C++2.0新特性(七)——<Smart Pointer(智能指针)之weak_ptr>
一、weak_ptr出现的意义
上一节提到过shared_ptr,它会自动释放“不再需要使用的对象”的相应的资源,但是它不是万能的,在某些时候(比如说循环引用),它会显得力不从心,这就是weak_ptr出现的意义;
1.1 weak_ptr 使用特性
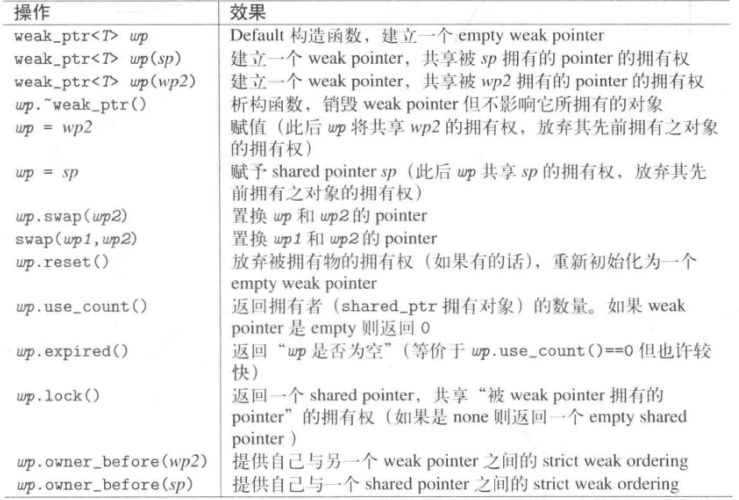
weak_ptr也是一个模板,只提供能接受一个shared_ptr的构造函数或者另一个weak_ptr的赋值,也就是说不能直接用它定义一个智能指针对象,它是为了搭配shared_ptr使用的,weak_ptr提供lock、swap、reset、expired、operator=、use_count等函数,相对shared_ptr多了lock、expired函数,却少了get函数,也不支持operator* 和 operator->
二、weak_ptr使用测试
2.1 以下例子在shared_ptr循环引用时的弊端
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
using namespace std; class Person {
public:
string name;
shared_ptr<Person> mother;
shared_ptr<Person> father;
vector<shared_ptr<Person>> kids; Person(const string& n,
shared_ptr<Person> m = nullptr,
shared_ptr<Person> f = nullptr)
: name(n), mother(m), father(f) {
} ~Person() {
cout << "delete " << name << endl;
}
}; shared_ptr<Person> initFamily(const string& name)
{
shared_ptr<Person> mom(new Person(name + "'s mom"));
shared_ptr<Person> dad(new Person(name + "'s dad"));
shared_ptr<Person> kid(new Person(name, mom, dad));
//以下是为了统计引用次数
cout << "1 mom is shared " << mom.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "1 dad is shared " << dad.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "1 kid is shared " << kid.use_count() << " times" << endl;
mom->kids.push_back(kid);
dad->kids.push_back(kid);
cout << "mom is shared " << mom.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "dad is shared " << dad.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "kid is shared " << kid.use_count() << " times" << endl;
return kid;
} int main()
{
shared_ptr<Person> p = initFamily("nico"); cout << "nico's family exists" << endl;
cout << "- nico is shared " << p.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "- name of 1st kid of nico's mom: "
<< p->mother->kids[]->name << endl; p = initFamily("jim");
cout << "jim's family exists" << endl;
}

上述例子解释:首先我们initFamily函数建立Person:mom 、dad和kid,根据传入的实参将所有姓名初始化,并且还将kid插入到其父母的容器中,最终initFamily函数返回kid并赋值给p,p其实指向上述家庭的最后一个handle,因此在p被赋值之前nico共被共享3次,现在如果我们释放这个p(释放方式:(1)给p指向一个新的person或者赋值为nullptr;(2)main()函数结束时离开p的作用域),但是我们看到程序输出的结果是没有任何person被释放(没有执行析构函数),因为他们都至少被一个shared_ptr指向,于是析构函数都无法执行,这就是循环指向的问题。
如下是引入weak_ptr来解决循环指向的问题:我们可以把kid申明为一个类型为weak_ptr类型的vector。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
using namespace std; class Person {
public:
string name;
shared_ptr<Person> mother;
shared_ptr<Person> father;
vector<weak_ptr<Person>> kids; // weak pointer !!! Person(const string& n,
shared_ptr<Person> m = nullptr,
shared_ptr<Person> f = nullptr)
: name(n), mother(m), father(f) {
} ~Person() {
cout << "delete " << name << endl;
}
}; shared_ptr<Person> initFamily(const string& name)
{
shared_ptr<Person> mom(new Person(name + "'s mom"));
shared_ptr<Person> dad(new Person(name + "'s dad"));
shared_ptr<Person> kid(new Person(name, mom, dad));
//以下是为了统计引用次数
cout << "1 mom is shared " << mom.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "1 dad is shared " << dad.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "1 kid is shared " << kid.use_count() << " times" << endl;
mom->kids.push_back(kid);
dad->kids.push_back(kid);
cout << "mom is shared " << mom.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "dad is shared " << dad.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "kid is shared " << kid.use_count() << " times" << endl;
return kid;
} int main()
{
shared_ptr<Person> p = initFamily("nico"); cout << "nico's family exists" << endl;
cout << "- nico is shared " << p.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "- name of 1st kid of nico's mom: "
<< p->mother->kids[].lock()->name << endl;
//上述使用了lock函数,lock函数来获取其对应的shared_ptr对象,下面详细解释 p = initFamily("jim");
cout << "jim's family exists" << endl;
}
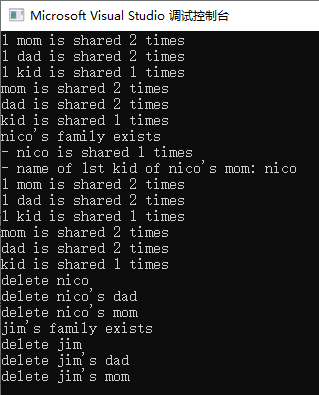
上述解析:关键就在于使用的weak_ptr相比于shared_ptr,没有增加kid的引用计数,所以再最后离开main作用域后能准确调用析构函数,上面例子重要的函数时lock,我们可以将mon(shared_ptr)指针直接赋值给weak_ptr(反之不行),其实weak_ptr 最重要的函数只有lock和expired两个函数,因为weak_ptr本身不会增加引用计数,所以当我们要使用时就要用lock函数,lock()会产生出一个shared_ptr(也就说使用之前必须复制到 shared_ptr)进而像普通指针一样使用。
关键函数解析:
operator=
void operator=(std::weak_ptr<T> desired) noexcept;为weak_ptr赋值,weak_ptr接受shared_ptr类型的变量赋值,但是反过来是行不通的,需要使用lock函数。
reset
void reset() noexcept;释放被管理对象的所有权。调用后 *this 不管理对象。
swap
void swap( weak_ptr& r ) noexcept;交换 *this 与 r 的内容。
use_count
long use_count() const noexcept;返回共享被管理对象所有权的 shared_ptr 实例数量,或 0 ,若被管理对象已被删除,即 *this 为空。
expired
bool expired() const noexcept;检查被引用的对象是否已删除,等价于 use_count() == 0,但是比use_count快,若被管理对象已被删除则为 true ,否则为 false 。由于不知道对象是否已经被析构,最好使用之前先使用expired函数检测一下。
lock
std::shared_ptr<T> lock() const noexcept;创建新的 std::shared_ptr 对象,它共享被管理对象的所有权。若无被管理对象,即 *this 为空,则返回亦为空的 shared_ptr ,等效地返回 expired() ? shared_ptr<T>() : shared_ptr<T>(*this) ,原子地执行。
2.2 常见成员函数以及分类介绍
C++2.0新特性(七)——<Smart Pointer(智能指针)之weak_ptr>的更多相关文章
- C++2.0新特性(六)——<Smart Pointer(智能指针)之shared_ptr>
Smart Pointer(智能指针)指的是一类指针,并不是单一某一个指针,它能知道自己被引用的个数以至于在最后一个引用消失时销毁它指向的对象,本文主要介绍C++2.0提供的新东西 一.Smart P ...
- C++2.0新特性(八)——<Smart Pointer(智能指针)之unique_ptr>
一.概念介绍 unique_ptr它是一种在异常发生时可帮助避免资源泄露的smart pointer,实现了独占式拥有的概念,意味着它可确保一个对象和其他相应资源在同一时间只被一个pointer拥有, ...
- 【C++11新特性】 C++11智能指针之weak_ptr
如题,我们今天要讲的是C++11引入的三种智能指针中的最后一个:weak_ptr.在学习weak_ptr之前最好对shared_ptr有所了解.如果你还不知道shared_ptr是何物,可以看看我的另 ...
- [CareerCup] 13.8 Smart Pointer 智能指针
13.8 Write a smart pointer class. A smart pointer is a data type, usually implemented with templates ...
- C++ smart pointer智能指针
在C++中,程序员可以直接操作内存,给编程增加了不少的灵活性.但是灵活性是有代价的,程序员必须负责自己负责释放自己申请的内存,否则就会出现内存泄露.智能指针就是为了解决这个问题而存在的.它和其他指 ...
- Smart pointer 智能指针小总结
Smart pointer line 58之后smart pointer里的计数已经是0,所以会真正释放它引用的对象,调用被引用对象的析构函数.如果继续用指针访问,会出现如下图的内存访问异常.所以说如 ...
- 【C++11新特性】 C++11智能指针之shared_ptr
C++中的智能指针首先出现在“准”标准库boost中.随着使用的人越来越多,为了让开发人员更方便.更安全的使用动态内存,C++11也引入了智能指针来管理动态对象.在新标准中,主要提供了shared_p ...
- Smart Pointer 智能指针
P76 参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/lanxuezaipiao/p/4132096.html http://blog.csdn.net/hackbuteer1/article/ ...
- Javaweb学习笔记——(七)——————myexlipse基本使用、jdk5.0新特性及反射讲解
1.debug调试模式: *使用这种模式,调试程序(看到程序运行停止在这一行) -显示出来行号 -双击左边,出现一个圆点,表示设置了一个断点 *使用debug as方式,运行程序 -特使是否进入到调试 ...
随机推荐
- 局域网电脑禁止ping通的解决方法
方法1:命令行模式进入服务器后 点击 开始——运行 输入命令:netsh firewall set icmpsetting 8这样就可以在外部ping到服务器了 非常简单实用!同样道理,如果想禁止Pi ...
- Java自学-数组 二维数组
Java 如何使用二维数组 这是一个一维数组, 里面的每一个元素,都是一个基本类型int int a[] =new int[]{1,2,3,4,5}; 这是一个二维数组,里面的每一个元素,都是一个一维 ...
- 旋转图像 给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵表示一个图像。
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵表示一个图像. 将图像顺时针旋转 90 度. 说明: 你必须在原地旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵.请不要使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像. 示例 : 给定 ma ...
- SG-UAP常用注解介绍
注解基本介绍 Annotation(注解)是JDK5.0及以后版本引入的.它可以用于创建文档,跟踪代码中的依赖性,甚至执行基本编译时检查.注解是以‘@注解名’在代码中存在的,根据注解参数的个数,我们可 ...
- nginx小结
1.nginx下部署网站 网站为:http://10.1.75.177:8000 nginx端口为80 配置如下: user nginx; worker_processes auto; error_l ...
- MySQL MHA--在线主库切换(Online master switch)
在线主库切换(Online master switch)条件 1.所有节点正常运行,无论时原主还是新主或者其他从库 if ( $#dead_servers >= 0 ) { $log->e ...
- MySQL--使用mysqldump进行数据库版本升级
在MySQL跨版本升级时,建议使用mysqldump方式导出用户权限和用户数据,即使是小版本升级,导出过程中也应忽略系统数据库,避免系统表不兼容. 导出用户数据库脚本和用户创建脚本 ##======= ...
- MYSQL使用source命令,导入SQL文件
命令 source D:/student.sql
- springboot注解@NotNull,@NotBlank,@Valid自动判定空值
一.前言 搭建springboot项目,我们都是采用的Restful接口,那么问题来了,当前端调用接口或者是其他项目调用时,我们不能单一靠调用方来控制参数的准确性,自己也要对一些非空的值进行判定. 二 ...
- Docker03-安装Docker运行环境
目录 Ubuntu 18 中安装Docker 查看Docker安装信息 查看Docker版本,命令:docker version 查看Docker运行信息,命令: docker info 检查安装是否 ...
