Java:逐行读、写文件、文件目录过滤的用法
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; public class HelloWord {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "my File.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file),"utf-8");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); List<String> lineItems=new ArrayList<String>();
String line = null;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] items = line.split(","); String item= items[1];
if(item.indexOf("花园")!=-1){
lineItems.add(line);
}
} bufferedReader.close();
inputStreamReader.close(); for(String my : lineItems){
System.out.println(my);
}
}
}
- 写文件用法:
List<String> lines = new ArrayList<>();
String wfilePath="e:\\1.txt";
File wfile = new File(wfilePath);
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(wfile), "utf-8");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter);
for (String eLine : lines) {
bufferedWriter.write(eLine);
bufferedWriter.newLine();
} bufferedWriter.close();
outputStreamWriter.close(); System.out.println("Complete...");
- 文件目录过滤:
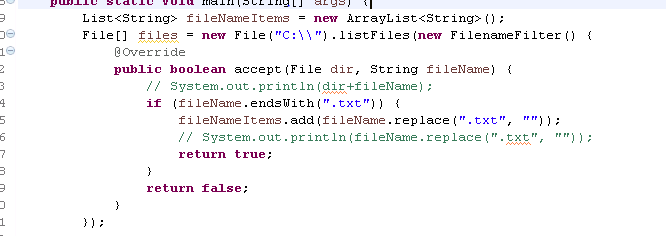
实例:
package com.dx.hibernate5.test; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map; public class HelloWord {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "E:\\丽水";
String wfilePath = "E:\\丽水_New";
parserCountyVsCode(filePath); parseCityCounty(filePath, wfilePath); System.out.println("Complete...");
} private static void parserCountyVsCode(String filePath)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException, FileNotFoundException, IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), "utf-8");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
// 缙云县:5782
// 云和县:5784
// 开发区:578B
// 龙泉市:5786
// 景宁县:5789
// 青田县:5783
// 景宁畲族自治县:5789
// 松阳县:5788
// 庆元县:5785
// 莲都区:5781
// 遂昌县:5787
List<String> countyList = new ArrayList<>();
countyList.add("5782");
countyList.add("5784");
countyList.add("578B");
countyList.add("5786");
countyList.add("5789");
countyList.add("5783");
countyList.add("5788");
countyList.add("5785");
countyList.add("5781");
countyList.add("5787"); Map<String, String> lineItems = new HashMap<String, String>();
String line = null;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] items = line.split(","); String address = items[3];
String county = items[2]; if (address.indexOf("莲都区") != -1) {
lineItems.put("莲都区", county);
} else if (address.indexOf("开发区") != -1) {
lineItems.put("开发区", county);
} else if (address.indexOf("青田县") != -1) {
lineItems.put("青田县", county);
} else if (address.indexOf("缙云县") != -1) {
lineItems.put("缙云县", county);
} else if (address.indexOf("遂昌县") != -1) {
lineItems.put("遂昌县", county);
} else if (address.indexOf("松阳县") != -1) {
lineItems.put("松阳县", county);
} else if (address.indexOf("云和县") != -1) {
lineItems.put("云和县", county);
} else if (address.indexOf("庆元县") != -1) {
lineItems.put("庆元县", county);
} else if (address.indexOf("景宁县") != -1 || address.indexOf("景宁畲族自治县") != -1) {
lineItems.put("景宁县", county);
} else if (address.indexOf("龙泉市") != -1) {
lineItems.put("龙泉市", county);
} else {
Boolean hasContains = false;
for (String coun : countyList) {
if (coun.equals(county)) {
hasContains = true;
}
}
if (!hasContains) {
System.out.println(line);
}
}
} bufferedReader.close();
inputStreamReader.close(); for (Map.Entry<String, String> kvEntry : lineItems.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(kvEntry.getKey() + ":" + kvEntry.getValue());
}
} private static void parseCityCounty(String filePath, String wfilePath)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException, FileNotFoundException, IOException {
Map<String, String> idVsCountry = new HashMap<>();
idVsCountry.put("5782", "缙云县");
idVsCountry.put("5784", "云和县");
idVsCountry.put("578B", "开发区");
idVsCountry.put("5786", "龙泉市");
idVsCountry.put("5789", "景宁县");
idVsCountry.put("5783", "青田县");
idVsCountry.put("5788", "松阳县");
idVsCountry.put("5785", "庆元县");
idVsCountry.put("5781", "莲都区");
idVsCountry.put("5787", "遂昌县"); List<String> lines = new ArrayList<>();
lines.add("abc0");
lines.add("abc1");
lines.add("abc2");
File file = new File(filePath);
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), "utf-8");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String line = null;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] items = line.split(","); String address = items[3];
String county = items[2];
String newLine = items[0] + ",丽水市," + idVsCountry.get(county) + "," + address;
// System.out.println(newLine);
lines.add(newLine);
} bufferedReader.close();
inputStreamReader.close(); File wfile = new File(wfilePath);
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(wfile), "utf-8");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter);
for (String eLine : lines) {
bufferedWriter.write(eLine);
bufferedWriter.newLine();
} bufferedWriter.close();
outputStreamWriter.close();
}
}
Java:逐行读、写文件、文件目录过滤的用法的更多相关文章
- 关于使用 Java 分片读\写文件
分片读取文件方法: /** * 分片读取文件块 * * @param path 文件路径 * @param position 角标 * @param blockSize 文件块大小 * @return ...
- java读/写文件
读取文件参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42129373/article/details/82154471 写入文件参考:https://blog.csdn.net/B ...
- Java基础之写文件——将素数写入文件中(PrimesToFile)
控制台程序,计算素数.创建文件路径.写文件. import static java.lang.Math.ceil; import static java.lang.Math.sqrt; import ...
- java中多种写文件方式的效率对比实验
一.实验背景 最近在考虑一个问题:“如果快速地向文件中写入数据”,java提供了多种文件写入的方式,效率上各有异同,基本上可以分为如下三大类:字节流输出.字符流输出.内存文件映射输出.前两种又可以分为 ...
- C++ 二进制文件 读 写文件
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include<fstream> 4 using namespace st ...
- read(),write() 读/写文件
read read()是一个系统调用函数.用来从一个文件中,读取指定长度的数据到 buf 中. 使用read()时需要包含的头文件: <unistd.h> 函数原型: ssize_t re ...
- 在Java中怎样逐行地写文件?
下边是写东西到一个文件里的Java代码. 执行后每一次,一个新的文件被创建,而且之前一个也将会被新的文件替代.这和给文件追加内容是不同的. public static void writeFile1( ...
- Java基础之写文件——从多个缓冲区写(GatheringWrite)
控制台程序,使用单个写操作将数据从多个缓冲区按顺序传输到文件,这称为集中写(GatheringWrite)操作.这个功能的优势是能够避免在将信息写入到文件中之前将信息复制到单个缓冲区中.从每个缓冲区写 ...
- java中IO写文件工具类
以下是一些依据经常使用java类进行组装的对文件进行操作的类,平时,我更喜欢使用Jodd.io中提供的一些对文件的操作类,里面的方法写的简单易懂. 当中jodd中提供的JavaUtil类中提供的方法足 ...
随机推荐
- GEETEST极验召集互联网大佬齐聚光谷,共同探讨交互安全问题
全球互联网技术在飞速发展的同时,网络安全事件也随之频发.除了直接带来经济损失的网络恶意攻击之外,企业在多个方面也遭受着不同程度的网络恶意攻击,包括品牌形象.管理时间.企业竞争力.客户成交量.用户行为等 ...
- Gauge----自动化测试工具--使用
开始吧 1 下载安装gauge(根据官网教程 http://getgauge.io/documentation/user/current/)测试:gauge -v step01 磁盘上新建一个空目录- ...
- Java异常机制简介
什么是异常? 异常一般是指程序在编译期没有问题,但是在程序运行期出现的错误,一个程序会因为出现异常而终止运行,也就是我们常说的挂掉,在多线程下,异常只会影响所在的线程,对其他线程没有影响. Java异 ...
- scanf()中的%c 不能正常输入的问题
#include <stdio.h> int main() { char a; int b; scanf("%d",&b); scanf("%c&qu ...
- 从 MVC 到前后端分离
从 MVC 到前后端分离 1 理解 MVC MVC 是一种经典的设计模式,全名为 Model-View-Controller,即 模型-视图-控制器. 其中,模型 是用于封装数据的载体,例如,在 Ja ...
- 百度API地图的标注不居中显示,而显示在左上角
前言:今天弄个百度地图,弄了半天就是不居中,之前使用一直没有遇到这个问题.所以就一直在找原因. 百度地图对地图所在的div做了显示隐藏之类操作,标注就不再居中显示,而显示在左上角. 查了很久,有人提出 ...
- Nginx代理转发Apache+svn
1.安装svn和httpd yum install httpd yum install subversion mod_dav_svn 创建仓库目录 mkdir -p /var/www/svn 3.创建 ...
- super、this
1)super(参数):调用基类中的某一个构造函数(应该为构造函数中的第一条语句) 2)this(参数):调用本类中另一种形成的构造函数(应该为构造函数中的第一条语句) 3)super: 它引用当前对 ...
- [bzoj1497][NOI2006]最大获利_网络流_最小割
最大获利 bzoj-1497 题目大意:可以建立一个点,花费一定的代价:将已经建立的两个点之间连边,得到一定收益.有些节点之间是不允许连边的. 注释:1<=点数<=5,000,1<= ...
- ansible之一:安装与配置
ansible特点: 1.不需要安装客户端,通过sshd去通信 2.基于模块工作,模块可以由任何语言开发 3.不仅支持命令行试用模块,也支持yaml格式得playbook 4.支持sudo 5.有提供 ...
