Linux: CPU C-states
0. Overview
There are various power modes of the CPU which are determined based on their current usage and are collectively called “C-states” or “C-modes.” With CPU C-states, the CPU can enter the idle status to optimize energy consumption.
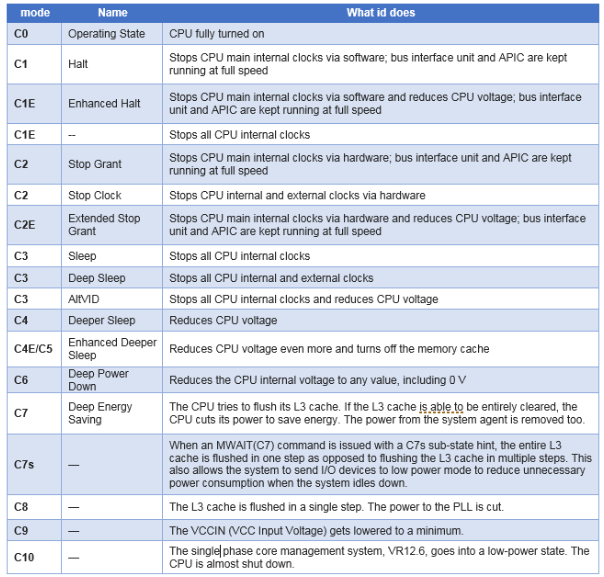
The CPU has a different C-state, and the deeper state means more energy saving. To save power/energy, stop the CPU clock and circuits. ie., so when CPU moving to the work(C0) state from idle state(Cx), it needs more switch time. The deeper the state, the more switch time is needed.
The CPU will switch the state from running to idle automatically, so when the fast path (lower latency) application has bound to the CPU, the application shall keep the busy state (ex: busy-loop) to avoid the state switch of the CPU, and for the slow path (no high require for latency), the application can allow the CPU wake up from idle to running for service.
1. CPU C-states
1.1 Enable CPU C-states
To enable the CPU C-state, an operator can set the max_cstate during BIOS installation. Take an example:
// server 1
# cat /sys/module/intel_idle/parameters/max_cstate
9
// server 2
# cat /sys/module/intel_idle/parameters/max_cstate
0
Let's see, server 1 has enabled a max 9 C-state, and server 2 has set no CPU C-state supported.
Note: It's an example of setting the C-state, more detailed information can refer to the CPU C-states
1.2 CPU C-states latency
We can also read the latency from cpu_dma_latency as:
// server 1
# hexdump -C /dev/cpu_dma_latency
00000000 00 94 35 77 |..5w|
00000004
# echo $(( 0x77359400 ))
2000000000
// server 2
# hexdump -C /dev/cpu_dma_latency
00000000 01 00 00 00 |....|
00000004
# echo $(( 0x00000001 ))
1
Here server 1 has 2000 seconds latency(from idle to C0 running state), and server 2 has 1 microsecond latency.
1.3 CPU C-states monitor
The cpupower-monitor can monitor the CPU processor and report processor frequency and idle statistics, for example:
# cpupower monitor
| Nehalem || Mperf || Idle_Stats
CPU| C3 | C6 | PC3 | PC6 || C0 | Cx | Freq || POLL | C1 | C1E | C6
0| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.53| 99.47| 2084|| 0.00| 0.01| 99.52| 0.00
24| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.26| 99.74| 2252|| 0.00| 0.24| 99.51| 0.00
1| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.33| 99.67| 2422|| 0.00| 0.00| 99.67| 0.00
25| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.90| 99.10| 2580|| 0.01| 0.26| 98.91| 0.00
2| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.20| 99.80| 1810|| 0.00| 0.00| 99.81| 0.00
26| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.84| 99.16| 2867|| 0.01| 0.29| 98.88| 0.00
3| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.83| 99.17| 2686|| 0.01| 0.55| 98.66| 0.00
27| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 1.47| 98.53| 2979|| 0.00| 0.00| 98.53| 0.00
4| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.40| 99.60| 1914|| 0.00| 0.02| 99.66| 0.00
28| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 1.61| 98.39| 2995|| 0.00| 0.00| 98.39| 0.00
5| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00| 0.00|| 0.73| 99.27| 2527|| 0.00| 0.29| 99.03| 0.00
There are three monitors Nehalem, Mperf and Idle_Stats has monitor the process information. From the report, we can see that most CPUs are in the C1E idle state.
To make the CPU switch to a running(C0) state, we can use stress to make a trial, after stress the CPU load is higher and higher, the more CPUs will switch from the C1E idle state to C0, the detailed information as the CPU C-states.
1.4 CPU C-states driver
To enable the CPU C-states, the hardware driver acpi_idle or intel_idle is needed.
- "acpi_idle" cpuidle driver: The acpi_idle cpuidle driver retrieves available sleep states (C-states) from the ACPI BIOS tables (from the _CST ACPI function on recent platforms or from the FADT BIOS table on older ones). The C1 state is not retrieved from ACPI tables. If the C1 state is entered, the kernel will call the hlt instruction (or mwait on Intel).
- "intel_idle" cpuidle driver: In kernel 2.6.36 the intel_idle driver was introduced. It only serves recent Intel CPUs (Nehalem, Westmere, Sandybridge, Atoms or newer). On older Intel CPUs the acpi_idle driver is still used (if the BIOS provides C-state ACPI tables). The intel_idle driver knows the sleep state capabilities of the processor and ignores ACPI BIOS exported processor sleep states tables.
To Check the cpuidle driver from /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/current_driver as:
// server 1
# cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/current_driver
intel_idle
// server 2
# cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/current_driver
acpi_idle
2. Reference
Linux: CPU C-states的更多相关文章
- Understanding Linux CPU stats
Your Linux server is running slow, so you follow standard procedure and run top. You see the CPU met ...
- Linux CPU亲缘性详解
前言 在淘宝开源自己基于nginx打造的tegine服务器的时候,有这么一项特性引起了笔者的兴趣.“自动根据CPU数目设置进程个数和绑定CPU亲缘性”.当时笔者对CPU亲缘性没有任何概念,当时作者只是 ...
- 查看线程linux cpu使用率
Linux下如何查看高CPU占用率线程 LINUX CPU利用率计算 转 http://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/4738113.html目录(?)[-] proc文件系统 p ...
- Linux CPU数量判断,通过/proc/cpuinfo.
Linux CPU数量判断,通过/proc/cpuinfo. 相同 physical id :决定一个物理处理器 如果“siblings”和“cpu cores”一致,则说明不支持超线程,或者超线程未 ...
- How do I Find Out Linux CPU Utilization?
From:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/how-do-i-find-out-linux-cpu-utilization.html Whenever a Linux sys ...
- Linux CPU监控指标
Linux CPU监控指标 Linux提供了非常丰富的命令可以进行CPU相关数据进行监控,例如:top.vmstat等命令.top是一个动态显示过程,即可以通过用户按键来不断刷新当前状态.如果在前台执 ...
- 转载: 一、linux cpu、内存、IO、网络的测试工具
来源地址: http://blog.csdn.net/wenwenxiong/article/details/77197997 记录一下 以后好找.. 一.linux cpu.内存.IO.网络的测试工 ...
- Linux CPU使用率含义及原理
相关概念 在Linux/Unix下,CPU利用率分为用户态.系统态和空闲态,分别表示CPU处于用户态执的时间,系统内核执行的时间,和空闲系统进程执行的时间. 下面是几个与CPU占用率相关的概念. CP ...
- Linux CPU Load Average
理解Linux系统负荷 LINUX下CPU Load Average的一点研究 Linux load average负载量分析与解决思路 Understanding Linux CPU Load - ...
- 理解Linux CPU负载和 CPU使用率
CPU负载和 CPU使用率 这两个从一定程度上都可以反映一台机器的繁忙程度. cpu使用率反映的是当前cpu的繁忙程度,忽高忽低的原因在于占用cpu处理时间的进程可能处于io等待状态但却还未释放进入w ...
随机推荐
- flask蓝图(这玩意就是django的子应用)
蓝图的概念类似django的子应用,作用就是分模块开发,有关联的都放在一起. 蓝图的创建步骤: 新建一个包(一个包就是一个模块.等同于一个子应用) 在包的__init__.py中创建蓝图对象 . 蓝图 ...
- Salesforce LWC学习(四十六) record-picker组件浅谈
本篇参考: https://developer.salesforce.com/docs/platform/lwc/guide/reference-graphql.html https://develo ...
- UE5: 探究Actor Tick的注册与执行
1. 前情提要 因工作需要,有在编辑器模式下执行Actor的Tick函数的需求.经过查阅资料,了解到重载Actor::ShouldTickIfViewportOnly函数可以实现在编辑器视口下也可以执 ...
- CSS 基础 1 - Block & Inline
CSS 基础 1 - Block & Inline display: inline/block/inline-block/none/flex/grid; block block 元素独占一行, ...
- Programming Abstractions in C阅读笔记:p197-p201
<Programming Abstractions in C>学习第64天,p196-p201总结. 一.技术总结 很难,唯有继续往下看才能让其变容易. 二.英语总结 1.psycholo ...
- Spring Boot3 系列:Spring Boot3 跨域配置 Cors
目录 什么是CORS? Spring Boot 如何配置CORS? 前端代码 注解配置 全局配置 过滤器配置 注意事项 什么是CORS? CORS,全称是"跨源资源共享"(Cros ...
- Langchain-Chatchat项目:1.2-Baichuan2项目整体介绍
由百川智能推出的新一代开源大语言模型,采用2.6万亿Tokens的高质量语料训练,在多个权威的中文.英文和多语言的通用.领域benchmark上取得同尺寸最佳的效果,发布包含有7B.13B的Bas ...
- 第三部分_Shell脚本简单四则运算
简单四则运算 算术运算:默认情况下,shell就只能支持简单的整数运算 运算内容:加(+).减(-).乘(*).除(/).求余数(%) 1. 四则运算符号 表达式 举例 $(( )) | echo $ ...
- 如何正确使用Python临时文件
摘要:临时文件通常用来保存无法保存在内存中的数据,或者传递给必须从文件读取的外部程序.一般我们会在/tmp目录下生成唯一的文件名,但是安全的创建临时文件并不是那么简单,需要遵守许多规则. 1.前言 临 ...
- 细说Python Lambda函数的用法,建议收藏!
摘要:今天我就和大家聊聊lambda函数,在Python编程中,大家习惯将其称为表达式. 名称是用于引用或寻址任何实体的约定.我们周围的几乎所有事物都有名字.编程领域也与此一致.但这是必须命名的吗?还 ...
