ES6中class的实现原理
一、在ES6以前实现类和继承
实现类的代码如下:
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.speakSomething = function () {
console.log("I can speek chinese");
};
实现继承的代码如下:一般使用原型链继承和call继承混合的形式
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.showName = function () {
return `名字是:${this.name}`;
};
function Student(name, skill) {
Person.call(this, name);//继承属性
this.skill = skill;
}
Student.prototype = new Person();//继承方法
二、ES6使用class定义类
class Parent {
constructor(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
speakSomething(){
console.log("I can speek chinese");
}
}
经过babel转码之后
function _classCallCheck(instance, Constructor) {
if (!(instance instanceof Constructor)) {
throw new TypeError("Cannot call a class as a function");
}
}
var Parent = function () {
function Parent(name, age) {
_classCallCheck(this, Parent);
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
_createClass(Parent, [{
key: "speakSomething",
value: function speakSomething() {
console.log("I can speek chinese");
}
}]);
return Parent;
}();
可以看到ES6类的底层还是通过构造函数去创建的。
通过ES6创建的类,是不允许你直接调用的。在ES5中,构造函数是可以直接运行的,比如Parent()。但是在ES6就不行。我们可以看到转码的构造函数中有_classCallCheck(this, Parent)语句,这句话是防止你通过构造函数直接运行的。你直接在ES6运行Parent(),这是不允许的,ES6中抛出Class constructor Parent cannot be invoked without 'new'错误。转码后的会抛出Cannot call a class as a function.能够规范化类的使用方式。
转码中_createClass方法,它调用Object.defineProperty方法去给新创建的Parent添加各种属性。defineProperties(Constructor.prototype, protoProps)是给原型添加属性。如果你有静态属性,会直接添加到构造函数defineProperties(Constructor, staticProps)上。
三、ES6实现继承
我们给Parent添加静态属性,原型属性,内部属性。
class Parent {
static height = 12
constructor(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
speakSomething(){
console.log("I can speek chinese");
}
}
Parent.prototype.color = 'yellow'
//定义子类,继承父类
class Child extends Parent {
static width = 18
constructor(name,age){
super(name,age);
}
coding(){
console.log("I can code JS");
}
}
经过babel转码之后
"use strict";
var _createClass = function () {
function defineProperties(target, props) {
for (var i = 0; i < props.length; i++) {
var descriptor = props[i];
descriptor.enumerable = descriptor.enumerable || false;
descriptor.configurable = true;
if ("value" in descriptor) descriptor.writable = true;
Object.defineProperty(target, descriptor.key, descriptor);
}
}
return function (Constructor, protoProps, staticProps) {
if (protoProps) defineProperties(Constructor.prototype, protoProps);
if (staticProps) defineProperties(Constructor, staticProps);
return Constructor;
};
}();
function _possibleConstructorReturn(self, call) {
if (!self) {
throw new ReferenceError("this hasn't been initialised - super() hasn't been called");
}
return call && (typeof call === "object" || typeof call === "function") ? call : self;
}
function _inherits(subClass, superClass) {
if (typeof superClass !== "function" && superClass !== null) {
throw new TypeError("Super expression must either be null or a function, not " + typeof superClass);
}
subClass.prototype = Object.create(superClass && superClass.prototype, {
constructor: {
value: subClass,
enumerable: false,
writable: true,
configurable: true
}
});
if (superClass) Object.setPrototypeOf ? Object.setPrototypeOf(subClass, superClass) : subClass.__proto__ = superClass;
}
function _classCallCheck(instance, Constructor) {
if (!(instance instanceof Constructor)) {
throw new TypeError("Cannot call a class as a function");
}
}
var Parent = function () {
function Parent(name, age) {
_classCallCheck(this, Parent);
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
_createClass(Parent, [{
key: "speakSomething",
value: function speakSomething() {
console.log("I can speek chinese");
}
}]);
return Parent;
}();
Parent.height = 12;
Parent.prototype.color = 'yellow';
//定义子类,继承父类
var Child = function (_Parent) {
_inherits(Child, _Parent);
function Child(name, age) {
_classCallCheck(this, Child);
return _possibleConstructorReturn(this, (Child.__proto__ || Object.getPrototypeOf(Child)).call(this, name, age));
}
_createClass(Child, [{
key: "coding",
value: function coding() {
console.log("I can code JS");
}
}]);
return Child;
}(Parent);
Child.width = 18;
构造类的方法都没变,只是添加了_inherits核心方法来实现继承。具体步骤如下:
首先是判断父类的类型,然后:
subClass.prototype = Object.create(superClass && superClass.prototype, {
constructor: {
value: subClass,
enumerable: false,
writable: true,
configurable: true
}
});
这段代码翻译下来就是
function F(){}
F.prototype = superClass.prototype
subClass.prototype = new F()
subClass.prototype.constructor = subClass
接下来就是subClass.__proto__ = superClass
_inherits核心思想就是下面两句:
subClass.prototype.__proto__ = superClass.prototype
subClass.__proto__ = superClass
如下图所示:
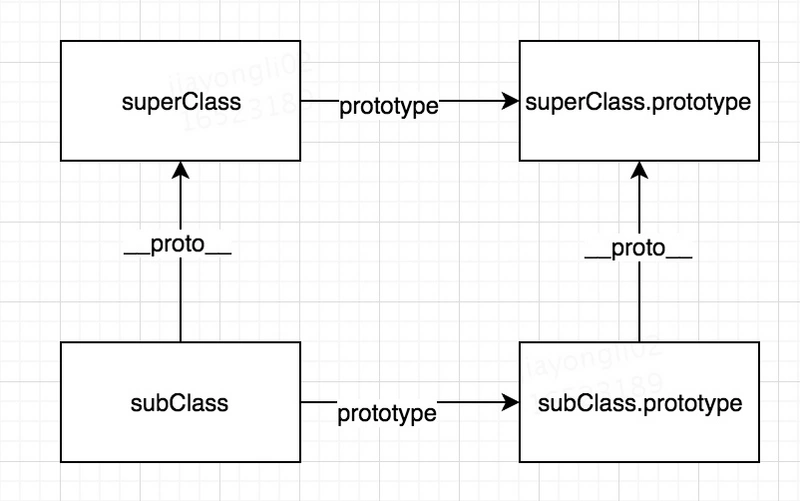
首先 subClass.prototype.__proto__ = superClass.prototype保证了子类的实例instanceof父类是true,子类的实例可以访问到父类的属性,包括内部属性,以及原型属性。
其次,subClass.__proto__ = superClass,保证了静态属性也能访问到,也就是这个例子中的Child.height。
ES6中class的实现原理的更多相关文章
- 前端知识体系:JavaScript基础-原型和原型链-理解 es6 中class构造以及继承的底层实现原理
理解 es6 中class构造以及继承的底层实现原理 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34149805/article/details/86105123 1.ES6 cla ...
- ES6中的Class
对于javascript来说,类是一种可选(而不是必须)的设计模式,而且在JavaScript这样的[[Prototype]] 语言中实现类是很蹩脚的. 这种蹩脚的感觉不只是来源于语法,虽然语法是很重 ...
- ES5和ES6中对于继承的实现方法
在ES5继承的实现非常有趣的,由于没有传统面向对象类的概念,Javascript利用原型链的特性来实现继承,这其中有很多的属性指向和需要注意的地方. 原型链的特点和实现已经在之前的一篇整理说过了,就是 ...
- ES6中的元编程-Proxy & Reflect
前言 ES6已经出来好久了,但是工作中比较常用的只有let const声明,通过箭头函数改this指向,使用promise + async 解决异步编程,还有些数据类型方法...所以单独写一篇文章学习 ...
- ES6中的类继承和ES5中的继承模式详解
1.ES5中的继承模式 我们先看ES5中的继承. 既然要实现继承,首先我们得要有一个父类. Animal.prototype.eat = function(food) { console.log(th ...
- es6中的类及es5类的实现
目录 类的特点 类的特点 1.类只能通过new得到 在es6中类的使用只能是通过new,如果你将它作为一个函数执行,将会报错. //es6的写法 class Child { constructor() ...
- ES6中的迭代器、Generator函数以及Generator函数的异步操作
最近在写RN相关的东西,其中涉及到了redux-saga ,saga的实现原理就是ES6中的Generator函数,而Generator函数又和迭代器有着密不可分的关系.所以本篇博客先学习总结了ite ...
- 大厂HR面试必备ES6中的深入浅出面试题知识点
ESMAScript6简介,ES6是JavaScript语言的下一代标准,目的是让JavaScript语言可以写复杂的大型应用程序,成为企业级语言.那么ECMAScript和JavaScript的关系 ...
- 如何让 node 运行 es6 模块文件,及其原理
如何让 node 运行 es6 模块文件,及其原理 最新版的 node 支持最新版 ECMAScript 几乎所有特性,但有一个特性却一直到现在都还没有支持,那就是从 ES2015 开始定义的模块化机 ...
随机推荐
- PCA 最大方差理论的直观解释
PCA 这个名字看起来比较玄乎,其实就是给数据换一个坐标系,然后非常生硬地去掉一些方差很小的坐标轴. 例:三维空间中,有一些数据只分布在一个平面上,我们通过"坐标系旋转变换",使得 ...
- spring cloud:hystrix-dashboard-turbine
hystrix-dashboard-turbine-server 1. File-->new spring starter project 2.add dependency <parent ...
- hdu5988(费用流,对数相乘做加法)
题意:一个网络流的图,有n个点,从1~n,然后m条边,每个点有两个值,一个是人的数量si一个是饭的数量bi.每条m边有容量ci,还有走上去可能踩断电线的概率pi(第一次踩上去没有事,之后都要p概率). ...
- php中处理汉字字符串长度:strlen和mb_strlen
PHP内置的字符串长度函数strlen()无法正确处理中文字符串,它得到的只是字符串所占的字节数.对于GB2312的中文编码,strlen得到的值是汉字个数的2倍,而对于UTF-8编码的中文,就是3倍 ...
- 条形码(barcode)code128生成代码
条形码(barcode)code128生成代码 很简单 多些这位兄弟https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/350125614 下面是我的DEMO 直接放到VS2005下面编译即可 # ...
- sh脚本获取当前目录
#!/bin/bashcurDir=$(pwd)echo "cur dir is:$curDir"
- sqlalchemy 中 desc 的使用
是这样: items = Item.query.order_by(Item.date.desc()).all() 而不是这样: items = Item.query.order_by(desc(Ite ...
- Java定时器Timer
Java定时器Timer在JDK库中,Timer类主要负责计划任务的功能,也就是在指定的时开始执行某一个任务.Timer类的主要作用就是设置计划任务,但封装任务的类却是TimerTask类,执行计划任 ...
- 送书福利| Python 完全自学手册
前言 这里不讨论「能不能学,要不要学,应不应该学 Python」的问题,这里只会告诉你怎么学. 首先需要强调的是,如果 Python 都学不会,那么我建议你考虑别的行业,因为 Python 之简单,令 ...
- Delphi XE2 之 FireMonkey 入门(42) - 控件基础: TComboBox、TComboEdit
Delphi XE2 之 FireMonkey 入门(42) - 控件基础: TComboBox.TComboEdit TListBox 有两个兄弟 TComboListBox.TComboEditL ...
