JDK1.8源码(二)——java.lang.Integer类
一、初识
1、介绍
int 是Java八大基本数据类型之一,占据 4 个字节,范围是 -2^31~2^31 - 1,即 -2147483648~2147483647。而 Integer 是 int 包装类。
Integer 是类,默认值为null;int是基本数据类型,默认值为0。
Integer 表示的是对象,用一个引用指向这个对象,而 int 是基本数据类型,直接存储数值。
二、自动装箱和拆箱
1、案例
先看如下代码执行结果:
1 int i1 = 59;
2
3 Integer i2 = 59;
4
5 Integer i3 = new Integer(59);
6 Integer i4 = new Integer(59);
7
8 Integer i5 = Integer.valueOf(59);
9 Integer i6 = Integer.valueOf("59");
10
11 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i2)); // true
12 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i3)); // true
13 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i4)); // true
14 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i5)); // true
15 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i6)); // true
16
17 System.out.println("----" + (i2 == i3)); // false
18 System.out.println("----" + (i2 == i4)); // false
19 System.out.println("----" + (i2 == i5)); // true
20 System.out.println("----" + (i2 == i6)); // true
21
22 System.out.println("----" + (i3 == i4)); // false
23 System.out.println("----" + (i3 == i5)); // false
24 System.out.println("----" + (i3 == i6)); // false
25
26 System.out.println("----" + (i4 == i5)); // false
27 System.out.println("----" + (i4 == i6)); // false
28
29 System.out.println("----" + (i5 == i6)); // true
结论:先记下上述结果,后续会详细解释。
①基本数据类型 int 和其他任何形式创建的 Integer 比较都是true;
②Integer 表示的是对象,它是一个引用,存储的是对象在堆空间的地址。如图:
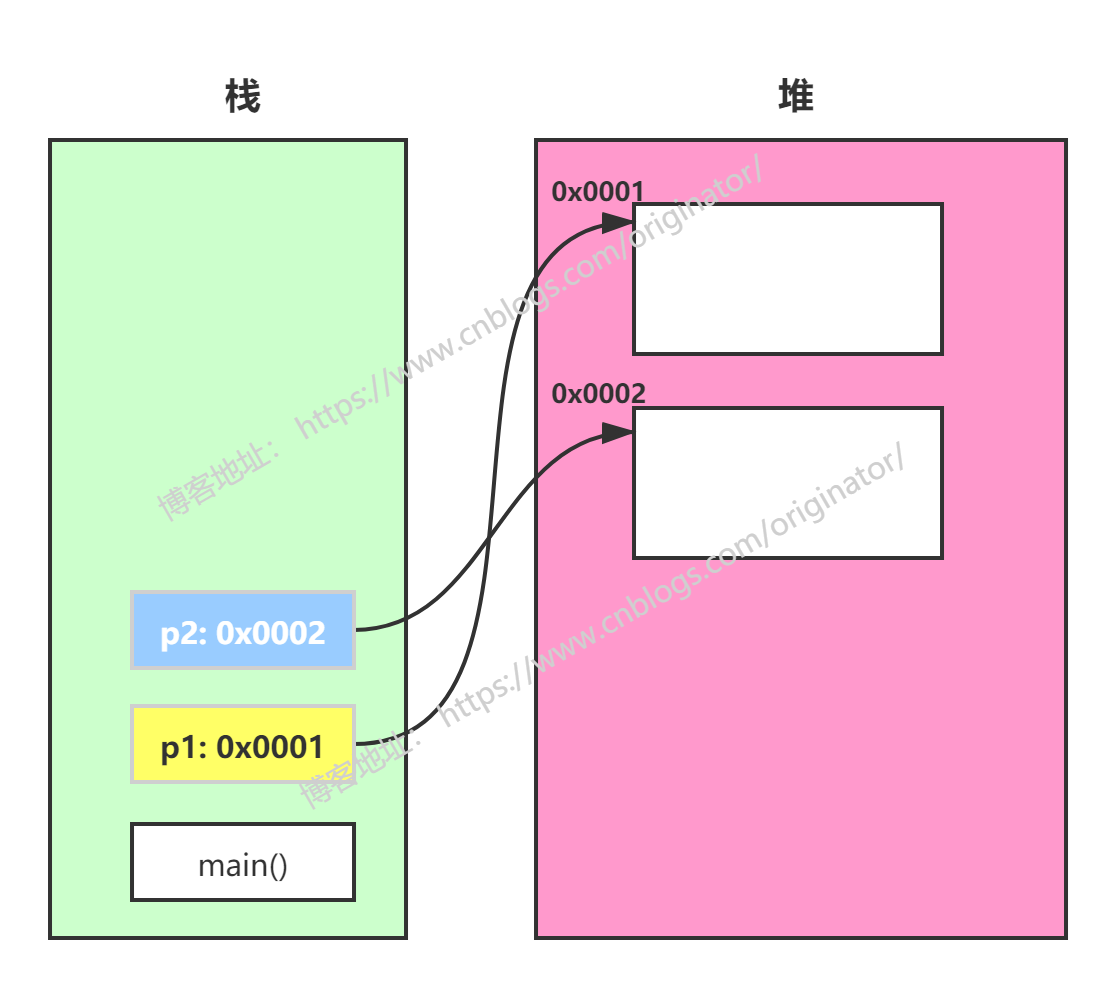
所以:int 的比较结果不难理解(后面还会解释),而对象的比较应该全是 false,因为他们创建了不同的对象,地址自然是不同的。那这里 i2 == i5,i2 == i6,i5 == i6 为什么是true呢?
因为 Integer 的自动拆箱和装箱原理,以及缓存机制。
自动拆箱和装箱是 JDK1.5 以后才有的功能,也是 Java 众多的语法糖之一,它的执行是在编译期,会根据代码的语法,在生成class文件的时候,决定是否进行拆箱和装箱动作。
2、自动拆箱
将 Integer 类表示的数据赋值给基本数据类型int,就执行了自动拆箱。
1 Integer a = new Integer(59);
2 int m = a;
反编译生成的class文件,上述表达式等价于:
1 Integer a = new Integer(59);
2 int m = a.intValue();
所以,在上述代码比较时,与 int 类型的比较都是true,因为包装类Integer会自动拆箱为数值型,数值的比较当然是true。等价于:
1 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i2.intValue())); // true
2 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i3.intValue())); // true
3 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i4.intValue())); // true
4 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i5.intValue())); // true
5 System.out.println("----" + (i1 == i6.intValue())); // true
3、自动装箱
一般地,创建对象是通过 new 关键字,比如:
1 Object obj = new Object();
对于 Integer 类,可以:
1 Integer a = 59;
反编译生成的class文件,上述表达式等价于:
1 Integer a = Integer.valueOf(59);
它其实等价的创建了一个对象,这种语法帮我们完成了而已。既然是对象,那么存储的就是引用,也就不难理解上述代码那些为 false 的结果。
那为什么 i2 == i5,i2 == i6,i5 == i6 是 true 呢?
4、缓存机制(新特性)
前面我们知道
1 Integer a = 59; 等价于 Integer a = Integer.valueOf(59);
查看一下valueOf()方法的源码,它有三个重载的方法。
源码示例:Integer.valueOf()


1 public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
2 return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10));
3 }
4
5 public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
6 if (i >= Integer.IntegerCache.low && i <= Integer.IntegerCache.high)
7 return Integer.IntegerCache.cache[i + (-Integer.IntegerCache.low)];
8 return new Integer(i);
9 }
源码示例
很容易看到,这里 -128 <= i <= 127,是直接 return 了 IntegerCache 里的对象,并没有新建对象。
数值在byte(-128~127)范围内,如果该数值已存在,则不会再开辟新的空间,会使用常量池,指向了同一个 Integer 对象。也就不难理解 i2 == i5,i2 == i6,i5 == i6 是 true。如果将上述代码的数值改为128,再执行,除了 int 的比较是true,其他就都是 false 了。读者可自行验证。
结论:
①int 型比较,由于自动拆箱,比较结果都是true;
②Integer 比较,由于自动装箱和缓存。数值在 -128~127 ,为true,否则为false。注意:如果通过 new 关键字新建的对象,是不存在缓存的概念的,不管数值的大小,都是 false。
三、类源码
1、介绍
源码示例:类声明
1 * @author Lee Boynton
2 * @author Arthur van Hoff
3 * @author Josh Bloch
4 * @author Joseph D. Darcy
5 * @since JDK1.0
6 */
7 public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> {
8 }
Integer 类在JDK1.0的时候就有了,它是一个类,是 int 基本数据类型的封装类,是用 final 声明的常量类,不能被任何类所继承,它继承了 Number 类和实现了 Comparable 接口。
Number 类是一个抽象类,8 中基本数据类型的包装类除了Character 和 Boolean 没有继承该类外,其他的都继承了 Number 类,该类的方法用于各种数据类型的转换。
Comparable 接口就一个 compareTo 方法,用于元素之间的比较。
官方文档:
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Integer.html
2、类构造器
源码示例:类构造器


1 public Integer(int value) {
2 this.value = value;
3 }
4
5 public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
6 // 其中s表示我们需要转换的字符串,10表示以十进制输出,默认也是10进制
7 this.value = parseInt(s, 10);
8 }
9
10
11 public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
12 throws NumberFormatException
13 {
14
15 // 如果转换的字符串为null,直接抛出数字格式异常
16 if (s == null) {
17 throw new NumberFormatException("null");
18 }
19
20 // 如果转换的radix(默认是10)<2 则抛出数字格式异常,因为进制最小是 2 进制
21 if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
22 throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
23 " less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
24 }
25
26 // 如果转换的radix>36,也一样
27 if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
28 throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
29 " greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
30 }
31
32 int result = 0;
33 boolean negative = false;
34 int i = 0, len = s.length(); //len是待转换字符串的长度
35 int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
36 int multmin;
37 int digit;
38
39 if (len > 0) {
40 char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
41 // 主要判断第一个字符是"+"或者"-",因为这两个字符的 ASCII码都小于字符'0'
42 if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
43 if (firstChar == '-') { // 如果第一个字符是'-'
44 negative = true;
45 limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
46 } else if (firstChar != '+') // 如果第一个字符不是'+'
47 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
48
49 // 待转换字符长度是1,不能是单独的"+"或者"-",否则抛出异常
50 if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
51 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
52 i++;
53 }
54 multmin = limit / radix;
55
56 //通过循环,将字符串除掉第一个字符之后,根据进制不断相乘在相加得到一个正整数
57 //比如 parseInt("2abc",16) = 2*16的3次方+10*16的2次方+11*16+12*1
58 //parseInt("123",10) = 1*10的2次方+2*10+3*1
59 while (i < len) {
60 // Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
61 digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);
62 if (digit < 0) {
63 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
64 }
65 if (result < multmin) {
66 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
67 }
68 result *= radix;
69 if (result < limit + digit) {
70 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
71 }
72 result -= digit;
73 }
74 } else {
75 // 如果待转换字符串长度小于等于0,直接抛出异常
76 throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
77 }
78 //根据第一个字符得到的正负号,在结果前面加上符号
79 return negative ? result : -result;
80 }
类构造器
3、toString()方法
这个方法有三个重载方法,能返回一个整型数据所表示的字符串形式。toString(int) 方法内部调用了 stringSize() 和 getChars() 方法。
源码示例:stringSize()


1 final static int [] sizeTable = { 9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999, 999999, 9999999,
2 99999999, 999999999, Integer.MAX_VALUE };
3
4 // Requires positive x
5 static int stringSize(int x) {
6 for (int i=0; ; i++)
7 if (x <= sizeTable[i])
8 return i+1;
9 }
stringSize()方法
stringSize() 它是用来计算参数 i 的位数,也就是转成字符串之后的字符串的长度,内部结合一个已经初始化好的int类型的数组sizeTable来完成这个计算。注意,负数包含符号位,所以对于负数的位数是 stringSize(-i) + 1。
源码示例:getChars()


1 static void getChars(int i, int index, char[] buf) {
2 int q, r;
3 int charPos = index;
4 char sign = 0;
5
6 if (i < 0) {
7 sign = '-'; // sign记下它的符号"-"
8 i = -i; // 将 i 转成正数。
9 }
10
11 // Generate two digits per iteration
12 while (i >= 65536) {
13 q = i / 100;
14 // really: r = i - (q * 100);
15 r = i - ((q << 6) + (q << 5) + (q << 2));
16 i = q;
17 buf [--charPos] = DigitOnes[r];
18 buf [--charPos] = DigitTens[r];
19 }
20
21 // Fall thru to fast mode for smaller numbers
22 // assert(i <= 65536, i);
23 for (;;) {
24 q = (i * 52429) >>> (16+3);
25 r = i - ((q << 3) + (q << 1)); // r = i-(q*10) ...
26 buf [--charPos] = digits [r];
27 i = q;
28 if (i == 0) break;
29 }
30 if (sign != 0) {
31 // 将 sign 的值放在char数组的首位。
32 buf [--charPos] = sign;
33 }
34 }
getChars()方法
i:被初始化的数字。
index:这个数字的长度(包括负数的符号"-")。
buf:字符串的容器,一个char型数组。
4、equals(Object obj)方法
源码示例:equals()


1 public boolean equals(Object obj) {
2 if (obj instanceof Integer) {
3 return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
4 }
5 return false;
6 }
equals()方法
5、hashCode()方法
源码示例:hashCode()


1 @Override
2 public int hashCode() {
3 return Integer.hashCode(value);
4 }
5
6 public static int hashCode(int value) {
7 return value;
8 }
hashCode()方法
直接返回其 int 类型的值作为哈希值。
6、parseInt()方法
这个方法有两个重载方法,能将字符串转换成整型输出。构造器中已经调用了parseInt()方法。
7、compareTo()/compare()方法
源码示例:


1 public int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) {
2 return compare(this.value, anotherInteger.value);
3 }
4
5 public static int compare(int x, int y) {
6 return (x < y) ? -1 : ((x == y) ? 0 : 1);
7 }
源码示例
这个源码不难读懂。值得注意的是,compareTo()方法是实现 Comparable 接口后,需要实现的方法。而 compare 是 Integer 内自己定义的一个方法。
四、其他
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 Integer i = 42;
3 Long j = 42L;
4 Double k = 42.0;
5
6 System.out.println(i == j); // java: 不可比较的类型: java.lang.Integer和java.lang.Long
7 System.out.println(i == k); // java: 不可比较的类型: java.lang.Integer和java.lang.Double
8 System.out.println(j == k); // java: 不可比较的类型: java.lang.Long和java.lang.Double
9
10 System.out.println(i.equals(j)); // false
11 System.out.println(i.equals(k)); // false
12 System.out.println(j.equals(k)); // false
13
14 System.out.println(j.equals(42L)); // true
15 }
JDK1.8源码(二)——java.lang.Integer类的更多相关文章
- JDK1.8源码(二)——java.lang.Integer 类
上一篇博客我们介绍了 java.lang 包下的 Object 类,那么本篇博客接着介绍该包下的另一个类 Integer.在前面 浅谈 Integer 类 博客中我们主要介绍了 Integer 类 和 ...
- JDK1.8源码(一)——java.lang.Object类
本系列博客将对JDK1.8版本的相关类从源码层次进行介绍,JDK8的下载地址. 首先介绍JDK中所有类的基类——java.lang.Object. Object 类属于 java.lang 包,此包下 ...
- JDK1.8源码(三)——java.lang.String 类
String 类也是java.lang 包下的一个类,算是日常编码中最常用的一个类了,那么本篇博客就来详细的介绍 String 类. 1.String 类的定义 public final class ...
- JDK1.8源码(三)——java.lang.String类
一.概述 1.介绍 String是一个final类,不可被继承,代表不可变的字符序列,是一个类类型的变量.Java程序中的所有字符串字面量(如"abc")都作为此类的实例实现,&q ...
- JDK1.8源码(八)——java.lang.ThreadLocal类
https://www.cnblogs.com/xdd666/p/14734047.html ThreadLocal https://www.cnblogs.com/yanfei1819/p/1473 ...
- JDK1.8源码(五)——java.util.Vector类
JDK1.8源码(五)--java.lang. https://www.cnblogs.com/IT-CPC/p/10897559.html
- JDK1.8源码(四)——java.util.Arrays类
一.概述 1.介绍 Arrays 类是 JDK1.2 提供的一个工具类,提供处理数组的各种方法,基本上都是静态方法,能直接通过类名Arrays调用. 二.类源码 1.asList()方法 将一个泛型数 ...
- JDK1.8源码(七)——java.util.HashMap 类
本篇博客我们来介绍在 JDK1.8 中 HashMap 的源码实现,这也是最常用的一个集合.但是在介绍 HashMap 之前,我们先介绍什么是 Hash表. 1.哈希表 Hash表也称为散列表,也有直 ...
- JDK1.8源码(四)——java.util.Arrays 类
java.util.Arrays 类是 JDK 提供的一个工具类,用来处理数组的各种方法,而且每个方法基本上都是静态方法,能直接通过类名Arrays调用. 1.asList public static ...
随机推荐
- Spring in Action学习笔记(2)
Spring基础 AOP 面向切面编程 通知.连接点.切点.切面 Spring提供 4 种类型的AOP支持: 基于代理的经典SpringAOP:使用ProxyFactoryBean. 纯POJO切面: ...
- DC-5 靶机渗透测试
DC-5 靶机渗透测试 冲冲冲,好好学习 .核心:footer 文件包含漏洞,wfuzz .收获总结写在文末. 谨记任务:找地方上传shell---> root. 操作机:kali 172.66 ...
- [源码解析]机器学习参数服务器ps-lite(4) ----- 应用节点实现
[源码解析]机器学习参数服务器ps-lite(4) ----- 应用节点实现 目录 [源码解析]机器学习参数服务器ps-lite(4) ----- 应用节点实现 0x00 摘要 0x01 基础类 1. ...
- Windows系统安装Mariadb数据库(zip包方式安装)--九五小庞
1.去Mariadb官网下载zip安装包 下载地址:https://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/10.3.31/ 2.解压压缩包到指定的安装位置 3.在安装包的data ...
- null是对象吗?
null是基本数据类型但是typeof null为object,这是因为在js存储中对象是以000开头的,而null是一个空,相当于全0,所以typeof null也是object 在js中,变量由类 ...
- Bugku-web-md5 collision(NUPT_CTF)
总结了两道MD5绕过的题目. 根据MD5的特性,有两点漏洞 1.两个开头为0的md5值相同. 2.md5不能处理数组. 3.==用法,0 == 字符串是成立的,从而可以绕过MD5检查. 根据特性,我们 ...
- k8s之Service详解-Service使用
实验环境准备 在使用service之前,首先利用deployment创建出3个pod,注意要为pod设置app=nginx-pod的标签 创建deployment.yaml,内容如下 apiVersi ...
- Python3中的List列表的相关操作
列表对象内建函数 1. append(obj) 在列表的末尾添加新元素obj.例: >>> a = ['a', 'b', 'c'] >>> a.append('d' ...
- 『Java』成员内部类 匿名内部类
成员内部类 成员方法类是定义在一个类中的方法外的类,例如: public class Outer{ // 外部类 class Inner { // 内部类 // 内部类成员 } // 外部类成员 } ...
- TortoiseSVN日志字体和字号调整
TortoiseSVN提供的"show log"功能很有用,但默认的显示文件log历史的字体太小看不清,这个字体的设置在[TortoiseSVN ->Settings-> ...
