Java 同步代码块 - Synchronized Blocks
java锁实现原理:
http://blog.csdn.net/endlu/article/details/51249156
The synchronized keyword can be used to mark four different types of blocks:
- Instance methods
- Static methods
- Code blocks inside instance methods
- Code blocks inside static methods
Instance methods & Code blocks inside instance methods
Java实例方法同步是同步在拥有该方法的对象上
同步构造器中用括号括起来的对象叫做监视器对象
public class SyncBlockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
final MySyncBlockClass syncBlockClass = new MySyncBlockClass();
es.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
syncBlockClass.mehtod1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
es.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
syncBlockClass.mehtod2();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
es.shutdown();
}
}
class MySyncBlockClass {
public synchronized void mehtod1() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method1 run.");
}
public synchronized void mehtod2() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method2 run.");
}
}
// method1较method2延迟了2000ms
// 1479350064132:method2 run.
// 1479350066132:method1 run.
实例方法同步
/**
* method1 与method2等效
* 同步构造器中用括号括起来的对象叫做监视器对象
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public synchronized void mehtod1() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method1 run.");
} public synchronized void mehtod2() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method2 run.");
}
}
实例方法中的同步块
Static methods & Code blocks inside static methods
静态方法的同步是指同步在该方法所在的类对象上。因为在Java虚拟机中一个类只能对应一个类对象,所以同时只允许一个线程执行同一个类中的静态同步方法。
public class SyncBlockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
final MySyncBlockClass syncBlockClass1 = new MySyncBlockClass();
final MySyncBlockClass syncBlockClass2 = new MySyncBlockClass();
es.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
syncBlockClass1.mehtod1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
es.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
syncBlockClass2.mehtod2();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
es.shutdown();
}
}
class MySyncBlockClass {
public static synchronized void mehtod1() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method1 run.");
}
public static synchronized void mehtod2() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method2 run.");
}
}
// method1较method2延迟了3000ms
// 1479358310630:method1 run.
// 1479358314631:method2 run.
静态方法同步
/**
* method1 与method2等效
* 静态方法中的同步块
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static synchronized void mehtod1() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method1 run.");
} public static synchronized void mehtod2() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (MySyncBlockClass.class) {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + ":method2 run.");
}
}
静态方法中的同步块
示例:
以下代码对应的Block关系如下:
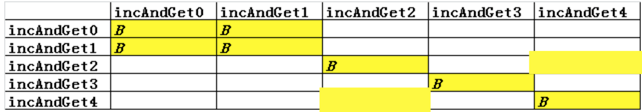
synchronized(class)与 static synchronized 等效
public class SyncMethod2 {
private int value = 0;
private final Object mutex = new Object();
public synchronized int incAndGet0() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("static synchronized void incAndGet0");
return ++value;
}
public int incAndGet1() {
synchronized(this){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("static synchronized void incAndGet1");
return ++value;
}
}
public int incAndGet2() {
synchronized(SyncMethod.class){
++value;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("static synchronized void incAndGet4");
}
return 0;
}
public int incAndGet3() {
synchronized(mutex){
return ++value;
}
}
public static synchronized void incAndGet4() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
System.out.println("static synchronized void incAndGet4");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
各种同步场景
Java 同步代码块 - Synchronized Blocks的更多相关文章
- java多线层同时运行的解决,同步代码块synchronized
/* 多个线层同时操作一个数据 会导制数据超出 同步代码块 synchronized(对像) { 需要同步的代码 } */ class Do7 { public static void main(St ...
- java 同步代码块与同步方法
同步代码块 synchronized (obj) { // 代码块 } obj 为同步监视器,以上代码的含义为:线程开始执行同步代码块(中的代码)之前,必须先获得对同步监视器的锁定. 代码块中的代码是 ...
- java 多线程:线程通信-等待通知机制wait和notify方法;(同步代码块synchronized和while循环相互嵌套的差异);管道通信:PipedInputStream;PipedOutputStream;PipedWriter; PipedReader
1.等待通知机制: 等待通知机制的原理和厨师与服务员的关系很相似: 1,厨师做完一道菜的时间不确定,所以厨师将菜品放到"菜品传递台"上的时间不确定 2,服务员什么时候可以取到菜,必 ...
- 彻底理解线程同步与同步代码块synchronized
public class Demo { public static synchronized void fun1(){ } public synchronized void fun2(){ } pub ...
- 36. 解决线程问题方式一(同步代码块synchronized)
解决线程问题: 方式一:同步代码块(synchronized) 语法: synchronized ("锁对象") { //需要锁定的代码 } ...
- JAVA之旅(十三)——线程的安全性,synchronized关键字,多线程同步代码块,同步函数,同步函数的锁是this
JAVA之旅(十三)--线程的安全性,synchronized关键字,多线程同步代码块,同步函数,同步函数的锁是this 我们继续上个篇幅接着讲线程的知识点 一.线程的安全性 当我们开启四个窗口(线程 ...
- Java基础8-多线程;同步代码块
作业解析 利用白富美接口案例,土豪征婚使用匿名内部类对象实现. interface White{ public void white(); } interface Rich{ public void ...
- Java之同步代码块处理实现Runnable的线程安全问题
/** * 例子:创建三个窗口卖票,总票数为100张.使用实现Runnable接口的方式 * * 1.问题:卖票过程中,出现了重票.错票 -->出现了线程的安全问题 * 2.问题出现的原因:当某 ...
- Java 基础 线程的Runnable接口 /线程的同步方法 /同步代码块
笔记: /**通过 Runnable接口来实现多线程 * 1. 创建一个实现runnable 接口的类 * 2. 在类中实现接口的run() 抽象方法 * 3. 创建一个runnable 接口实现类的 ...
随机推荐
- [BZOJ1146][CTSC2008]网络管理Network
[BZOJ1146][CTSC2008]网络管理Network 试题描述 M公司是一个非常庞大的跨国公司,在许多国家都设有它的下属分支机构或部门.为了让分布在世界各地的N个 部门之间协同工作,公司搭建 ...
- "转" CXF+JAXB处理复杂数据
CXF简单数据类型以及类(JavaBean)都提供了较好的支持. 但是对于一些复杂类型(集合或者Map的嵌套)的处理时,就需要我们进行“”人工干预“.在网上找了一些文章,其中这篇写的最为详细,再次备注 ...
- mac在终端下中用sublime text 2 打开文件
alias subl=\''/Applications/Sublime Text 2.app/Contents/SharedSupport/bin/subl'\'然后subl 要打开的文件名即可但是这 ...
- October 22nd Week 43rd Saturday, 2016
Beware the barrenness of a busy life. 当心忙碌的生活荒芜了人生. Recently I was busy in debugging an equipment, I ...
- 无法打开之前cuda的vs项目,打开之后变灰色
解决办法: 打开convolution_vs2010.vcxproj文件,将之前cuda 5.5全部改成cuda7.5. 就可以打开了.
- PHP字符串函数
php字符串处理函数大全 addcslashes — 为字符串里面的部分字符添加反斜线转义字符addslashes — 用指定的方式对字符串里面的字符进行转义bin2hex — 将二进制数据转换成十六 ...
- win7远程桌面连接总是显示凭证不工作解决方法总结
使用远程桌面连接可以在网络的另一端控制某台计算机,对计算机进行实时操作,但有时会出现连接失败的情况,比如总是显示您的凭证不工作,下面是我对此问题解决办法的总结. 方法一: 1.在开始菜单内的运行框里输 ...
- iis 7.0 asp.net发布问题
问题1: 配置错误:不能在此路径中使用此配置节.如果在父级别上锁定了该节,便会出现这种情况.锁定是默认设置的………… 解决方案: 因为 IIS 7 采用了更安全的 web.config 管理机制,默认 ...
- 第二十八篇:SOUI中自定义控件开发过程
在SOUI中已经提供了大部分常用的控件,但是内置控件不可能满足用户的所有要求,因此一个真实的应用少不得还要做一些自定义控件. 学习一个新东西,最简单的办法就是依葫芦画瓢.事实上在SOUI系统中内置控件 ...
- linux安装open block chain
Compile the source code Step 1. 安装git sudo apt-get install git Step 2. 安装vagrant(ubuntu系统) 下载地址https ...
