基于Spring源码分析AOP的实现机制
Spring一个重要的特性就是提供了AOP,使得我们可以在原有的基础上增加我们自己的系统业务逻辑。使得我们系统业务逻辑与应用业务逻辑相分离,耦合性降低,并且大大的提高了开发的效率。Spring的AOP利用的就是动态代理方式,在Spring的AOP中,有两种实现方式。第一种,就是利用JDK的Proxy,另外一种就是采用CGLIB来实现的。
基本概念:
Advice:
通知,制定在连接点做什么,在Sping 中,他主要描述Spring 围绕方法调用注入的额外的行为,具有增强的功能 ,只能应用于所有方法,主要是由aopalliance.jar中包含aop定义中的接口,按这个接口实现aop标准。
PointCut
切点,其决定一个 advice 应该应用于哪个连接点,也就是需要插入额外处理的地方的集合,例如,被某个advice 作为目标的一组方法。Spring pointcut 通常意味着标示方法,可以选择一组方法调用作为pointcut。
Advisor:
通知器,把Advice封闭起来,加入Pointcut(切入点),Spring就可以知道在什么方法上拦截,以及拦截后所要做的具体行为了。Advisor有两种实现NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor按方法名字匹配。RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor,按正则匹配。
AOP创建:
AOP的创建主要分为两种一种是JDK的Proxy还有一种是CGLIB的,整个创建AOP的时序图一样,只不过差异在于最终AOPProxy产生AOP的过程。
首先AOP的具体创建的时序图如下:
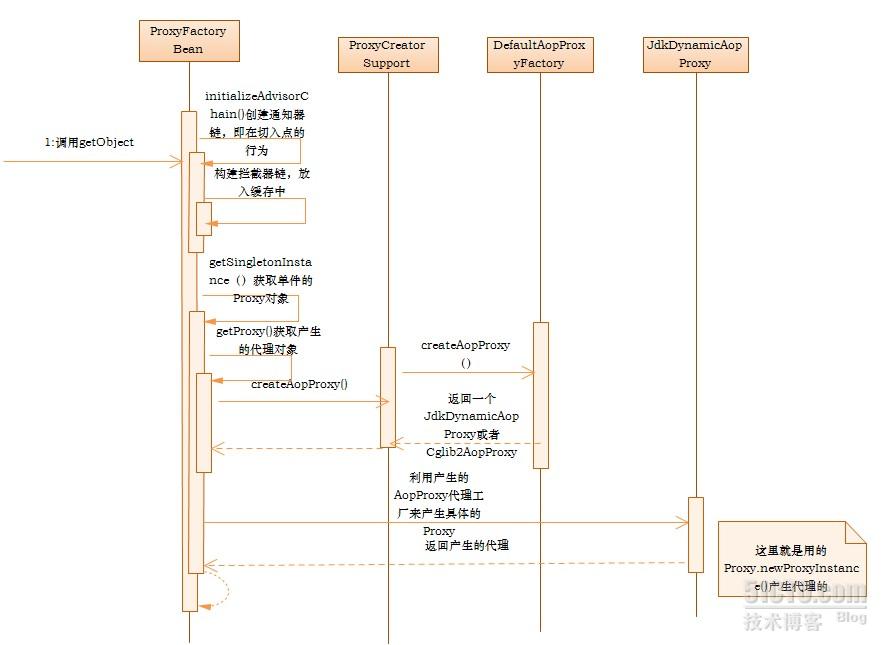
以该时序图来分析我们AOP的创建过程。当我们使用AOP需要对某一个对象进行切面系统业务的时候,Spring会为该对象生成一个代理。具体是使用ProxyFactoryBean来配置我们的代理对象和方面行为。而具体的代理实现是通过JDK的Proxy或者CGLIB来完成的。ProxyFactoryBean是FactoryBean,调用该getObject方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public Objectthrows BeansException //初始化通知器链,实际上就是注册拦截器 initializeAdvisorChain(); if (isSingleton()) //返回生成的一个单件Proxy return getSingletonInstance(); } else { .... //返回生成的Prototype的Proxy return newPrototypeInstance(); }} |
整个方法包含了拦截器的初始化,以及获取代理对象的代理的过程。
第一行主要就是初始化通知器链,注册被代理对象上的拦截器。
当判断是一个单例对象的时候,就会通过getSingletonInstance()来获取单件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
private synchronized Object{ if (this.singletonInstancenull){ this.targetSource if (this.autodetectInterfaces0 && { //获取要代理的类 Class ...设置该类的接口类型 setInterfaces(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(targetClass,this.proxyClassLoader)); } super.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); //这里才是真正的获取Proxy, this.singletonInstance } return this.singletonInstance;} |
在获取单件的时候,首先要做的就是要获取目标对象的接口,然后再次创建一个AopProxy来用于创建我们的AOP对象,这里createAopProxy的调用就是调用具体父类ProxyCreatorSupport来完成创建一个DefaultAopProxyFactory。当我们new一个ProxyFactoryBean的时候,它会调用父类的无参构造器,这里面就会默认的创建一个DefaultAopProxyFactory。这个就是我们默认的AOP代理工厂,最终是由它来决定我们到底使用JDK的Proxy还是CGLIB来创建代理的过程。在该类的成员属性中cglibAvailable初始化的时候会监测
ClassUtils.isPresent("net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer", DefaultAopProxyFactory.class.getClassLoader());是否当前路径有cglib2
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public AopProxythrows AopConfigException{if (config.isOptimize() Class //代理类为空的时候 if (targetClassnull) .... } // if (targetClass.isInterface()) return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } if (!cglibAvailable) } eturn } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } |
当我们的AopProxy产生后,接着就可以调用getProxy来返回产生的代理对象,这里以JdkDynamicAopProxy为例来分析其创建的过程。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public Object if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) ....} Class[]this.advised); findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces); return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader,this);} |
当我们的Spring创建了代理对象后,当调用目标对象上的方法时,将都会被代理到InvocationHandler类的invoke方法中执行。在这里JdkDynamicAopProxy类实现了InvocationHandler接 口。
AOP拦截器
当使用JDK和CGLIB会生成不同的AopProxy代理对象,从而构造了不同的回调方法来启动对拦截器链的调用,比如在JdkDynamicAopProxy中的invoke方法,以及Cglib2AopProxy中使用DynamicAdvisedInterceptor的intercept方法。它们都使用了不同的AopProxy代理对象,但最终对AOP拦截的处理都是基本一样:它们对拦截器链的调用都是在ReflectiveMethodInvocation中通过proceed方法实现的。在这个proceed方法里,会逐个运行拦截器的拦截方法。在运行拦截器的拦截方法之前,需要对代理方法完成一个匹配判断,通过这个匹配判断来决定拦截器是否满足切面增强的要求。
AOP拦截器的实现的时序图如下:

对目标的对象都会首先被代理至代理对象的invoke来调用,不管使用哪种创建代理对象的过程
下面是invoke的方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
public Objectthrows Throwable MethodInvocation Objectnull; boolean setProxyContextfalse; TargetSourcethis.advised.targetSource; Classnull; Objectnull; try { if (!this.equalsDefined return equals(args[0]); } if (!this.hashCodeDefined return hashCode(); } if (!this.advised.opaque method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) // return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, } Object if (this.advised.exposeProxy) oldProxy setProxyContexttrue; } //获取所要代理的对象 target if (targetnull) targetClass } // List<Object>this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, //是否定义拦截器,否则直接调用目标对象的方法 if (chain.isEmpty()) //直接调用目标对象的方法 retVal } else { //如果不为空,则就创建一个ReflectiveMethodInvocation对象来先调用拦截器后调用目标方法 invocationnew ReflectiveMethodInvocation (proxy, // retVal } if (retValnull && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) retVal } return retVal; } finally { if (targetnull && targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } |
对目标对象的方法直接调用是利用AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection,该方法内部直接调用method.invoke(target, args),利用jdk自身的反射机制实现的;对拦截器链的调用时由ReflectiveMethodInvocation的proceed方法来实现的。
在proceed方法中,依然会首先判断是否拦截器结束了,否则就从拦截器链获取一个个的拦截器来执行前置行为,最后调用完了才真正调用我们的目标方法。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
public Objectthrows Throwable//直接调用目标方法,可能是拦截器调用结束或者无拦截器//interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers这个其实就是目标方法上的拦截器链的大小if (this.currentInterceptorIndexthis.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size()1) return invokeJoinpoint();}//调用拦截器链上的对象,依次Objectthis.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher){ // InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) return dm.interceptor.invoke(this); }else { //调用拦截器链中的下一个拦截器 return proceed(); }}else { // // return ((MethodInterceptor)this); }} |
本文出自 “在云端的追梦” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://computerdragon.blog.51cto.com/6235984/1251718
基于Spring源码分析AOP的实现机制的更多相关文章
- spring源码分析(二)Aop
创建日期:2016.08.19 修改日期:2016.08.20-2016.08.21 交流QQ:992591601 参考资料:<spring源码深度解析>.<spring技术内幕&g ...
- Spring源码分析之AOP从解析到调用
正文: 在上一篇,我们对IOC核心部分流程已经分析完毕,相信小伙伴们有所收获,从这一篇开始,我们将会踏上新的旅程,即Spring的另一核心:AOP! 首先,为了让大家能更有效的理解AOP,先带大家过一 ...
- 【Spring源码分析】配置文件读取流程
前言 Spring配置文件读取流程本来是和http://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/p/6285358.html一文放在一起的,这两天在看Spring自定义标签的时候,感觉对Spri ...
- spring源码分析系列 (1) spring拓展接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.BeanFactoryPostProcessor.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor简述与demo示例 ...
- spring源码分析系列 (3) spring拓展接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例 二.InstantiationAwareBean ...
- spring源码分析系列 (2) spring拓展接口BeanPostProcessor
Spring更多分析--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.BeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例 二.BeanPostProcessor源码分析:注册时机和触发点 (源码基于 ...
- Spring源码分析之循环依赖及解决方案
Spring源码分析之循环依赖及解决方案 往期文章: Spring源码分析之预启动流程 Spring源码分析之BeanFactory体系结构 Spring源码分析之BeanFactoryPostPro ...
- spring源码分析之spring-core总结篇
1.spring-core概览 spring-core是spring框架的基石,它为spring框架提供了基础的支持. spring-core从源码上看,分为6个package,分别是asm,cgli ...
- Spring源码分析——BeanFactory体系之抽象类、类分析(二)
上一篇分析了BeanFactory体系的2个类,SimpleAliasRegistry和DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry——Spring源码分析——BeanFactory体系之 ...
- Spring源码分析——资源访问利器Resource之实现类分析
今天来分析Spring的资源接口Resource的各个实现类.关于它的接口和抽象类,参见上一篇博文——Spring源码分析——资源访问利器Resource之接口和抽象类分析 一.文件系统资源 File ...
随机推荐
- 全网最适合入门的面向对象编程教程:43 Python 常用复合数据类型-扩展内置数据类型
全网最适合入门的面向对象编程教程:43 Python 常用复合数据类型-扩展内置数据类型 摘要: 在 Python 中,内置数据类型(如列表.字典.集合等)非常强大,但在某些情况下,可能需要扩展这些数 ...
- Docker 优化NUXT镜像体积
FROM node:xxx-alpine # 环境变量赋值 ENV 参数名 参数值 RUN mkdir -p /app COPY ./app/package.json /app/package.jso ...
- 【YashanDB知识库】kettle从DM8的number类型同步到YashanDB的varchar类型,存入是科学计数法形式的数据
[标题]kettle从DM8的number类型同步到YashanDB的varchar类型,存入是科学计数法形式的数据 [问题分类]数据导入导出 [关键字]数据同步,number类型,科学计数法 [问题 ...
- Goby漏洞发布 | CVE-2024-4879 ServiceNowUI /login.do Jelly模板注入漏洞【已复现】
漏洞名称:ServiceNowUI /login.do Jelly模板注入漏洞(CVE-2024-4879) English Name:ServiceNowUI /login.do Input Val ...
- Bit, Byte, ASCII, Unicode, UTF, Base64
前言 做项目偶尔会接触到 stream 这个感念,不管是 memory stream 还是 file stream,它们又会提到 bytes. 还有像 Identity – 安全基础知识 中提到的 S ...
- 常回家看看之house_of_cat
house_of_cat 前言: house of cat 这个利用手法和前面提到的 house of kiwi ,和 house of emma 利用的手法是一个链子,当程序无法通过main函数返回 ...
- MyBatis——案例——查询-查询详情
查询-查询详情 (根据id获取商品全部信息(即商品对象)) 1.编写Mapper接口方法:Brand selectById(int id); 2.编写SQL ...
- oneforall配置环境,报错cannot import name 'sre_parse' from 're' 解决方法
高版本python中re模块没有了sre_parse模块, 可以修改python中的exrex.py 代码,直接导入sre_parse模块
- string的find()与npos
在 C++ 中,std::string::find() 是一个用于在字符串中查找子字符串或字符的成员函数.查找成功时返回匹配的索引位置,查找失败时返回 std::string::npos,表示未找到. ...
- C++第五节课 函数默认值 函数重载
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // C++的函数默认值和函数重载 // 函数参数的入栈规则从右往左开始入栈 // 函数重载机制(第一种静 ...
