XGBoost对波士顿房价进行预测
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ["SimHei"]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error import xgboost as xgb
def notEmpty(s):
return s != ''
names = ['CRIM','ZN', 'INDUS','CHAS','NOX','RM','AGE','DIS','RAD','TAX','PTRATIO','B','LSTAT']
path = "datas/boston_housing.data"
## 由于数据文件格式不统一,所以读取的时候,先按照一行一个字段属性读取数据,然后再按照每行数据进行处理
fd = pd.read_csv(path, header=None)
data = np.empty((len(fd), 14))
for i, d in enumerate(fd.values):
d = map(float, filter(notEmpty, d[0].split(' ')))
data[i] = list(d) x, y = np.split(data, (13,), axis=1)
y = y.ravel() print ("样本数据量:%d, 特征个数:%d" % x.shape)
print ("target样本数据量:%d" % y.shape[0])
样本数据量:506, 特征个数:13
target样本数据量:506
# 查看数据信息
X_DF = pd.DataFrame(x)
X_DF.info()
X_DF.describe().T
X_DF.head()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 506 entries, 0 to 505
Data columns (total 13 columns):
0 506 non-null float64
1 506 non-null float64
2 506 non-null float64
3 506 non-null float64
4 506 non-null float64
5 506 non-null float64
6 506 non-null float64
7 506 non-null float64
8 506 non-null float64
9 506 non-null float64
10 506 non-null float64
11 506 non-null float64
12 506 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(13)
memory usage: 51.5 KB

#数据的分割,
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, train_size=0.8, random_state=14)
print ("训练数据集样本数目:%d, 测试数据集样本数目:%d" % (x_train.shape[0], x_test.shape[0]))
训练数据集样本数目:404, 测试数据集样本数目:102
# XGBoost将数据转换为XGBoost可用的数据类型
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(x_train, label=y_train)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(x_test)
# XGBoost模型构建
# 1. 参数构建
params = {'max_depth':2, 'eta':1, 'silent':1, 'objective':'reg:linear'}
num_round = 2
# 2. 模型训练
bst = xgb.train(params, dtrain, num_round)
# 3. 模型保存
bst.save_model('xgb.model')
# XGBoost模型预测
y_pred = bst.predict(dtest)
print(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
24.869737956719252
# 4. 加载模型
bst2 = xgb.Booster()
bst2.load_model('xgb.model')
# 5 使用加载模型预测
y_pred2 = bst2.predict(dtest)
print(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred2))
24.869737956719252
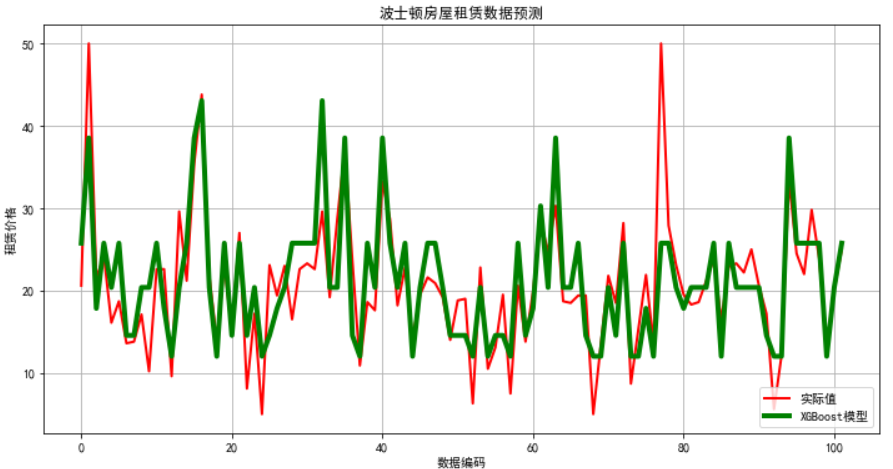
# 画图
## 7. 画图
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6), facecolor='w')
ln_x_test = range(len(x_test)) plt.plot(ln_x_test, y_test, 'r-', lw=2, label=u'实际值')
plt.plot(ln_x_test, y_pred, 'g-', lw=4, label=u'XGBoost模型')
plt.xlabel(u'数据编码')
plt.ylabel(u'租赁价格')
plt.legend(loc = 'lower right')
plt.grid(True)
plt.title(u'波士顿房屋租赁数据预测')
plt.show()
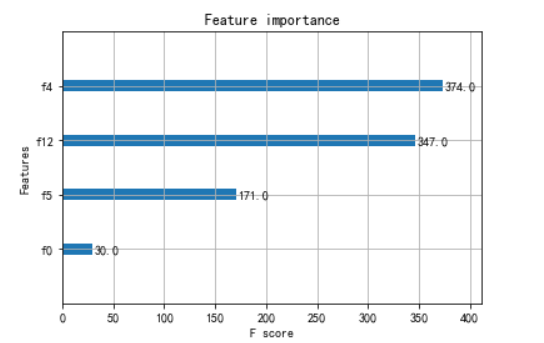
from xgboost import plot_importance
from matplotlib import pyplot
# 找出最重要的特征
plot_importance(bst,importance_type = 'cover')
pyplot.show()
XGBoost对波士顿房价进行预测的更多相关文章
- 波士顿房价预测 - 最简单入门机器学习 - Jupyter
机器学习入门项目分享 - 波士顿房价预测 该分享源于Udacity机器学习进阶中的一个mini作业项目,用于入门非常合适,刨除了繁琐的部分,保留了最关键.基本的步骤,能够对机器学习基本流程有一个最清晰 ...
- Tensorflow之多元线性回归问题(以波士顿房价预测为例)
一.根据波士顿房价信息进行预测,多元线性回归+特征数据归一化 #读取数据 %matplotlib notebook import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib. ...
- 机器学习实战二:波士顿房价预测 Boston Housing
波士顿房价预测 Boston housing 这是一个波士顿房价预测的一个实战,上一次的Titantic是生存预测,其实本质上是一个分类问题,就是根据数据分为1或为0,这次的波士顿房价预测更像是预测一 ...
- AdaBoost 算法-分析波士顿房价数据集
公号:码农充电站pro 主页:https://codeshellme.github.io 在机器学习算法中,有一种算法叫做集成算法,AdaBoost 算法是集成算法的一种.我们先来看下什么是集成算法. ...
- 《用Python玩转数据》项目—线性回归分析入门之波士顿房价预测(二)
接上一部分,此篇将用tensorflow建立神经网络,对波士顿房价数据进行简单建模预测. 二.使用tensorflow拟合boston房价datasets 1.数据处理依然利用sklearn来分训练集 ...
- 机器学习之路:python 集成回归模型 随机森林回归RandomForestRegressor 极端随机森林回归ExtraTreesRegressor GradientBoostingRegressor回归 预测波士顿房价
python3 学习机器学习api 使用了三种集成回归模型 git: https://github.com/linyi0604/MachineLearning 代码: from sklearn.dat ...
- 机器学习之路: python 回归树 DecisionTreeRegressor 预测波士顿房价
python3 学习api的使用 git: https://github.com/linyi0604/MachineLearning 代码: from sklearn.datasets import ...
- 机器学习之路:python k近邻回归 预测波士顿房价
python3 学习机器学习api 使用两种k近邻回归模型 分别是 平均k近邻回归 和 距离加权k近邻回归 进行预测 git: https://github.com/linyi0604/Machine ...
- 机器学习之路: python 线性回归LinearRegression, 随机参数回归SGDRegressor 预测波士顿房价
python3学习使用api 线性回归,和 随机参数回归 git: https://github.com/linyi0604/MachineLearning from sklearn.datasets ...
随机推荐
- js中回调函数,promise 以及 async/await 的对比用法 对比!!!
在编程项目中,我们常需要用到回调的做法来实现部分功能,那么在js中我们有哪些方法来实现回调的? 方法1:回调函数 首先要定义这个函数,然后才能利用回调函数来调用! login: function (f ...
- 11-ESP8266 SDK开发基础入门篇--软硬件定时器
https://www.cnblogs.com/yangfengwu/p/11094009.html 定时器有两种,软件定时器和硬件定时器 软件定时器就是靠里面的任务延时实现的,,这样的定时器其实延时 ...
- POJ 1741.Tree and 洛谷 P4178 Tree-树分治(点分治,容斥版) +二分 模板题-区间点对最短距离<=K的点对数量
POJ 1741. Tree Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 30000K Total Submissions: 34141 Accepted: 11420 ...
- nginx中的upstream使用
upstream的基本使用 upstream admin{server 127.0.0.1:9090 down;server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=2;server 127.0. ...
- js中判断变量不为空或null
var content=$("content").val(); if(!content){ alert("请输出内容!"); return; ...
- rsync实时同步
假设有如下需求: 假设两个服务器: 192.168.0.1 源服务器 有目录 /opt/test/ 192.168.0.2 目标服务器 有目录 /opt/bak/test/ 实现的目的就是保持这两 ...
- Monkey框架(基础知识篇) - monkey启动与参数介绍
一.monkey启动 直接PC启动:> adb shell monkey [options] <count> shell 端启动:> adb shell >monkey ...
- ArrayList: java之ArrayList详细介绍(转)
1 ArrayList介绍 ArrayList简介 ArrayList 是一个数组队列,相当于 动态数组.与Java中的数组相比,它的容量能动态增长.它继承于AbstractList,实现了List ...
- 三层架构BLL+DAL+Model & MVC & MVVM
三层架构 - 国内版 Binghttps://cn.bing.com/search?FORM=U227DF&PC=U227&q=%E4%B8%89%E5%B1%82%E6%9E%B6% ...
- 算法名称 Alias Method
public class AliasMethod { /* The probability and alias tables. */ private int[] _alias; private dou ...
