集合(六) WeakHashMap与LinkedHashMap
5.WeakHashMap
(1) 简介
WeakHashMap与HashMap几乎都是相同的,就是它的键是“弱引用”。
第一个问题:何为弱引用?即WeakReference类对象。
String a = new String ("A"); //Strong Reference
WeakReference <String> b = new WeakReference ("B"); //Weak Reference
以上即为强引用和弱引用的典型例子。
第二个:那么他们的区别在哪里?
当弱引用不再被使用时,就会被回收。也就是说,在WeakHashMap中有一个键的引用失效后,将会移除对应的节点。
第三个:这又有什么用呢?
坦率来说,我平常编代码时没用过WeakHashMap。WeakHashMap一般用在作为大量缓存的情况之下,可以有效地节省内存。
(2)WeakHashMap的使用和特点展示
由于WeakHashMap的特点决定了它不会非常地常用,并且大量代码、使用方法、数据结构都与HashMap完全相同,因此不会对它进行过于详细地解读。构造函数就与HashMap的形式相同,成员域多了一个队列,作用是存储已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。
WeakHashMap<String,String> wh = new WeakHashMap();
HashMap<String,String> hm = new HashMap();
String a = new String ("A");
String b = new String("B");
wh.put(a,"first");
wh.put(b,"second");
hm.put(a,"first");
hm.put(b,"second"); System.out.println(wh);
System.out.println(hm);
上述代码仅仅实现了插入两个元素,接下来展示弱引用的特点:
hm.remove(a);
a=null;
b=null;
System.gc();
System.out.println(hm);
System.out.println(wh);
来看一下结果,
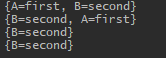
前面三个都没有问题,可是最后一个WeakHashMap怎么也少了一个元素?原因就是这个节点的键——即引用a已经没有指向了,所以也会在WeakHashMap中删除了。可能有人会问引用b不是也赋值为null了吗?为什么不删除,那是因为b还有用!b仍作为HashMap中一个键的引用发挥着作用,因此达不到回收的条件。
6.LinkedHashMap
HashMap是无序的,TreeMap是可以按照自定义的顺序排列,但是LinkedHashMap可以按照插入或者访问的顺序进行遍历,这还是很有实用性的。以下为LinkedHashMap的基本操作:
LinkedHashMap lh = new LinkedHashMap();
lh.put(1,"w");
lh.put(2,"u");
lh.put(3," ");
lh.put(4,"y");
lh.put(5,"i");
lh.put(6," ");
lh.put(7,"m");
lh.put(8,"i");
lh.put(9,"n");
lh.put(10,"g"); Collection<String> c = lh.values(); for(String s:c)
System.out.print(s);
wu yi ming
可以看出,只要按照顺序就可以了!
因为LinkedHashMap是继承HashMap实现的,所以特性和HashMap都是相同的,比如说可以有null元素,以及不是线程安全的,当然关于构造函数,除了和HashMap重复的,只有一个构造函数需要单独解释一下.
/**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the specified initial capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/ public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the specified initial capacity and a default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* Constructs an insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with
* the same mappings as the specified map. The <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt>
* instance is created with a default load factor (0.75) and an initial
* capacity sufficient to hold the mappings in the specified map.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super();
accessOrder = false;
putMapEntries(m, false);
} /**
* Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
LinkedHashMap Constructor
emmm。。。。全是直接调用父类的方法,只不过多了要给accessOrder的boolean变量。这个变量默认是false的,即按照插入顺序遍历,但是最后哪个构造函数可以将其设置为true,此时将会按照访问顺序遍历。
public static void main(String [] args)
{
LinkedHashMap lh = new LinkedHashMap(16,.75f,true); // accessOrder设置为按照访问顺序
lh.put(1,"w");
lh.put(2,"u");
lh.put(3," ");
lh.put(4,"y");
lh.put(5,"i");
lh.put(6," ");
lh.put(7,"m");
lh.put(8,"i");
lh.put(9,"n");
lh.put(10,"g"); Collection<String> c = lh.values(); for(String s:c)
System.out.print(s);
System.out.println(); lh.get(5); //访问键为5的节点 Set se = lh.entrySet();
Iterator ii = se.iterator();
while(ii.hasNext())
{
Map.Entry map_entry = (Map.Entry)ii.next();
System.out.print(map_entry.getValue());
} }
按照访问顺序会使你最近访问的元素置于最新的位置(相当于按插入顺序的最新插入的地位),其结果如下:
wu yi ming
wu y mingi
LinkedHashMap是如何实现这种效果的呢?其实原理也简单,即一个HashMap加上一个链表,可是LinkedHashMap是继承与HashMap的,那它的链表是在哪里实现的呢?先来看一下LinkedHashMap的成员域:
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
final boolean accessOrder;
当然也会继承HashMap的所有成员,上述除了accessOrder已经讲过了,还增加了一个头节点和尾节点,记录第一个和最后一个LinkedHashMap节点。之前HashMap是继承Map.Entry接口的,而这里的LinkedHashMap.Entry是继承HashMap的Node类的:
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
增加了前驱节点和后继节点。这样就很好理解遍历LinkedHashMap究竟如何实现了,按照链表的方式即可,现在我关心的是如何实现按照访问顺序的。那我们接着看源码,想找相关的代码,直接的想法是找遍历代码,但是遍历代码仅仅是链表方式并没有任何关于accessOrder相关的。这是我想到会不会在get()方法呢?果然,直接上get方法的代码:
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
逻辑倒也不复杂,就是看看是不是有这个key,没有就直接返回null了,后面跟了一个判断accessOrder的逻辑,1的话执行一个afterNodeAccess(e)方法。(e就是刚访问的节点) 接着挖afterNodeAccess()方法咯:
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
额,只是将这个节点放在了链表结尾处。。。值得注意的是,这里hash结构并没有任何改变,要学会剥离的看待HashMap和链表,否则只会徒增麻烦!借一个图来简单的解释一下,
https://www.jianshu.com/p/8f4f58b4b8ab
集合(六) WeakHashMap与LinkedHashMap的更多相关文章
- JAVA提高十九:WeakHashMap&EnumMap&LinkedHashMap&LinkedHashSet深入分析
因为最近工作太忙了,连续的晚上支撑和上班,因此没有精力来写下这篇博客,今天上午正好有一点空,因此来复习一下不太常用的集合体系大家族中的几个类:WeakHashMap&EnumMap&L ...
- map,set,list等集合解析以及HashMap,LinkedHashMap,TreeMap等该选谁的的区别
前言: 今天在整理一些资料时,想起了map,set,list等集合,于是就做些笔记,提供给大家学习参考以及自己日后回顾. Map主要用于存储健值对,根据键得到值,因此不允许键重复(重复了覆盖了),但允 ...
- Java集合之WeakHashMap
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行 --陆游 问渠那得清如许,为有源头活水来 --朱熹 WeakHashMap继承于AbstractMap,同时实现了Map接口. 和HashMap一样,Weak ...
- 学习JDK1.8集合源码之--LinkedHashMap
1. LinkedHashMap简介 LinkedHashMap继承自HashMap,实现了Map接口. LinkedHashMap是HashMap的一种有序实现(多态,HashMap的有序态),可以 ...
- Java 集合框架 LinkedHashSet 和 LinkedHashMap 源码剖析
总体介绍 如果你已看过前面关于HashSet和HashMap,以及TreeSet和TreeMap的讲解,一定能够想到本文将要讲解的LinkedHashSet和LinkedHashMap其实也是一回事. ...
- 【JDK1.8】JDK1.8集合源码阅读——LinkedHashMap
一.前言 在上一篇随笔中,我们分析了HashMap的源码,里面涉及到了3个钩子函数,用来预设给子类--LinkedHashMap的调用,所以趁热打铁,今天我们来一起看一下它的源码吧. 二.Linked ...
- 【Java集合源代码剖析】LinkedHashmap源代码剖析
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/37867985 前言:有网友建议分析下LinkedHashMap的源代码.于是花了一晚上时间 ...
- 死磕 java集合之WeakHashMap源码分析
欢迎关注我的公众号"彤哥读源码",查看更多源码系列文章, 与彤哥一起畅游源码的海洋. 简介 WeakHashMap是一种弱引用map,内部的key会存储为弱引用,当jvm gc的时 ...
- Java之集合(十三)WeakHashMap
转载请注明源出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lighten/p/7423818.html 1.前言 本章介绍一下WeakHashMap,这个类也很重要.要想明白此类的作用,先要明白 ...
随机推荐
- C++学习笔记-异常处理
程序设计的要求之一就是程序的健壮性.希望程序在运行时能够不出或者少出问题.但是,在程序的实际运行时,总会有一些因素会导致程序不能正常运行.异常处理(Exception Handling)就是要提出或者 ...
- babel-plugin-equire - 一个按需加载 echarts 模块的 babel 插件
参考链接:https://juejin.im/entry/5a1c1bc9f265da430d57bd3f?utm_medium=hao.caibaojian.com&utm_source=h ...
- [Nowcoder212D]禁书目录_概率期望
禁书目录 题目大意:清教需要定期给Index清除记忆,在此之前需要把当中的十万三千本禁书取出来......不幸的是,禁书一旦离开了Index就非常脆弱,具体来说,每一本禁书都有一个魔力值 ai ,其记 ...
- Win7/Win2008下IIS配置Asp站点启用父路径的设置方法
iis日志错误如下: 修改路径文件权限问题依旧. 解决方式:
- linux下对服务器性能监控shell脚本
#!/bin/bash #提取本服务器的IP地址信息 ENO1=`ifconfig | sed -n '1,1p' | awk -F ' ' '{print $1}'` IP=` -d -d &quo ...
- log4j rootLogger配置示例(log4j.properties)
log4j.rootLogger=INFO,commonLogger, log4j.appender.commonLogger=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppenderlog4 ...
- 【IntelliJ IDEA】从资源文件读取出来就中文乱码的解决方法
在application.properties资源文件中设置两个自定义的属性以及属性值: com.sxd.name = "德玛西亚" com.sxd.want = "王者 ...
- winfrom 点击按钮button弹框显示颜色集
1.窗体托一个按钮button: 2.单击事件: private void btnForeColor_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { using (ColorD ...
- 【原创】大数据基础之Chronos
官方:https://mesos.github.io/chronos/ mesos集群中替换crontab Chronos A fault tolerant job scheduler for Mes ...
- 题解 POJ1964/UVA1330/SP277 【City Game】
题目链接: https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/UVA1330 http://poj.org/problem?id=1964 https://www.luogu ...
