day52 进程与守护进程
http://www.cnblogs.com/Eva-J/articles/8253549.html 博客参考.








多进程聊天
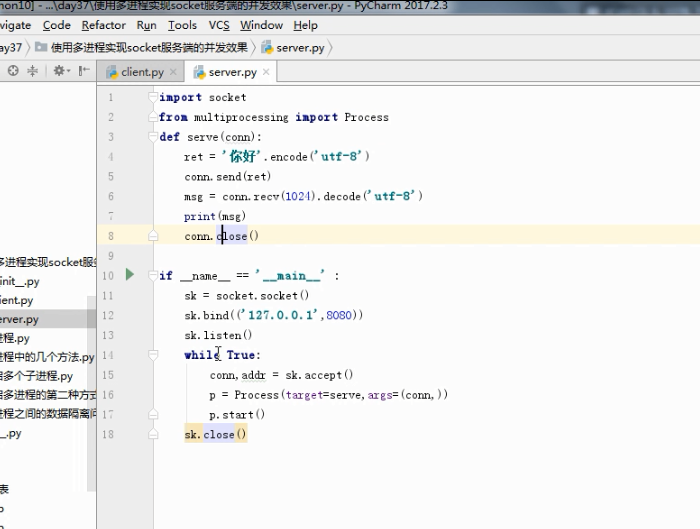
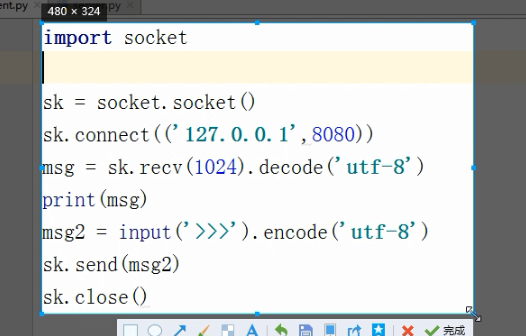
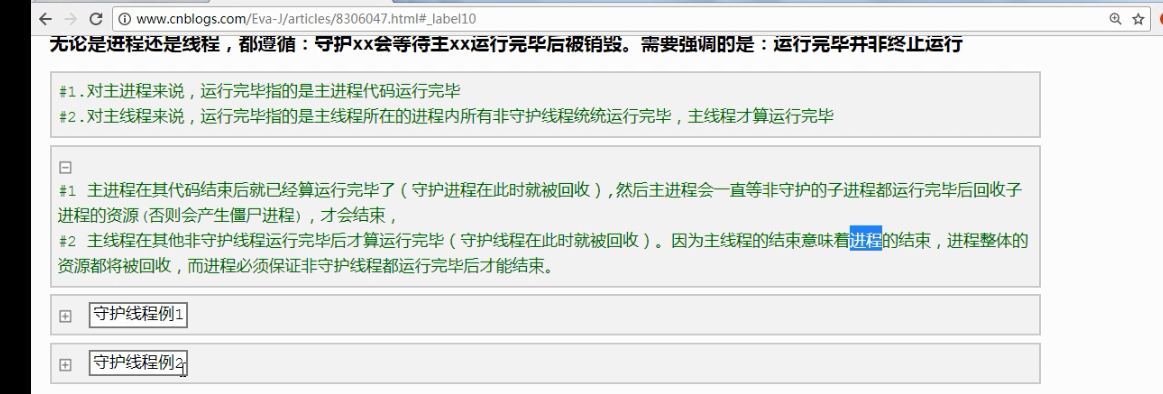
守护进程.
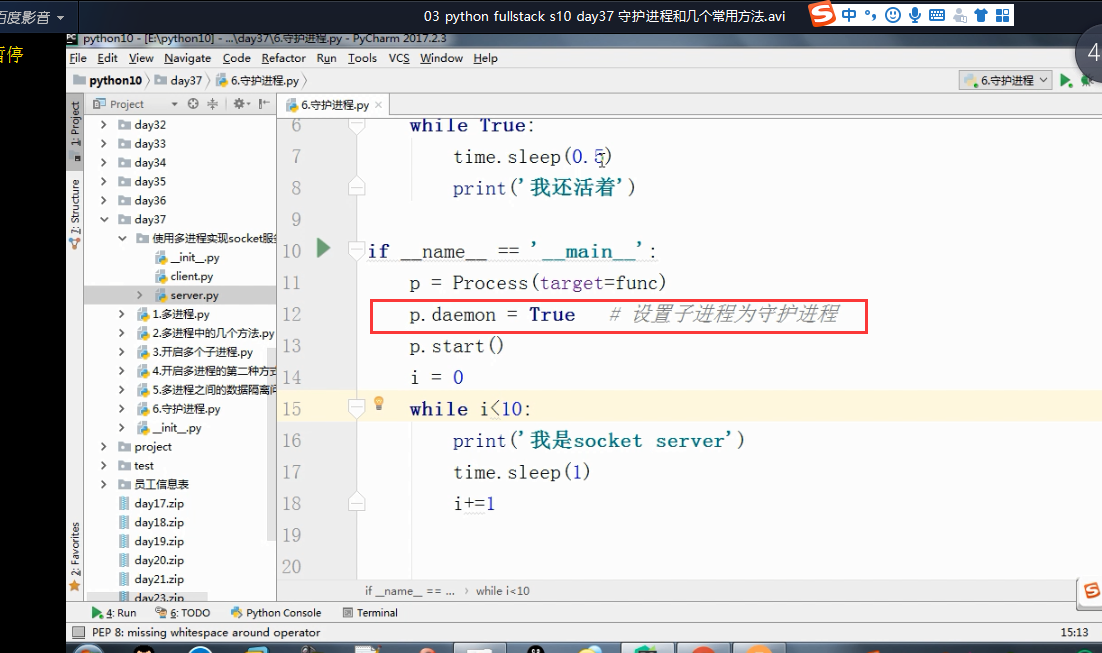
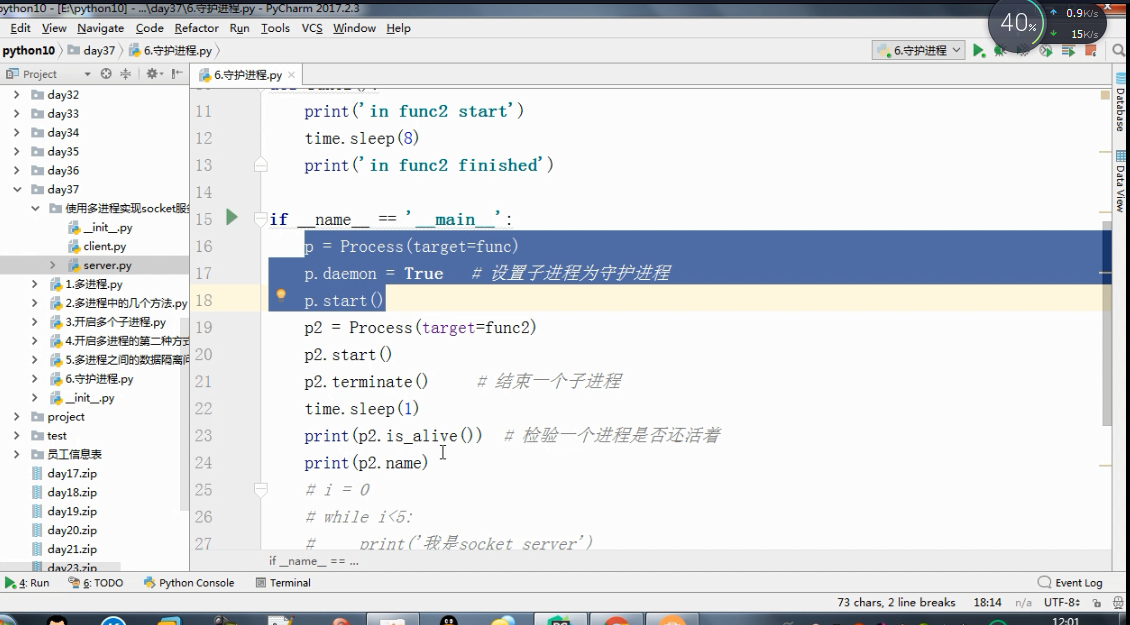
多进程
1、Unix/Linux:fork()调用实现多进程。
2、Windows没有fork(),multiprocessing模块就是跨平台版本的多进程模块。multiprocessing模块提供了一个Process类来代表一个进程对象。
#启动一个子进程并等待其结束:
from multiprocessing import Process
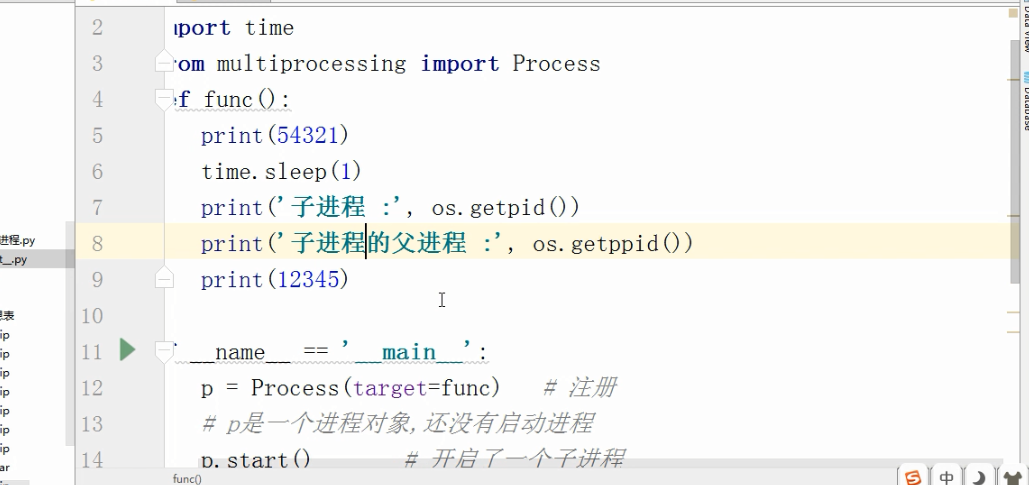
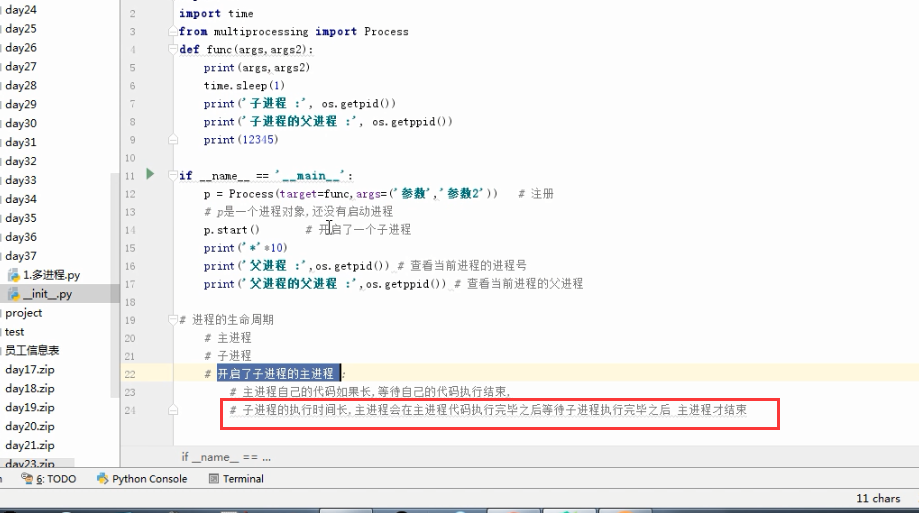
import os # 子进程要执行的代码
def run_proc(name):
print('Run child process %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid())) #主函数
if __name__=='__main__':
print('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid()) #创建子进程时,只需要传入一个执行函数和函数的参数,
#创建一个Process实例,用start()方法启动。
p = Process(target=run_proc, args=('test',))
print('Child process will start.')
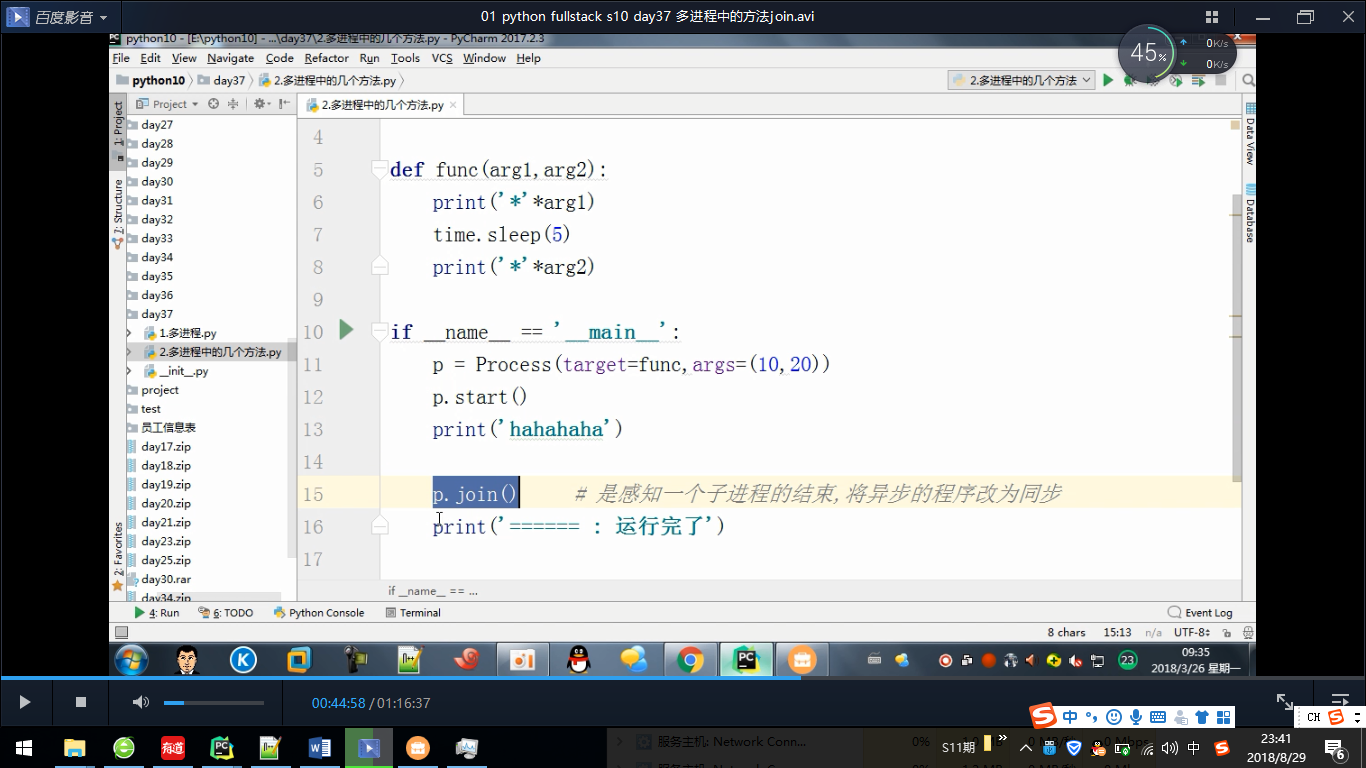
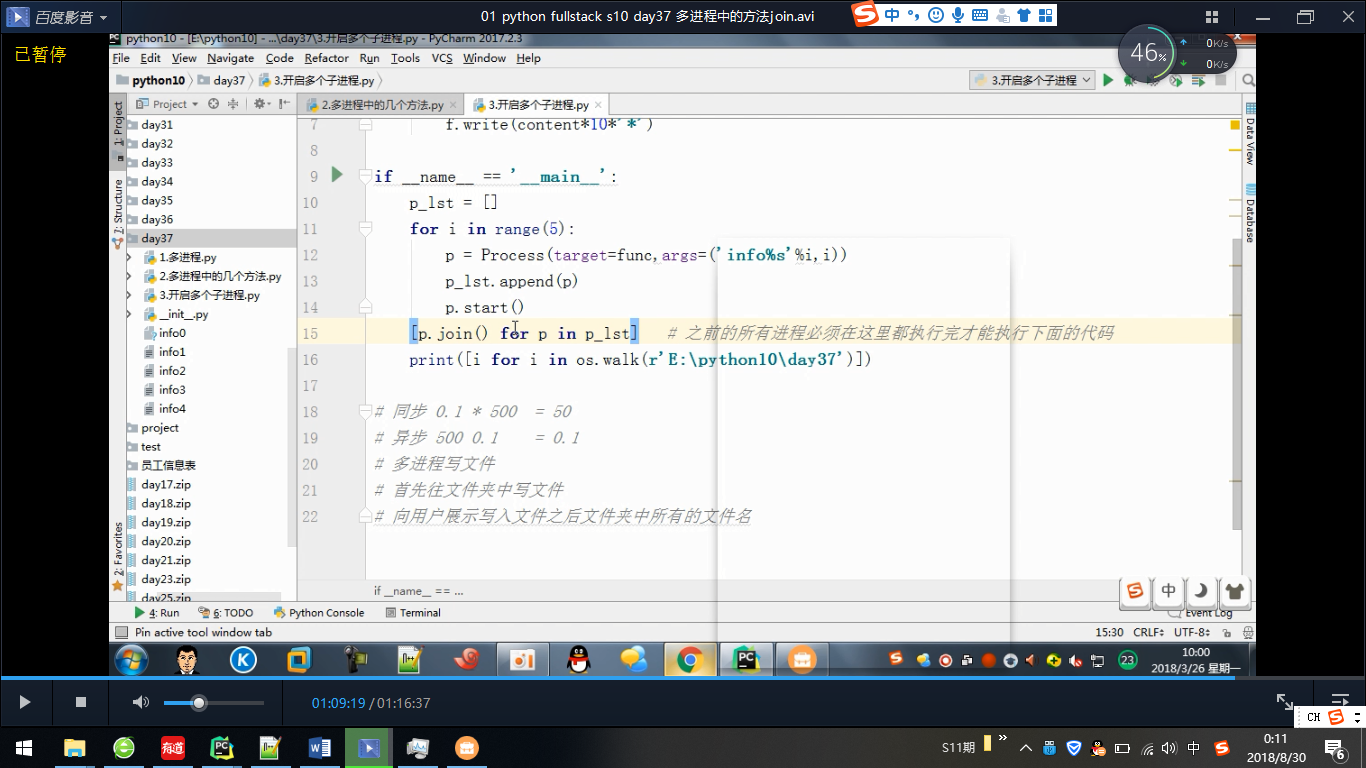
p.start() #join()可等待子进程结束后再继续往下运行,通常用于进程间的同步。
p.join()
print('Child process end.') 结果:
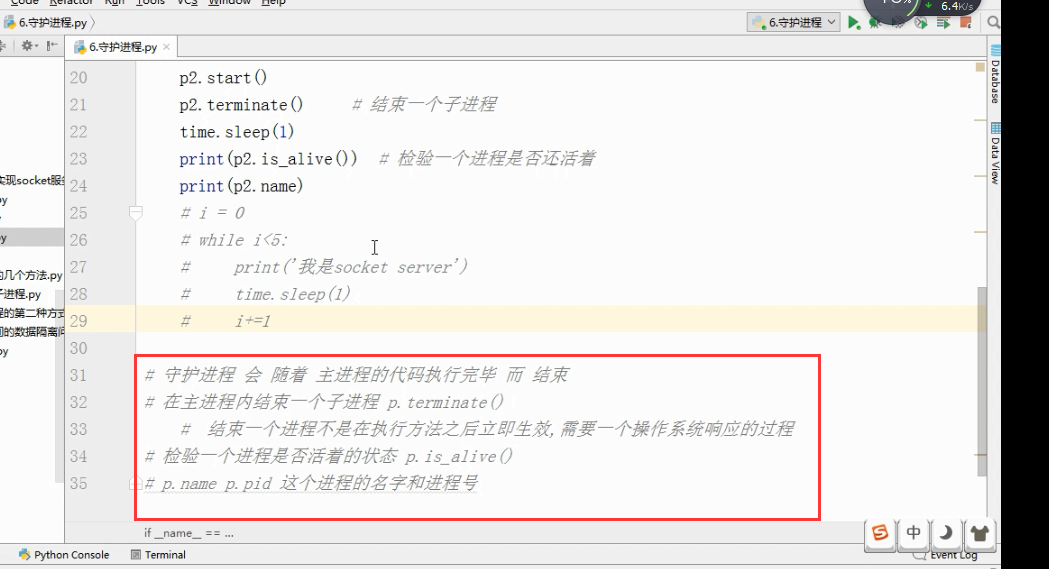
Parent process 928.
Process will start.
Run child process test (929)...
Process end.
进程间通信
1、Process之间肯定是需要通信的,Python的multiprocessing模块包装了底层的机制,提供了Queue、Pipes等多种方式来交换数据。
以Queue为例,在父进程中创建两个子进程,一个往Queue里写数据,一个从Queue里读数据:
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue
import os, time, random # 写数据进程执行的代码:
def write(q):
print('Process to write: %s' % os.getpid())
for value in ['A', 'B', 'C']:
print('Put %s to queue...' % value)
q.put(value)
time.sleep(random.random()) # 读数据进程执行的代码:
def read(q):
print('Process to read: %s' % os.getpid())
while True:
value = q.get(True)
print('Get %s from queue.' % value) if __name__=='__main__':
# 父进程创建Queue,并传给各个子进程:
q = Queue()
pw = Process(target=write, args=(q,))
pr = Process(target=read, args=(q,))
# 启动子进程pw,写入:
pw.start()
# 启动子进程pr,读取:
pr.start()
# 等待pw结束:
pw.join()
# pr进程里是死循环,无法等待其结束,只能强行终止:
pr.terminate() 结果:
Process to write: 50563
Put A to queue...
Process to read: 50564
Get A from queue.
Put B to queue...
Get B from queue.
Put C to queue...
Get C from queue.
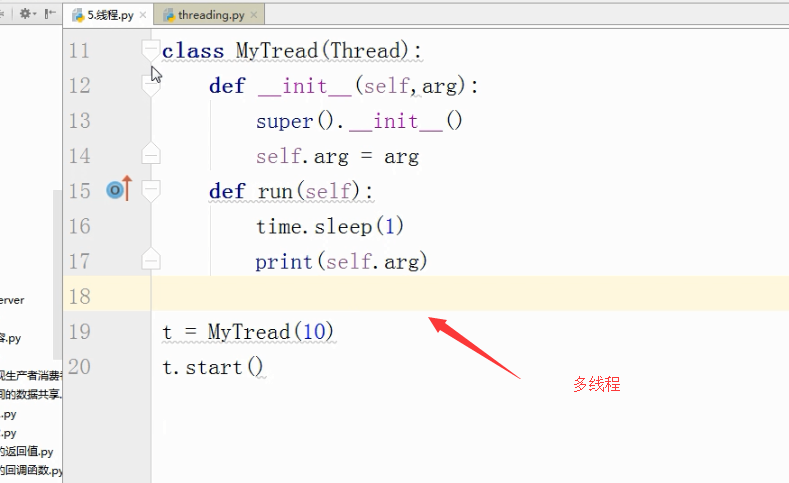
多线程
1、Python的标准库提供了两个模块:_thread(低级模块)和threading(高级模块,对_thread进行了封装)。绝大多数情况下,我们只需要使用threading这个高级模块。
2、启动一个线程就是把一个函数传入并创建Thread实例,然后调用start()开始执行:
import time, threading # 新线程执行的代码:
def loop():
print('thread %s is running...' % threading.current_thread().name)
n =
while n < :
n = n +
print('thread %s >>> %s' %(threading.current_thread().name, n))
time.sleep()
print('thread %s ended.' % threading.current_thread().name) print('thread %s is running...' % threading.current_thread().name)
t = threading.Thread(target=loop, name='LoopThread')
t.start()
t.join()
print('thread %s ended.' % threading.current_thread().name) 结果:
thread MainThread is running...
thread LoopThread is running...
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread ended.
thread MainThread ended.
由于任何进程默认就会启动一个线程(主线程),主线程又可以启动新的线程,current_thread()永远返回当前线程的实例。主线程实例的名字叫MainThread,子线程的名字在创建时指定。名字仅仅在打印时用来显示,完全没有其他意义,如果不起名字Python就自动给线程命名为Thread-1,Thread-2……
3、
多进程:同一个变量,各自有一份拷贝存在于每个进程中,互不影响。
多线程:所有变量都由所有线程共享。所以,任何一个变量都可以被任何一个线程修改,因此,线程之间共享数据最大的危险在于多个线程同时改一个变量,把内容给改乱了。
#来看看多个线程同时操作一个变量怎么把内容给改乱了
import time, threading # 假定这是你的银行存款:
balance = def change_it(n):
# 先存后取,结果应该为0:
global balance
balance = balance + n
balance = balance - n def run_thread(n):
for i in range():
change_it(n) t1 = threading.Thread(target=run_thread, args=(,))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=run_thread, args=(,))
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print(balance)



信号量:
Event事件
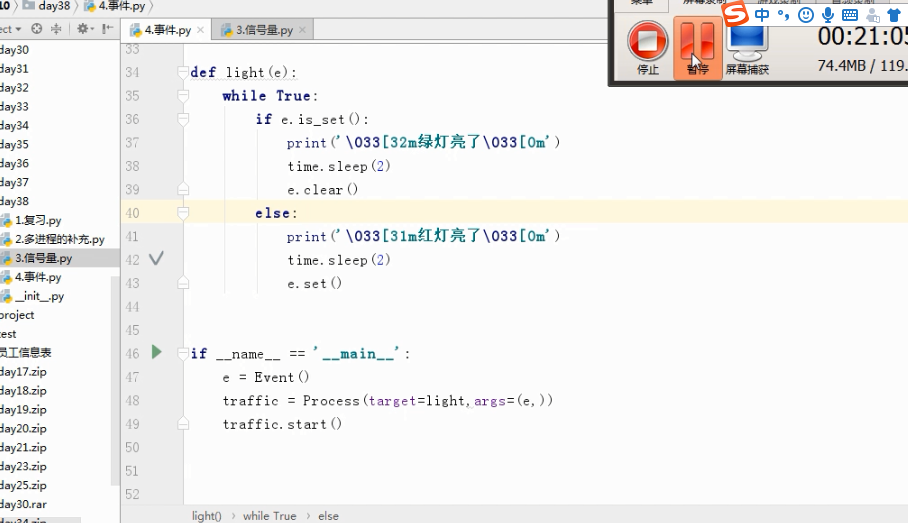

队列

线程:

守护线程:
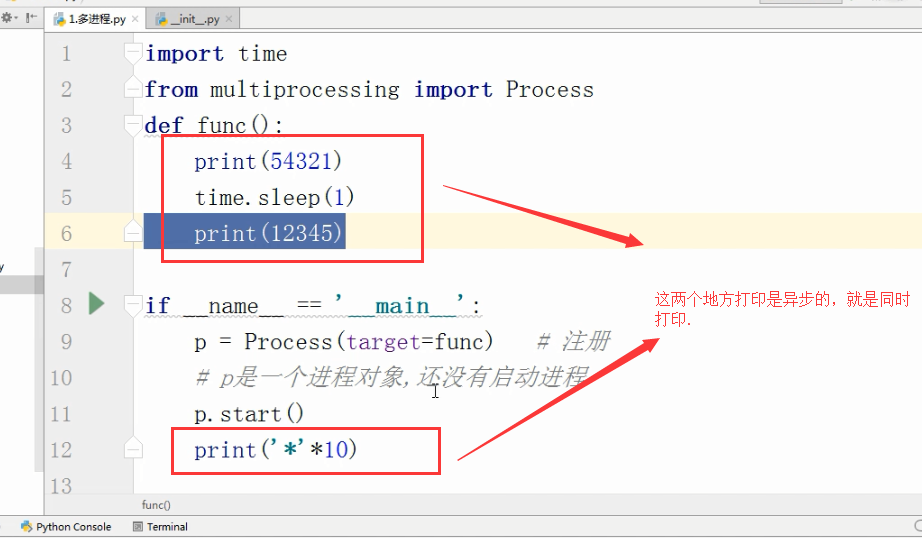
import time
from multiprocessing import Process
def func():
time.sleep()
print("func1") if __name__=="__main__":
Process(target=func).start()
print() 打印结果: func1 先打印999,打印完后等待两秒打印func1

案例2
import time
from threading import Thread
def func1():
while True:
print('*'*10)
time.sleep(1)
def func2():
print('in func2')
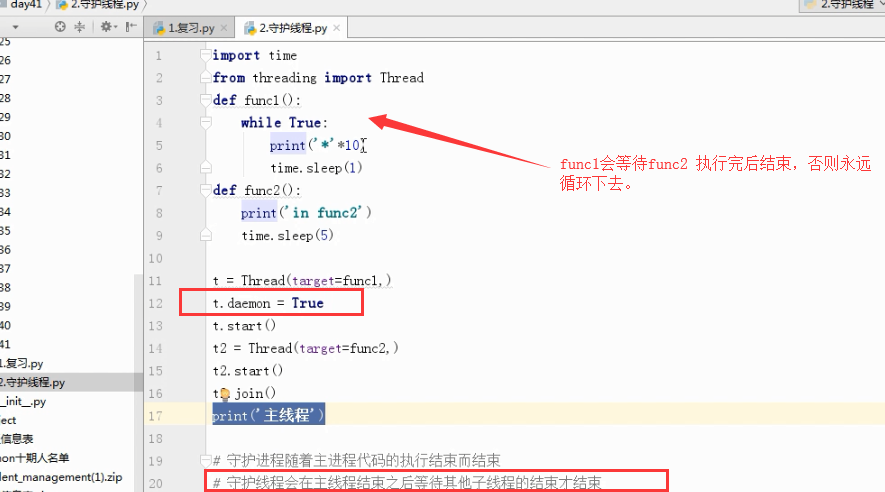
time.sleep(5) t = Thread(target=func1,)
t.daemon = True
t.start()
t2 = Thread(target=func2,)
t2.start()
t2.join() #join 语句的执行会等待最后打印“”主线程“”
print('主线程')
打印结果:
**********
in func2
**********
**********
**********
**********
主线程
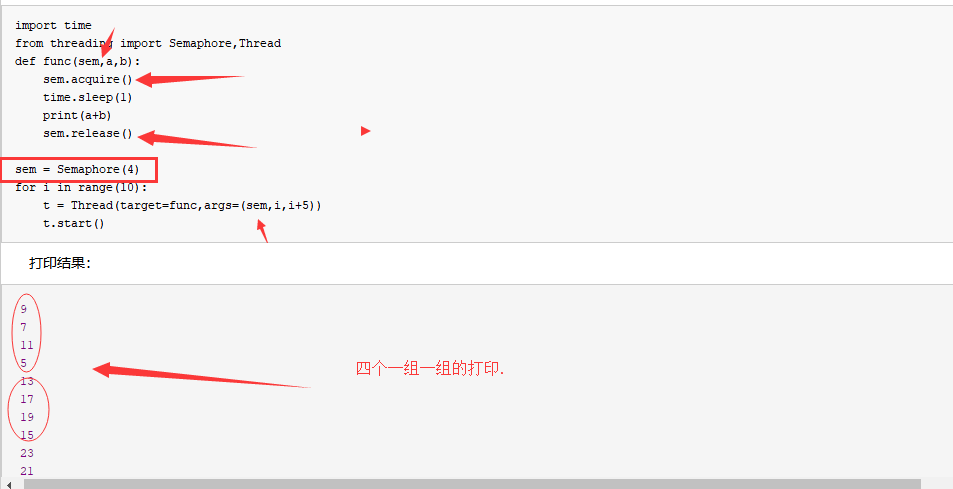
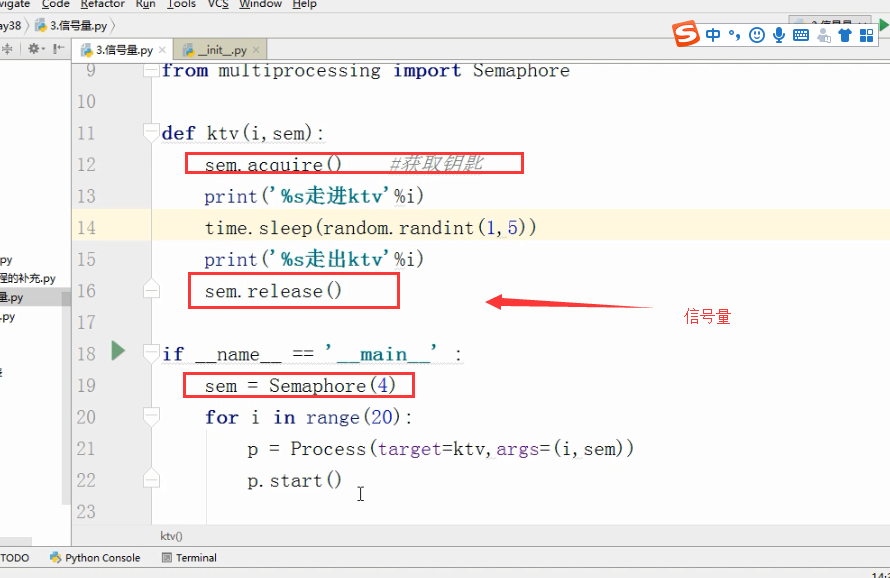
信号量 信号量
import time
from threading import Semaphore,Thread
def func(sem,a,b):
sem.acquire()
time.sleep(1)
print(a+b)
sem.release() sem = Semaphore(4)
for i in range(10):
t = Thread(target=func,args=(sem,i,i+5))
t.start()
打印结果:
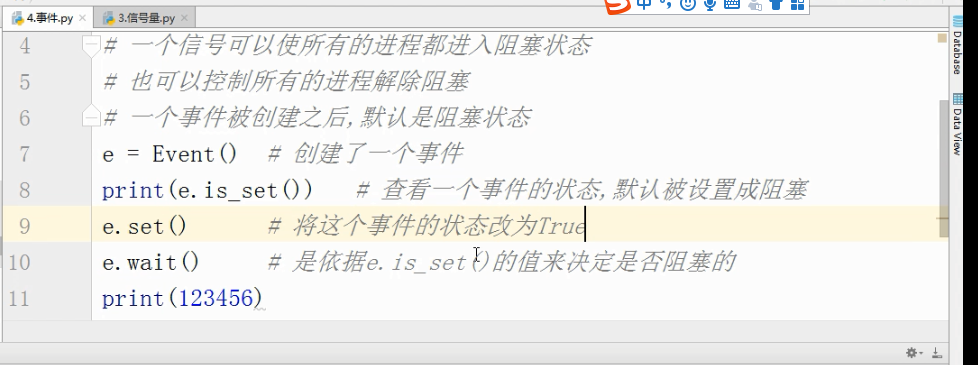
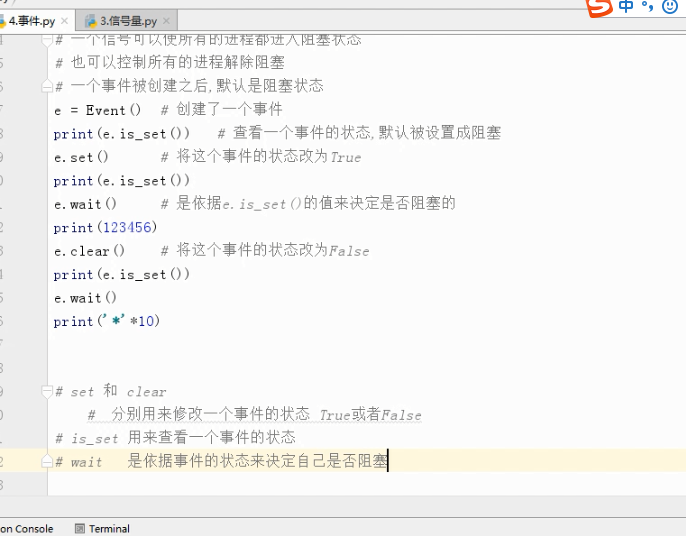
事件 :
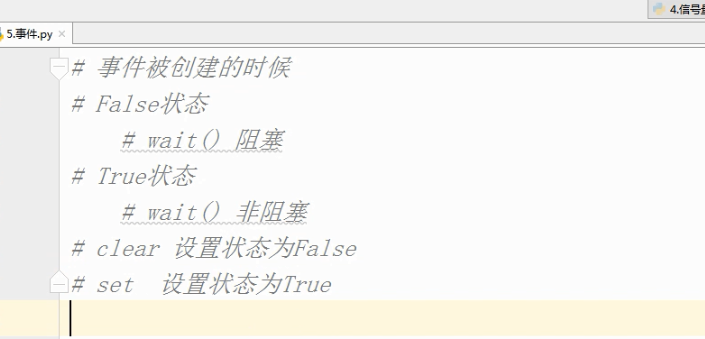
# 事件被创建的时候
# False状态
# wait() 阻塞
# True状态
# wait() 非阻塞
# clear 设置状态为False
# set 设置状态为True # 数据库 - 文件夹
# 文件夹里有好多excel表格
# .能够更方便的对数据进行增删改查
# .安全访问的机制 # 起两个线程
# 第一个线程 : 连接数据库
# 等待一个信号 告诉我我们之间的网络是通的
# 连接数据库
# 第二个线程 : 检测与数据库之间的网络是否连通
# time.sleep(,)
# 将事件的状态设置为True
import time
import random
from threading import Thread,Event
def connect_db(e):
count =
while count < :
e.wait(0.5) # 状态为False的时候,我只等待1s就结束
if e.is_set() == True:
print('连接数据库')
break
else:
count +=
print('第%s次连接失败'%count)
else:
raise TimeoutError('数据库连接超时') def check_web(e):
time.sleep(random.randint(,))
e.set() e = Event()
t1 = Thread(target=connect_db,args=(e,))
t2 = Thread(target=check_web,args=(e,))
t1.start()
t2.start()
条件
# 条件
from threading import Condition # 条件
# 锁
# acquire release
# 一个条件被创建之初 默认有一个False状态
# False状态 会影响wait一直处于等待状态
# notify(int数据类型) 造钥匙
from threading import Thread,Condition
def func(con,i):
con.acquire()
con.wait() # 等钥匙
print('在第%s个循环里'%i)
con.release()
con = Condition()
for i in range():
Thread(target=func,args = (con,i)).start()
while True:
num = int(input('>>>'))
con.acquire()
con.notify(num) # 造钥匙
con.release()
定时器
https://www.jb51.net/article/139000.htm
import time
from threading import Timer
def func():
print('时间同步') #- while True:
t = Timer(,func).start() # 非阻塞的
time.sleep()
队列和栈:
队列 ,先进先出
import queue
q =queue.Queue()
q.put(100)
q.put(200)
结果:
栈,先进后出.
q = queue.LifoQueue()#栈 ,先进后出,
q.put()
q.put()
q.put()
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
打印结果:
优先级队列
q=queue.PriorityQueue() #优先级队列
q.put((,"a"))
q.put((,"b"))
q.put((,"c"))
q.put((,"d")) print(q.get())
打印结果:
(, 'b')
优先级高的是数字最小的。
池 .concurrent.futures.
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def func(n):
time.sleep()
print(n)
return n*n def call_back(m):
print('结果是 %s'%m.result()) tpool = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=) # 默认 不要超过cpu个数*
for i in range():
tpool.submit(func,i).add_done_callback(call_back) # tpool.map(func,range()) # 拿不到返回值
# t_lst = []
# for i in range():
# t = tpool.submit(func,i)
# t_lst.append(t)
# tpool.shutdown() # close+join #
# print('主线程')
# for t in t_lst:print('***',t.result()) # ftp
# 并发编程
Event(事件)
Event(事件):事件处理的机制:全局定义了一个内置标志Flag,如果Flag值为 False,那么当程序执行 event.wait方法时就会阻塞,如果Flag值为True,那么event.wait 方法时便不再阻塞。
Event其实就是一个简化版的 Condition。Event没有锁,无法使线程进入同步阻塞状态。
Event()
- set(): 将标志设为True,并通知所有处于等待阻塞状态的线程恢复运行状态。
- clear(): 将标志设为False。
- wait(timeout): 如果标志为True将立即返回,否则阻塞线程至等待阻塞状态,等待其他线程调用set()。
- isSet(): 获取内置标志状态,返回True或False。
Event案例1
场景:小伙伴a和b准备就绪,当收到通知event.set()的时候,会执行a和b线程
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
# coding:utf-8import threadingimport timeevent = threading.Event()def chihuoguo(name): # 等待事件,进入等待阻塞状态 print '%s 已经启动' % threading.currentThread().getName() print '小伙伴 %s 已经进入就餐状态!'%name time.sleep(1) event.wait() # 收到事件后进入运行状态 print '%s 收到通知了.' % threading.currentThread().getName() print '小伙伴 %s 开始吃咯!'%name# 设置线程组threads = []# 创建新线程thread1 = threading.Thread(target=chihuoguo, args=("a", ))thread2 = threading.Thread(target=chihuoguo, args=("b", ))# 添加到线程组threads.append(thread1)threads.append(thread2)# 开启线程for thread in threads: thread.start()time.sleep(0.1)# 发送事件通知print '主线程通知小伙伴开吃咯!'event.set() |
运行结果:
Thread-1 已经启动
小伙伴 a 已经进入就餐状态!
Thread-2 已经启动
小伙伴 b 已经进入就餐状态!
主线程通知小伙伴开吃咯!
Thread-1 收到通知了.
小伙伴 a 开始吃咯!
Thread-2 收到通知了.
小伙伴 b 开始吃咯!
Event案例2
场景:当小伙伴a,b,c集结完毕后,请客的人发话:开吃咯!
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
# coding:utf-8import threadingimport timeevent = threading.Event()def chiHuoGuo(name): # 等待事件,进入等待阻塞状态 print '%s 已经启动' % threading.currentThread().getName() print '小伙伴 %s 已经进入就餐状态!'%name time.sleep(1) event.wait() # 收到事件后进入运行状态 print '%s 收到通知了.' % threading.currentThread().getName() print '%s 小伙伴 %s 开始吃咯!'%(time.time(), name)class myThread (threading.Thread): # 继承父类threading.Thread def __init__(self, name): '''重写threading.Thread初始化内容''' threading.Thread.__init__(self) self.people = name def run(self): # 把要执行的代码写到run函数里面 线程在创建后会直接运行run函数 '''重写run方法''' chiHuoGuo(self.people) # 执行任务 print("qq交流群:226296743") print("结束线程: %s" % threading.currentThread().getName())# 设置线程组threads = []# 创建新线程thread1 = myThread("a")thread2 = myThread("b")thread3 = myThread("c")# 添加到线程组threads.append(thread1)threads.append(thread2)threads.append(thread3)# 开启线程for thread in threads: thread.start()time.sleep(0.1)# 发送事件通知print '集合完毕,人员到齐了,开吃咯!'event.set() |
运行结果:
Thread-1 已经启动
小伙伴 a 已经进入就餐状态!
Thread-2 已经启动
小伙伴 b 已经进入就餐状态!
Thread-3 已经启动
小伙伴 c 已经进入就餐状态!
集合完毕,人员到齐了,开吃咯!
Thread-1 收到通知了.
1516780957.47 小伙伴 a 开始吃咯!
qq交流群:226296743
结束线程: Thread-1
Thread-3 收到通知了.
1516780957.47 小伙伴 c 开始吃咯!Thread-2 收到通知了.
qq交流群:2262967431516780957.47 小伙伴 b 开始吃咯!结束线程: Thread-3
qq交流群:226296743
结束线程: Thread-2
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
day52 进程与守护进程的更多相关文章
- Linux 普通进程 后台进程 守护进程
一.普通进程与后台进程 默认情况下,进程是在前台运行的,这时就把shell给占据了,我们无法进行其它操作.对于那些没有交互的进程,很多时候,我们希望将其在后台启动,可以在启动参数的时候加一个'& ...
- PHP如何将进程作为守护进程
看了这篇:http://blog.codinglabs.org/articles/write-daemon-with-php.html 对里面的posix_setsid()不解 文档解释是" ...
- Linux进程学习(孤儿进程和守护进程)
孤儿进程和守护进程 通过前面的学习我们了解了如何通过fork()函数和vfork()函数来创建一个进程.现在 我们继续深入来学习两个特殊的进程:孤儿进程和守护进程 一.孤儿进程 1.什么是 孤儿进程如 ...
- UNIX基础--进程和守护进程
进程和守护进程 Processes and Daemons 进程(Processes) FreeBSD 是一个多任务操作系统. 这就意味着好像一次可以运行一个以上的程序. 每个占用一定时间运行的程序就 ...
- python进程之守护进程
标签(空格分隔): 守护进程 主进程创建子进程,然后将该进程设置成守护自己的进程,守护进程就好比崇祯皇帝身边的老太监,崇祯皇帝已死老太监就跟着殉葬了: 关于守护进程需要强调两点: 其一:守护进程会在主 ...
- 【Linux 进程】孤儿进程、僵尸进程和守护进程
1.孤儿进程: 孤儿进程:一个父进程退出,而它的一个或多个子进程还在运行,那么那些子进程将成为孤儿进程.孤儿进程将被init进程(进程号为1)所收养,并由init进程对它们完成状态收集工作.孤儿进程是 ...
- Linux进程学习 - 孤儿进程和守护进程
孤儿进程和守护进程 通过前面的学习我们了解了如何通过fork()函数和vfork()函数来创建一个进程.现在 我们继续深入来学习两个特殊的进程:孤儿进程和守护进程 一.孤儿进程 1.什么是 孤儿进程如 ...
- Linux 普通进程 后台进程 守护进程(转)
一.普通进程与后台进程 默认情况下,进程是在前台运行的,这时就把shell给占据了,我们无法进行其它操作.对于那些没有交互的进程,很多时候,我们希望将其在后台启动,可以在启动参数的时候加一个'& ...
- python并发编程之进程1(守护进程,进程锁,进程队列)
进程的其他方法 P = Process(target=f,) P.Pid 查看进程号 查看进程的名字p.name P.is_alive() 返回一个true或者False P.terminate( ...
- 8.9 day30 并发编程 进程理论 进程方法 守护进程 互斥锁
多道技术 1.空间上的复用 多个程序共用一套计算机硬件 多道技术原理 2.时间上的复用 切换+保存状态 1.当一个程序遇到IO操作 操作系统会剥夺该程序的CPU执行权限( 提高了CPU的利用率 ...
随机推荐
- NetworkStateReceiver的简单应用
一.网络状态接收者是一个广播接收者当网络状态发生改变时会收到网络状态改变的广播 本例当网络状态改变时会进行相应处理 例如当断网时会发出通知点击通知后 会打开网络设置界面 代码如下: package c ...
- jmeter写好的脚本检查无误之后就是无法执行成功
今天,用jmeter写好的脚本,检查了好几遍,没有任何错误,但是执行的时候命令发送总是失败,没有cookie,请教高手,才得以解决. 重新创建一个HTTP request,把之前写好的都一一拷贝过来, ...
- [转]微信公众平台(测试接口)开发前的准备工作(转载自walkingmanc的专栏)
本文转自:http://blog.csdn.net/jiangweicpu/article/details/21228949 http://blog.csdn.net/walkingmanc/arti ...
- Tomcat的杂七杂八
localhost_access_log.2016-01-15.txt 原来这里面有访问记录. /logs/catalina.2016-01-22.log 这里有显示失败的信息 2016-01-23 ...
- xxnet 360浏览器设置
开xxnet全局pac只能代理. 然后选择360浏览器里面使用ie代理设置就行
- .NET中的Func委托用法
MSDN对于Func<T, TResult>)的官方解释: 封装一个具有一个参数并返回 TResult 参数指定的类型值的方法. 下面通过几个例子对比下,就容易知道其用法: 以下例子演示了 ...
- java实现从url路径中下载pdf文档到本地
package com.cellstrain.icell.util; import java.io.*;import java.net.*; public class DownloadPdf { /* ...
- 2018.10.23 vijo1243生产产品(单调队列优化dp)
传送门 这道单调队列真的有点难写啊. 方程感觉挺简单的. f[i][j]f[i][j]f[i][j]表示在第iii个车间结束前jjj次步骤的最小代价. 然后用单调队列毒瘤优化一下就行了. 代码: #i ...
- schwarz( 施瓦兹)不等式证明
证明 如果: 函数 y=ax^2+2bx+c 对任意x >=0 时 y>=0; 函数图象在全部x轴上方,故二次方程判别式 b^2-4ac<=0;(即方程无实数解) 即(2b)^2&l ...
- phonegap android插件,启动activity并返回值
Your execute menthod is not quite right. When you do: return new PluginResult(PluginResult.Status.OK ...