CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 8
▶ 线程束表决函数(Warp Vote Functions)
● 用于同一线程束内各线程通信和计算规约指标。
// device_functions.h,cc < 9.0
__DEVICE_FUNCTIONS_STATIC_DECL__ int __all(int a)
{
int result;
asm __volatile__("{ \n\t"
".reg .pred \t%%p1; \n\t"
".reg .pred \t%%p2; \n\t"
"setp.ne.u32 \t%%p1, %1, 0; \n\t"
"vote.all.pred \t%%p2, %%p1; \n\t"
"selp.s32 \t%0, 1, 0, %%p2; \n\t"
"}" : "=r"(result) : "r"(a));
return result;
} __DEVICE_FUNCTIONS_STATIC_DECL__ int __any(int a)
{
int result;
asm __volatile__("{ \n\t"
".reg .pred \t%%p1; \n\t"
".reg .pred \t%%p2; \n\t"
"setp.ne.u32 \t%%p1, %1, 0; \n\t"
"vote.any.pred \t%%p2, %%p1; \n\t"
"selp.s32 \t%0, 1, 0, %%p2; \n\t"
"}" : "=r"(result) : "r"(a));
return result;
} __DEVICE_FUNCTIONS_STATIC_DECL__
#if defined(__CUDACC_RTC__) || defined(__CUDACC_INTEGRATED__)
unsigned int __ballot(int a)
#else
int __ballot(int a)
#endif
{
int result;
asm __volatile__("{ \n\t"
".reg .pred \t%%p1; \n\t"
"setp.ne.u32 \t%%p1, %1, 0; \n\t"
"vote.ballot.b32 \t%0, %%p1; \n\t"
"}" : "=r"(result) : "r"(a));
return result;
} // device_functions.h,cc≥9.0,改进并废弃了原来的三个,增加两个
int __all_sync(unsigned int mask, int predicate);
int __any_sync(unsigned int mask, int predicate);
int __uni_sync(unsigned int mask, int predicate);
unsigned int __ballot_sync(unsigned int mask, int predicate);
unsigned int __activemask(); //sm_30_intrinsics.hpp,cc ≥ 9.0
__SM_30_INTRINSICS_DECL__ int __all_sync(unsigned mask, int pred)
{
extern __device__ __device_builtin__ int __nvvm_vote_all_sync(unsigned int mask, int pred);
return __nvvm_vote_all_sync(mask, pred);
} __SM_30_INTRINSICS_DECL__ int __any_sync(unsigned mask, int pred)
{
extern __device__ __device_builtin__ int __nvvm_vote_any_sync(unsigned int mask, int pred);
return __nvvm_vote_any_sync(mask, pred);
} __SM_30_INTRINSICS_DECL__ int __uni_sync(unsigned mask, int pred)
{
extern __device__ __device_builtin__ int __nvvm_vote_uni_sync(unsigned int mask, int pred);
return __nvvm_vote_uni_sync(mask, pred);
} __SM_30_INTRINSICS_DECL__ unsigned __ballot_sync(unsigned mask, int pred)
{
extern __device__ __device_builtin__ unsigned int __nvvm_vote_ballot_sync(unsigned int mask, int pred);
return __nvvm_vote_ballot_sync(mask, pred);
} __SM_30_INTRINSICS_DECL__unsigned __activemask()
{
unsigned ret;
int predicate = ;
asm volatile ("{ .reg .pred p; setp.ne.u32 p, %1, 0; vote.ballot.b32 %0, p; } " : "=r"(ret) : "r"(predicate));
return ret;
}
● 在设备代码的一个线程中调用 _all(predicate),__any(mask, predicate),__ballot(mask, predicate) 时,该线程所在的线程束中所有线程(标号 0 ~ 31,称为 lane ID)求变量 predicate 的值,并按照一定的规律返回一个整形值。
● _all() 当且仅当所有线程的 predicate 非零时返回 1,否则返回 0。
● _any() 当且仅当至少有一个线程的 predicate 非零时返回 1,否则返回 0。
● _ballot() 返回一个无符号整数,代表了该线程束内变量 predicate 的非零值分布情况。线程 predicate 为零的该函数返回值该位为 0,线程 predicate 非零的该函数返回值该位为 1 。
● CUDA9.0 对以上函数进行了改进,变成了 _all_sync(),_any_sync(),_ballot_sync() 。添加了参数 unsigned int mask(注意也是 32 bit),用来指定线程束中的特定位参与 predicate 的计算(而不像 CUDA8.0 中那样全员参与),不参加计算的线程结果按 0 计。函数强制同步了所有被 mask 指定的线程,就算被指定的线程不活跃,也要包含该函数的调用,否则结果未定义。
● _uni_sync() 当且仅当被 mask 指定线程的 predicate 全部非零或全部为零时返回 1,否则返回 0。
● __activemask() 返回一个无符号整数,代表了该线程束内活动线程的分布情况。该线程活动则返回值该位为 1,否则为 0 。该函数没有 mask参数,必须全员参加。
● CUDA8.0 上的测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include "device_functions.h" __global__ void vote_all(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = a[tid];
b[tid] = __all(temp > );
} __global__ void vote_any(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = a[tid];
b[tid] = __any(temp > );
} __global__ void vote_ballot(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = a[tid];
b[tid] = __ballot(temp > && temp < );
} int main()
{
int *h_a, *h_b, *d_a, *d_b;
int n = , m = ;
int nsize = n * sizeof(int); h_a = (int *)malloc(nsize);
h_b = (int *)malloc(nsize);
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
h_a[i] = i;
memset(h_b, , nsize);
cudaMalloc(&d_a, nsize);
cudaMalloc(&d_b, nsize);
cudaMemcpy(d_a, h_a, nsize, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemset(d_b, , nsize); vote_all << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
printf("vote_all():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%d ", h_b[i]);
}
printf("\n"); vote_any << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
printf("vote_any():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%d ", h_b[i]);
}
printf("\n"); vote_ballot << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
printf("vote_ballot():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%u ", h_b[i]);// 用无符号整数输出
}
printf("\n"); getchar();
return ;
}
● 输出结果。其中 209510410 = 0000 0000 0001 1111 1111 1000 0000 00002,即第二个线程束(标号 32 ~ 63)的第 11 位(含0,标号43)起连续 10 位为 1,其余为 0 。
vote_all(): vote_any(): vote_ballot():
● CUDA9.0 上的测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include "device_functions.h" __global__ void vote_all(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = a[tid];
b[tid] = __all_sync(0xffffffff, temp > );// 注意添加了参数 mask
} __global__ void vote_any(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = a[tid];
b[tid] = __any_sync(0xffffffff, temp > );
} __global__ void vote_ballot(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = a[tid];
b[tid] = __ballot_sync(0xffffffff, temp > && temp < );
} __global__ void vote_union(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = a[tid];
b[tid] = __uni_sync(0xffffffff, temp > && temp < );
} __global__ void vote_active(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n || tid % )// 毙掉了所有偶数号线程
return;
int temp = a[tid];
b[] = __activemask();
} int main()
{
int *h_a, *h_b, *d_a, *d_b;
int n = , m = ;
int nsize = n * sizeof(int); h_a = (int *)malloc(nsize);
h_b = (int *)malloc(nsize);
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
h_a[i] = i;
memset(h_b, , nsize);
cudaMalloc(&d_a, nsize);
cudaMalloc(&d_b, nsize);
cudaMemcpy(d_a, h_a, nsize, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemset(d_b, , nsize); vote_all << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
printf("vote_all():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%d ", h_b[i]);
}
printf("\n"); vote_any << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
printf("vote_any():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%d ", h_b[i]);
}
printf("\n"); vote_union << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
printf("vote_union():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%d ", h_b[i]);
}
printf("\n"); vote_ballot << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
printf("vote_ballot():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%u ", h_b[i]);// 用无符号整数输出
}
printf("\n"); vote_active << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
printf("vote_active():\n%u ", h_b[]);// 用无符号整数输出
printf("\n"); getchar();
return ;
}
● 输出结果。其中 2095104 同 CUDA8.0 中的情况;143165576510 = 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 0101 01012,即所有偶数号线程都不活跃(提前 return 掉了)。
vote_all(): vote_any(): vote_union(): vote_ballot(): vote_active():
▶ 线程束匹配函数(Warp Match Functions),要求 cc ≥ 7.0 的设备。
● 与线程束表决函数类似,对线程束内指定的线程进行计算,返回满足条件的线程编号构成的无符号整数。T 可以是 int,unsigned int,long,unsigned long,long long,unsigned long long,float,double 。
unsigned int __match_any_sync(unsigned mask, T value);
unsigned int __match_all_sync(unsigned mask, T value, int *pred);
● __match_any_sync() 比较 mask 指定的所有线程中的变量 value,返回具有相同值的线程编号构成的无符号整数。
● __match_all_sync() 比较 mask 指定的所有线程中的变量 value,当所有被指定的线程具有相同值的时候返回 mask 且 *pred 被置为 true,否则返回 0 且置 *pred 为 false。
▶ 线程束统筹函数(Warp Shuffle Functions)
● 定义在 sm_30_intrinsics.hpp 中,与 Warp Vote Functions 两者构成了整个头文件。T 可以是 int,unsigned int,long,unsigned long,long long,unsigned long long,float,double,__half,__half2 。
// sm_30_intrinsics.h,cuda < 9.0
T __shfl(int var, int srcLane, int width);
T __shfl_up(int var, int srcLane, int width);
T __shfl_down(int var, int srcLane, int width);
T __shfl_xor(int var, int srcLane, int width); // sm_30_intrinsics.h,cuda ≥ 9.0
T __shfl_sync(unsigned mask, T var, int srcLane, int width = warpSize);
T __shfl_up_sync(unsigned mask, T var, unsigned int delta, int width = warpSize);
T __shfl_down_sync(unsigned mask, T var, unsigned int delta, int width = warpSize);
T __shfl_xor_sync(unsigned mask, T var, int laneMask, int width = warpSize);
● 此处说明的图,以及后面的规约计算代码来源:http://blog.csdn.net/bruce_0712/article/details/64926471
● __shfl_sync() 被 mask 指定的线程返回标号为 srcLane 的线程中的变量 var 的值,其余线程返回0 。如下图例子中,调用 shfl_sync(mask, x, 2, 16); ,则标号为 2 的线程向标号为 0 ~ 15 的线程广播了其变量 x 的值;标号为 18 的线程向标号为 16 ~ 31 的线程广播了其变量 x 的值。

● __shfl_up_sync() 被 mask 指定的线程返回向前偏移为 delta 的线程中的变量 var 的值,其余线程返回0 。如下图例子中,调用 shfl_up_sync(mask, x, 2, 16); ,则标号为 2 ~15 的线程分别获得标号为 0 ~ 13 的线程中变量 x 的值;标号为 18 ~31 的线程分别获得标号为 16 ~ 29 的线程中变量 x 的值。

● __shfl_down_sync() 被 mask 指定的线程返回向后偏移为 delta 的线程中的变量 var 的值,其余线程返回0 。如下图例子中,调用 shfl_down_sync(mask, x, 2, 16); ,则标号为 0 ~13 的线程分别获得标号为 2 ~ 15 的线程中变量 x 的值;标号为 16 ~29 的线程分别获得标号为 18 ~ 31 的线程中变量 x 的值。
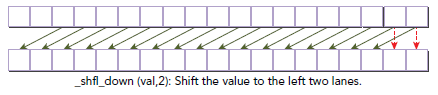
● __shfl_xor_sync() 被 mask 指定的线程返回向后偏移为 delta 的线程中的变量 var 的值,其余线程返回0 。如下图例子中,调用 shfl_down_sync(mask, x, 1, 16); ,则标号为 0 ~13 的线程分别获得标号为 2 ~ 15 的线程中变量 x 的值;标号为 16 ~29 的线程分别获得标号为 18 ~ 31 的线程中变量 x 的值。
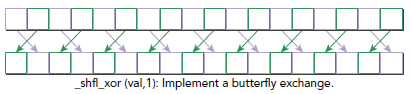
● __shfl_xor_sync() 的参数 laneMask 说明:
■ 当 n = 2k 时,表现为将连续的 n 个元素看做一个整体,与其后方连续的 n 个元素的整体做交换,但是两个整体的内部不做交换。例如 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] 做 n = 2 的变换得到 [2, 3, 0, 1, 6, 7, 4, 5] 。
■ 当 n ≠ 2k 时,先将 n 拆分成若干 2k 之和,分别做这些层次上的变换。这种操作是良定义的(二元轮换满足交换律和结合律)。例如 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] 做 n = 3 的变换时,先做 n = 2 的变换,得到 [2, 3, 0, 1, 6, 7, 4, 5],再做 n = 1 的变换,得到 [3, 2, 1, 0, 7, 6, 5, 4] 。
● 测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include "device_functions.h" __global__ void shfl(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = -a[tid];// 广播的值为线程原值的相反数
b[tid] = a[tid]; // 先将值赋成原值 b[tid] = __shfl_sync(0x00000000, temp, , );
// mask 作用不明,无论是调整为 0xffffffff 还是 0x55555555 还是 0x00000000 结果都没有变化
// temp 要广播的变量
// 0 广播源线程编号。若参数超出32,则自动取模处理(如输入为 99,则自动变成 99 % 32 = 3)
// 16 广播宽度。默认值 32(线程束内广播),可以调整为不超过 32 的 2 的整数次幂,超出 32 操作未定义(实测结果被当成 32 处理)
} __global__ void shfl_up(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = -a[tid];
b[tid] = a[tid]; b[tid] = __shfl_up_sync(0x00000000, temp, , );
// 1 偏移量,而不是源线程编号
} __global__ void shfl_down(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = -a[tid];// 广播的值为线程原值的相反数
b[tid] = a[tid]; // 先将值赋成原值 b[tid] = __shfl_down_sync(0x00000000, temp, , );
// 1 偏移量,而不是源线程编号
} __global__ void shfl_xor(int *a, int *b, int n)
{
int tid = threadIdx.x;
if (tid > n)
return;
int temp = -a[tid];// 广播的值为线程原值的相反数
b[tid] = a[tid]; // 先将值赋成原值 b[tid] = __shfl_xor_sync(0x00000000, temp, , );
// 1 移动块大小,比较复杂,见前面的函数说明
} int main()
{
int *h_a, *h_b, *d_a, *d_b;
int n = , m = ;
int nsize = n * sizeof(int); h_a = (int *)malloc(nsize);
h_b = (int *)malloc(nsize);
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
h_a[i] = i;
memset(h_b, , nsize);
cudaMalloc(&d_a, nsize);
cudaMalloc(&d_b, nsize);
cudaMemcpy(d_a, h_a, nsize, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemset(d_b, , nsize); printf("Inital Array:");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%4d ", h_a[i]);
}
printf("\n"); shfl << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
printf("shfl():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%4d ", h_b[i]);
}
printf("\n"); shfl_up << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
printf("shfl_up():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%4d ", h_b[i]);
}
printf("\n"); shfl_down << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
printf("shfl_down():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%4d ", h_b[i]);
}
printf("\n"); shfl_xor << <, n >> >(d_a, d_b, n);
cudaMemcpy(h_b, d_b, nsize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
printf("shfl_xor():");
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i)
{
if (!(i % m))
printf("\n");
printf("%4d ", h_b[i]);
}
printf("\n"); getchar();
return ;
}
● 输出结果
Inital Array: shfl():
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
shfl_up():
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
shfl_down():
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
shfl_xor():
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
● 用 __shfl() 函数进行规约计算的代码(只给出核函数代码):
__global__ void reduce1(int *dst, int *src, const int n)
{
int tidGlobal = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x * blockIdx.x;
int tidLocal = threadIdx.x; int sum = src[tidGlobal]; __syncthreads(); for (int offset = WARP_SIZE / ; offset > ; offset /= )
sum += __shfl_down(sum, offset);// 每次把后一半的结果挪到前一半并做加法 if (tidLocal == )
dst[blockIdx.x] = sum;
}
▶ B.16. Warp matrix functions [PREVIEW FEATURE](略过),要求 cc ≥ 7.0 的设备。
▶ B.17. Profiler Counter Function(略过)
//device_functions.h
#define __prof_trigger(X) asm __volatile__ ("pmevent \t" #X ";")
● 原文:Each multiprocessor has a set of sixteen hardware counters that an application can increment with a single instruction by calling the __prof_trigger() function. Increments by one per warp the per-multiprocessor hardware counter of index counter. Counters 8 to 15 are reserved and should not be used by applications. The value of counters 0, 1, ..., 7 can be obtained via nvprof by nvprof --events prof_trigger_0x where x is 0, 1, ..., 7. All counters are reset before each kernel launch (note that when collecting counters, kernel launches are synchronous as mentioned in Concurrent Execution between Host and Device).
CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 8的更多相关文章
- CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 5
附录 A,CUDA计算设备 附录 B,C语言扩展 ▶ 函数的标识符 ● __device__,__global__ 和 __host__ ● 宏 __CUDA_ARCH__ 可用于区分代码的运行位置. ...
- CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 4
▶ 图形互操作性,OpenGL 与 Direct3D 相关.(没学过,等待填坑) ▶ 版本号与计算能力 ● 计算能力(Compute Capability)表征了硬件规格,CUDA版本号表征了驱动接口 ...
- CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 2
▶ 纹理内存使用 ● 纹理内存使用有两套 API,称为 Object API 和 Reference API .纹理对象(texture object)在运行时被 Object API 创建,同时指定 ...
- CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 10【坑】
▶ 动态并行. ● 动态并行直接从 GPU 上创建工作,可以减少主机和设备间数据传输,在设备线程中调整配置.有数据依赖的并行工作可以在内核运行时生成,并利用 GPU 的硬件调度和负载均衡.动态并行要求 ...
- CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 13
▶ 纹理内存访问补充(见纹理内存博客 http://www.cnblogs.com/cuancuancuanhao/p/7809713.html) ▶ 计算能力 ● 不同计算能力的硬件对计算特性的支持 ...
- CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 9
▶ 协作组,要求 cuda ≥ 9.0,一个简单的例子见 http://www.cnblogs.com/cuancuancuanhao/p/7881093.html ● 灵活调节需要进行通讯的线程组合 ...
- CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 7
▶ 可缓存只读操作(Read-Only Data Cache Load Function),定义在 sm_32_intrinsics.hpp 中.从地址 adress 读取类型为 T 的函数返回,T ...
- CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 3
▶ 表面内存使用 ● 创建 cuda 数组时使用标志 cudaArraySurfaceLoadStore 来创建表面内存,可以用表面对象(surface object)或表面引用(surface re ...
- CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 1
1. 简介 2. 编程模型 ▶ SM version 指的是硬件构架和特性,CUDA version 指的是软件平台版本. 3. 编程接口.参考 http://chenrudan.github.io/ ...
随机推荐
- StyleCop 是什么,可以帮助团队带来什么价值?
StyleCop 本质上是一个 C# 源代码规则分析器,可以帮助团队成员强制执行一组代码样式和一致性规则. 本文将简述 StyleCop 以及它能为团队带来的价值. 本文内容 StyleCop 是什么 ...
- 2017年最新cocoapods安装教程(解决淘宝镜像源无效以及其他源下载慢问题)
首先,先来说一下一般的方法吧,就是把之前的淘宝源替换成一个可用的的源: 使用终端查看当前的源 gem sources -l gem sources -r https://rubygems.org/ # ...
- MySQL--REPLACE INTO更新自增列值引发的异常
##=====================================================================##测试环境:MySQL版本:MySQL 5.7.19复制 ...
- centos6 yum安装最新版mysql5.7
在看来mysql5.7诸多改进介绍后,决定也安装一个试用下:本文将使用rpm的方式来安装. 环境:OS: CentOS6.5 x86_64 最小化安装MEM: 1GCPU: 1 1. 本文连着上一篇安 ...
- python 典型文件结构
#/usr/bin/env/ python #(1) 起始行 "this is a test module" #(2) 模块文档(文档字符串) import sys import ...
- meta标签和JS实现页面刷新与重定向
下面列了五个例子来详细说明,这几个例子的主要功能是:在5秒后,自动跳转到同目录下的hello.html(根据自己需要自行修改)文件.1) html的实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 <head& ...
- electron热更新与windows下的安装包
帮朋友公司做了点东西,他说有很多bug,我一看,基本问题都是浏览器兼容引起的,而electron内带Chromium内核,正好一直想尝试下electron,所以研究了一波.这里只是简单的使用elect ...
- Spring IOC - 控制反转(依赖注入) - 入门案例 - 获取对象的方式 - 别名标签
1. IOC - 控制反转(依赖注入) 所谓的IOC称之为控制反转,简单来说就是将对象的创建的权利及对象的生命周期的管理过程交 由Spring框架来处理,从此在开发过程中不再需要关注对象的创建和生命周 ...
- gradle使用心得
gradle是语言式构建,和maven配置型还是差别挺大,琢磨了2天 1.在解析setting.gradle之后,开始解析build.gradle之前,这里如果要干些事情(更改build.gradle ...
- jpgraph中文使用手册之文本和字体控制教程
摘要:在之前的php jpgraph安装配置教程中已介绍过jpgraph字体的安装与配置方法,jpgraph类库中字体和文本的使用是非常重要的,jpgraph既可以控 制文本的旋转.对齐方式.字体大小 ...
