Struts2值栈
一、前言
很多事儿啊,就是“成也萧何败也萧何”,细想一些事儿心中有感,当然,感慨和本文毛关系都没有~想起之前有篇Struts2中值栈的博客还未完工,就着心中的波澜,狂咽一把~
二、正文
博文基于:struts-core-2.5.2.jar,ognl-3.1.10.jar
和值栈的邂逅还是大学学习Struts2的时候,老师当时在台上津津有味,我却在底下晕头转向~很长时间都没有去理清这个值栈到底是什么,实现原理是什么,偶然的际遇,让我又遇到了它,所以我决定以我现有的知识储备再次去追根溯源~
那从概念上,我们要怎么去理解值栈呢?你可以将它理解为一个容器(就像装水的杯子,只不过它里面“装”的不是水,而是java对象),这边“装”的意思是“引用”了其他类或者对象,我想这样说应该能理解吧~其实呢,作为开发人员,再精准的文字描述也很难让自己理解到技术的精华,所以看源码是进阶的必经之路~源码的精妙有些时候会让人如痴如醉,编程,就应该是一门艺术~
在Struts2中,值栈和ActionContext是同步创建的,这个创建过程可以在Struts2的核心过滤器:org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter中,doFilter方法中查看,源码如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
String uri = RequestUtils.getUri(request);
if (excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) {
LOG.trace("Request {} is excluded from handling by Struts, passing request to other filters", uri);
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
LOG.trace("Checking if {} is a static resource", uri);
boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response);
if (!handled) {
LOG.trace("Assuming uri {} as a normal action", uri);
prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
prepare.createActionContext(request, response);
prepare.assignDispatcherToThread();
request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);
ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);
if (mapping == null) {
LOG.trace("Cannot find mapping for {}, passing to other filters", uri);
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
LOG.trace("Found mapping {} for {}", mapping, uri);
execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
}
}
}
} finally {
prepare.cleanupRequest(request);
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们可以看到17行“prepare.createActionContext(request, response);”就是创建ActionContext的代码,其具体实现的源码如下:
public ActionContext createActionContext(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ActionContext ctx;
Integer counter = 1;
Integer oldCounter = (Integer) request.getAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER);
if (oldCounter != null) {
counter = oldCounter + 1;
}
ActionContext oldContext = ActionContext.getContext();
if (oldContext != null) {
// detected existing context, so we are probably in a forward
ctx = new ActionContext(new HashMap<>(oldContext.getContextMap()));
} else {
ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class).createValueStack();
stack.getContext().putAll(dispatcher.createContextMap(request, response, null));
ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
}
request.setAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER, counter);
ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
return ctx;
}
进入14行中的createValueStack方法内部可以知道值栈的实现者为:OgnlValueStack
//class OgnlValueStackFactory
public ValueStack createValueStack() {
ValueStack stack = new OgnlValueStack(xworkConverter, compoundRootAccessor, textProvider, allowStaticMethodAccess);
container.inject(stack);
stack.getContext().put(ActionContext.CONTAINER, container);
return stack;
}
值栈OgnlValueStack中包含两个重要的成员变量,CompoundRoot root(这其实是一个ArrayList)和context.(我们通常称为contextMap):
CompoundRoot root;
transient Map<String, Object> context; //其中CompoundRoot的声明如下
public class CompoundRoot extends CopyOnWriteArrayList<Object>
再进入OgnlValueStack的构造函数和setRoot方法:
protected OgnlValueStack(ValueStack vs, XWorkConverter xworkConverter, CompoundRootAccessor accessor, boolean allowStaticAccess) {
setRoot(xworkConverter, accessor, new CompoundRoot(vs.getRoot()), allowStaticAccess);
}
protected void setRoot(XWorkConverter xworkConverter, CompoundRootAccessor accessor, CompoundRoot compoundRoot,
boolean allowStaticMethodAccess) {
this.root = compoundRoot;
this.securityMemberAccess = new SecurityMemberAccess(allowStaticMethodAccess);
this.context = Ognl.createDefaultContext(this.root, accessor, new OgnlTypeConverterWrapper(xworkConverter), securityMemberAccess);
context.put(VALUE_STACK, this);
Ognl.setClassResolver(context, accessor);
((OgnlContext) context).setTraceEvaluations(false);
((OgnlContext) context).setKeepLastEvaluation(false);
}
从第11行我们可以看出,OgnlValueStack中的context有包含了对自身的引用,我们回头再来看看第10行Ognl.createDefaultContext方法内部的实现:
//class Ognl.java
public static Map createDefaultContext(Object root, ClassResolver classResolver,TypeConverter converter, MemberAccess memberAccess)
{
return addDefaultContext(root, classResolver, converter, memberAccess, new OgnlContext());
} public static Map addDefaultContext(Object root, ClassResolver classResolver,TypeConverter converter, MemberAccess memberAccess, Map context)
{
OgnlContext result; if (!(context instanceof OgnlContext)) {
result = new OgnlContext();
result.setValues(context);
} else {
result = (OgnlContext) context;
}
if (classResolver != null) {
result.setClassResolver(classResolver);
}
if (converter != null) {
result.setTypeConverter(converter);
}
if (memberAccess != null) {
result.setMemberAccess(memberAccess);
} result.setRoot(root);
return result;
}
从方法addDefaultContext可以得知,OnglValueStack中的context是OnglContext对象。第27行可以看出,这个context还包含了对OgnlValueStack中“CompoundRoot root”的引用。
接下来,我们回到PrepareOperation.java类中的“createActionContext”方法(StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter.java中doFilter中调用这个方法,正文最开始已经贴出了源码):
public ActionContext createActionContext(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ActionContext ctx;
Integer counter = 1;
Integer oldCounter = (Integer) request.getAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER);
if (oldCounter != null) {
counter = oldCounter + 1;
}
ActionContext oldContext = ActionContext.getContext();
if (oldContext != null) {
// detected existing context, so we are probably in a forward
ctx = new ActionContext(new HashMap<>(oldContext.getContextMap()));
} else {
ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class).createValueStack();
stack.getContext().putAll(dispatcher.createContextMap(request, response, null));
ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
}
request.setAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER, counter);
ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
return ctx;
}
从之前的源码分析,我们知道,14行的ValueStack存储的是OgnlValueStack对象,这个对象的getContext方法获取成员变量context(Map类型,具体实现类为OgnlContext)。我们再来看看15行dispatcher.createContextMap的源码:
// class Dispacher.java public Map<String,Object> createContextMap(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
ActionMapping mapping) { // request map wrapping the http request objects
Map requestMap = new RequestMap(request); // parameters map wrapping the http parameters. ActionMapping parameters are now handled and applied separately
Map params = new HashMap(request.getParameterMap()); // session map wrapping the http session
Map session = new SessionMap(request); // application map wrapping the ServletContext
Map application = new ApplicationMap(servletContext); Map<String,Object> extraContext = createContextMap(requestMap, params, session, application, request, response); if (mapping != null) {
extraContext.put(ServletActionContext.ACTION_MAPPING, mapping);
}
return extraContext;
}
看着上面Map类型的requestMap、params等变量,是不是觉得很熟悉?我们在使用ActionContext的时候是不是经常有如下用法,这些值就在这边设置的:
ActionContext.getContext().getParameters();
ActionContext.getContext().get("request");
ActionContext.getContext().getSession();
等等,是不是又有读者要问了,我值栈ValueStack中的context怎么又和ActionContext扯上关系了?有迷惑的读者,请往前两段代码看下createActionContext的第16行:
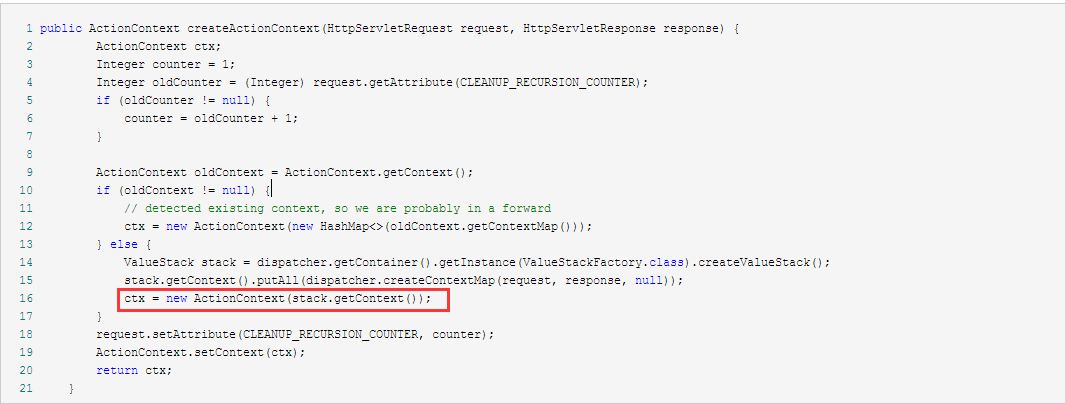
再看下类ActionContext的声明和构造函数:
.........................................................................................
public class ActionContext implements Serializable { static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> actionContext = new ThreadLocal<>();
private Map<String, Object> context; public ActionContext(Map<String, Object> context) {
this.context = context;
}
public static void setContext(ActionContext context) {
actionContext.set(context);
}
public static ActionContext getContext() {
return actionContext.get();
}
........................................................................
}
OgnlValueStack将成员变量context传递给ActionContext对象的context成员变量,之前在OgnlValueStack设置的值便都能在ActionContext的对象中获取~当然这边还有一个非常关键的一步:

这一步将ActionContext实例变量设置到ThreadLocal变量中,这个就使得ActionContext实例变量可以在同一个线程中的不同类间传递,对于ThreadLocal使用不太清晰的读者,请参考我之前的博文:ThreadLocal 验明正身。
至此,已经从源码的角度将Struts2中的“值栈”说清楚了~下面附张图,可以更好的帮助读者去理解本文内容~(别人画的,本文参考链接中有贴出原链接 )

(本图用来说明OnglValueStack中context和ActionContext中context的关系)
总结:
当初会去深究Struts2中的值栈,起因是在使用Ognl表达式时,获取“值栈”中某些值,有些表达式要加“#”有些不要,然后就有了去深究的冲动~
“值栈”由两部分组成:
1)ObjectStack (保存为root属性,类型CompoundRoot) ----- ArrayList 2)ContextMap(保存为context属性, 类型 ) ------ Map
Struts2 会把下面这些映射压入 ContextMap 中:
parameters: 该 Map 中包含当前请求的请求参数
request: 该 Map 中包含当前 request 对象中的所有属性
session: 该 Map 中包含当前 session 对象中的所有属性
application:该 Map 中包含当前 application 对象中的所有属性
attr: 该 Map 按如下顺序来检索某个属性: request, session, application
注:CompoucdRoot继承了ArrayList,实际上就是一个集合,用于存储元素的数据,OgnlContext实现了Map, 其中持有CompoucdRoot对象的引用,其key为_root
在JSP页面内,通过 <s:property>等标签去访问值栈的数据,访问root中数据,不需要“#”,访问 Context中数据必须以“#”开始。
当Struts2接受一个请求时,会迅速创建ActionContext,ValueStack,action ,然后把action存放进ValueStack,所以action的实例变量可以被OGNL访问。
Action对象会被保存root 对象栈中,Action所有成员变量属性,都位于root中 ,访问root中数据不需要“#”。
再附一张图,图中“ValueStack(值栈,根对象)”指的是OgnlValueStack类中的CompoundRoot root成员变量:

三、链接
http://blog.csdn.net/javaliuzhiyue/article/details/9357337
http://www.cnblogs.com/x_wukong/p/3887737.html
http://blog.csdn.net/elvis12345678/article/details/7909936
http://www.cnblogs.com/hlhdidi/p/6185836.html
四、联系本人
为方便没有博客园账号的读者交流,特意建立一个企鹅群(纯公益,非利益相关),读者如果有对博文不明之处,欢迎加群交流:261746360,小杜比亚-博客园
Struts2值栈的更多相关文章
- struts2值栈内部数据结构详解
值栈是struts2内部一片很重要的区域,我在初学的时候,发现对于值栈这个数据结构的理解不是很深刻.例如OGNLContext是什么,ActionContext和值栈有什么关系.为什么ActionCo ...
- struts2值栈分析
前段日子对ognl表达式不是很理解,看了几本书上关于ognl表达式的描述后还是感觉很难,前几天学习了struts2中值栈的内容,现在感觉ognl表达式其实很容易. struts2中利用值栈来存储数据, ...
- Struts2值栈详解
1. 关于值栈: 1). helloWorld 时, ${productName} 读取 productName 值, 实际上该属性并不在 request 等域对象中, 而是从值栈中获取的. 2). ...
- 【基于初学者的SSH】struts2 值栈的详解与struts2标签库+ognl表达式
一:什么是值栈:struts2里面本身提供的一种存储机制,类似于域对象,值栈,可以存值和取值 特点:先进后出,最上面的元素叫做栈顶,也叫压栈. <s:debug></s:debug& ...
- Struts2 - 值栈(ValueStack)
1. 关于值栈: 1). helloWorld 时, ${productName} 读取 productName 值, 实际上该属性并不在 request 等域对象中, 而是从值栈中获取的. 2). ...
- struts2 值栈分析
目录 一.值栈分为两个逻辑部分 二.Struts2 利用 s:property 标签和 OGNL表达式来读取值栈中的属性值 1.值栈中的属性值: 2.读取对象栈中对象的属性: 3.默认情况下,Acti ...
- 10.Struts2值栈
1.什么是值栈 * 值栈就相当于Struts2框架的数据的中转站,向值栈存入一些数据.从值栈中获取到数据. * ValueStack 是 struts2 提供一个接口,实现类 OgnlValueSta ...
- struts2值栈ValueStack中都有哪些东西?
com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletRequest application com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher ...
- Struts2 值栈总结(ValueStack)
1.获取值栈 //获取值栈的第一种方式 ValueStack valueStack1 = (ValueStack) ServletActionContext.getRequest().getAttri ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ3668: [Noi2014]起床困难综合症(贪心 二进制)
Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MBSubmit: 2708 Solved: 1576[Submit][Status][Discuss] Descript ...
- Linux计算某一列的和
ll | awk '{print $5}' | egrep -v "^$"| paste -sd+|bc 简单说明: ll:拿到当前目录下所有的文件大小 awk:拿到第几列 egr ...
- SQL:检索数据-基本检索
检索数据 1.select语句 增删改查四大操作之"查",即检索: 一般包括:what,where:查什么,从哪里选择 2.检索单个列 例:想从products表中检索名为prod ...
- 转:java中的定时任务
引自:http://www.cnblogs.com/wenbronk/p/6433178.html java中的定时任务, 使用java实现有3种方式: 1, 使用普通thread实现 @Test p ...
- Python数值
一.python数值类型 python数值类型有以下四种: int(整数) float(浮点数) complex(复数) bool(布尔型) 注意:python3取消了long型. 二.python ...
- CentOS下配置jdk
CentOS下配置jdk 1.在jdk官网上下载最新版本的jdk 2.将jdk放到相应的位置,使用如下命令来解压. .0_181 /opt/data/ tar -zxf jdk-8u181-linux ...
- Python全栈day 02
Python全栈day 02 一.循环语句 while 用法 num = 1 while num <= 10: print(num) num += 1 # 循环打印输出1-10 while el ...
- POJ3687 反向拓扑排序
Labeling Balls Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 16032 Accepted: 4713 D ...
- P1346 电车(dijkstra)
P1346 电车 题目描述 在一个神奇的小镇上有着一个特别的电车网络,它由一些路口和轨道组成,每个路口都连接着若干个轨道,每个轨道都通向一个路口(不排除有的观光轨道转一圈后返回路口的可能).在每个路口 ...
- P1078 文化之旅
P1078 文化之旅 题目描述 有一位使者要游历各国,他每到一个国家,都能学到一种文化,但他不愿意学习任何一 种文化超过一次(即如果他学习了某种文化,则他就不能到达其他有这种文化的国家).不 同的国家 ...
