day21 模块 异常处理
常用模块:http://www.cnblogs.com/Eva-J/articles/7228075.html
今日概要:
#time
# —— 时间:时间戳 字符串 结构化时间
#collections —— 扩展数据类型的模块:可命名元祖,有序字典,默认字典,双端队列,计数器
#sys —— 和py解释器打交道的模块
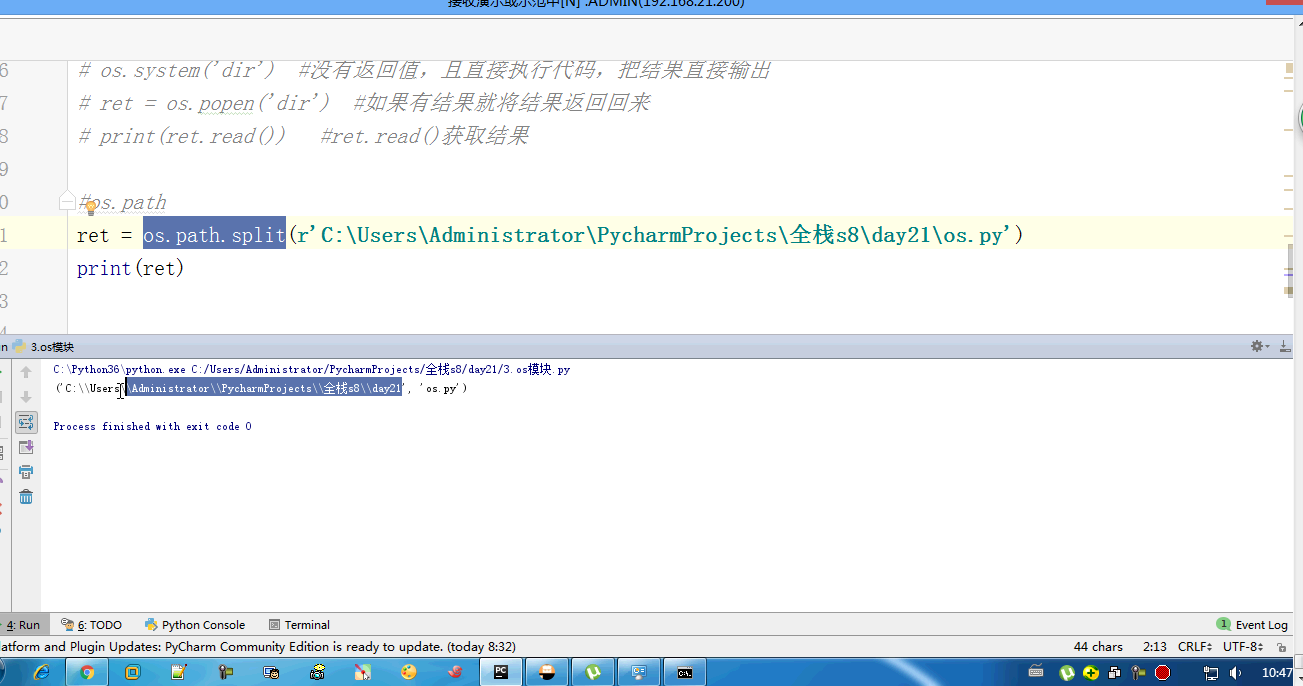
#—— sys.path : 和路径有关,且关系到模块导入相关的路径
#—— sys.argv : [xxx.py,argv1,argv2],python xxx.py argv1 argv2 ... #常用模块
# random 随机数相关 ***
# os 操作系统相关 *****
# 序列化
# json *****
# pickle ****
# shelve ***
#异常处理 *****
random模块:
import random
# print(random.random()) #0-1之间的小数
# print(random.uniform(10,12)) #n,m 之间的小数 #生成随机整数
# print(random.randint(1,2)) #必须是两个参数,规定一个范围 [1,2]
# print(random.randrange(100)) #一个参数
# print(random.randrange(1,2)) #两个个参数 [1,2)
# print(random.randrange(90,100,2)) #三个参数,最后一个是步长 #从一个序列中随机选择:一个 choice,多个 sample
# print(random.choice('abc'))
# print(random.sample([1,'23',[4,5]],2)) #打乱一个序列的顺序
# item=[1,3,5,7,9]
# random.shuffle(item) #改变了原列表
# print(item) #验证码
#生成一个6位数字随机验证码
#randint(100000,999999)
#randrange(100000,1000000)
# l = []
# for i in range(6):
# rand_num = random.randint(0,9)
# l.append(str(rand_num))
# print(''.join(l)) #生成一个6位数字随机验证码,不能有重复,少了好多种情况
# print(random.sample(range(0,10),6)) #[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] #生成一个6位数字+字母的验证码
#0-9 randrange(0,10)
#a-z 65-90,97-122
#几个数字几个字母
# 方法一
# l = ['a','b'...,'z','0','1','2'...'9'] sample 取6个
# for i in range(6):
# rand_val = random.choice(l)
#方法二
# alpha = random.randint(65,90) #random.randrange(65,91)
# alpha2 = chr(alpha)
# print(alpha2)
# num = random.randint(0,9) #random.randrange(0,10)
# print(num)
# print(random.choice([alpha2,str(num)]))
l = []
for i in range(6):
alpha = chr(random.randint(65, 90)) # random.randrange(65,91)
alpha_lower = chr(random.randint(97, 122)) # random.randrange(65,91)
num = str(random.randint(0, 9))
ret = random.choice([alpha,num,alpha_lower])
l.append(ret)
print(''.join(l))
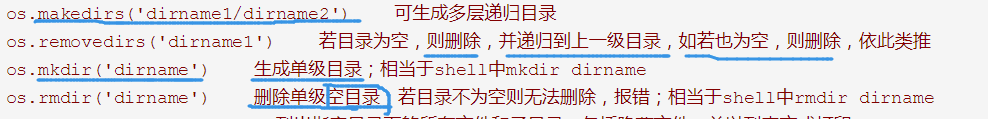
os模块:
import random
# print(random.random()) #0-1之间的小数
# print(random.uniform(10,12)) #n,m 之间的小数 #生成随机整数
# print(random.randint(1,2)) #必须是两个参数,规定一个范围 [1,2]
# print(random.randrange(100)) #一个参数
# print(random.randrange(1,2)) #两个个参数 [1,2)
# print(random.randrange(90,100,2)) #三个参数,最后一个是步长 #从一个序列中随机选择:一个 choice,多个 sample
# print(random.choice('abc'))
# print(random.sample([1,'23',[4,5]],2)) #打乱一个序列的顺序
# item=[1,3,5,7,9]
# random.shuffle(item) #改变了原列表
# print(item) #验证码
#生成一个6位数字随机验证码
#randint(100000,999999)
#randrange(100000,1000000)
# l = []
# for i in range(6):
# rand_num = random.randint(0,9)
# l.append(str(rand_num))
# print(''.join(l)) #生成一个6位数字随机验证码,不能有重复,少了好多种情况
# print(random.sample(range(0,10),6)) #[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] #生成一个6位数字+字母的验证码
#0-9 randrange(0,10)
#a-z 65-90,97-122
#几个数字几个字母
# 方法一
# l = ['a','b'...,'z','0','1','2'...'9'] sample 取6个
# for i in range(6):
# rand_val = random.choice(l)
#方法二
# alpha = random.randint(65,90) #random.randrange(65,91)
# alpha2 = chr(alpha)
# print(alpha2)
# num = random.randint(0,9) #random.randrange(0,10)
# print(num)
# print(random.choice([alpha2,str(num)]))
l = []
for i in range(6):
alpha = chr(random.randint(65, 90)) # random.randrange(65,91)
alpha_lower = chr(random.randint(97, 122)) # random.randrange(65,91)
num = str(random.randint(0, 9))
ret = random.choice([alpha,num,alpha_lower])
l.append(ret)
print(''.join(l))
序列化模块:
# 什么叫做序列化
# 字符串 列表 字典 元组
# 字典和列表 不能写到文件里
#{[]} ==str== str({[]})
#str({[]}) == eval('')
# s_dic = str({'k':'v'})
# print(repr(s_dic))
# print(repr(eval(s_dic)),type(eval(s_dic)))
# 序列化方法
# 格式转换
# 把python中的数据转换成str —— 序列化
# 可以str转换成python的数据 —— 反序列化 #json
#所有的语言都通用,它能序列化的数据是有限的:字典列表元组
#序列化中的内容只能包含:字典 列表 数字 字符串,如果是元组——自动转成列表的样子
import json
# ret = json.dumps({'k':(1,2,3)})
# print(repr(ret),type(ret))
# ret2 = json.loads(ret)
# print(repr(ret2),type(ret2))
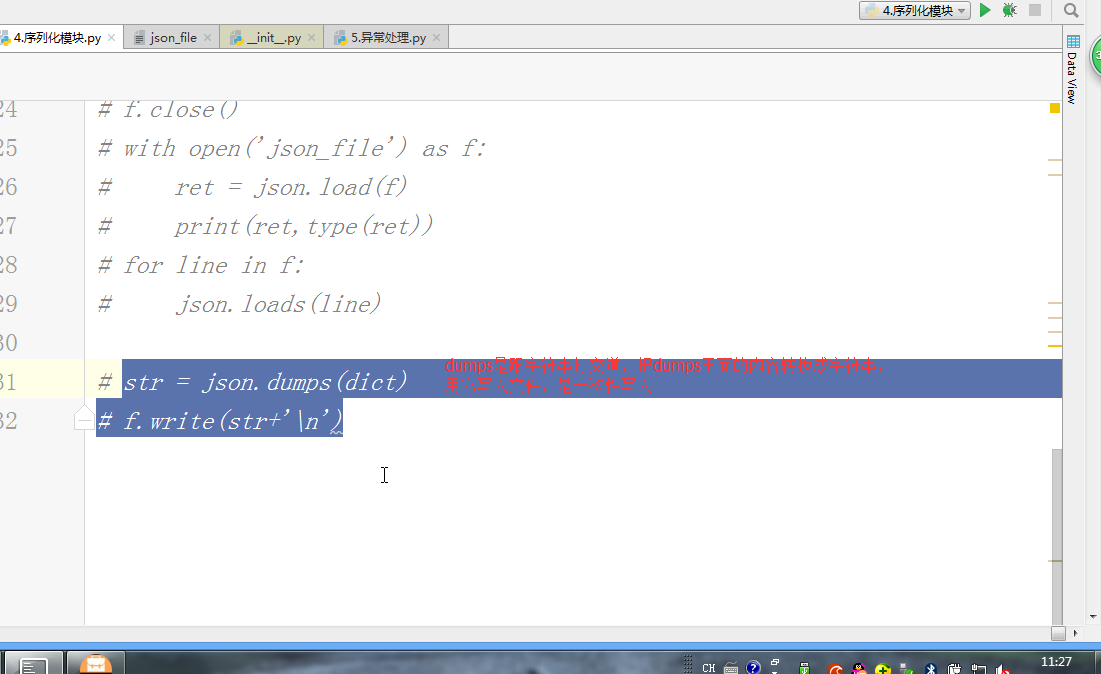
# f = open('json_file','a')
# json.dump({'k':'v'},f)
# f.close()
# with open('json_file') as f:
# ret = json.load(f)
# print(ret,type(ret))
# for line in f:
# json.loads(line) # str = json.dumps(dict)
# f.write(str+'\n') #回去自己练 #pickle是py特有的
#dumps
#loads
#dump
#load
#pickle ---- 序列化任何数据类型,python专有的不能和其他语言兼容,结果是bytes
# import pickle #用pickle序列化的数据,反序列化也必须用pickle
# ret = pickle.dumps({1,2,3,4})
# print(ret) #shelve 只提供一个open,shelve.open('文件名')拿到一个文件句柄,这个文件句柄就可以当做字典操作
#正常情况下shelve打开的文件句柄感知不到值的修改,设置writeback = True就可以保存修改内容了
#正常情况下不支持多个人同时写,支持多个人同时读,如果只是读的化,就设置flag=‘r’
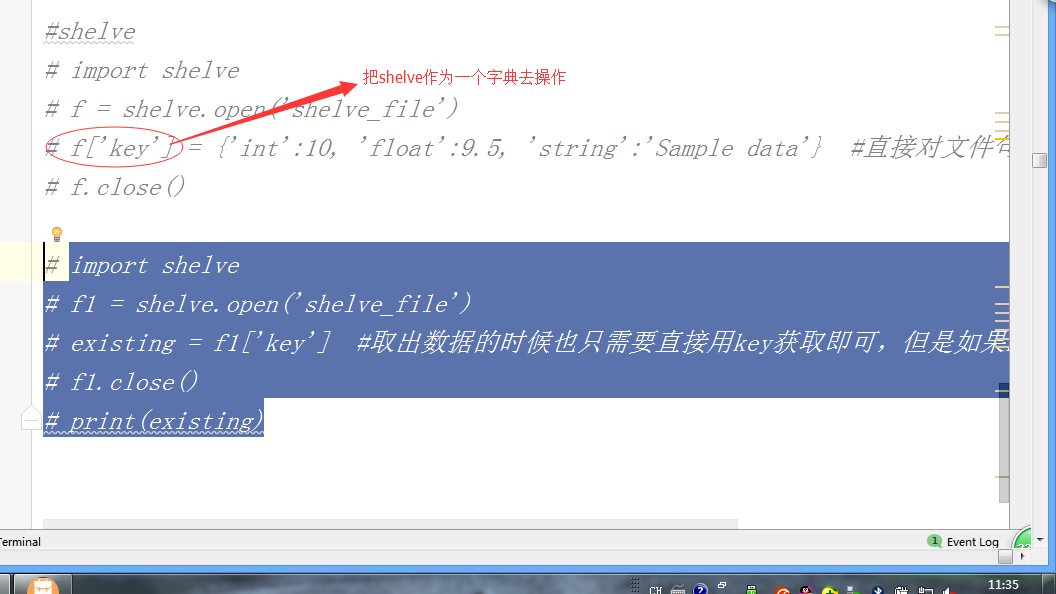
# import shelve
# f = shelve.open('shelve_file')
# f['key'] = {'int':10, 'float':9.5, 'string':'Sample data'} #直接对文件句柄操作,就可以存入数据
# f.close() # import shelve
# f1 = shelve.open('shelve_file')
# existing = f1['key'] #取出数据的时候也只需要直接用key获取即可,但是如果key不存在会报错
# f1.close()
# print(existing) #不支持多个人同时写,支持多个人同时读,如果只是读的化,就设置flag=‘r’
# import shelve
# f = shelve.open('shelve_file',flag='r')
# f['key'] = {'int':10, 'float':9.5, 'string':'Sample data'} #直接对文件句柄操作,就可以存入数据
# f.close() # f1 = shelve.open('shelve_file')
# print(f1['key'])
# f1['key']['new_value'] = 'this was not here before' #改
# f1.close()
#
# f = shelve.open('shelve_file',flag='r')
# print(f['key'])
# f.close() #正常情况下shelve打开的文件句柄感知不到值的修改,设置writeback = True就可以保存修改内容了
import shelve
# f2 = shelve.open('shelve_file', writeback=True)
# print(f2['key'])
# f2['key']['new_value'] = {1,2,3}
# f2.close()
# import shelve
f = shelve.open('shelve_file',flag='r')
print(f['key'])
f.close() #json :所有语言通用,能转换的数据类型有限 *****
#pickle :只限于python,能转换所有的数据类型 做游戏的时候
#shelve : 只限于python语言,能转换所有的数据类型,使用方法类似字典
异常处理:
#异常
# a #NameError 错误
# 2+'' #TypeError 错误
# 1/0 #ZeroDivisionError 错误
#iter([]).next() #AttributeError 错误
# iter([]).__next__() #StopIteration 异常
# import hahaha #ModuleNotFoundError
# [][4] #IndexError # try:
# a=1
# except NameError:
# print('NameError')
# print(123)
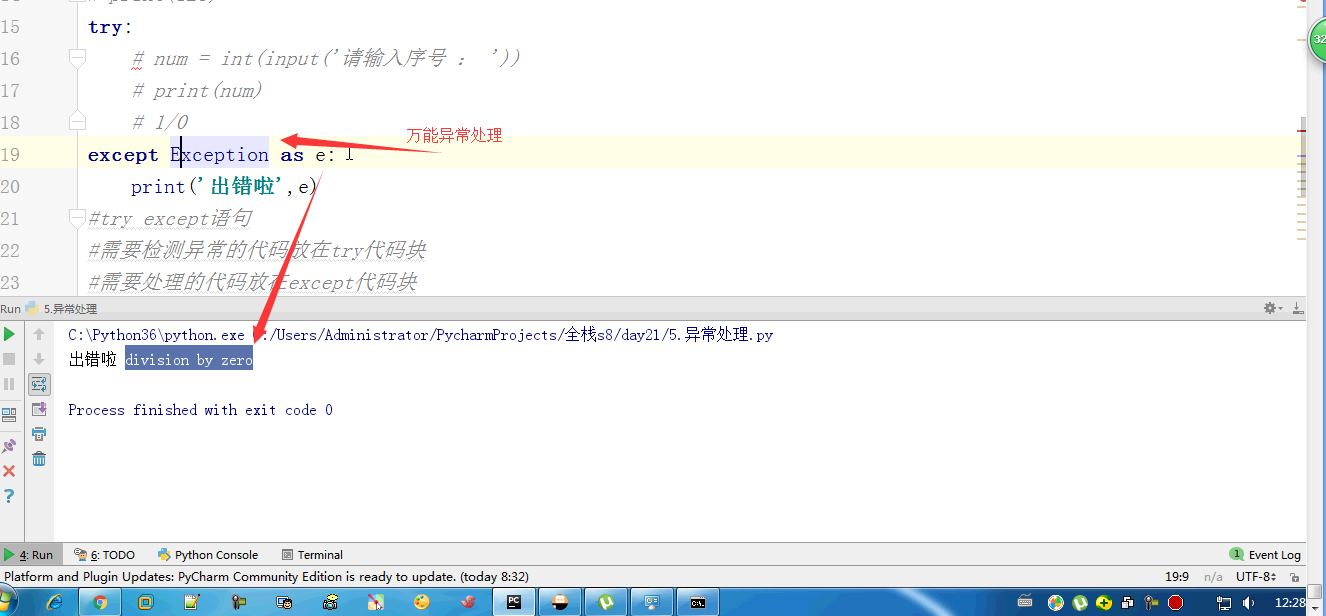
# try:
# num = int(input('请输入序号 : '))
# # print(num)
# # 1/0
# except ValueError as e:
# print('出错啦',e)
# except Exception as e:
# print('')
#try except语句
#需要检测异常的代码放在try代码块
#需要处理的代码放在except代码块
#不报错不执行except内的代码,except处理的错误名称应该和实际报错一致,否则无效
#如果报错try中报错之后的代码不执行
#不影响try外面的代码
#except ErrorName as 变量名:变量名中存储的就是错误的具体提示
#except支持多分支处理的方式,从上到下先找到能处理的error类型,就执行该except中的内容
#万能异常 except Exception as e,e表示错误提示,应该放在所有except之后
#对于你已经预料到的错误 应该使用指定的异常进行特殊处理
#万能异常是用来处理预料不到的异常类型的
# try:
# num = int(input('请输入序号 : '))
# except Exception as e:
# print('异常啦')
# else: #如果try中的代码不会发生异常,就走这个else中的内容
# print('没毛病') # try:
# num = int(input('请输入序号 : '))
# except Exception as e:
# print('异常啦')
# else: #如果try中的代码不会发生异常,就走这个else中的内容
# print('没毛病')
# finally:
# print('不管异常不异常我都走这个') def func():
f = open('f','w')
try:
for i in range(10):
f.write(i)
except Exception:
print(123)
return
finally: #在一个函数中 操作一个文件 需要关闭,在finally中关闭
print('before close')
f.close()
print('after close') func() #异常处理:不要在大段代码外面加 ********* def main():
func()
func() try:
main()
except Exception:
pass












day21 模块 异常处理的更多相关文章
- day21 03 异常处理
day21 03 异常处理 1.什么是异常 异常:程序运行时发生错误的信号 错误:语法错误(一般是不能处理的异常) 逻辑错误(可处理的异常) 特点:程序一旦发生错误,就从错误的位置停下来,不再继续执行 ...
- json等序列化模块 异常处理
今日学习内容如下: 1.序列化模块 什么叫序列化——将原本的字典.列表等内容转换成一个字符串的过程就叫做序列化. 比如,我们在python代码中计算的一个数据需要给另外一段程序使用,那我们怎么给? 现 ...
- python学习之正则表达式,StringIO模块,异常处理,搭建测试环境
python正则表达式 引入一个强大的匹配功能来匹配字符串 import re 正则表达式的表示类型raw string类型(原生字符串类型) r'sa\\/sad/asd'用r转为raw strin ...
- python笔记7 logging模块 hashlib模块 异常处理 datetime模块 shutil模块 xml模块(了解)
logging模块 日志就是记录一些信息,方便查询或者辅助开发 记录文件,显示屏幕 低配日志, 只能写入文件或者屏幕输出 屏幕输出 import logging logging.debug('调试模式 ...
- drf框架的解析模块-异常处理模块-响应模块-序列化模块
解析模块 为什么要配置解析模块 (1).drf给我们通过了多种解析数据包方式的解析类. (2).我们可以通过配置来控制前台提交的那些格式的数据台解析,那些数据不解析. (3).全局配置就是针对一个视图 ...
- django-rest-framework-源码解析002-序列化/请求模块/响应模块/异常处理模块/渲染模块/十大接口
简介 当我们使用django-rest-framework框架时, 项目必定是前后端分离的, 那么前后端进行数据交互时, 常见的数据类型就是xml和json(现在主流的是json), 这里就需要我们d ...
- day21.模块和包
博客整理来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/Eva-J/articles/7292109.html 模块 1.什么是模块 常见的场景:一个模块就是一个包含了python定义和声明的文件 ...
- Python day21模块介绍4(logging模块,configparser模块)
1.日志等级从上往下依次降低 logging.basicConfig(#日志报错打印的基础配置 level=logging.DEBUG, filename="logger.log" ...
- day21 模块
目录 模块 import 与 from...import 循环导入问题 解决方案一 解决方案二 Python文件的两种用途 从普通的面条型代码,到函数型代码,其实是在做什么? 封装代码,一个函数差不多 ...
随机推荐
- ModelSerializer序列化(Apiview)
url部分: url(r'^book/$',views.book.as_view()),url(r'^books/(\d+)/$', views.bookdetail.as_view(),name=' ...
- GDOI2018 滑稽子图 [斯特林数,树形DP]
传送门并没有 思路 见到那么小的\(k\)次方,又一次想到斯特林数. \[ ans=\sum_{T} f(T)^k = \sum_{i=0}^k i!S(k,i)\sum_{T} {f(T)\choo ...
- iOS 10 申请隐私权限的一些常用选项
Privacy - Photo Library Usage Description 访问相册 Privacy - Camera Usag ...
- 修改MongoDB密码
修改MongoDB密码 禁用管理员(root)密码 1.找到配置文件mongod.conf,并进入 vim /etc/mongod.conf 2.禁用管理员(root)密码 找到: security: ...
- Java的小实验——各种测试以及说明
日期:2018.10.07 星期五 博客期:014 一.Java中的位运算 代码如下: package Morts107; public class Test107 { public static v ...
- idea导入java项目
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37106742/article/details/70154244 ( 主要 )https://blog.csdn.net/u012099869/ar ...
- gitlab报错502及处理
报错截图: 解决: 1.端口问题 如上面写的815端口,那配置文件的8080端口都改成815端口 之后重新载入配置文件,并开启 gitlab-ctl reconfigure gitlab-ctl st ...
- 调试WebApi的一些方法
1.Get方法时,直接用浏览器访问 2.Postman 3.用HttpClient调用 privatevoid GetData() { using (HttpClient client = new H ...
- python 垃圾回收
# 垃圾回收 # 小整数对象池 # a = 100# python对小整数的定义是[-5,257],这些证书对象是提前创建好的,不会被垃圾回收,再一个python的程序中,所有位于这个范围内的正式使用 ...
- GoogleTest入门
Googletest入门 来源:https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/googletest/docs/primer.md P.S. gmoc ...
