Linux驱动之输入子系统简析
输入子系统由驱动层、输入子系统核心、事件处理层三部分组成。一个输入事件,如鼠标移动、键盘按下等通过Driver->Inputcore->Event handler->userspace的顺序到达用户控件的应用程序。
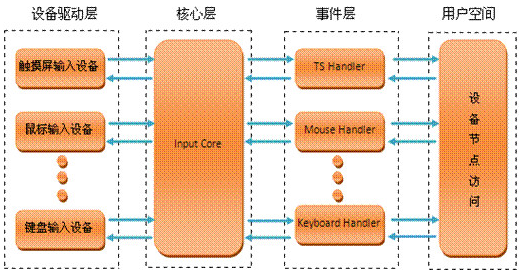
系统框图
假设打开一个字符设备驱动程序/dev/event0,event代表的是输入子系统的设备文件,当应用程序调用C库的open函数后,open函数会进入系统调用,最后定位到drivers\input\input.c文件下(这个文件就是核心层)的。这个函数的功能主要是根据设备的次设备号找到新的fops结构,然后切换到新的fops结构,然后调用它的打开函数。输入子系统的主设备号恒为#define INPUT_MAJOR 13,定义在include\linux\major.h中。
static int input_open_file(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct input_handler *handler = input_table[iminor(inode) >> ];//根据次设备号找到在input_table表中找到handler结构体
const struct file_operations *old_fops, *new_fops = NULL;
int err; /* No load-on-demand here? */
if (!handler || !(new_fops = fops_get(handler->fops)))//判断handler结构体是否存在,存在的话将里面的fops变量赋给new_fops
return -ENODEV; /*
* That's _really_ odd. Usually NULL ->open means "nothing special",
* not "no device". Oh, well...
*/
if (!new_fops->open) {
fops_put(new_fops);
return -ENODEV;
}
old_fops = file->f_op;
file->f_op = new_fops;//切换f_op变量,以后调用诸如read、write等系统调用时会进入到new_fops的read、write函数 err = new_fops->open(inode, file);//调用new_fops的open函数 if (err) {
fops_put(file->f_op);
file->f_op = fops_get(old_fops);
}
fops_put(old_fops);//释放掉老的fops结构
return err;
}
接着先来看到input_table表的建立,可以看到它是一个静态变量,在本文件(drivers\input\input.c)中搜索它,可以看到它位于input_register_handler函数,这是一个全局的函数,可以供外部的文件调用,这个函数的主要功能是注册一个handler结构体,这个结构体中存在minor这个设备的次设备号,这个结构所在的函数对应的其实就是上述的事件层。
int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler)
{
struct input_dev *dev; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&handler->h_list);//初始化handler的h_list结构体,这是一个双向链表 if (handler->fops != NULL) {
if (input_table[handler->minor >> ])//检查是否已经存在这个次设备号的handler结构
return -EBUSY; input_table[handler->minor >> ] = handler;//将handler结构次设备号放入input_table表
} list_add_tail(&handler->node, &input_handler_list);//将handler结构根据node成员放入input_handler_list链表 list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node)//根据node这个成员在input_dev_list链表中循环查找dev结构
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);//对于每一个dev结构调用input_attach_handler函数 input_wakeup_procfs_readers();//将这个设备信息写入proc文件系统
return ;
}
接着搜索input_register_handler,抽取drivers\input\evdev.c这个文件,可以看到在这个模块的入口函数调用了注册函数
static int __init evdev_init(void)
{
return input_register_handler(&evdev_handler);
}
接着看到evdev_handler这个结构体,在这个结构体里面找到了evdev_fops这个结构
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.connect = evdev_connect,
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect,
.fops = &evdev_fops,
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE,
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids,
};
接着看到evdev_fops结构体,可以看到应用层调用的read、write等函数在这里被定义
static const struct file_operations evdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = evdev_read,
.write = evdev_write,
.poll = evdev_poll,
.open = evdev_open,
.release = evdev_release,
.unlocked_ioctl = evdev_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = evdev_ioctl_compat,
#endif
.fasync = evdev_fasync,
.flush = evdev_flush
};
知道了事件层对应的位置,那么设备驱动层在哪里呢?接着往下看,回到input_register_handler函数,在里面看到如下语句,这句语句的作用是将事件层与驱动层联系起来。
list_for_each_entry(dev, &input_dev_list, node)//根据node这个成员在input_dev_list链表中循环查找dev结构
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);//对于每一个dev结构调用input_attach_handler函数
这里可以看到一个新的结构体dev,先看一下dev结构体,它的原型为input_dev,跟抽取drivers\input\evdev.c这个文件一样,搜索input_dev这个结构体,先列出input_dev这个结构体
struct input_dev {
void *private;
const char *name;
const char *phys;
const char *uniq;
struct input_id id;
unsigned long evbit[NBITS(EV_MAX)];
unsigned long keybit[NBITS(KEY_MAX)];
unsigned long relbit[NBITS(REL_MAX)];
unsigned long absbit[NBITS(ABS_MAX)];
unsigned long mscbit[NBITS(MSC_MAX)];
unsigned long ledbit[NBITS(LED_MAX)];
unsigned long sndbit[NBITS(SND_MAX)];
unsigned long ffbit[NBITS(FF_MAX)];
unsigned long swbit[NBITS(SW_MAX)];
unsigned int keycodemax;
unsigned int keycodesize;
void *keycode;
int (*setkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev, int scancode, int keycode);
int (*getkeycode)(struct input_dev *dev, int scancode, int *keycode);
struct ff_device *ff;
unsigned int repeat_key;
struct timer_list timer;
int state;
int sync;
int abs[ABS_MAX + ];
int rep[REP_MAX + ];
unsigned long key[NBITS(KEY_MAX)];
unsigned long led[NBITS(LED_MAX)];
unsigned long snd[NBITS(SND_MAX)];
unsigned long sw[NBITS(SW_MAX)];
int absmax[ABS_MAX + ];
int absmin[ABS_MAX + ];
int absfuzz[ABS_MAX + ];
int absflat[ABS_MAX + ];
int (*open)(struct input_dev *dev);
void (*close)(struct input_dev *dev);
int (*flush)(struct input_dev *dev, struct file *file);
int (*event)(struct input_dev *dev, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value);
struct input_handle *grab;
struct mutex mutex; /* serializes open and close operations */
unsigned int users;
struct class_device cdev;
union { /* temporarily so while we switching to struct device */
struct device *parent;
} dev;
struct list_head h_list;
struct list_head node;
};
接着看到drivers\input\tablet\kbtab.c这个文件,这个文件代表的就是设备驱动层,简单分析一下,可以看到它也是一个内核的模块,可以动态加载,一旦加载后,它会调用kbtab_init函数,最终会调用到kbtab_probe这个函数,可以看到最终又定位到了input_register_device这个注册设备的函数,它位于核心层,即drivers\input\input.c文件下。
static int kbtab_probe(struct usb_interface *intf, const struct usb_device_id *id)
{
...
...
input_dev = input_allocate_device();//分配一个input_dev 结构体
if (!kbtab || !input_dev)
goto fail1; ...
... input_dev->name = "KB Gear Tablet";//初始化input_dev 结构体
input_dev->phys = kbtab->phys;
usb_to_input_id(dev, &input_dev->id);
input_dev->dev.parent = &intf->dev; input_set_drvdata(input_dev, kbtab); input_dev->open = kbtab_open;
input_dev->close = kbtab_close; input_dev->evbit[] |= BIT(EV_KEY) | BIT(EV_ABS) | BIT(EV_MSC);
input_dev->keybit[LONG(BTN_LEFT)] |= BIT(BTN_LEFT) | BIT(BTN_RIGHT) | BIT(BTN_MIDDLE);
input_dev->keybit[LONG(BTN_DIGI)] |= BIT(BTN_TOOL_PEN) | BIT(BTN_TOUCH);
input_dev->mscbit[] |= BIT(MSC_SERIAL);
input_set_abs_params(input_dev, ABS_X, , 0x2000, , );
input_set_abs_params(input_dev, ABS_Y, , 0x1750, , );
input_set_abs_params(input_dev, ABS_PRESSURE, , 0xff, , ); ...
... error = input_register_device(kbtab->dev);//注册input_dev结构体
...
...
}
接着看到input_register_device这个函数,它根input_register_handler相对应,前一个注册设备驱动层,后一个注册事件层。列出input_register_device函数,它同样位于drivers\input\input.c文件中。
int input_register_device(struct input_dev *dev)
{
static atomic_t input_no = ATOMIC_INIT();
struct input_handler *handler;
const char *path;
int error; set_bit(EV_SYN, dev->evbit);//设置同步事件 /*
* If delay and period are pre-set by the driver, then autorepeating
* is handled by the driver itself and we don't do it in input.c.
*/ init_timer(&dev->timer);//初始化一个定时器
if (!dev->rep[REP_DELAY] && !dev->rep[REP_PERIOD]) {//按键是否需要重复,如果需要设置重复函数与重复时间
dev->timer.data = (long) dev;
dev->timer.function = input_repeat_key;
dev->rep[REP_DELAY] = ;
dev->rep[REP_PERIOD] = ;
} if (!dev->getkeycode)
dev->getkeycode = input_default_getkeycode;//获得按键值默认函数 if (!dev->setkeycode)
dev->setkeycode = input_default_setkeycode;//设置按键值默认函数 list_add_tail(&dev->node, &input_dev_list);//将dev->node放入input_dev_list链表 snprintf(dev->cdev.class_id, sizeof(dev->cdev.class_id),
"input%ld", (unsigned long) atomic_inc_return(&input_no) - ); if (!dev->cdev.dev)
dev->cdev.dev = dev->dev.parent; error = class_device_add(&dev->cdev);
if (error)
return error; path = kobject_get_path(&dev->cdev.kobj, GFP_KERNEL);
printk(KERN_INFO "input: %s as %s\n",
dev->name ? dev->name : "Unspecified device", path ? path : "N/A");
kfree(path); list_for_each_entry(handler, &input_handler_list, node)//根据node这个成员在input_handler_list链表中循环查找handler结构
input_attach_handler(dev, handler);//对于每一个handler结构调用input_attach_handler函数 input_wakeup_procfs_readers();//将这个设备信息写入proc文件系统 return ;
}
可以看到它同样也调用了input_attach_handler函数,将设备驱动层与事件层联系起来。这个函数也位于drivers\input\input.c文件中。它的主要功能是
1、根据handler->id_table的值匹配dev,找到id
2、调用调用handler->connect进行匹配
static int input_attach_handler(struct input_dev *dev, struct input_handler *handler)
{
const struct input_device_id *id;
int error; if (handler->blacklist && input_match_device(handler->blacklist, dev))
return -ENODEV; id = input_match_device(handler->id_table, dev);//根据handler->id_table的值匹配dev,找到id
if (!id)
return -ENODEV; error = handler->connect(handler, dev, id);//调用handler->connect进行匹配
if (error && error != -ENODEV)
printk(KERN_ERR
"input: failed to attach handler %s to device %s, "
"error: %d\n",
handler->name, kobject_name(&dev->cdev.kobj), error); return error;
}
接着看到input_match_device函数
static const struct input_device_id *input_match_device(const struct input_device_id *id,
struct input_dev *dev)
{
int i; for (; id->flags || id->driver_info; id++) {//循环查找支持的id if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_BUS)
if (id->bustype != dev->id.bustype)
continue; if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR)
if (id->vendor != dev->id.vendor)
continue; if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT)
if (id->product != dev->id.product)
continue; if (id->flags & INPUT_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VERSION)
if (id->version != dev->id.version)
continue; MATCH_BIT(evbit, EV_MAX);//
MATCH_BIT(keybit, KEY_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(relbit, REL_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(absbit, ABS_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(mscbit, MSC_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(ledbit, LED_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(sndbit, SND_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(ffbit, FF_MAX);
MATCH_BIT(swbit, SW_MAX); return id;
} return NULL;
再看到handler->connect函数,这里选取的是evdev_handler ->evdev_connect函数,这个函数的主要作用就是将handle、handler、evdev三者相互匹配起来
static int evdev_connect(struct input_handler *handler, struct input_dev *dev,
const struct input_device_id *id)
{
struct evdev *evdev;
struct class_device *cdev;
dev_t devt;
int minor;
int error; for (minor = ; minor < EVDEV_MINORS && evdev_table[minor]; minor++);//取得次设备号,如果还没有利用则evdev_table为空
if (minor == EVDEV_MINORS) {
printk(KERN_ERR "evdev: no more free evdev devices\n");//没有剩余的空间可以用了
return -ENFILE;
} evdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct evdev), GFP_KERNEL);//分配一个evdev
if (!evdev)
return -ENOMEM; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&evdev->client_list);
init_waitqueue_head(&evdev->wait); evdev->exist = ; //evdev初始化
evdev->minor = minor;
evdev->handle.dev = dev; //初始化evdev->handle.dev
evdev->handle.name = evdev->name;
evdev->handle.handler = handler; //初始化evdev->handle.handler
evdev->handle.private = evdev;
sprintf(evdev->name, "event%d", minor);//打印次设备号,每次注册新的设备驱动都会打印 evdev_table[minor] = evdev;//将分配的evdev放入evdev_table[minor] devt = MKDEV(INPUT_MAJOR, EVDEV_MINOR_BASE + minor), cdev = class_device_create(&input_class, &dev->cdev, devt,
dev->cdev.dev, evdev->name);//创建一个字符设备节点
if (IS_ERR(cdev)) {
error = PTR_ERR(cdev);
goto err_free_evdev;
} /* temporary symlink to keep userspace happy */
error = sysfs_create_link(&input_class.subsys.kobj,
&cdev->kobj, evdev->name);
if (error)
goto err_cdev_destroy; /*
llist_add_tail(&handle->d_node, &handle->dev->h_list);//将&handle->d_node 放入&handle->dev->h_list链表
list_add_tail(&handle->h_node, &handler->h_list); //将&handle->h_node 放入 &handler->h_list链表?
*/
error = input_register_handle(&evdev->handle);//注册evdev->handle
if (error)
goto err_remove_link; return ; err_remove_link:
sysfs_remove_link(&input_class.subsys.kobj, evdev->name);
err_cdev_destroy:
class_device_destroy(&input_class, devt);
err_free_evdev:
kfree(evdev);
evdev_table[minor] = NULL;
return error;
}
再回过头来看一下应用层是怎么读取按键值得:应用层调用C库的read函数,通过前面的分析可以知道,最终会通过系统调用会定位到内核的evdev_handler ->fops ->evdev_read,下面看到evdev_read函数,它位于事件层,这个函数根据读取方式的不同采取不同的方式,如果是阻塞方式打开的话最终会当前进程放入等待队列,一直等到有数据才将进程唤醒。
static ssize_t evdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
struct evdev_client *client = file->private_data;
struct evdev *evdev = client->evdev;
int retval; if (count < evdev_event_size())
return -EINVAL; if (client->head == client->tail && evdev->exist && (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))//如果采用非阻塞方式读取,并且每天数据直接返回
return -EAGAIN; retval = wait_event_interruptible(evdev->wait,
client->head != client->tail || !evdev->exist);//阻塞方式读取,先将当前进程休眠,等待有数据后被唤醒
if (retval)
return retval; if (!evdev->exist)
return -ENODEV; while (client->head != client->tail && retval + evdev_event_size() <= count) {//头!=尾表示有数据 struct input_event *event = (struct input_event *) client->buffer + client->tail; if (evdev_event_to_user(buffer + retval, event))//将得到的数据考回给用户层
return -EFAULT; client->tail = (client->tail + ) & (EVDEV_BUFFER_SIZE - );
retval += evdev_event_size();
} return retval;
}
接下来的问题就是谁将进程唤醒,我们直接看到设备驱动层,即drivers\input\tablet\kbtab.c,在这个文件中有一个kbtab_irq函数,它是一个中断处理函数,它位于设备驱动层,负责将中断过来的按键数据上报调用的是input_report_key函数,input_report_key函数最终调用的是input_event函数,他们全部都属于核心层。接着看一下input_event的核心代码
list_for_each_entry(handle, &dev->h_list, d_node)//根据dev设备驱动层的h_list找出handle结构体
if (handle->open)
handle->handler->event(handle, type, code, value);//调用事件层的handle->handler->event进行处理
再回过头看事件层的event,即evdev_event函数,可以看到在这个函数里将按键的相关的值取出后,最终进程的唤醒函数在这里调用wake_up_interruptible。
static void evdev_event(struct input_handle *handle, unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
struct evdev *evdev = handle->private;
struct evdev_client *client; if (evdev->grab) {
client = evdev->grab; do_gettimeofday(&client->buffer[client->head].time);
client->buffer[client->head].type = type;
client->buffer[client->head].code = code;
client->buffer[client->head].value = value;
client->head = (client->head + ) & (EVDEV_BUFFER_SIZE - ); kill_fasync(&client->fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
} else
list_for_each_entry(client, &evdev->client_list, node) { do_gettimeofday(&client->buffer[client->head].time);//时间 8字节
client->buffer[client->head].type = type; //按键类型 2字节
client->buffer[client->head].code = code; //按键码 2字节
client->buffer[client->head].value = value; //按键值,按下或松开 4字节
client->head = (client->head + ) & (EVDEV_BUFFER_SIZE - ); kill_fasync(&client->fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);//异步通知
} wake_up_interruptible(&evdev->wait);//唤醒进程
}
总结一下整个输入子系统的调用过程:
app_open->input_open_file->evdev_open
应用层 核心层 事件层
app_read->evdev_read->kbtab_irq->input_report_key->input_event->evdev_event->evdev_read
应用层 事件层 设备层 核心层 核心层 事件层 事件层
如果要自己添加一个输入子系统的设备,只需要添加设备层的文件即可。
1、在里面添加设备层input_dev结构并初始化
2、编写中断处理程序
Linux驱动之输入子系统简析的更多相关文章
- Linux驱动之中断处理体系结构简析
S3C2440中的中断处理最终是通过IRQ实现的,在Linux驱动之异常处理体系结构简析已经介绍了IRQ异常的处理过程,最终分析到了一个C函数asm_do_IRQ,接下来继续分析asm_do_IRQ, ...
- linux驱动模型<输入子系统>
在linux中提供一种输入子系统的驱动模型,其主要是实现在input.c中. 在输入子系统这套模型中,他把驱动分层分类.首先分为上下两层,上层为input.c .下层为驱动的实现,下层分为两部分,一部 ...
- Linux驱动之异常处理体系结构简析
异常的概念在单片机中也接触过,它的意思是让CPU可以暂停当前的事情,跳到异常处理程序去执行.以前写单片机裸机程序属于前后台程序,前台指的就是mian函数里的while(1)大循环,后台指的就是产生异常 ...
- Linux网络性能优化方法简析
Linux网络性能优化方法简析 2010-12-20 10:56 赵军 IBMDW 字号:T | T 性能问题永远是永恒的主题之一,而Linux在网络性能方面的优势则显而易见,这篇文章是对于Linux ...
- Linux 目录结构学习与简析 Part2
linux目录结构学习与简析 by:授客 QQ:1033553122 ---------------接Part 1-------------- #1.查看CPU信息 #cat /proc/cpuinf ...
- Linux 目录结构学习与简析 Part1
linux目录结构学习与简析 by:授客 QQ:1033553122 说明: / linux系统目录树的起点 =============== /bin User Bi ...
- Linux 驱动框架---input子系统框架
前面从具体(Linux 驱动框架---input子系统)的工作过程学习了Linux的input子系统相关的架构知识,但是前面的学习比较实际缺少总结,所以今天就来总结一下输入子系统的架构分层,站到远处来 ...
- Linux 驱动框架---input子系统
input 子系统也是作为内核的一个字符设备模块存在的,所以他也是字符设备自然也会有字符设备的文件接口.input子系统的注册过程主要分为两步,先注册了一个input class然后再注册一个字符设备 ...
- ARM Linux内核Input输入子系统浅解
--以触摸屏驱动为例 第一章.了解linux input子系统 Linux输入设备总类繁杂,常见的包括有按键.键盘.触摸屏.鼠标.摇杆等等,他们本身就是字符设备,而linux内核将这些 ...
随机推荐
- Excel技巧--分隔工资条
要将上图的工资表,做成每行都带标题而且有空行间隔的工资条,可以这么做: 1.表格右侧添加一列数据列:输入1,2,选定,并双击单元格右下角形成一升序数字列: 2.再将该列复制,粘贴到该列末尾: 3.点一 ...
- Custom Grid Columns - FireMonkey Guide
原文 http://monkeystyler.com/guide/Custom-Grid-Columns ack to FireMonkey Topics As we saw in TGrid a F ...
- Tag (input) should be an empty-element tag.
因为:<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.o ...
- Android之listview添加数据篇
一.ListView: 1. ListView通常有两个职责: 1.向布局填充数据 2.处理选择点击等操作 2.ListView的创建需要3个元素: 1. ListView中的每一列的View. 2. ...
- Web jsp开发学习——网上直播聊天室的简单开发
整个界面为chat.jsp: 如果用户没有登录,就不能进行聊天. 为将发言的句子传到页面上,要设置一个<iframe></iframe>虚拟框架,将allmessage.jsp ...
- sed -i命令详解
[root@www ~]# sed [-nefr] [动作] 选项与参数: -n :使用安静(silent)模式.在一般 sed 的用法中,所有来自 STDIN 的数据一般都会被列出到终端上.但如果加 ...
- hessian的简单使用以及与spring整合
Hessian是一个由Caucho Technology开发的轻量级二进制RPC协议.和其他Web服务的实现框架不同的是,Hessian是一个使用二进制格式传输的Web服务协议的框架,相对传统soap ...
- 用户名、密码等15个常用的js正则表达式
本文收集整理了15个常用的javaScript正则表达式,其中包括用户名.密码强度.整数.数字.电子邮件地址(Email).手机号码.身份证号.URL地址. IPv4地址. 十六进制颜色. 日期. Q ...
- JSX
有一个 Babel 插件,用于在 Vue 中使用 JSX 语法,它可以让我们回到更接近于模板的语法上.JSX语法返回一个vnode对象 import AnchoredHeading from './A ...
- spring学习1
1.<context:property-placeholder/> :用于从外部属性文件中获取Bean的配置 <context:property-placeholder locati ...
