d655d71
Hash algo: sha1
Hash value: 25ab4e15cd4b8a5144610394560d9c318ce52def
Default Configuration: 'conf@1'
Configuration 0 (conf@1)
Description: Boot Linux kernel with FDT blob
Kernel: kernel@1
FDT: fdt@1
在当前目录下就可以找到kernel_fdt.itb,itb文件就可以加载到设备上启动。
> tftp 900000 /path/to/tftp/location/kernel_fdt.itb
Using FEC device
TFTP from server 192.168.1.1; our IP address is 192.168.160.5
Filename '/path/to/tftp/location/kernel_fdt.itb'.
Load address: 0x900000
Loading: #################################################################
###########
done
Bytes transferred = 1109776 (10ef10 hex)
=> iminfo
## Checking Image at 00900000 ...
FIT image found
FIT description: Simple image with single Linux kernel and FDT blob
Created: 2008-03-11 15:29:22 UTC
Image 0 (kernel@1)
Description: Vanilla Linux kernel
Type: Kernel Image
Compression: gzip compressed
Data Start: 0x009000ec
Data Size: 1092037 Bytes = 1 MB
Architecture: PowerPC
OS: Linux
Load Address: 0x00000000
Entry Point: 0x00000000
Hash algo: crc32
Hash value: 2c0cc807
Hash algo: sha1
Hash value: 264b59935470e42c418744f83935d44cdf59a3bb
Image 1 (fdt@1)
Description: Flattened Device Tree blob
Type: Flat Device Tree
Compression: uncompressed
Data Start: 0x00a0abdc
Data Size: 16384 Bytes = 16 kB
Architecture: PowerPC
Hash algo: crc32
Hash value: 0d655d71
Hash algo: sha1
Hash value: 25ab4e15cd4b8a5144610394560d9c318ce52def
Default Configuration: 'conf@1'
Configuration 0 (conf@1)
Description: Boot Linux kernel with FDT blob
Kernel: kernel@1
FDT: fdt@1
=> bootm
## Booting kernel from FIT Image at 00900000 ...
Using 'conf@1' configuration
Trying 'kernel@1' kernel subimage
Description: Vanilla Linux kernel
Type: Kernel Image
Compression: gzip compressed
Data Start: 0x009000ec
Data Size: 1092037 Bytes = 1 MB
Architecture: PowerPC
OS: Linux
Load Address: 0x00000000
Entry Point: 0x00000000
Hash algo: crc32
Hash value: 2c0cc807
Hash algo: sha1
Hash value: 264b59935470e42c418744f83935d44cdf59a3bb
Verifying Hash Integrity ... crc32+ sha1+ OK
Uncompressing Kernel Image ... OK
## Flattened Device Tree from FIT Image at 00900000
Using 'conf@1' configuration
Trying 'fdt@1' FDT blob subimage
Description: Flattened Device Tree blob
Type: Flat Device Tree
Compression: uncompressed
Data Start: 0x00a0abdc
Data Size: 16384 Bytes = 16 kB
Architecture: PowerPC
Hash algo: crc32
Hash value: 0d655d71
Hash algo: sha1
Hash value: 25ab4e15cd4b8a5144610394560d9c318ce52def
Verifying Hash Integrity ... crc32+ sha1+ OK
Booting using the fdt blob at 0xa0abdc
Loading Device Tree to 007fc000, end 007fffff ... OK
[ 0.000000] Using lite5200 machine description
[ 0.000000] Linux version 2.6.24-rc6-gaebecdfc (m8@hekate) (gcc version 4.0.0 (DENX ELDK 4.1 4.0.0)) #1 Sat Jan 12 15:38:48 CET 2008
bootm启动不同的配置
对于FIT Image,bootm有多种启动方式。
1. bootm <addr1>
2. bootm [<addr1>]:<subimg1>
3. bootm [<addr1>]#<conf>[#<extra-conf[#...]]
4. bootm [<addr1>]:<subimg1> [<addr2>]:<subimg2>
5. bootm [<addr1>]:<subimg1> [<addr2>]:<subimg2> [<addr3>]:<subimg3>
6. bootm [<addr1>]:<subimg1> [<addr2>]:<subimg2> <addr3>
7. bootm [<addr1>]:<subimg1> - [<addr3>]:<subimg3>
8. bootm [<addr1>]:<subimg1> - <addr3>
对于有多种镜像,多套配置的itb,都是以configurations 中default 指定的配置启动。
bootm 200000
也可以手动指定使用那套配置
bootm 200000#cfg@1
也可以手动搭配不同的镜像节点启动
bootm 200000:kernel@1 800000:ramdisk@2
bootm 200000:kernel@1 800000:ramdisk@1 800000:fdt@1
bootm 200000:kernel@2 200000:ramdisk@2 600000
bootm 200000:kernel@2 - 200000:fdt@1
如果bootm的时候不指定地址,则会使用CONFIG_SYS_LOAD_ADDR配置的地址。
总结
本文对FIT Image作了简单的介绍,更详细的内容可以参考官方文档。后面有时间会动手制作一个FIT Image在板子上跑下。
FIT Image可以兼容于多种板子,而无需重新进行编译烧写。 对于有多个kernel节点或者fdt节点等等,兼容性更强。同时,可以有多种configurations,来对kernel、fdt、ramdisk来进行组合。
本文参考
https://www.elecfans.com/emb/20190402899374.html
http://www.wowotech.net/u-boot/fit_image_overview.html
howto.txt
command_syntax_extensions.txt
source_file_format.txt
secure boot (一)fit image的更多相关文章
- secure boot(安全启动)下为内核模块签名
上一篇随笔中提到了如何在secure boot下安装Nvidia显卡驱动 >>上一篇随笔 如果不需要安装Nvidia显卡驱动,而且要生成密钥,可以参考>> 这篇文章 这里假设生 ...
- Linux secure boot(安全启动)时添加Nvidia显卡驱动
开启Secure boot情况下,在Fedora 21下安装Nvidia 显卡驱动的方法. Nvidia显卡驱动可以从官网上下载最新版>> 点击进入 下载后添加可执行权限: #chmod ...
- 华硕笔记本之secure boot
在ubuntu下安装cuda的时候,一直装不好,cuda-7.5.run已经装好了,但是编译cuda的例程时失败,提示cuda的库链接不上. 初步判断是secure boot的问题,因为在开启X的情况 ...
- 反Secure Boot垄断:兼谈如何在Windows 8电脑上安装Linux
感谢HQSQ的投递一.自由软件基金会的呼吁上周,2012年将近结束的时候,自由软件基金会(FSF)发出呼吁,要求人们继续支持反Secure Boot垄断,希望签名者能达到5万人(目前是4万).我觉得, ...
- Linux Foundation Secure Boot System Released
As promised, here is the Linux Foundation UEFI secure boot system. This was actually released to us ...
- 小米笔记本怎么关闭secure boot
关闭Secure Boot的步骤: 一.关闭 "快速启动" 功能 1.右键-开始菜单- 电源选项,进入后 点击"选择电源按钮的功能". 2.进入电源选项设置后, ...
- EDK II之Secure Boot简述
密钥对:公钥分发,私钥自留.常见的公钥格式:cer/der,常见的私钥格式:pfx. BIOS中Secure Boot的原理:把公钥包在code里面,当使用gBS->LoadImage()去加载 ...
- 笔记本 原来win10系统改装win7系统遇到 invaid signature detected.check secure boot policy setup问题
这次操作的笔记本电脑是 华硕R414U 大家如果遇到类似问题的话也可以参考这个方法,但是必须搞清楚电脑的型号,型号不同操作起来有差别的 我这里选择的重装系统的方法是最简单粗暴的硬盘安装方法,怎么硬 ...
- UEFI、BIOS、Secure Boot的关系和知识介绍
从Windows 8操作系统时代开始,安装操作系统的方法也有了很大的改变,Windows 8采用了Secure Boot引导启动的方式,而不是过去Win XP和Win 7的Legacy启动方式,从 ...
- [加密]ESP32 -Secure Boot 安全方案
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/espressif/article/details/79362094 Secure Boot 功能概述 方案概述 Secure Boot 的目的是保证 ...
随机推荐
- vertx的学习总结4之异步数据和事件流
一.异步数据和事件流 1.为什么流是事件之上的一个有用的抽象? 2.什么是背压,为什么它是异步生产者和消费者的基础? 3.如何从流解析协议数据? 1. 答:因为它能够将连续的事件序列化并按照顺序进行 ...
- SpringBoot项目整合微信登录
一.开通微信登录 去微信开发者平台 1.注册 2.邮箱激活 3.完善开发者资料 4.开发者资质认证 准备营业执照,1-2个工作日审批.300元 5.创建网站应用 6.提交审核,7个工作日审批 7.熟悉 ...
- 5分钟攻略Spring-Retry框架实现经典重试场景
前言 今天分享干货,控制了篇幅,5分钟内就能看完学会. 主题是Spring-Retry框架的应用,做了一个很清晰的案例,代码可下载自测. 框架介绍 Spring-Retry框架是Spring自带的功能 ...
- catcat-new【目录穿透+特殊文件】
catcat-new[目录穿透+特殊文件] 题目界面 点击任何一只猫猫,发现路径泄露: 解题步骤 测试目录遍历漏洞 路径: ?file=../../../../etc/passwd 成功读取到pass ...
- flask蓝图(这玩意就是django的子应用)
蓝图的概念类似django的子应用,作用就是分模块开发,有关联的都放在一起. 蓝图的创建步骤: 新建一个包(一个包就是一个模块.等同于一个子应用) 在包的__init__.py中创建蓝图对象 . 蓝图 ...
- CentOS 7.3 操作系统 详解安装手册
CentOS 7.3 操作系统 安装手册 在安装ESPC前(绿盟WAF.IPS等外置日志中心),需要确保已经在计算机中正确安装CentOS 7.3 x86_64(内核版本为3.10.0-514.el7 ...
- Windows Server 2012 R2 无法更新问题
Windows Server 2012 R2 无法更新问题 新安装的ISO镜像由于年久失修,原先的Update服务器可能已经失效,需要安装更新补丁,才可以正常指向新的更新服务器,甚至连系统激活(输入正 ...
- BUUCTF Web CyberPunk WriteUp
想直接查看payload的点这里 前言 二次注入(Second-Order Injection)是指攻击者在应用程序中注入恶意数据,然后在稍后的操作或不同的上下文中再次使用该恶意数据,导致安全漏洞.它 ...
- Vue3中使用TypeScript封装axios遇到的问题(AxiosRequestConfig)
如果您有更好的解决方法,欢迎评论区评论. 版本 "dependencies": { "axios": "^1.4.0", "van ...
- .NET技术分享日活动20221022
2022年10月22日下午,个人组织举办了山东地区的第六次.NET技术分享日活动.围绕.NET.低代码Low Code.云原生 Cloud Native.大数据.算法等方向进行创新技术的实践分享. 本 ...
