scala.XML处理
XML
scala提供了对xml字面量的内建支持,我们可以很容易的在程序代码中生成xml片段,
scala类库也包含了对xml常用处理的支持
有时候scala会错误识别出xml字面量 如x < y 没问题,x <y 错误,解决方法就是在<后加一个
空格
scala> val doc= <html><head><title>hello world!</title></head><body></body></html> //有空格
doc: scala.xml.Elem = <html><head><title>hello world!</title></head><body></body></html>
scala> val doc=<html><head><title>hello world!</title></head><body></body></html> //没有空格
|
|
You typed two blank lines. Starting a new command.
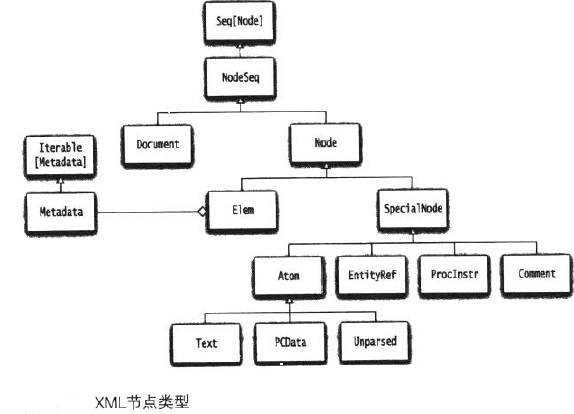
xml节点
node类是所有xml节点类的祖先,它有两个最重要的子类Text和Elem。
Elem类描述的是xml元素
scala> val elm= <a href="http://salca-lang.org"> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
elm: scala.xml.Elem = <a href="http://salca-lang.org"> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
label属性产出标签名称(这里是“a”),child对应的是后代的序列,本例中是两个text一个elem节点
如下:
scala> for(i<-elm.child)println(i)
the
<em>scala</em>
language
节点序列类型是NodeSeq,它是Seq[Node]的子类,加入了对类XPATH 操作的支持,你可以对xml节点序列
使用Seq操作。
单个节点相当于长度为1的序列
注释<!--.........-->,实体引用<&.....;>处理指令<?....?> 也分别有节点类与之对应
如果通过编程方式构建节点序列,可以使用NodeBuffer,它是ArrayBuffer[Node]的子类
scala> val item=new NodeBuffer()
item: scala.xml.NodeBuffer = ArrayBuffer()
scala> item+=<li>apple</li> //无空格报错
<console>:17: error: value +=< is not a member of scala.xml.NodeBuffer
item+=<li>apple</li>
scala> item+= <li>apple</li>
res11: item.type = ArrayBuffer(<li>apple</li>)
scala> item+= <li>banana</li>
res12: item.type = ArrayBuffer(<li>apple</li>, <li>banana</li>)
scala> item+= <li>pear</li>
res13: item.type = ArrayBuffer(<li>apple</li>, <li>banana</li>, <li>pear</li>)
scala> item+= <li>orange</li>
res15: item.type = ArrayBuffer(<li>apple</li>, <li>banana</li>, <li>pear</li>, <li>orange</li>)
scala> item
res16: scala.xml.NodeBuffer = ArrayBuffer(<li>apple</li>, <li>banana</li>, <li>pear</li>, <li>orange</li>)
scala> val nodes:NodeSeq=item
nodes: scala.xml.NodeSeq = NodeSeq(<li>apple</li>, <li>banana</li>, <li>pear</li>, <li>orange</li>)
NodeBuffer是一个Seq[Node],可以被隐式转换为NodeSeq,一旦完成,最好别再修改它,因为XML节点
序列应该是不可变的
元素属性
要处理某个元素的属性和值,可以使用 Atrributes属性,它将产生一个matedata的对象,
几乎等同于从一个属性键到属性值的映射,你可以用()操作符访问给定键的值;
产生的结果是一个节点序列,而不是一个字符串,因为XML属性可以包含实体引用
scala> elm
res22: scala.xml.Elem = <a href="http://salca-lang.org"> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
scala> elm.attribute("href")
res23: Option[Seq[scala.xml.Node]] = Some(http://salca-lang.org)
scala> elm.attributes("href")
res24: Seq[scala.xml.Node] = http://salca-lang.org
如果确定属性中不存在未被解析的实体,可以使用text方法将节点列表转化为字符串
scala> elm.attributes("href").text
res48: String = http://salca-lang.org
scala> elm.attributes("gg")
res52: Seq[scala.xml.Node] = null
scala> elm.attributes.get("name")
res53: Option[Seq[scala.xml.Node]] = None
scala> for(it<-elm.attributes) println(it.key+":"+it.value)
href:http://salca-lang.org
内嵌表达式
你可以在xml字面量里面中包含scala代码,动态计算出元素内容;
代码块产生的是一个节点序列,节点序列会被直接添加到XML。所有其他值都会被放到
一个Atom[T]中,这是一个针对类型T的容器,通过这种方式,你可以在xml中放任何值
;你也可以通过Atom节点的data属性取回这些值。
scala> item
res65: scala.xml.NodeBuffer = ArrayBuffer(<li>apple</li>, <li>banana</li>, <li>pear</li>, <li>orange</li>)
scala> val tmp= <fruit>{for(i<-item) yield i}</fruit>
tmp: scala.xml.Elem = <fruit><li>apple</li><li>banana</li><li>pear</li><li>orange</li></fruit>
scala> arr
res69: Array[String] = Array(banana, apple, orange, pear)
//xml可以包含scala代码,scala代码中也可以包含xml字面量
//fruit元素中包含了scala代码<fruit>{.........}</fruit>;字面量 <li>{i}</li>
//包含了另一个scala代码块{i}
scala> val tmp= <fruit>{for(i<-arr) yield <li>{i}</li>}</fruit>
tmp: scala.xml.Elem = <fruit><li>banana</li><li>apple</li><li>orange</li><li>pear</li></fruit>
scala> val tmp= <fruit>{for(i<-arr) yield <li>i</li>}</fruit>
tmp: scala.xml.Elem = <fruit><li>i</li><li>i</li><li>i</li><li>i</li></fruit>
scala> val tmp= <fruit>{arr}</fruit>
tmp: scala.xml.Elem = <fruit>banana apple orange pear</fruit>
属性中使用表达式
scala> url
res80: String = www.baidu.com
//内嵌的代码块也可以产出一个节点序列,如果代码块返回null或者none,
//该属性就不会被设置
scala> val bb= <a href={url}> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
bb: scala.xml.Elem = <a href="www.baidu.com"> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
scala> val bb= <a href={url}>{for(i<- 0 to 2) yield <num>{i}</num>}</a>
bb: scala.xml.Elem = <a href="www.baidu.com"><num>0</num><num>1</num><num>2</num></a>
特殊节点类型 ??未研究
类xpath表达式
NodeSeq类提供了类似xpath中 / 和 //的操作符方法,在scala中用\ 和 \\代替(//在scala中是注释)
\操作符定位某个节点或节点序列的直接后代
scala> tmp
res90: scala.xml.Elem = <fruit><li>banana</li><li>apple</li><li>orange</li><li>pear</li></fruit>
scala> tmp \ "li"
res91: scala.xml.NodeSeq = NodeSeq(<li>banana</li>, <li>apple</li>, <li>orange</li>, <li>pear</li>)
scala> for (i<- tmp \"li") println(i)
<li>banana</li>
<li>apple</li>
<li>orange</li>
<li>pear</li>
通配符可以匹配任何元素
\\ 可以定位任何深度的后代
scala> val tmp2= <fruit nm="shuiguo"><li>banana</li><li><li>green apple</li><li>red apple</li></li><li>orange</li><li>pear</li></fruit>
tmp2: scala.xml.Elem = <fruit nm="shuiguo"><li>banana</li><li><li>green apple</li><li>red apple</li></li><li>orange</li><li>pear</li></fruit>
scala> tmp2 \ "li"
res108: scala.xml.NodeSeq = NodeSeq(<li>banana</li>, <li><li>green apple</li><li>red apple</li></li>, <li>orange</li>, <li>pear</li>)
scala> for(i<-tmp2 \"li")println(i)
<li>banana</li>
<li><li>green apple</li><li>red apple</li></li>
<li>orange</li>
<li>pear</li>
scala> tmp2 \\ "li"
res109: scala.xml.NodeSeq = NodeSeq(<li>banana</li>, <li><li>green apple</li><li>red apple</li></li>, <li>green apple</li>, <li>red apple</li>, <li>orange</li>, <li>pear</li>)
scala> for(i<-tmp2 \\"li")println(i)
<li>banana</li>
<li><li>green apple</li><li>red apple</li></li>
<li>green apple</li>
<li>red apple</li>
<li>orange</li>
<li>pear</li>
以@开头的可以定位属性
scala> val tmp1= <fruit nm="shuiguo"><li>banana</li><li>apple</li><li>orange</li><li>pear</li></fruit>
tmp1: scala.xml.Elem = <fruit nm="shuiguo"><li>banana</li><li>apple</li><li>orange</li><li>pear</li></fruit>
scala> tmp1 \ "@nm"
res105: scala.xml.NodeSeq = shuiguo
scala> tmp1 \\ "@nm"
res110: scala.xml.NodeSeq = NodeSeq(shuiguo)
scala> (tmp2 \ "li").text
res120: String = bananagreen applered appleorangepear
模式匹配
可以用表达式匹配单个后代
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{_}</li> =>println(node.text);case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> tmp
res38: scala.xml.Elem = <fruit><li>banana</li><li>apple</li><li>orange</li><li>pear</li></fruit>
scala> xmlmatch(tmp)
not match
scala> items
res40: scala.xml.NodeBuffer = ArrayBuffer(<li>apple</li>, <li>banana</li>, <li>orange</li>)
scala> xmlmatch(items)
<console>:21: error: type mismatch;
found : scala.xml.NodeBuffer
required: scala.xml.Node
xmlmatch(items)
^
scala> xmlmatch(items(0))
apple
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{_}</li> => println(node);case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(items(0))
<li>apple</li>
如果li元素有多个后代
scala> aa
res49: scala.xml.Elem = <li><a>green apple</a><b>red apple</b></li>
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{_}</li> => println(node) ;case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(aa)
not match
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{_*}</li> => println(node) ;case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(aa)
<li><a>green apple</a><b>red apple</b></li>
在xml中,{ }表示代码模式,而不是被求值的代码
除了通配符,还可以使用变量名。
scala> items
res64: scala.xml.NodeBuffer = ArrayBuffer(<li>apple</li>, <li>banana</li>, <li>orange</li>)
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{child}</li> => println(child) ;case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(items(0))
apple
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{child}</li> => println(node) ;case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(items(0))
<li>apple</li>
要匹配一个文本:
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{Text(child)}</li> => println(child) ;case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(items(0))
apple
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{Text(child)}</li> => println(node) ;case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(items(0))
<li>apple</li>
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{Text(node)}</li> => println(node) ;case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(items(0))
apple
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match {case <li>{Text(_)}</li> => println(node) ;case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(items(0))
<li>apple</li>
把节点绑定到变量
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match { case <li>{sub @ _*}</li> =>println(sub);case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> aa
res75: scala.xml.Elem = <li><a>green apple</a><b>red apple</b></li>
scala> xmlmatch(aa)
ArrayBuffer(<a>green apple</a>, <b>red apple</b>)
scala> def xmlmatch(node:Node){node match { case <li>{sub @ _*}</li> =>for(i<-sub) println(i);case _=>println("not match")}}
xmlmatch: (node: scala.xml.Node)Unit
scala> xmlmatch(aa)
<a>green apple</a>
<b>red apple</b>
在case语句中,只能用一个节点
xml模式不能有属性;要匹配到属性,需要守卫
修改元素和属性
scala中,xml节点和序列是不可变的,如果想编辑一个节点,则必须创建一个copy,给出需要做的修改,然后copy未被修改的部分。
新旧两个列表aa,bb后代是共享的
拷贝Elem节点,使用copy方法,它有5个带名参数:label,attributes,child,还有用于命名空间的prifix和scope
scala> aa
res83: scala.xml.Elem = <li><a>green apple</a><b>red apple</b></li>
scala> val bb=aa.copy(label="app")
bb: scala.xml.Elem = <app><a>green apple</a><b>red apple</b></app>
添加一个后代
scala> val cc=aa.copy(child=aa.child ++ <c>yellow apple</c>)
cc: scala.xml.Elem = <li><a>green apple</a><b>red apple</b><c>yellow apple</c></li>
添加或修改一个属性,可用%操作符
scala> elm
res94: scala.xml.Elem = <a href="http://salca-lang.org"> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
//Attribute(null,"href","baidu.com",Null) 第一个参数是命名空间,最后一个是额外的元数据列表
scala> val elm100=elm % Attribute(null,"href","baidu.com",Null) //修改
elm100: scala.xml.Elem = <a href="baidu.com"> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
scala> val elm100=elm % Attribute(null,"href1","baidu.com",Null)//添加
elm100: scala.xml.Elem = <a href1="baidu.com" href="http://salca-lang.org"> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
//修改和添加可以串联一块操作
scala> val elm100=elm % Attribute(null,"href1","baidu.com",Attribute(null,"href","sohu.com",Null))
elm100: scala.xml.Elem = <a href="sohu.com" href1="baidu.com"> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
scala> val elm100=elm % Attribute(null,"href1","baidu.com",Attribute(null,"href","sohu.com",Attribute(null,"href2","sohu.com",Null)))
elm100: scala.xml.Elem = <a href2="sohu.com" href="sohu.com" href1="baidu.com"> the <em>scala</em> language</a>
XML变换
未验证成功
加载和保存
import scala.xml._
scala> val xml=XML.loadFile("/root/tmpdata/xml.txt")
xml: scala.xml.Elem =
<breakfast_menu>
<food><name>Belgian Waffles</name>
............................
scala> println(xml)
<breakfast_menu>
<food><name>Belgian Waffles</name>
<price>$5.95</price>
<description>Two of our famous Belgian Waffles with plenty of real maple syrup</description>
<calories>650</calories>
</food>
<food>
<name>Strawberry Belgian Waffles</name>
<price>$7.95</price>
<description>Light Belgian waffles covered with strawberries and whipped cream</description>
<calories>900</calories>
</food>
<food>
<name>Berry-Berry Belgian Waffles</name>
<price>$8.95</price>
<description>Light Belgian waffles covered with an assortment of fresh berries and whipped cream</description>
<calories>900</calories>
</food>
<food>
<name>French Toast</name>
<price>$4.50</price>
<description>Thick slices made from our homemade sourdough bread</description>
<calories>600</calories>
</food>
<food>
<name>Homestyle Breakfast</name>
<price>$6.95</price>
<description>Two eggs, bacon or sausage, toast, and our ever-popular hash browns</description>
<calories>950</calories>
</food>
</breakfast_menu>
scala> xml \\ "name"
res13: scala.xml.NodeSeq = NodeSeq(<name>Belgian Waffles</name>, <name>Strawberry Belgian Waffles</name>, <name>Berry-Berry Belgian Waffles</name>, <name>French Toast</name>, <name>Homestyle Breakfast</name>)
scala> for(x<- xml \\ "name") println(x.text)
Belgian Waffles
Strawberry Belgian Waffles
Berry-Berry Belgian Waffles
French Toast
Homestyle Breakfast
scala> (xml \ "food").size
res18: Int = 5
scala> for(i<-xml.child if i.child.size>0) println ((i \ "name").text->(i \ "price").text)
(Belgian Waffles,$5.95)
(Strawberry Belgian Waffles,$7.95)
(Berry-Berry Belgian Waffles,$8.95)
(French Toast,$4.50)
(Homestyle Breakfast,$6.95)
scala> val yy=for(i<-xml.child if i.child.size>0) yield ((i \ "name").text->(i \ "price").text)
yy: Seq[(String, String)] = List((Belgian Waffles,$5.95), (Strawberry Belgian Waffles,$7.95), (Berry-Berry Belgian Waffles,$8.95), (French Toast,$4.50), (Homestyle Breakfast,$6.95))
scala> yy.toMap
res72: scala.collection.immutable.Map[String,String] = Map(Strawberry Belgian Waffles -> $7.95, Belgian Waffles -> $5.95, French Toast -> $4.50, Berry-Berry Belgian Waffles -> $8.95, Homestyle Breakfast -> $6.95)
scala.XML处理的更多相关文章
- SCALA XML pattern attrbute(属性)
from: Working with Scala's XML Support 虽然这个guy炒鸡罗嗦,但是还是讲到我要的那句话: Because Scala doesn't support XML ...
- 【scala】 scala xml 处理(⑨)
1.scala 处理xml 2. 获取属性 3.修改节点 4.遍历 5.模式匹配 6.命名空间 7.文件加载 import scala.xml._ /** * @author xwolf * @sin ...
- Scala XML
XML 直接在代码中使用 XML 字面量 val doc: Elem = <html><head><title>Test</title></hea ...
- spark报错 java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: scala/xml/MetaData
代码: 报错信息: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: scala/xml/MetaData 原因:确失jar包 <dependency> <groupI ...
- 初试Scala解析XML
使用Scala解析XML,充分体现了函数式编程的特点,简洁和明了.用Java去解析不是不行,只不过代码不够清晰明了. 首先先把XML文件读入到内存里: val someXml = XML.loadFi ...
- Scala的XML操作
8. XML 8.1. 生成 Scala原生支持xml,就如同Java支持String一样,这就让生成xml和xhtml非常easy优雅: val name = "james ...
- scala 加载与保存xml文档
package scala_enhance.xml import scala.xml.XML import scala.io.Source import jdk.internal.org.xml.sa ...
- Scala入门到精通——第二十七节 Scala操纵XML
本节主要内容 XML 字面量 XML内容提取 XML对象序列化及反序列化 XML文件读取与保存 XML模式匹配 1. XML 字面量 XML是一种很重要的半结构化数据表示方式,眼下大量的应用依赖于XM ...
- Scala学习十六——XML处理
一.本章要点 XML字面量<like>this</like>的类型为NodeSeq 可以在XML字面量中内嵌Scala代码 Node的child属性产出后代节点 Node的at ...
随机推荐
- HDU 2072 单词数 详细解答
题目 单词数 Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submis ...
- HDU 4681 string 求最长公共子序列的简单DP+暴力枚举
先预处理,用求最长公共子序列的DP顺着处理一遍,再逆着处理一遍. 再预处理串a和b中包含串c的子序列,当然,为了使这子序列尽可能短,会以c 串的第一个字符开始 ,c 串的最后一个字符结束 将这些起始位 ...
- stenciljs 学习十三 @stencil/router 组件使用说明
@stencil/router 组件包含的子组件 stencil-router stencil-route-switch stencil-route stencil-route-link stenci ...
- hadoop之 map个数控制
hadooop提供了一个设置map个数的参数mapred.map.tasks,我们可以通过这个参数来控制map的个数.但是通过这种方式设置map的个数,并不是每次都有效的.原因是mapred.map. ...
- Elasticsearch 知识点
Elasticsearch 知识点 table th:first-of-type { width: 200px; } table th:nth-of-type(2) { } 功能 curl命令 运行 ...
- Python中的类(classes)
Python的类机制使用尽可能少的新语法和语义将类引入语言.python的类提供了面向对象程序设计语言所有的 标准特性:类继承机制允许有多个基类,一个派生类可以覆盖基类中的任何方法,一个方法可以使用相 ...
- WIN7\win10下使用批处理配置JAVA环境变量
我找了很多环境变量批处理的教程,都不太满意,因此综合修改了下,拼凑出了这么一个版本. 下面这个是我主要参考的博客,大部分的代码都是来自这里: http://blog.csdn.net/lpy36543 ...
- python 如何将md5转为16字节
python的hashlib库中提供的hexdigest返回长度32的字符串. md5sum是128bit,也就是16字节,如何将python生成字符串的转为16字节呢? 请看下面代码 import ...
- 查看 linux cpu 、内存、服务器型号和序列号、磁盘、raid 的信息
yum -y install dmidecode 查看cpu的型号: 查看cpu的颗数:dmidecode -t processor |grep "Version"dmidecod ...
- IplImage的数据结构以及遍历方法
一般我们需要对图像直接进行操作的时候,需要知道图像存储的数据结构,这要也就知道了它的遍历方式 在opencv2.4.4版本下,IplImage的数据结构如下(貌似在别的版本下差别也不会太大) 其中比较 ...
