(译)IOS block编程指南 2 block开始
Getting Started with Blocks(开始block)
The following sections help you to get started with blocks using practical examples.
Declaring and Using a Block (定义和使用block)
You use the ^ operator to declare a block variable and to indicate the beginning of a block literal. The body of the block itself is contained within {}, as shown in this example (as usual with C, ; indicates the end of the statement):
你使用^操作定义一个block值同时表示了一个block的开始。block的主题被{}包围,就像例子中展示的那样(就像通常的C中,分号;申明了一个语句的结束):
int multiplier = ;
int (^myBlock)(int) = ^(int num) {
return num * multiplier;
};
The example is explained in the following illustration:
这个例子在下面的说面中得到了解释:
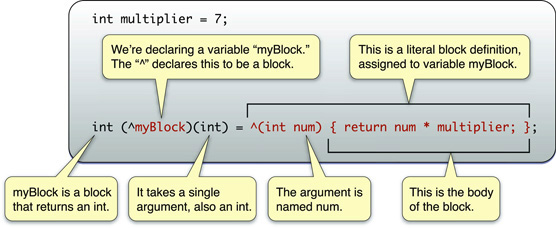
- myBlock 的返回值是int类型的 。
- 我们使用^声明了一个myBlock的block。
- 只需要一个参数,也是int类型的。
- 参数名是num。这是一个块的定义,
- 给myblock赋值。
- 这是block的主体。
Notice that the block is able to make use of variables from the same scope in which it was defined.
If you declare a block as a variable, you can then use it just as you would a function:
注意block可以使用定义在block定义作用用中的变量。
如果你把block定义成了一个变量,你可以像使用函数一样使用block。
int multiplier = ;
int (^myBlock)(int) = ^(int num) {
return num * multiplier;
}; printf("%d", myBlock());
// prints "21"
Using a Block Directly(直接使用block)
In many cases, you don’t need to declare block variables; instead you simply write a block literal inline where it’s required as an argument. The following example uses the qsort_b function. qsort_b is similar to the standard qsort_r function, but takes a block as its final argument.
在很多情况下你不需要把block定义成一个变量;相反的你可以直接写出一个block作为参数。下面的例子用到了qsort_b函数,qsort_b很类似标准的qsort_r函数,是指使用一个block作为一最后一个参数。
char *myCharacters[] = { "TomJohn", "George", "Charles Condomine" };
qsort_b(myCharacters, , sizeof(char *), ^(const void *l, const void *r) {
char *left = *(char **)l;
char *right = *(char **)r;
return strncmp(left, right, );
});
// myCharacters is now { "Charles Condomine", "George", "TomJohn" }
Blocks with Cocoa(cocoa中的block)
Several methods in the Cocoa frameworks take a block as an argument, typically either to perform an operation on a collection of objects, or to use as a callback after an operation has finished. The following example shows how to use a block with the NSArray methodsortedArrayUsingComparator:. The method takes a single argument—the block. For illustration, in this case the block is defined as anNSComparator local variable:
Cocoa 框架中有一些方法使用block作为一个参数,特别是对多个对象进行操作,或者在一个操作结束之后回调。下面的例子展示了NSArray怎样在方法sortedArrayUsingComparator:中使用block。这个方法使用了一个参数——block。为了说明,这个block被定义为NSComparator类型的一个局部变量:
NSArray *stringsArray = @[ @"string 1",
@"String 21",
@"string 12",
@"String 11",
@"String 02" ]; static NSStringCompareOptions comparisonOptions = NSCaseInsensitiveSearch | NSNumericSearch |
NSWidthInsensitiveSearch | NSForcedOrderingSearch;
NSLocale *currentLocale = [NSLocale currentLocale]; NSComparator finderSortBlock = ^(id string1, id string2) { NSRange string1Range = NSMakeRange(, [string1 length]);
return [string1 compare:string2 options:comparisonOptions range:string1Range locale:currentLocale];
}; NSArray *finderSortArray = [stringsArray sortedArrayUsingComparator:finderSortBlock];
NSLog(@"finderSortArray: %@", finderSortArray); /*
Output:
finderSortArray: (
"string 1",
"String 02",
"String 11",
"string 12",
"String 21"
)
*/
__block Variables(_block 类型变量)
A powerful feature of blocks is that they can modify variables in the same lexical scope. You signal that a block can modify a variable using the__block storage type modifier. Adapting the example shown in Blocks with Cocoa, you could use a block variable to count how many strings are compared as equal as shown in the following example. For illustration, in this case the block is used directly and uses currentLocale as a read-only variable within the block:
block的另一个强大的特性是可以修改同一词法范围的变量。你可以把一个block想修改的变量声明成_block类型。改写Blocks with Cocoa中的例子,你可以在下面的例子中使用block变量统计有多少字符串是相同的。为了说明需要,例子中直接使用block,同时把currentLocate作为一个block中的只读变量。
NSArray *stringsArray = @[ @"string 1",
@"String 21", // <-
@"string 12",
@"String 11",
@"Strîng 21", // <-
@"Striñg 21", // <-
@"String 02" ]; NSLocale *currentLocale = [NSLocale currentLocale];
__block NSUInteger orderedSameCount = ; NSArray *diacriticInsensitiveSortArray = [stringsArray sortedArrayUsingComparator:^(id string1, id string2) { NSRange string1Range = NSMakeRange(, [string1 length]);
NSComparisonResult comparisonResult = [string1 compare:string2 options:NSDiacriticInsensitiveSearch range:string1Range locale:currentLocale]; if (comparisonResult == NSOrderedSame) {
orderedSameCount++;
}
return comparisonResult;
}]; NSLog(@"diacriticInsensitiveSortArray: %@", diacriticInsensitiveSortArray);
NSLog(@"orderedSameCount: %d", orderedSameCount); /*
Output: diacriticInsensitiveSortArray: (
"String 02",
"string 1",
"String 11",
"string 12",
"String 21",
"Str\U00eeng 21",
"Stri\U00f1g 21"
)
orderedSameCount: 2
*/
This is discussed in greater detail in Blocks and Variables.
更详细的讨论请看:Blocks and Variables.
(译)IOS block编程指南 2 block开始的更多相关文章
- (译)IOS block编程指南 1 介绍
Introduction(介绍) Block objects are a C-level syntactic and runtime feature. They are similar to stan ...
- iOS多线程编程指南
iOS多线程编程指南(拓展篇)(1) 一.Cocoa 在Cocoa上面使用多线程的指南包括以下这些: (1)不可改变的对象一般是线程安全的.一旦你创建了它们,你可以把这些对象在线程间安全的传递.另一方 ...
- (译文)IOS block编程指南 4 声明和创建blocks
Declaring and Creating Blocks (声明和创建blocks) Declaring a Block Reference (声明一个block引用) Block variable ...
- (译文)IOS block编程指南 3 概念总览
Conceptual Overview(概览) Block objects provide a way for you to create an ad hoc function body as an ...
- iOS多线程编程指南(一)关于多线程编程(转)
原文:http://www.dreamingwish.com/article/ios-multi-threaded-programming-a-multi-threaded-programming.h ...
- iOS 并发编程指南
iOS Concurrency Programming Guide iOS 和 Mac OS 传统的并发编程模型是线程,不过线程模型伸缩性不强,而且编写正确的线程代码也不容易.Mac OS 和 iOS ...
- <译>Spark Sreaming 编程指南
Spark Streaming 编程指南 Overview A Quick Example Basic Concepts Linking Initializing StreamingContext D ...
- iOS ---Extension编程指南
当iOS 8.0和OS X v10.10发布后,一个全新的概念出现在我们眼前,那就是应用扩展.顾名思义,应用扩展允许开发者扩展应用的自定义功能和内容,能够让用户在使用其他app时使用该项功能.你可以开 ...
- iOS多线程编程指南(二)线程管理
当应用程序生成一个新的线程的时候,该线程变成应用程序进程空间内的一个实体.每个线程都拥有它自己的执行堆栈,由内核调度独立的运行时间片.一个线程可以和其他线程或其他进程通信,执行I/O操作,甚至执行任何 ...
随机推荐
- ConcurrentHashMap并不是完全的线程安全
ConcurrentHashMap通过分段锁的方式实现了高效率的线程安全,但是它能否在所有高并发场景中都能保证线程安全呢? public class TestClass { private Concu ...
- Struts2基本使用
Struts2:本质servlet 1.接受页面参数 a.使用原生的ServletAPI接受(不推荐) request.getParameter(name) 获取元素request方式: --Http ...
- CF1045G AI robots(动态开点线段树)
题意 火星上有$N$个机器人排成一行,第$i$个机器人的位置为$x_{i}$,视野为$r_{i}$,智商为$q_{i}$.我们认为第$i$个机器人可以看到的位置是$[x_{i}-r_{i},x_{i} ...
- CF1059E Split the Tree(倍增)
题意翻译 现有n个点组成一棵以1为根的有根树,第i个点的点权为wi,需将其分成若干条垂直路径使得每一个点当且仅当被一条垂直路径覆盖,同时,每条垂直路径长度不能超过L,点权和不能超过S,求最少需要几条垂 ...
- 报错org.springframework.dao.DataIntegrityViolationException
最简单的原因可能是数据库外键字段选择了不能为空, 改为允许为空就行了.
- iOS 优雅地隐藏导航栏NavigationBar (Objc)
@interface FSViewController () <UINavigationControllerDelegate> @end @implementation FSViewCon ...
- Hexo搭建博客教程(3) - 远程部署到GitHub Pages
本章讲的是如何将本地的个人项目远程部署到 GitHub Pages,涉及到GitHub的项目仓库.Git的使用,以及Hexo的远程部署等. 1. 安装 hexo-deployer-git 插件 想要将 ...
- Centos 6.x 搭建 Zabbix Server
zabbix(音同 zæbix)是一个基于WEB界面的提供分布式系统监视以及网络监视功能的企业级的开源解决方案. zabbix能监视各种网络参数,保证服务器系统的安全运营:并提供灵活的通知机制以让 ...
- 跟我一起玩Win32开发(16):ListView的多个视图
在上一个例子中,我们只用到了ListView的Report视图,也就是详细视图.本文我们再把上一篇文章中所用的例子进行一下扩展,例子源码可以到俺的资源区下载. 我们为ListView中显示的数据加上图 ...
- python之url编码
import urllib.parsempp='besttest 自动化测试'print(urllib.parse.quote_plus(mpp)) #url编码print(urllib.parse. ...
